The biggest danger that can threaten an individual heating system is freezing during the winter when there is a power outage. To avoid such situations, many use antifreeze for the heating system of a country house, protecting the boiler and heating pipes from deformation.
The construction market offers various brands of antifreeze for heating systems, the composition of automotive antifreeze liquids is similar, the most famous of which is Antifreeze. Therefore, many homeowners have a reasonable question: is it possible to use Antifreeze as an antifreeze for the heating circuit of an individual home and is it profitable from a financial point of view?
To get answers to this question, you should consider the physicochemical characteristics of Antifreeze and compare it with special liquids designed to protect the heating system from freezing.
Rice. 1 Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house - popular brands Teply Dom, Dixis, Thermagent
Water or antifreeze - comparison of parameters
Water is a common natural element, widely used as a heat carrier, but due to its too high freezing point, it has to be replaced in domestic heating with glycol antifreeze, which have the following indicators in comparison with water:
- Their specific thermal capacity is 15% lower than that of water, which means that with the same volume, glycol accumulates 15% less energy when heated and, accordingly, releases less. Consequently, to transport the same amount of heat as water per unit time, its speed of movement through the pipeline must be greater by the same amount.
- The density of antifreeze is slightly higher (by 5 - 10%) than water, and the viscosity is 30 - 50% higher than water indicators - this means that when the liquid moves through the pipeline, the hydraulic resistance increases. Compared with water coolant, the circulation pump will require more power and, accordingly, electricity consumption to move the same volume of antifreeze as water.
- Their thermal expansion coefficient is 30 - 40% greater than water; when heated, the glycol coolant increases in volume by 5%, the expansion is insignificant, but sometimes a slightly larger hydraulic tank may be needed.
- Due to their low surface tension, they are 50% more fluid than water - this places increased demands on sealing. Conventional rubber gaskets will have to be replaced with paronite gaskets; it often happens that the internal gaskets of heating radiators are not designed to work with glycols and measures will have to be taken to eliminate leaks between sections (modern radiators usually do not have such problems).
Rice. 2 Properties of antifreeze compared to water
- A significant drawback of relatively cheap antifreezes based on ethylene glycol is a high danger to human health; the substance is poisonous with a lethal concentration of 2 mg. per 1 kg. weight. Therefore, ethylene glycol is prohibited from being poured into systems with an open storage tank in the attic; the circuit must be closed.
- They have a short service life, designed for 10 seasons and amounting to no more than 5 years, this is due to the decomposition of anti-corrosion additives during operation. After this, you will have to drain the antifreeze from the system, dispose of it (with poisonous ethylene glycol this is a definite problem) and pour new coolant into the circuit - this will entail unjustified financial expenses.
- Unlike neutral water, low-quality or expired glycols decompose over a certain period, forming solid sediment that clogs fittings and destroys pipeline fittings.
- Another significant drawback of non-freezing coolants is the relatively high cost: a 20-liter canister of ethylene glycol with crystallization at -30º C will cost 15 USD, the price of the same volume of propylene glycol will be 30 USD.
- It should also be noted that during operation, antifreezes are very sensitive to critical temperatures - when overheated, the glycols and additives included in their composition decompose with the formation of solid insoluble precipitates and acids. This leads to the appearance of carbon deposits on the heating elements of the boiler that come into contact with the coolant; the metals are subject to destructive corrosion, and the sealing elements also suffer. The process is accompanied by increased foaming, leading to airing of the system and disruption of its functioning.
- They have restrictions in their use; their use in electrolysis boilers and pipelines made of galvanized steel is prohibited - the metal is subject to increased corrosion with the formation of an insoluble precipitate of white flakes.
Rice. 3 Features of glycol-based coolants and their cost
- A significant disadvantage of using antifreeze is the refusal of many heating boiler manufacturers to provide warranty service if glycols are poured into the system.
- The only and main advantage of antifreeze in comparison with water is the low freezing point, reaching up to -70º C. Even when a higher-temperature composition freezes (it is obtained after dilution with water in a certain concentration), the substance turns into a jelly-like mass with minimal expansion. Therefore, if you pour antifreeze into the heating system, the integrity of the pipes and boiler is guaranteed at any natural negative freezing temperatures of the circuit.
From the above, it becomes clear that water as a coolant is significantly superior to all antifreezes in its physical and chemical parameters, with the exception of its 10% expansion upon freezing, which led to the search for alternative options.
Rice. 4 Antifreeze in the heating system of a private house - instructions
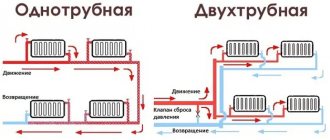
What is a coolant and what should it be like?
The coolant in a liquid heating system is the substance through which heat is transferred from the boiler to the radiators. Our systems use water or special antifreeze liquids as a coolant. When choosing, you must be guided by several criteria:
- Safety. From time to time, heating systems leak or require maintenance and repair. To ensure that repair work is not dangerous, the coolant must be harmless.
- Harmless to heating system components.
- Must have high thermal capacity to transfer heat effectively.
- Have a long service life.
The coolant for heating systems is selected according to operating conditions
Taking into account these requirements, the most suitable liquid for the heating system is water. It is safe, harmless, has a high heat capacity, and its service life is unlimited. But in those heating systems where there is a high probability of downtime in winter, water can do a poor job. If it freezes, it will burst pipes and/or radiators. That’s why antifreeze is used in such systems. At subzero temperatures they lose fluidity, but the equipment does not tear. So choosing a coolant for a heating system from this point of view is easy: if the system is always under supervision and in working order, you can use water. If the house is temporary (dacha) or can be left unattended for a long time (business trips, winter vacation), if frequent and/or long-term power outages are possible in the region, it is better to pour antifreeze into the system.
Antifreeze for the heating system of a country house - properties and types
The construction market offers two main brands of antifreeze for heating systems in private homes: ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. Typically, in anti-freeze products the main component is glycol (30 - 65% depending on the concentration of the solution), deionized water occupies 30 - 50% of the total volume and there are 3 - 4% additives consisting of corrosion inhibitors, scale and sediment solvents, substances that prevent foaming.
Due to its composition, from the beginning of crystallization to the transformation of the non-freezing composition into gel-like slush, an interval of 10 - 15º C is required, the temperature inside of which changes gradually and takes a long time.
Manufacturers supply antifreeze packaged in 10-liter or 20-liter canisters to the retail chain in the following concentrations:
- Concentrate with crystallization at -65º C, which can be diluted with water to obtain the required freezing point.
- A solution that freezes at -30º C; it is used both in finished form and diluted to obtain higher temperature parameters from -20 to -15º C.
It is important for the consumer to know that when diluting the concentrate with water, there is no linear dependence on its percentage (graph in Fig. 8). For example, if we dilute 20 liters of a 65% concentrate with crystallization at -65º C with the same amount of water, then we will get 40 liters of liquid with a crystallization point of about - 20º C, and not - 32.5º C, as happens, for example, when diluting alcohol Therefore, to obtain the required temperature, tables of lower limits of the temperature dependence of glycols on their concentration are used (Fig. 9).
How antifreeze works
As we all know from the school curriculum, water freezes at zero degrees and takes the form of ice. In this case, expansion occurs, and the vessels (in our case, pipes) may simply not be able to withstand it. If such a situation arises, it is necessary to change the elements of the heating system (pipes or radiators).
However, if you use antifreeze, this can be avoided. It mixes very well with water and even at a very small concentration the freezing point becomes different. Expansion will undoubtedly occur, but not sharply, and it will not cause any damage.
Antifreeze as a coolant in a heating system
Antifreeze is a development of Soviet engineers in 1971; its abbreviation comes from the name of the department of the Soviet State Research Institute of Organic Chemistry - Technology of Organic Synthesis with the addition of a prefix typical for the name of alcohols.
Antifreeze is usually produced in cans with a crystallization temperature of -40º C of various colors, the colors of antifreeze red green blue indicate the types of automobile radiators into which it is recommended to fill the composition (red - for brass or copper, blue, green - for aluminum).
Although the main component in Antifreeze is ethylene glycol and it is visually no different from glycol-based antifreezes, there are the following differences in the composition and technology of their production:
- In addition to glycol and water, Antifreeze contains nitrate, phosphate, silicate, borate and amine additive components, due to which the liquid boils at a temperature of 100º C and decomposes at 105º C. When used in automotive equipment, Antifreeze is designed for 40,000 km.
- Antifreezes are manufactured using carboxylate technology and contain additives from salts of organic acids, due to which the solution has high anti-corrosion, anti-cavitation and anti-foam characteristics. The boiling point of glycol solutions reaches 115º C; a car filled with antifreeze can travel a distance of 240,000 km. without replacing it.
It is easy to notice that obsolete Antifreeze is significantly inferior in its characteristics to modern antifreezes for automotive vehicles, produced from imported raw materials using carboxylate technology, which is inaccessible to domestic manufacturers.
Rice. 7 Antifreeze - appearance
New mineral coolants
We decided to highlight the description of these liquids, since they are made based on the natural mineral - bischofite. The substance is a magnesium salt of hydrochloric acid, the full name is magnesium chloride hexahydrate. The manufacturer declares the following characteristics of the finished antifreeze, designed for a minimum temperature of minus 30 degrees:
- the color of the aqueous solution is light yellow, the density is 1117...1250 kg/m³;
- boiling threshold - 116 °C, freezing point - minus 30 °C;
- specific heat capacity - 0.77 kcal/kg •°С (3.23 kJ/kg•°С);
- thanks to the additives, there is no foaming and no aggressive effect on various seals - silicone, paronite, EPDM and BMS rubber;
- the substance is not toxic;
- In terms of viscosity and fluidity, the drug is very close to glycol chemicals.
Reference. The product appeared on the market after 2010. The price of liquid as of 2022 is about 1 USD. e. per liter of finished coolant (-30 ° C).
Compared to traditional glycol analogues, mineral antifreeze benefits due to its high boiling point, cost and health safety. The negative point is the increased density and low heat capacity, 23% worse than that of water.
The practical use of the coolant has revealed a number of shortcomings, as evidenced by reviews from homeowners:
- The fluidity of the solution is extremely high. There have been cases where antifreeze penetrated through the soldered joint of polypropylene pipes.
- Upon contact with air, the liquid fraction quickly evaporates, leaving a noticeable salt build-up. Similar phenomena are observed in heat exchangers and pipelines where air bubbles have penetrated.
- The substance reacts with bare metal on welds. Stalactites of iron and salt form inside the system, reducing the flow area and clogging the mud traps.
- In case of overheating, antifreeze turns into a slurry of unknown color.
User responses about this type of “anti-freeze” can be read on the well-known construction forum: https://www.stroimdom.com.ua/forum/showthread.php?t=157650
Taking into account the experience of users, we do not dare to recommend mineral antifreezes for use in heating systems of private houses. Perhaps over time, manufacturers will eliminate the above problems and the magnesium chloride solution will be able to compete on equal terms with glycols.
Why it is not recommended to pour antifreeze into the heating system
Due to the low cost, some homeowners may have the idea of using Antifreeze in the home heating system as antifreeze, to make sure that this idea is futile, consider the consequences of this decision:
- In addition to the fact that Antifreeze has fully absorbed all the disadvantages of glycols, it is made using a different technology and decomposes at a lower boiling point of 105º C. When using high-temperature solid fuel boilers, the danger of its overheating increases significantly, and decomposition can lead to failure of the circular electric pump, clogging of taps and fittings. The damage will be many times greater than the penny saved on an unusable composition.
- The additives included in Antifreeze are not intended for heating systems; they will not only be useless, but are also likely to cause damage to the elements of the heating circuit, fittings and pumping equipment after some time.
- The most compelling argument is the pointlessness of using Antifreeze for the sake of saving money - in automotive technology its service life is 6 times less than modern antifreeze, a similar situation with similar temperature conditions will occur in the heating system. Antifreeze will have to be drained from the pipeline at least every year, as a result, the costs of using it will increase several times.
- Also, antifreeze produced using traditional methods is strictly forbidden to be mixed with modern antifreezes due to the difference in manufacturing technologies - a chemical reaction occurs, some additive components precipitate and clog the flow channels.
Considering the above, it will not be difficult to answer the question of whether it is possible to pour Antifreeze into the heating system; one can say more categorically - Antifreeze is the worst of all possible options.
Rice. 8 Graph of freezing temperature versus glycol concentration
Malfunctions associated with the use of low-quality antifreeze.
In recent years, Russian motorists have realized the importance of using high-quality consumables and oils when servicing their equipment. Unfortunately, this statement does not apply to the coolants used.
Many motorists are still fully confident that the use of low-quality antifreeze or antifreeze cannot seriously affect the performance of the car. You can often hear the following statement: “Previously, water was poured in and nothing…”. Meanwhile, according to the results of research by the world's leading automotive engineers, it was found that approximately 40% of all engine breakdowns are directly or indirectly related to improper maintenance of the engine cooling system.
The main types of malfunctions associated with the use of low-quality antifreeze and improper maintenance of the cooling system.
- Cavitation of the pump impeller Possible causes: Lack of anti-cavitation and anti-foam additives, impaired circulation of coolant in the system caused by deposits, increased operating temperature of the engine, lack of pressure in the cooling system, aeration of the coolant. Problems that arise: Pump failure, engine overheating, unplanned financial losses.
- Cavitation of a wet liner. Possible reasons: Lack of anti-cavitation and anti-foam additives, increased engine operating temperature, lack of pressure in the cooling system. Problems that arise: Engine seizure, antifreeze getting into the oil, engine overhaul, unplanned financial losses.
- Corrosion of parts of the engine cooling system. Possible causes: Lack of anti-corrosion and buffer additives or their imbalance, increased or decreased pH of the coolant, glycol oxidation due to overheating or ingress of fuel and lubricants, the presence of stray currents. Emerging problems: Destruction of engine parts, deterioration of heat dissipation/engine overheating, impaired coolant circulation/engine overheating/premature aging of oil, engine overhaul, unplanned financial losses.
- Deposits in the radiator and other parts of the cooling system. Possible causes: Use of hard water to dilute the coolant, excessive mineralization of the coolant, errors when adding additional additives. Emerging problems: Deterioration of heat dissipation/impaired coolant circulation/engine overheating/premature aging of oil, thermostat jamming, destruction of gaskets and seals, engine overhaul, unplanned financial losses.
- Formation of silicate gels. Possible reasons: Excessive mineralization of the coolant, errors when adding additional additives, lack of stabilizers. Emerging problems: Deterioration of heat dissipation/impaired coolant circulation/engine overheating/premature aging of oil, thermostat jamming, destruction of gaskets and seals, engine overhaul, unplanned financial losses.
And you still think you're saving money by using cheap, low-quality coolants?
What to look for when choosing antifreeze
To choose a coolant for a heating system, you should consider all the pros and cons of the solutions offered on the market. It is taken into account that in closed circuits toxic ethylene glycol compounds can be used without great risk if the expansion tank is open and harmless propylene glycol is poured into the circuit.
The construction market offers products from a wide range of manufacturers, and since they are made mainly from high-quality imported raw materials and have approximately the same price and a shelf life of no more than 5 years, it is difficult to give preference to any company.
If manufacturers offer antifreeze liquid at too low a price, you can check the authenticity of the solution using traditional methods: since counterfeits mostly contain an acid base, they use soda to check. If a pinch of soda, poured into a small amount of liquid, enters into a violent chemical reaction with it, then the purchased product is fake; with neutral interaction, the authenticity of the product should not raise doubts.
You can determine a branded product using a hydrometer - a device that measures density; the technique allows you to find out the percentage of water in the product. When taking measurements, the density of the composition should not be less than 1.075 g/cm3; if the value is lower, the liquid is most likely diluted with water.
Rice. 9 Temperature dependence of ethylene glycol on concentration
When the coolant is not used
Antifreeze sometimes cannot be used. Recommendations:
- When the heating network of a building is based on a 2-circuit boiler, no antifreeze is used. The substance may penetrate into the building's water supply circuit.
- Antifreeze is prohibited in open heating networks. The coolant will steam and the homeowner will have to top it up regularly.
- It is forbidden to pour the product into a system that consists of a galvanized pipeline. This provokes a change in the chemical composition of the antifreeze and its loss of its performance qualities.
- Antifreeze, when compared to water, has a lower heat capacity. If it is to be used as a heat carrier, then powerful radiator elements must be used when organizing the heating network.
- The antifreeze composition is viscous, so you cannot do without a strong circulation pump.
If the homeowner 100% decides to add antifreeze, then it is better to prefer products based on propylene or glycerin. The former are expensive, the latter have the lowest thermal conductivity and weigh more. Propylene glycol products are more innovative, which is why many people purchase them. Ethylene glycol liquids are prohibited for the home, since the risk of contact with residents is high, and maintaining a network with a toxic substance is a big problem.
Features of filling with ethylene glycol antifreeze
Considering the toxicity of ethylene glycol, it is necessary to pour this coolant into the heating system with extreme caution, using containers that are no longer needed in the household for the purpose of their further disposal. Coolant is usually pumped into the system using an inexpensive electric pump or a special hand pump for a press operator; budget vibration models costing about $20 are suitable. After use, they are thoroughly washed with hot water and detergents and subsequently used for watering gardens in personal plots or for technical needs.
If the system uses an open circuit, and financial resources do not allow you to purchase expensive propylene glycol, you can add ethylene glycol-based antifreeze, taking simple safety precautions. To do this, the storage tank on the top floor or attic is tightly closed with a lid (to improve sealing, you can use rubber gaskets or heat-resistant sealants), and a sealed tube is inserted into it, which is led outside the house through a window or roof.
Propylene glycol products
In appearance, propylene glycol cannot be distinguished from ethylene glycol; many of their physical properties are the same. But propylene glycol has fluidity and if a leak is not noticed in time, it can leak out completely.
Propylene glycol-based antifreezes are green in color due to the presence of a food additive in it, which suggests that it is not toxic. Moreover, this additive is widely used in the production of various cosmetics and food industries. And if a leak suddenly occurs, it will not cause any terrible harm.
The temperature at which it freezes (or rather, changes consistency) is higher than ethylene glycol antifreeze and is about minus 50 degrees. Propylene glycol antifreeze does not damage the internal surface of systems, but, on the contrary, has the opposite effect. Which carries such positive qualities as less resistance and less energy loss.
Preparation of antifreeze solution for heating
If, due to various circumstances, there are no better options at hand, you can use Antifreeze in houses with a small number of heating circuits and plumbing fixtures; it is better to use radiators made of aluminum. Blue and green antifreeze is available for sale in plastic containers of various capacities; its standard freezing point is -40º C. Since ethylene glycol is the main component of the solution, the corresponding tables can be used when diluting with water.
For example, to obtain a crystallization temperature of -20º C (35% ethylene glycol), we determine from the tables that the Antifreeze solution with a freezing point of -40º C contains 54% ethylene glycol. Using a simple mathematical formula (35 x 100 / 54), we determine that 35% water should be added to antifreeze to obtain a freezing threshold of -20º C.
The percentage of added water is calculated in a similar way for other temperature limits of the coolant.
Rice. 11 Antifreeze for the heating system - how to fill it
Water quality requirements
If it is necessary to dilute antifreeze, it is necessary to use distilled water.
If distilled water is not available, the quality of the water used must meet all the requirements listed below. Elevated levels of calcium and magnesium contribute to scale problems, while excess levels of chlorides and sulfates can cause corrosion of the cooling system. If tap or natural water is used, the levels of impurities in it should not exceed the specified limits for use in cooling systems. Table - Water quality requirements
| Substance | Maximum permissible level |
| Calcium, magnesium (hardness) | 170 ppm (as CaCO3) |
| Chlorides | 40 ppm (as Cl) |
| Sulfates | 100 ppm (as SO4) |
Pouring Antifreeze into the heating system
As noted above, the use of Antifreeze is justified only in emergency situations; to pour Antifreeze into the heating system, work is performed in the following sequence:
- The coolant is drained through the filling valve located at the lowest point next to the water heating boiler (this possibility should be provided for at the design stage of the system).
- The dirt filter is removed, cleaned and replaced, then using an inexpensive vibration electric pump (Malysh) water is poured into the system under a standard pressure of no more than 2 bar.
- After filling the pipeline, close the inlet valve, turn on the heating boiler for heating water and the circulation pump. Set the heating temperature to about 60 C. and pump water for an hour; at the end of the time, monitor the condition of the dirt filter.
- If too much dirt remains on the filter cartridge, turn off the circulation pump and boiler, drain the water, clean the filter and repeat the entire washing procedure again.
Rice. 12 Antifreeze viscosity chart
- Having made sure that there is practically no dirt in the system, after draining the water, they begin to fill in the Antifreeze. It is poured into a large container, a vibration pump is immersed there and they begin to pump it into the system under a pressure of about 2 bar.
- Typically, underfloor heating circuits are connected through manifolds on which automatic air vents are placed to bleed air - they cope with their task without human presence. On heating radiators, you will have to bleed air manually through Mayevsky taps. To do this, use a flat screwdriver or wrench to unscrew the slot in the upper part of the radiator and drain the coolant, thus bypassing all batteries, starting from the upper floors. If the pressure drops after draining the coolant, it is periodically pumped up.
- Bleeding water from the radiators and pumping is repeated again, then turn on the circulation pump and boiler to a temperature of about 60º C and then manually check the batteries for uniform heating on both sides. If one half of the radiator heats up less, bleed the air again and pump up antifreeze.
- If there is increased foaming during the injection of antifreeze, turn off all equipment for several hours, giving the Antifreeze a chance to settle.
Antifreeze has a short service life; its final phase can be determined visually - if the liquid has a rusty color, this indicates decomposition of the inhibitors and the circuit is urgently released from the coolant.
Rice. 13 Heating boilers in a private house
Rating of the best non-freezing liquids
TOP 5 antifreezes for the home will allow you to easily choose what you need. If problems arise, you can always contact the manager of a specialized store.
Knowing the advantages and disadvantages, it is important to buy a good heating fluid. The following brands of antifreeze are the most popular among users.
DIXIS-65
Ideal for use in gas and electric boiler equipment of any type of installation. Excellent transfer of heat at external temperatures from -65 °C to +9 °C.
This antifreeze composition is ideal for cast iron, copper, aluminum, and brass heating pipes. Does not damage joints, does not harm pipelines and plastic tanks. Together with the anti-freeze system, a sticker is issued for the heating boiler, where you can see fields for entering the fill date, volume and other details - this is indispensable when maintaining the system.
Experts gave the leading position in the rating to this particular non-freezing liquid, since its crystallization occurs only at -66 °C. This is the best substance for heating lines in northern regions - it will survive severe frosts and keep the pipeline and radiators intact.
When used in regions where the temperature in winter is not lower than -20 °C, the antifreeze liquid is diluted with water 1 to 1 - this is a serious money saving.
Pros:
- fire resistant;
- increased antifreeze rate;
- five-year warranty;
- protection of containers from burglary.
Minuses:
- liquid heat capacity is 10% lower;
- high viscosity;
- cannot be used in galvanized heating pipelines;
- prohibited in boiler equipment with electrodes.
THERMAGENT-65
Domestic liquid produced from German raw materials. The unique technology of Organic Technology is used in production. The antifreeze substance does not contain amines or other toxins. It is poured into boiler systems operating on liquid fuel, gas and current.
According to consumers, the drug does not spoil rubber, sealants and parasites. The manufacturer included additives that prevent the growth of bacteria and foaming, so the heating pipes will remain clean and with high-quality permeability.
The non-freezing coolant is included in the TOP 5, as it has a low level of crystallization at a temperature of -65 ° C, as well as a long service life. It protects against rust for up to ten years and is used for up to twenty seasons without losing its properties. This is more than economical.
Pros:
- raw materials for the production of antifreeze composition for heating are imported from Germany;
- the liquid does not freeze at low temperatures;
- can be bred;
- contains no toxins.
Minuses:
- ethylene is present;
- cannot be used in Galan type heating equipment;
- when combined with water, the quality of rust protection is reduced;
- functions poorly with wood-burning boilers due to overheating.
RODA
Antifreeze liquid from a well-known brand that creates boiler equipment from neighboring countries. The manufacturer also took care of the careful handling of heating systems.
Glycerin-based coolant is one of the safest. Contains an anti-foaming additive. The liquid does not freeze even at -30 °C. It boils after +105 °C, so it is suitable for a larger number of heating lines and equipment.
Contains a fluorescent dye for rapid detection of leaks in pipes and heating radiators. Non-freezing liquid is produced in containers of 10 and 20 kg. It is poured into the system in proportions of 113 kg per 100 liters.
Experts recommend this liquid for heating networks with open circuits, where the expansion tank is not equipped with a sealed lid. The organic antifreeze composition is not dangerous when evaporated. Therefore, this type of heating fluid can be used even in food industry enterprises. The advantage of the coolant is that it is allowed to be used in galvanized pipelines.
Pros:
- service life eight to ten years;
- fire resistance;
- will not harm circulation pumping equipment;
- When switching to this type, there is no need to flush the heating line.
Minuses:
- relatively high price for 10 kg;
- it is forbidden to overheat the liquid;
- cannot be used with non-polar plastic materials.
AMT-300
Antifreeze heating agent from a domestic manufacturer, supplied to the market in barrels weighing 20, 30 or 180 kg. This makes it possible to immediately buy the required volume for your home at an affordable price. It is based on an oily substance with flavorings. Products must undergo catalysis and adsorption for a higher level of purification.
Not suitable for open communication systems. The density of the oil substance is 940 kg/m3, therefore it is suitable for relatively warm climates. Antifreeze from this manufacturer is mainly used in southern regions, where it rarely gets colder than -15 °C.
Antifreeze for heating entered the TOP due to its increased thermal stability when heated and the impossibility of ignition under the influence of high temperatures. The boiling point of the oil is almost +300 oC. Therefore, it is even poured into equipment that runs on solid fuel, but only with powerful pumping units to increase circulation so that the non-freezing coolant does not overheat in the exchanger.
Pros:
- almost zero acidity is gentle on heating system components, rubber, plastic, metal, sealant;
- high-quality fluidity in a heated state;
- high anti-corrosion properties, regardless of the period of use;
- does not accumulate condensation and does not form plaque.
Flaws:
- antifreeze composition is prohibited for open boilers;
- crystallizes at -15°C;
- it is necessary to use powerful pumping equipment.
It's better to make a decision in advance
If the choice of boiler power is made before determining the coolant of the system, then the calculation of all materials, radiators, circulation pump, etc., directly depends on the selected medium and is carried out taking into account its characteristics. It should be repeated that in conditions where there are guaranteed to be no risks of defrosting expensive elements of the water heating system design, the choice of water as the best transfer of heat into the premises will be fully justified.
Properly prepared water, using the necessary inhibitors, will work great.
But with possible interruptions and power outages or a drop in pressure in the gas main, the risk of accidents increases sharply
in winter Then it is better to choose antifreeze. This non-freezing liquid has nothing to do with oils such as “spindles”, car antifreeze or alcohol emulsions. We can only talk about specialized antifreezes for heating. They do not contain prohibited components and do not pose a risk of fire.