In the process of building and furnishing a two-story house made of wood, it is important to choose the right method for heating the second floor. Standard radiators do not always provide an acceptable level of heat; you have to increase the temperature of the boiler, but this is fraught with discomfort and unnecessary expenses - it is too hot on the ground floor, and the overall consumption of resources increases.
[contents]
The optimal solution to the problem would be a water floor on the 2nd floor in a wooden house. Its installation, with correct calculations that take into account the heat loss of the building and the average annual temperatures of the cold season in a particular region, solves a lot of problems:
- Current utility costs are reduced by lowering the temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
- Heat is evenly distributed over the entire area of the premises.
- The safety factor, reliability and durability are increased.
Due to these benefits, the “warm floor” system is in the vast majority of cases preferable to radiator or combined heating.
Warm floor with temperature sensor
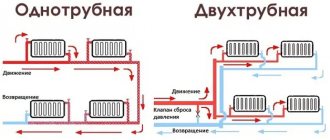
Connecting radiators, one-pipe and two-pipe systems
There are no special tricks in connecting radiators.
As expected, a Mayevsky tap is screwed into one of the upper outlets; hot water can be supplied through the second. However, the lower side pipe supply will be more aesthetically pleasing. The modern word in this regard is considered to be single-point connection devices, due to which it is possible to run both the supply and return into the same lower outlet of the radiator.
Using the same principle, you can make a point-to-point connection, but only on one side. This harness looks less cumbersome, plus there are many standard solutions. Typically, threaded connections on radiators are no more than one inch, so they can also be packaged using FUM tape.
rmnt.ru
17.03.17
Natural circulation scheme
To understand the principle of operation of the gravity system, study the typical diagram used in two-story private houses. Combined wiring is implemented here: the supply and return of coolant occurs through two horizontal lines, connected by single-pipe vertical risers with radiators.
How gravity heating of a two-story house works:
- The specific gravity of the water heated by the boiler becomes smaller. The colder and heavier coolant begins to displace hot water upward and take its place in the heat exchanger.
- The heated coolant moves along a vertical collector and is distributed along horizontal lines laid with a slope towards the radiators. The current speed is low - about 0.1-0.2 m/s.
- Dividing through the risers, the water enters the radiators, where it successfully releases heat and cools. Under the influence of gravity, it returns to the boiler through a return manifold, which collects coolant from the remaining risers.
- The increase in water volume is compensated by an expansion tank installed at the highest point. Typically, the insulated container is located in the attic of the building.
In modern designs, gravity systems are equipped with pumps that accelerate circulation and heating of rooms. The pumping unit is placed on a bypass parallel to the supply line and operates when electricity is available. When the light is turned off, the pump is inactive, and the coolant circulates due to gravity.
Scope of application and disadvantages of gravity feeding
The purpose of the gravity circuit is to supply heat to homes without connection to electricity, which is important in remote regions with frequent power outages. The network of gravity pipelines and batteries can work together with any energy-independent boiler or stove (previously they said steam) heating.
Let's look at the negative aspects of using gravity:
- due to the low flow rate, it is necessary to increase the coolant flow by using large-diameter pipes, otherwise the radiators will not warm up;
- in order to “spur” natural circulation, horizontal sections are laid with a slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of the highway;
- healthy pipes running under the ceiling of the second floor and above the floor of the first floor spoil the appearance of the rooms, which is noticeable in the photo;
- automatic control of air temperature is difficult - for batteries you need to buy only full-bore thermostatic valves that do not interfere with the convective circulation of the coolant;
- the scheme is unable to work with heated floors in a 3-story building;
- An increased volume of water in the heating network implies prolonged heating and high fuel consumption.
To fulfill requirement No. 1 (see the first section) in conditions of unreliable power supply, the owner of a two-story private house will have to bear the costs of materials - pipes of increased diameter and cladding for the manufacture of decorative boxes. The remaining disadvantages are not critical - slow heating is eliminated by installing a circulation pump, lack of efficiency - by installing special thermal heads on radiators and insulating pipes.
Design Tips
If you have taken the development of a gravity heating scheme into your own hands, be sure to consider the following recommendations:
- The minimum diameter of the vertical section coming from the boiler is 50 mm (meaning the internal size of the nominal diameter of the pipe).
- The horizontal distributing and collecting manifold can be reduced to 40 mm, before the last batteries - to 32 mm.
- A slope of 2-3 mm per 1 linear line of the pipeline is made towards the radiators on the supply and the boiler on the return.
- The inlet pipe of the heat generator should be located below the radiators on the first floor, taking into account the slope of the return line. It may be necessary to make a small pit in the boiler room to install a heat source.
- On the connections to heating devices on the second floor, it is better to install a direct bypass of small diameter (15 mm).
- Try to place the upper distribution manifold in the attic so as not to run under the ceilings of the rooms.
- Use an open-type expansion tank with an overflow pipe leading outside and not into the sewer. This makes it easier to monitor when the container is overfilled. The system will not work with a membrane tank.
The calculation and design of gravity heating in a cottage with a complex layout should be entrusted to specialists. And lastly: lines Ø50 mm or more will have to be made of steel pipes, copper or cross-linked polyethylene. The maximum size of metal-plastic is 40 mm, and the diameter of polypropylene will be simply menacing due to the thickness of the walls.
Using two combi boilers
Devices that can operate on several types of fuel, such as a gas-wood boiler, are becoming increasingly popular. But the use of such a device only solves the problem of convenience, while the reliability of the system remains low. To correct the situation, you need to install 2 units.
How Sharing Is Possible?
Manufacturers of combination boilers do not prohibit connecting several devices to 1 system. A common chimney can only be used if both devices operate at the same time using the same fuel.
Design and principle of operation
A combined gas-solid fuel boiler has 2 fireboxes located one below the other. The lower one contains a gas burner, the upper one is used for burning wood or coal.
Switching modes is carried out in 2 ways:
- in budget class models - manually;
- in expensive ones - automatically.
The second option is more practical. A flame sensor or thermostat monitors the state of the firebox and, when firewood reaches it, sends a signal to the controller to start the gas burner.
Combination boiler design.
When using wood, install a tray for combustion products. This makes cleaning the unit much easier.
Some models are additionally equipped with electric heating elements. The heater will prevent freezing of the coolant if all types of fuel are unavailable.
Selection of gas burner
The characteristics of this unit affect the efficiency of fuel combustion, and therefore the efficiency of the boiler.
According to the possibility of regulation, there are 3 types of burners:
- fixed;
- multi-stage;
- modulation.
The first type is characterized by a simple design and low cost. The burner operates at constant power. To adjust the level of heat transfer, the boiler periodically extinguishes it and lights it again. This is the least economical mode.
The selection of a gas burner affects the efficiency of fuel combustion.
2- and 3-stage devices are capable of operating at 40, 70 and 100% of rated power. The optimal one is selected automatically.
The advantages of such burners:
- fuel economy;
- increasing the service life of the device.
Disadvantages: high cost and expensive repairs.
Modulation burners are the most expensive. They smoothly change power in the range from 10 to 100%, which allows the heater to operate without shutdowns. This further extends its service life and saves fuel.
Connection diagram
Combination boilers are connected to the system in the same ways as simple ones:
- consistent;
- parallel;
- with separator;
- with heat accumulator;
- with primary-secondary rings;
- with 3-way valve.
Boiler connection diagram.
The choice depends on the size of the heated object and available finances.
There are cases when a unit has been purchased, but there is no possibility of connecting to the main gas pipeline. This problem can be solved if you know how to convert a gas boiler to a solid fuel one.
Types of two-pipe heating
This type of heating can be divided according to the type of circuit and the type of wiring. Let's look briefly at each classification.
Layout – vertical or horizontal?
The system can be divided into vertical and horizontal, which depends on the location of the connecting pipes.
- Horizontal two-pipe systems are often installed in one-story houses of considerable length. This is extremely convenient for frame-panel objects, in places where it is desirable to install risers in corridors or on landings.
A feature of the vertical system is that all its parts will be attached to the riser in a vertical position. It costs an order of magnitude more, but during operation no air pockets will form. It is used mainly in houses with several floors, since each of them (floors) will be separately attached to the riser.
Both types of circuit are characterized by increased hydraulic and thermal stability. But in the second case you will have to balance the vertical risers, and in the first - the hinges.
What is the wiring like?
The wiring of two-pipe systems can be of the following types.
- Bottom. Here the hot pipeline will be laid in the basement, basement or under the flooring. The return line, which returns water to the boiler, will be located even lower. With this type of wiring, it is necessary to include an upper air line in the circuit, through which excess air will be removed from the system. Moreover, the boiler must be deepened in order to stimulate coolant circulation. The fact is that radiators should be placed above the boiler itself.
- In the case of top distribution, the distribution line is installed from above; moreover, an expansion tank should be placed at the highest point of the system (often this point is the attic of the house, pre-insulated).
Important! The overhead distribution system is not suitable for single-story buildings with a flat roof. It is characteristic that both horizontal and vertical wiring diagrams are suitable for both methods of arranging system parts
It is worth remembering that the upper distribution is not suitable for both lines, since sludge will accumulate in the lower one
It is characteristic that both horizontal and vertical wiring diagrams are suitable for both methods of arranging system parts. It is worth remembering that the upper wiring is not suitable for both lines, since sludge will accumulate in the lower one.
Types of direction of coolant movement
It is also worth noting another classification, which is based on the direction in which the coolant will move through the system. Thus, we get the following.
- A dead-end system in which the supply and return pipelines are directed in different directions.
Direct-flow two-pipe heating system, in which the movement in both lines is directed in one direction.
In addition, the system may have a built-in special pump designed to stimulate the movement of the coolant; this is sometimes also called forced circulation. Also, such movement can be caused by differences in temperatures and the slope of the highway, therefore, this type of circulation can be considered natural.
Note that for greater productivity of the heating structure, such a pump should be installed, moreover, even at the initial stages of installation. Natural circulation is more suitable for buildings with only one floor.
Important! If a horizontal system is planned, and the circulation will be natural, then the slope of the lines should be directed directly towards the heating boiler
HOUSE FOR A YEAR. Screed for a warm floor on the second floor // FORUMHOUSE
During the year, our House will be heated only with warm floors, including on the second floor. We'll show you how to screed after installing a heated floor, and we'll do it in two different ways!
Main page of the project and competition: https://www.forumhouse.ru/domView stages of construction: https://www.forumhouse.ru/stories
FORUMHOUSE is the most popular and authoritative portal in Russia dedicated to construction and country life.www.forumhouse.ru
More than 300,000 people have already subscribed to our channel: https://www.youtube.com/subscription_center?add_user=forumhousetv
FORUMHOUSE is hundreds of thousands of topics on the forum, thousands of articles and hundreds of videos on various topics covering all areas of construction and life outside the city. Here you can learn about a variety of construction technologies, find calculations and estimates, select the necessary engineering solutions and ideas for arranging your garden. Design, landscape design and even farming - on all these topics you can learn both the authoritative opinion of professionals and gain experience from ordinary people who have already gone through what is yet to come.
Chat on the forum: https://www.forumhouse.ru/
Find a construction team and place an order: https://www.forumhouse.ru/exchange
Read articles on construction and dacha topics: https://www.forumhouse.ru/articles
New videos every week: https://www.forumhouse.ru/video
Join us on social networks: https://vk.com/FORUMHOUSEhttps://www.facebook.com/FORUMHOUSEhttps://ok.ru/FORUMHOUSEhttps://plus.google.com/+%D1%84%D0 %BE%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BC%D1%85%D0%B0%D1%83%D1%81
Administrator
buildelsam.ru
What is the best heating scheme for a two-story house?
If to heat a small one-story private residential building you can use an ordinary stone or brick stove, then for heating large houses and cottages, all kinds of water heating schemes for a two-story house, designed for the use of gas or solid fuel heating boilers, are more effective.
In order to study this issue in more detail, this article will present a brief overview of instructions in which I plan to consider the three most common heating schemes for a two-story house using water radiators and underfloor heating systems.
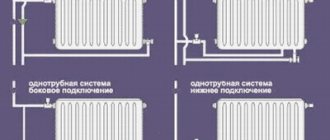
Option 1. Single-pipe connection diagram
The most stable, but at the same time the least effective, is the single-pipe heating system for a two-story house, which is a chain of heating radiators installed in different rooms, which are connected in series with each other using metal or plastic water pipes.
Options for connecting radiators in a two-story house using a two-pipe and one-pipe scheme
This type of connection allows you to minimize the amount of materials used and work performed, however, it has some significant disadvantages.
- Heated water, passing through pipes and radiators, gives off its heat unevenly, and as it moves to remote rooms of the house, it gradually cools down.
- To compensate for this phenomenon, in order to increase the heat transfer area, it is necessary to install more water radiators in remote rooms.
- With this connection option, it becomes impossible to independently adjust the optimal temperature for each individual room in a residential building.
Single-pipe heating circuit
Option 2. Two-pipe connection
More efficient, but at the same time more expensive, is a two-pipe water heating scheme for a two-story house, the installation of which requires the consumption of more materials and labor costs.
With this connection, each water radiator is individually connected with an inlet pipe to the direct heating circuit, and an outlet pipe to the return circuit of the heating system.
Connecting the first and second floors using a two-pipe scheme
For two-story houses, this connection option is considered the most optimal, as it has the following advantages:
- Thanks to uniform heat transfer, equal heating of all rooms of a residential building is ensured, regardless of their relative location relative to the heating boiler.
- Separate connection of each section makes it possible to independently regulate the required temperature for each specific room or room of a residential building.
- More efficient heat distribution leads to increased energy efficiency of the entire system, and accordingly to significant fuel savings.
Two-pipe heating scheme in a two-story house
Among other things, a two-pipe connection allows you to remove the main forward and return pipelines from prying eyes by placing them under the finished floor or behind decorative wall decoration elements.
Option 3. Combined connection diagram
When designing and building a residential building with a heated floor system, the most rational would be a combined heating scheme for a private two-story house, combining both a single-pipe and a two-pipe connection.
Heating system design with a combined circuit
In this case, parallel to the forward and return pipelines, a separate manifold for the coolant is connected through a three-way valve. This, in turn, is sequentially connected to a warm water floor system.
This connection has all the advantages of a two-pipe circuit. In addition, this option allows you to separately turn on heating radiators and a heated floor system, which makes it possible to more flexibly regulate the required temperature in the room.
Schematic diagram of the combined connection of underfloor heating and water radiators
In parallel with the water collectors of the underfloor heating system, you can also connect water heaters and heated towel rails located in the bathroom, shower room or kitchen.
Why choose a double-circuit boiler
Heating a two-story house with a double-circuit boiler can be a very profitable option if you select the right equipment in terms of power and other technical parameters. This option differs from a single-circuit boiler in the presence of an additional heat exchanger, which works to heat water, and not for heating. A double-circuit boiler has several important advantages:
Maximum completeness. In fact, such a boiler is a mini-boiler room, and you don’t have to buy anything extra for it: modern devices are already equipped with an expansion tank of the required volume, valves, fittings, etc. Such a device only needs to be connected to the gas and water supply system, as well as to the installed chimney. Economic benefit. You don’t have to constantly maintain a high water temperature in the boiler and waste fuel on it: the water becomes hot exactly when you need it. Compact convenient sizes. A double-circuit boiler can be an ideal solution for small houses; it is much easier for it to find a suitable location and connection option. For a single-circuit system with a boiler, it is advisable to allocate a special room equipped in accordance with all fire safety requirements.
A double-circuit boiler is an opportunity to equip your home with independent, reliable heating and at the same time provide the whole family with the necessary level of convenience. At the same time, the cost will be cheaper than purchasing all the necessary equipment separately and having it professionally installed. This will make the purchase not only reliable, but also profitable.
In which houses is it beneficial to install single-pipe pumping systems?
A reduction in the length of heating pipes relative to two-pipe schemes is inherent in multi-storey residential buildings and industrial buildings (workshops, warehouses), characterized by heating circuit lengths of hundreds of meters. The use of “one-pipe” in them really saves heating pipes. Widespread use in individual construction is explained by a misunderstanding of the real cost-benefit ratio of this type of heating by customers and practical heating engineers.
In small two-story houses with an area of about 100 sq.m. (50 sq.m. on the first floor, 50 sq.m. on the second floor), a “one-pipe” is often installed, which works well with short circuits containing 4-5 heating devices. Large houses with many radiators are not well suited for single-pipe circuits, although objects with a dozen batteries in a floor circuit actually work, as in the mixed vertical-horizontal single-pipe circuit shown below.
Single-pipe system of mixed (vertical - horizontal) type.
Zoning
Designers do not advise giving in to fashion trends and copying design ideas without taking into account dimensions, location and other nuances. Before planning and arranging furniture, every detail is thought through.
There are several simple rules that experts advise you to follow:
- Let the room have natural light. To do this, remove excess walls (except for load-bearing ones).
- If the rooms in the apartment are small (12 sq. m or 16 sq. m), the layout of the kitchen combined with the dining room will be the right solution.
- If the ventilation system is not designed correctly, the smell of food will spread throughout the apartment.
Installation recommendations
In addition to the general rules for installing heating equipment and heating networks, when assembling single-pipe systems with your own hands, you need to take into account its features. Here are some recommendations on the topic:
- first make a correct calculation of pipe diameters, especially for a gravity flow scheme;
- think carefully about the laying of branches or risers so that the former do not cross doorways, and the latter do not fall on the windows;
- Connect radiators for artificial circulation using a DN15 pipe, and for natural circulation – DN20;
- Observe slopes. For a gravity system - at least 5 mm per 1 m, pressure - 3 mm;
- the height of the accelerating manifold should be 2.2 m;
- the expansion tank in an unheated attic must be insulated, and the overflow pipe must be taken outside;
- if the boiler heat exchanger is made of cast iron, do not add cold water directly to the return line near the heat generator;
Do not load one ring of the heating circuit with a large number of batteries, otherwise the last ones will be cold.
Types of forced circulation of coolant in heating
The use of forced circulation heating schemes in two-story houses is used due to the length of the system lines (more than 30 m). This method is carried out using a circulation pump that pumps the liquid from the circuit. It is mounted at the inlet of the heating device, where the coolant temperature is lowest.
In a closed circuit, the degree of pressure that the pump develops does not depend on the number of floors and area of the building. The speed of the water flow becomes greater, so when passing through the pipeline lines the coolant does not cool down much. This contributes to a more uniform distribution of heat throughout the system and the use of the heat generator in a gentle mode.
The expansion tank can be located not only at the highest point of the system, but also near the boiler. To perfect the circuit, the designers introduced an accelerating collector into it. Now, if the power goes out and the pump stops, the system will continue to operate in convection mode.
- with one pipe;
- two;
- collector
You can install each one yourself or invite specialists.
One-pipe circuit option
Shut-off valves are also installed at the entrance to the battery, which serves to regulate the temperature in the room, as well as necessary when replacing equipment. A valve is installed on top of the radiator to bleed air.
Valve for batteries
To increase the uniformity of heat distribution, radiators are installed along the bypass line. If you do not use this scheme, then you will need to select batteries of different capacities, taking into account the loss of coolant, that is, the further from the boiler, the more sections.
The use of shut-off valves is not necessary, but without them the maneuverability of the entire heating system is reduced. If necessary, you will not be able to disconnect the second or first floor from the network to save fuel.
To avoid uneven distribution of the coolant, circuits with two pipes are used.
- dead end;
- passing;
- collector
Options for dead-end and passing circuits
The associated option makes it easy to control the heat level, but it is necessary to increase the length of the pipeline.
The most effective is the collector circuit, which allows a separate pipe to be connected to each radiator. Heat flows evenly. There is one disadvantage - the high cost of the equipment, as the amount of consumables increases.
Scheme of collector horizontal heating
There are also vertical options for supplying the coolant, which are found with lower and upper wiring. In the first case, the drain with the supply of coolant passes through the floors, in the second, the riser goes up from the boiler to the attic, where pipes are routed to the heating elements.
Vertical scheme
Two-story houses can have a very different area, ranging from several tens to hundreds of square meters. They also differ in the location of the rooms, the presence of extensions and heated verandas, and their position to the cardinal points. Based on these and many other factors, you should decide on natural or forced coolant circulation.
A simple diagram of coolant circulation in a private house with a heating system with natural circulation.
Heating schemes with natural coolant circulation are distinguished by their simplicity. Here, the coolant moves through the pipes on its own, without the help of a circulation pump - under the influence of heat it rises, enters the pipes, is distributed among the radiators, cools down and enters the return pipe to return to the boiler. That is, the coolant moves by gravity, obeying the laws of physics.
Scheme of a closed two-pipe heating system for a two-story house with forced circulation
- More uniform heating of the entire household;
- Significantly large length of horizontal sections (depending on the power of the pump used, it can reach several hundred meters);
- Possibility of more efficient connection of radiators (for example, in a diagonal pattern);
- Possibility of installing additional fittings and bends without the risk of pressure dropping below the minimum limit.
Thus, in modern two-story houses it is best to use heating systems with forced circulation. It is also possible to install a bypass, which will help you choose between forced or natural circulation in order to select the most optimal option. We make a choice towards coercive systems as more effective.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=olrD9qxCAhM
Forced circulation has a couple of disadvantages - the need to purchase a circulation pump and the increased noise level associated with its operation.
Air is a more economical alternative to water
The obvious advantage of a heating scheme for a two-story house using ordinary air is its efficiency.
It is believed that such a system is not very universal, since if the air supply is cut off, the building will quickly cool down. But what happens if the water suddenly turns off? That's it. There is always a risk of breakdown. Unfortunately, there are no systems that work forever. There are two types of air-based heating - forced and gravity ventilation. If you choose the latter, the air will move due to natural circulation, which arises due to the temperature difference in the passage areas. The disadvantage lies in the following - due to the penetration of cold into the premises through windows, doors and other elements of the structure, the air flow is disrupted. The result is that the upper part of the rooms heats up, while the lower part, on the contrary, cools down.
With forced ventilation, things are a little different. Air circulates reliably thanks to fans. Through some openings it enters the premises and then is blown out through others. There are also disadvantages. For example, equipment often creates noise that interferes with concentration or sleep.
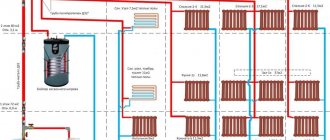
Collector heating system
Horizontal collector-type wiring in private houses with two or more floors is most common. Among its obvious advantages is the ability to mount a separate collector circuit on each floor and hide the pipeline elements in the floors or under the baseboards.
To implement the scheme, you should install a collector comb on each floor in a special cabinet (or niche), and run pipes under the floor; then, in addition to their direct purpose, these elements will heat the floor.
Two pipes are connected to each radiator - supply and exhaust. Each of them departs from a manifold unit, which includes two manifolds, which are connected to the supply and return pipelines. If desired, you can install shut-off valves on each supply pipe to turn off any individual radiator without stopping the operation of the others - for example, to regulate the room temperature or to service this radiator.
Horizontal layout
The horizontal type of pipe routing, in turn, is divided into:
- beam (collector);
- consistent.
The collector circuit, which, as the most popular, will be described in more detail below, is characterized by the presence of a separate supply for each radiator.
The sequential method implies the existence of a single branch extending from the riser, running along the perimeter of all floors and containing supply and return pipes.
Advantages of horizontal wiring:
- high level of hydraulic stability;
- the ability to automatically set and maintain the temperature in each individual room;
- when using the scheme, it is allowed to install separate heat meters, either two or more;
- Wiring of this type can be placed discreetly without spoiling the appearance of the rooms with pipeline parts.
Disadvantages of wiring:
- a complicated heating startup scheme: to ensure uninterrupted operation, gently release the air from it first;
- on all radiators it is required to install taps to release air pockets;
- the cost of a project involving a collector is quite high, since more building materials need to be purchased for the arrangement.
Systems with natural and forced circulation - which is better?
The difference between these two types of circulation is the way water moves through the CO. To implement a forced scheme, it is necessary to install special equipment, in particular a circulation pump; for a natural scheme there is no such need.
The EC is characterized by a number of advantages:
- absence of noise and vibration during system operation;
- simplicity of installation and maintenance;
- long service life.
Installation of a natural circulation system
At the same time, COs with natural circulation start up quite slowly; the water in the pipes of such systems can freeze at sub-zero temperatures outside. Another disadvantage is the need to install large cross-section pipes (they are more expensive and more difficult to install).
Nowadays such systems are used quite rarely. Users prefer a more modern and efficient heating scheme. This is forced circulation CO, which has the following important advantages:
- the possibility of constructing wiring of any length in a private house;
- independence of heating quality from coolant temperature indicators;
- simple adjustment of operating modes.
CO with forced circulation
In versions with forced circulation, hot water flows through pipes due to the operation of pumping equipment. The water comes from the boiler, in which it is heated, under the action of a special pump (it is called a circulation pump).
With such a heating scheme, Mayevsky valves and taps are installed on each radiator. The first make it possible to select the heating temperature of a specific battery. Valves can be automatic or manual. And the Mayevsky valve allows you to remove unnecessary air from the system.
Mayevsky valves and taps
Experts advise installing CO in two-story cottages with a double-circuit boiler and forced circulation. Then it will be very easy for you to install a “warm floor” in your house, install heated towel rails and always control the operation of the CO, setting the most comfortable temperature for yourself.
Partitions
The interior of the kitchen and living room begins to be thought out from the junction of the two zones.
- Here are some of the ways and objects that delimit space:
- installation of a bar counter;
- kitchen island;
- big table;
- installation of a low partition.
Designers advise installing a wide counter, since you can sit at it like at a regular table, and high chairs are quite suitable for the whole family.
However, in small rooms (16 sq m), narrow counters are installed. Kitchen islands are convenient to use, but are only suitable for large kitchen-dining rooms (25 sq m or 30 sq m). Capital low partitions are installed only if it has been decided in advance what they will be used for (for example, as a TV stand).
Water heating
Advantages and disadvantages of water heating
This type of heating has several disadvantages, but there are many more advantages. Let's list the pros and cons of this option.
Operating principle of a water heating system
The principle of operation of the system is quite simple: water is heated in the boiler and goes through pipes to the radiators. Through them it gives off heat and then goes back to the boiler along another circuit. One of the main tasks of a heating system is to start water and make it move through the pipes. This is realized in one of two ways: natural and forced. In the first case, water moves according to the laws of physics when cold water is displaced by hot water. In the second case, the movement of water is started using a circulation pump.
What are the main components of a water heating system?
The entire system consists of the following elements:
- A boiler in which water is heated and from which the heated water is sent to the heating circuit.
- Pipes.
- Radiators.
- Circulation pump.
- Expansion tank.
- Automation devices.
Where to start designing heating in your private home?
At the initial stage, you need to select the type of heating and calculate all the materials and work that will need to be purchased and performed. All this needs to be done and chosen as economically and efficiently as possible. In order for heating to function with maximum efficiency, the house must be well insulated and have the ability to retain heat for a long time. Heating is designed and installed during the installation of all communications.
What options exist for implementing a water heating system?
The easiest to implement is a single-pipe system. In this case, as the name implies, the coolant moves through one single pipe. That is, the radiators are connected to each other in series and water from the boiler flows into the first of them, then into the subsequent ones. After passing the last radiator, the water goes back to the boiler through a pipe that leads from the last radiator into the boiler. This option is one of the easiest to implement and very economical because it requires a minimum of equipment and materials.
In which houses is single-pipe “gravity flow” beneficial?
Just not in a 3-story building. The “gravity” coolant moves “lazyly”. The existing 20 kg difference in the weight of a ton of heated and cold water will not create a sufficient pressure difference between the supply and return for intensive movement through pipes and radiators.
In a two-story house, gravity flow will work well, but the second floor must be full, with an attic that allows the installation of an expansion tank. From the boiler in the basement (pit) to the tank there is a main vertical supply riser. The so-called riser extends from the riser. "lounger" sloping downwards. From the “lounger” the risers go down to the floor radiators. This vertical system, shown in the figure below, resembles the heating device of a multi-story building.
Gravity single-pipe vertical system of a 2-story building.
The attic second floor of your house, which has windows in the roof (low walls), makes it difficult to install a gravity system. The attic excludes the installation of an open expansion tank filled with antifreeze. A sealed tank with a gas outlet pipe leading outside will save the situation, increasing costs.
Inclined “lounger” pipes do not fit well into the attic space and can cross window openings, spoiling the interior of the room.
“Gravity” is more suitable for one-story houses in areas characterized by unreliable power supply.
How does heating work without a pump?
To understand how a forced circulation system works, it is worth understanding how buildings are heated using natural coolant circulation. As the latter, various special compounds and water can be used. For a one-story house, water heating is most often chosen.
The movement of water through pipelines is carried out according to the laws of physics. Having heated up in the boiler to a given temperature, it begins to rise up the riser. Due to this, all pipes and radiators of the system are gradually heated. The newly incoming hot water gradually displaces the cold water down to the boiler.
After the cooled coolant heats up again in the boiler, it will begin to rise up the riser to displace the cooled down. This cycle will be repeated as long as the boiler operates. Obviously, the larger the diameter of the pipe, the more coolant will pass through its cross section per unit time.
That is why, with natural circulation, the diameter of the pipeline and the dimensions of the mounted radiators are of great importance. If the area of the latter is insufficient, it will be difficult to warm the room to a comfortable level.
General operating principle
The operation of any heating system is to convert the energy of burned gas, solid (liquid) fuel or electricity into heat. Heated water (antifreeze) flows through pipes into radiators, where it releases heat into the space.
Gravity system
Pipe slope during natural circulation in the heating system
The operation is based on the laws of physics. If the contours provide for the natural movement of water, then such a scheme is called gravitational.
It is extremely difficult to create a heated floor circuit in gravity systems without the use of additional pumps. A difference of several millimeters in the pipes in the floor leads to airing and cessation of coolant movement.
The density of the heated coolant is lower than that of the cold one. Due to the difference in density, water/antifreeze from the boiler rises upward along the supply riser (diameter 60 - 80 mm). An open or closed expansion tank is installed at the top of the entire system.
The upper circuit of the wiring is laid along the perimeter of the second floor premises. A pipe with a diameter of 40-50 mm is installed with a slope of 2-3 cm per meter of length. In places where radiators are installed, pipes with a diameter of 16 - 25 mm are welded into the wiring. The liquid flows through them into the radiators. The coolant then enters the radiators on the ground floor.
At the level of the boiler or slightly lower, along the perimeter of the building, a lower circuit (return) is laid, into which the cooled water is collected.
The circuit is used in places where the electricity needed to operate the pumps is often cut off. Gas boilers in this case are equipped with non-volatile safety devices.
The same scheme is needed for systems with solid fuel boilers. In the event of a power outage, circulation stops, and wood/coal continues to heat the water. You can stop the operation of a solid fuel boiler only by quickly removing the burning fuel, which is extremely problematic. Increased pressure occurs, which can destroy pipes and radiators.