Planning a heating system is not only about radiators and a boiler, but also about other elements that are part of the overall heating scheme and ensure trouble-free operation and full functionality. The choice of expansion tank for the heating system is an important part of such planning. It is the expansion tank that provides compensation for temperature expansion and ensures the normal operation of all equipment.
When choosing an expansion tank, you must immediately decide on the type of system, the principle of coolant circulation, and the total volume of water. In some cases, it will be necessary to install additional equipment, for example, a circulation pump.
Expansion tank for heating, what is it for and how it works
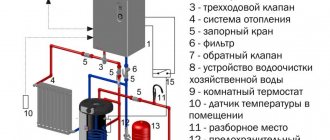
What is a heating tank, how to choose an expansion tank for a heating system? Such equipment compensates for the thermal expansion of the liquid when it heats up or cools down. After all, an increase in the volume of coolant in the heating system occurs every time it is started, that is, the normal functioning of the heating completely depends on the correctly selected expansion tank.
When the system starts, the heated water increases in volume, its excess enters the cavity of the tank, protecting the pipes from rupture. When cooling, the “excess” water is returned to the system and then goes to the boiler for heating, after which the cycle is repeated. In what other cases is an expansion tank necessary? It is this equipment that protects the system from air bubbles that can stop the circulation of the coolant.
Types and features of the expansion tank
The design of expansion tanks involves dividing equipment into three types:
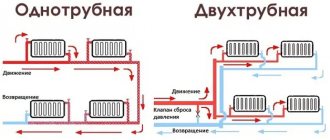
- Open tanks. Such equipment is used for systems with natural circulation; these are open containers that are connected to the general system using a connector in the bottom of the tank. They are mounted at the highest point of the heating system, usually in the attic.
- Closed tanks. This equipment is designed for heating systems with forced circulation without make-up. The installation of expansion tanks is carried out in a specially equipped boiler room; additional protection against freezing or maintenance is not required.
- Diaphragm expansion tanks. Modern type of equipment operating in automatic mode. The operating principle is similar to closed systems, but such equipment has an elastic membrane, which makes the tank more reliable and convenient to use.
Open and closed heating systems
Open tanks are used for heating systems where the coolant circulates by gravity. The container is usually cylindrical or rectangular in shape with an open top; the connection to the heating system is made through an outlet at the bottom.
Such tanks have the following advantages:
- the system is completely energy independent;
- The design of the tank is extremely simple.
There are many more disadvantages of using open tanks:
- Regular maintenance is required;
- heat loss in the system is quite high;
- the internal walls of the tank are susceptible to corrosion;
- During installation, additional pipe laying is required;
- installation is carried out in the attic, which requires additional reinforcement of the floors due to the large weight of the tank.
An example of an open expansion tank made of stainless steel.
Closed tanks can be used for any heating system, but they are usually in demand for forced heating. The tank is closed, that is, there is no contact between the coolant and the surrounding air. In addition, sealed tanks can be equipped with automatic or manual valves, pressure gauges for measuring pressure in the system.
There are many advantages of such equipment:
- the tank can be installed in a boiler room; it does not require frost protection;
- the pressure level in the system can be quite high;
- the tank is more protected from corrosion, its service life is longer;
- the coolant does not evaporate;
- no heat loss;
- Maintenance of the system is simpler; there is no need to monitor the pressure and water level.
WESTER closed expansion tank
Closed membrane tank
For the membrane system, a sealed tank is used, the functioning of which is similar to a conventional closed one. The principle of operation is very simple - when heated, the coolant expands, “extra” water enters one compartment of the tank, putting pressure on the elastic membrane. When cooling, the pressure decreases, the air from the second container pushes cool water back into the system, that is, it circulates.
Features of choosing an expansion tank for a heating system, several nuances
When choosing an expansion tank, you need to pay attention to the following criteria:
- installation location;
- type of heating system (with natural and forced circulation);
- operating parameters of the system, including pressure (it is necessary to perform pressure calculations for the tank, coolant, heat exchanger);
- volume of the expansion tank (cannot be less than 10% of the total volume of water in the system);
- the need for automated control;
- features of the tank operation (autonomous, non-volatile, with forced circulation and connected to the electrical network)
One of the criteria for choosing equipment is the calculation of water and its pressure. In such calculations of the heating system, the following are taken into account:
- the volume of water in the boiler unit (it is indicated in the passport for the boiler);
- the volume of water for radiators (must be calculated separately for each radiator and sum the resulting values);
- the volume of coolant in the system pipes (calculated for all circuits using the formula Vtotal = π × D2 × L/4, where D is the pipe diameter, L is the pipe length).
This calculation determines what volume the tank should have. Typically, when designing, it is stipulated that the volume of the expansion tank cannot be less than 10-15%. This value will be sufficient to remove air from the heating circuit and protect equipment from ruptures or leaks due to thermal expansion.
Eventually
As you can see, calculating the heating capacity comes down to calculating the total value of the four above elements.
Not everyone can determine the required capacity of the working fluid in a system with mathematical accuracy. Therefore, not wanting to perform the calculation, some users act as follows. To begin with, fill the system to approximately 90%, after which the functionality is checked. Next, the accumulated air is released and filling continues.
During operation of the heating system, a natural decline in the coolant level occurs as a result of convection processes. In this case, there is a loss of power and productivity of the boiler. This implies the need to have a reserve tank with working fluid, from where it will be possible to monitor the loss of coolant and, if necessary, replenish it.
Installation of a membrane expansion tank: subtleties of work
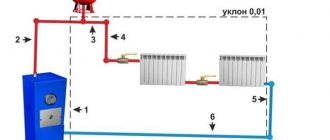
To install expansion tanks, you must use the following algorithm:
- the tank itself and its volume are selected (for forced systems a membrane-type model is required);
- Next, the device is fastened (the installation location of the tank must be level, reliable fixation is required, for open containers additional connecting pipes are laid);
- Next, a connection is made into the return pipeline, for which you can use plastic or steel pipes of the appropriate diameter (it must correspond to the diameter of the expansion tank chamber);
- after connecting the pipes and installing the American tap, it is necessary to check the pressure and operating conditions of the heating expansion tank (the container is filled with water, excess air itself leaves the gas chamber through a special valve);
- if necessary, you can install an emergency drain, which will be located after the American tap (for this, a tee with a branch is installed to install a half-inch tap to drain excess water).
At this point, the installation of the expansion tank for heating is completed, you can begin setting up the system and starting it up. To correctly determine the operating pressure, it is necessary not only to pre-calculate the volume of the tank, but also to determine parameters such as pressure indicators in the general system, the air chamber of the tank, for recharging equipment (if necessary) and the level of the maximum possible pressure.
Safety precautions
This is important for all structures operating under pressure - this is exactly the case. In addition to selecting containers with suitable characteristics, you should check whether the valves are in working condition and whether they allow pressure to be relieved. It is best if there is an adjustment option that changes the maximum pressure. The possibility of forced opening is mandatory - there is a possibility that the expansion tank for the water supply will fail. This feature is necessary for independent inspection.
Particular importance in safety is given to the condition of the membrane and its characteristics. You should pay attention to the quality of workmanship, resistance to diffusion processes, operating temperature range and service life. For expansion tanks, it is mandatory to have certificates confirming quality and safety - it is useful to familiarize yourself with them.
You should also not forget about personal safety. This applies both to direct work with expansion tanks and to staying near them during use. If a problem arises, you should always remember that the coolant is heated to high temperatures and there is a high probability of getting a burn if you come into contact with it.
A few important notes
In order for the system and expansion tank to function normally, it is necessary to take into account such points as setup, maintenance and calculations of pressure and coolant volume.
Setting up the tank for operation in the heating system, taking into account differences and pressure levels
How to start the tank after installation? It is necessary to correctly calculate the pressure level in the network, taking into account the following indicators:
- Pst is the static pressure, which will be equal to the height of the water column, determined by the height of the overall heating system from the point of installation of the tank to the top element;
- P0 is the air pressure in the gas (air) chamber of the tank;
- Pstart is the initial pressure for recharging the equipment;
- Pext – settings for the pressure created in the system;
- Pkon – the level of pressure that is created as a result of additional replenishment;
- Pkl – pressure level for the safety valve (for private houses this pressure can be 3 bar);
- Pmax is the level of maximum operating pressure for which the boiler heat exchanger is designed (it is the element of the entire heating network that is most sensitive to this parameter).
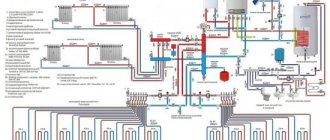
Boiler - which one to choose
Since the closed heating system of a private house can operate autonomously, it makes sense to install a heating boiler with automation. In this case, having configured the parameters, you do not need to return to this. All modes are supported without human intervention.
The most convenient gas boilers in this regard. They have the ability to connect a room thermostat. The temperature set on it is maintained with an accuracy of one degree. It dropped by a degree, the boiler turned on, heating the house. As soon as the thermostat is activated (the temperature is reached), the operation stops. Comfortable, convenient, economical.
Some models have the ability to connect weather-dependent automation - these are external sensors. Based on their readings, the boiler adjusts the power of the burners. Gas boilers in closed heating systems are good equipment that can provide comfort. The only pity is that gas is not available everywhere.
Two-pipe closed heating system in a house on two floors (diagram)
Electric boilers can provide a no less degree of automation. In addition to traditional units, induction and electrode units have recently appeared on heating elements. They are distinguished by their compact size and low inertia. Many believe that they are more economical than boilers using heating elements. But even this type of heating unit cannot be used everywhere, since power outages in winter are a common occurrence in many regions of our country. And provide the boiler with electricity. 8-12 kW from the generator is a very difficult matter.
Solid or liquid fuel boilers are more versatile and independent in this regard. An important point: to install a liquid fuel boiler, a separate room is required - this is a requirement of the fire service. Solid fuel boilers can be installed in the house, but this is inconvenient, since a lot of debris falls from the fuel during combustion.
Modern solid fuel boilers, although they remain periodic equipment (they warm up during combustion and cool down when the fuel burns out), but they also have automation that allows you to maintain a given temperature in the system, regulating the intensity of combustion. Although the degree of automation is not as high as that of gas or electric boilers, it is there.
Example of a closed heating system with an induction boiler
Pellet boilers are not very common in our country. In fact, this is also solid fuel, but boilers of this type operate in continuous mode. Pellets are automatically fed into the firebox (until the stock in the burner is finished). If the fuel quality is good, ash cleaning is required once every few weeks, and all operating parameters are controlled automatically. The only thing holding back the spread of this equipment is its high price: the manufacturers are mainly European, and their prices are corresponding.
A little about calculating boiler power for closed-type heating systems. It is determined according to the general principle: per 10 sq. meters of area with normal insulation take 1 kW of boiler power. It’s just not recommended to take it “back to back”. First, there are unusually cold periods during which you may not have enough rated power. Secondly, working at the power limit leads to rapid wear of the equipment. Therefore, it is advisable to take the boiler power for the system with a margin of 30-50%.