Residential buildings, as well as public buildings, industrial facilities and all kinds of ancillary buildings, as a rule, are heated using water heating systems. Most often they use natural circulation of coolant, but in recent years the use of pump circulation has been gaining popularity. The main advantage of using pumps is more uniform heating of rooms, saving energy resources, and, consequently, reducing financial costs for heat supply.
Why are circulation pumps needed?
Circulation pumps allow you to increase the speed of movement of the coolant, that is, under their influence, the water in the pipes flows more energetically, rather increasing the heat in the rooms. Yes, and it cools down in the “return” pipes, that is, in those coming from the heating radiators, more slowly, and in different areas of the heat supply the temperature is evened out, whereas without pumps it can differ significantly in different areas of the rooms.
The consequence of forced circulation is a noticeable reduction in energy consumption: less fuel is needed to heat water, be it gas, coal, electricity or liquid energy. Accordingly, both the supplying organization and the consumer will have to pay less for heat. It is especially beneficial to install such pumps of the required power in private homes; here the savings are the most impressive.
Another good thing about such units is the ability to regulate the heat supply, room temperature, and energy consumption. With the help of simple automation, it is easy to configure the system for the optimal functioning option, without overheating the room and irrational dispersion of heat. Fuel savings when using circulation pumps are up to 30%.
Circulation pump device
When choosing the most convenient pump, you should pay attention to the parameters of reliability and service life, features of energy consumption, level of automation, ease of maintenance and minimal vibration and noise.
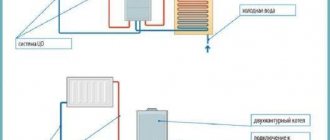
Turnkey heating connection in country houses
Turnkey heating connection in country houses is the most convenient option - you don’t have to delve into the intricacies of designing, installing and launching the system - everything will be done by professionals. Another advantage of connecting heating on a turnkey basis is the guarantee that is provided for the work of the craftsmen.
Note that in the absence of experience, when connecting a heating system yourself, more materials are wasted, because certain areas have to be redone, and the materials themselves are not used optimally.
If you want to order a turnkey heating connection, just fill out the form and our specialists will quickly and with a quality guarantee arrange the heating of your home.
Classification of the most commonly used heating schemes
Circulation pumps can be used in a wide variety of water heating schemes, and there are not many of them, especially those that are used everywhere. They are classified according to the fuel used, according to the algorithm of coolant movement, according to the layout of pipes and a number of other characteristics.
Thus, a distinction is made between upper and lower pipe routing, horizontal and vertical layout. There are single-pipe or double-pipe systems.
Heating system wiring
The latter are divided into radial, dead-end and associated. The first “rays” diverge from the heat source. In a dead-end circuit, the coolant, having reached the furthest radiators, moves back in the direction opposite to the original one. Passing, in accordance with the name, is a scheme in which the return flows in the same direction as the water carrying heat.
Application cases
A heating system equipped with a pump for forced pumping of coolant is appropriate in cases where the liquid cannot overcome hydraulic resistance and therefore does not rise up through the pipes. In heating systems with natural circulation of water, the slope and diameter of the pipes must be strictly observed, and the slightest mistake will damage the entire complex.
This limits the use of the system to compact rooms: after all, the larger the heated area, the longer the circuit, and, accordingly, the weaker the water flow. Even when using a powerful boiler, the coolant pressure rarely exceeds 0.6 MPa. And changing the pipe wiring to improve fluid flow will be expensive.
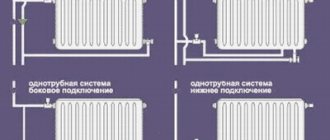
Single-pipe system: simplicity plus savings
With a one-pipe heating system, a return pipeline is not required: the heating radiators are connected in series to one pipe. They are much easier and faster to install and the cost of such a system is less than a two-pipe system. Single-pipe circuits are distinguished:
- according to the installation diagram - vertical or horizontal connection is used;
- according to the connection method - associated (flow) circuits and dead-end circuits.
Associated and dead-end heating schemes
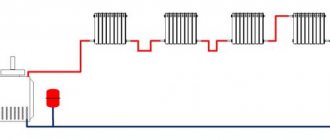
The flow-through option does not even require supply risers; heated water flows by gravity from top to bottom, warming radiators connected in series. The lower batteries will inevitably be colder, since the water passing through the upper sections of the system, giving them some of the heat, is cooled. It is often hot at the top, and cool zones are created below; these areas have to be equipped with batteries with a large number of sections. Therefore, such schemes are rarely used today, usually in private two-story houses, in order to save on hardware. And the lower floor in such cases, as a rule, is technical, utility.
The second method of a similar scheme with one pipe is distinguished by the use of closing sections with special jumpers - bypasses. This option is somewhat more complicated and more expensive, but still more economical than two-pipe analogues. And the heat in this case is distributed more evenly.
The most popular models of pumping units
Manufacturers offer a wide selection of equipment of different capacities, designed for pumping liquid media with various parameters. But we are only interested in flow-through models that operate in home heating and hot water supply networks.
How to distinguish circulation units from centrifugal and other types of pumps:
- in shape - the electric motor and impeller are installed in one housing, the pipes come out on the sides of the lower part (not in the middle);
- by the presence of a “wet” rotor, which significantly reduces the noise of impeller rotation;
- 2 standard sizes, installation length 130 and 180 mm;
- nominal diameter of the pipes is 15, 20, 25 and 32 mm, connection is coupling (threaded);
- nameplate pressure – 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 Bar.
The specified parameters can be easily determined by the product labeling. Example: the numbers in the name Wilo Star-RS 15/4 indicate an internal diameter of the connecting pipes of 15 mm (DN 15) and a pressure of 4 m of water column (0.4 Bar). Example two: the Grundfos ALPHA2 25-60 device is connected to DN 25 pipes and develops a pressure of 0.6 Bar (6 meters).
Reference. Manufacturers usually release extended product lines. The German brand Wilo offers circulation blowers with a pressure of 2, 4, 6, 7 and 8 m of water. Art. But the “running” models still remain “fours” and “sixes”, less often – “eights”.
The design of a pump with a “wet” rotor
Of course, there are more powerful pumps, whose pressure reaches 1...10 Bar, but they are not used in private homes. Small units 130 mm long with ½ and ¾ inch pipes are usually installed inside boilers, large ones (18 cm, 1 and 1 ¼") are cut into the heating lines.
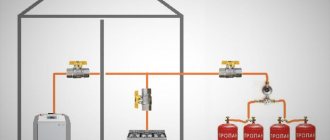
Two-pipe systems: more heat and automation
In practice, we usually come across two-pipe heating systems; they are installed with two lines connected at once: a supply and an outgoing (return) pipeline to each radiator. Water moves in parallel, in the same direction or in the opposite direction, depending on the specific type of pipe installation.
The return water (waste water), having left the radiator, goes back to the heating boiler, where it is heated again. This allows you to maintain a uniform temperature level throughout the entire circuit. Modern systems are also equipped with thermostats that operate automatically.
There are only two disadvantages to such a reliable and efficient system: high costs for pipes and the need to attract qualified specialists for installation.
Carrying out installation work
Heating systems equipped with a pump can be either single-pipe or double-pipe. Any scheme involves installing the device on a pipe through which the cooled coolant is returned to the boiler. This is explained by the fact that the rubber cuffs and seals of the pump, when heated by hot water, change their consumer properties and quickly wear out. In the return circuit, the water is cooled and does not harm the equipment.
If you are designing a system with forced circulation from scratch, it is better to immediately buy pipes of small diameter in order to save money. This will not affect the quality of heating in any way, but will make the operation of the equipment cheaper.
Expansion tank
An important element of the circuit is the expansion tank. It is connected to the return circuit and serves as a reference point: here the pressure force changes its sign - in the circuit up to the tank it is pumped, pushing water through the pipes, and after that it is rarefied, so that the pump sucks in the liquid. You need to remember the rule: when the pump is turned on, the hydrostatic pressure at any point in the suction zone must remain high - then the water circulation will not be disrupted.
An expansion tank is also needed to compensate for the lack of space in a closed system when the coolant expands - water turns into steam and increases its volume. If it were not for the tank, then when the water overheated it would be released. In addition, to avoid overheating and other problems, it is recommended to install only modern automated boilers.
Pump installation
It is better to install the pump at home in a horizontal position: this way the equipment will produce less noise.
The pump is fastened to threaded connections; shut-off valves are inserted into the circuit - one valve on a straight section of the pipe, one on the outlet directly in front of the pump, and one more on the outlet behind it. This is necessary in order to cut off the pump from the coolant if necessary.
Vertical or horizontal?
Experts consider a horizontal pipe layout to be more economical. It involves the installation of a common riser, which is located on stairwells or in corridors, that is, it does not hide the space of living quarters. The distribution pipes, both upper and lower, are connected to it, and then the radiators. It is most often installed in buildings with one floor, but a large area, where the contour length is significant.
Horizontal heating distribution
The disadvantage of this type of system is its airing, especially after temporary shutdowns, both emergency and technological. Special air vents, also known as Mayevsky taps, have to be attached to the radiators to bleed off the accumulated air.
The vertical system does not have this drawback; air pockets do not accumulate in it. But it also costs more, but it is convenient in multi-story buildings.
Varieties of horizontal schemes
Without going into details of rarely seen diagrams of horizontal water heating systems, we will describe in more detail the three most common varieties.
The simplest to implement, and therefore the most popular, is the beam scheme. Each radiator is separately connected to a collector or a central riser; it actually turns out to be a complex of “beams” of pipes. Quite a lot of them are required, since return branches are also needed. A big plus: high quality heating of rooms, and the pipeline is laid, as a rule, in the floor screed, that is, it does not spoil the aesthetics of the house.
Radiant heating distribution
Dead-end scheme: bringing the coolant to the final radiators and countercurrent return of the return. With such an installation system, fewer pipes are required, installation is somewhat simplified, and this is a fairly economical method. But it also has negative aspects. The main disadvantage: if you use this scheme without a circulation pump, then the remote radiators will warm up worse, and accordingly, the temperature in their environment will be lower. Maximum heating is observed near the heating boiler, in the area where the first radiators are installed.
Dead end heating circuit
This problem can be solved by installing several circulation rings of minimal duration instead of one long line. But it is still better to install dead-end systems in small houses, and there should be no more than five radiators on one branch.
The most effective, as experience shows, is the associated heating scheme. The reverse outflow of water is carried out in the same direction as the forward one; to install such a system, it is necessary to use a large footage of pipes. This increases the cost of the object, and there is one more minus: this iron “web” does not look the best, it does not fit well into the interior, unless the lady owner is a fan of high-tech.
Associated heating scheme
But the scheme also has a clear advantage: the most uniform heating of the room due to the fact that the circulation rings have the same length (a supply pipe and a return pipe of the same length are connected to each radiator).