Due to the territorial and climatic features of Russia, the issue of heating always remains very important. Requirements for heating devices such as radiators are constantly growing. In light of this trend, aging cast iron radiators are being replaced by similar devices made of aluminum and bimetal.
Despite the fact that outwardly these two types of radiators are quite similar, they have many technical differences that are quite of interest to potential buyers.
We will try to understand the difference between aluminum and bimetallic radiators, their features, nuances and advantages in this article.
Aluminum radiators
Aluminum radiators require a coolant that is as pure as possible. For this reason, they are best used in private houses with an autonomous heating system, which is very rare in apartment buildings.
It is in an autonomous heating system that you can control the quality of the coolant , as well as the pressure in the pipes of the system itself. In autonomous systems there is virtually no risk of leaks due to water hammer.
Aluminum radiators
Modern aluminum radiators have an aesthetic and elegant appearance, as well as a stylish design. All this, coupled with good user characteristics and affordable prices, brings them to the top of sales among owners of private country houses. The service life of aluminum radiators varies between 10-25 years, if, of course, you follow all the instructions for their use.
Aluminum radiators have the following standard center distances: 200, 350 and 500 mm. In addition, there are vertical models of greater height with a center distance of 850 mm.
Technical characteristics of cast iron batteries
Of course, the most important parameters of heating structures are characteristics such as thermal output and power
Manufacturers prescribe power indicators in the technical documentation and, what is important, for a single section
On average, the sectional power of a cast iron heating radiator is 160 W.
The thermal output of cast iron structures is two times worse than that of aluminum or bimetallic ones. However, this disadvantage is due to slight inertia. Cast iron is able to retain thermal energy much longer. These heating structures show themselves most effectively in systems with natural circulation of liquid.
Power of cast iron heating radiators and its comparison with other types of batteries.
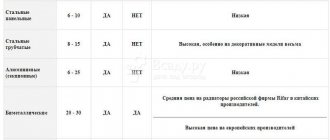
| Radiator type | Heat transfer of one section, W | Working pressure, bar | Crimping pressure, bar | Section weight, kg | Section capacity, l |
| Cast iron with a gap between the axes of sections of 500 mm | 160 | 9 | 15 | 7,12 | 1,45 |
| Cast iron with a gap between the axes of sections of 300 mm | 140 | 9 | 15 | 5,4 | 1,1 |
| Bimetallic with a gap between the axes of sections 500 mm | 204 | 20 | 30 | 1,92 | 0,2 |
| Bimetallic with a gap between the axes of sections 350 mm | 136 | 20 | 30 | 1,36 | 0,18 |
| Aluminum with a gap between the axes of sections 500 mm | 183 | 20 | 30 | 0,27 | 0,27 |
| Aluminum with a gap between the axes of sections 350 mm | 139 | 20 | 30 | 1,2 | 0,19 |
Another important parameter is the weight of cast iron heating radiators. One section weighs from 3 to 7 kilograms
The number of sections is different for each model. Much depends on the chosen model, as well as the size of the heated room. After the fasteners for cast iron heating radiators have been installed, sections can be added or removed as desired.
An equally important indicator is the size of the battery. The width of one section is from 8 to 10 cm, the height is from 37 to 57 cm, the depth is from 7 to 12 cm.
The volume of space from the inside can be 0.7-1.5 liters.
It is worth mentioning the working pressure. This is the load exerted by the liquid during circulation through the heating system. Typically the values are 6-10 atmospheres.
Maximum operating pressure. This is the load at which the battery can operate during a period of heavy water impact. When checking the heating system, a load is created inside the lines that is very close to the maximum. New cast iron models can withstand pressure of 12-18 atmospheres.
The average service life of cast iron heating radiators is 30 years. Of course, with careful treatment and favorable conditions, structures can last 60 years. This is a pretty good indicator, which is much higher than that of modern aluminum or bimetal batteries. Such a long service life of cast iron heating radiators is due to the considerable size of the internal channels, which prevents clogging from the inside.
Cast radiators
With the casting method, an alloy is poured into molds, then silicon is added for strength. Thanks to this, the radiator sections are sealed and can withstand pressures of up to 16 bar. During testing, the batteries are subjected to pressure testing at 25 bar.
In addition, the vast majority of radiators have fins in the shape of petals, which play the role of convectors to position the direction of the warm air flow into the heated room. Depending on the number of such channels, heat transfer and heat transfer will increase.
Cast aluminum radiators are divided into collapsible sections, so the number of sections can be reduced or increased to increase or decrease the thermal power. Thus, a failed section can be easily replaced with a new one.
Calculation of the number of sections
To effectively heat a particular room, a certain number of battery sections will be required. If there are not enough of them, the system will not be able to warm up the home in winter. To correctly calculate the quantity, there are special formulas.
The first option is by area. This method is used if the ceiling height in the room is standard, not higher than 2.6 m.
The formula looks like this: N = S × 100/Q, where:
- S is the area of the room;
- Q is the thermal power parameter of section 1;
- N is the required number of sections.
It is recommended to round up, with a margin.
The second option is a calculation for a room with a non-standard ceiling height, by volume. Based on the recommendations of SNiP, heating 1 m3 of area requires 41 W of equipment power. The formula is: N = V × 41/Q. The letter “V” indicates the volume of the room.
Even if the calculations were made incorrectly, you should not be upset. Aluminum batteries can be expanded, that is, additional sections can be added to them. To do this, you will need a special key for radiators, and the blocks themselves are connected using steel nipples.
Extrusion method
In this method, the heat exchange part is manufactured in an extruder under pressure, and the lower and upper manifolds are cast separately. All parts are then joined together by flaring, welding or pressing. In general, such radiators are not monolithic.
It is impossible to repair damaged components, as well as to increase or decrease the number of sections - everything must be calculated and before that, estimate what heat transfer and power you need.
In extreme conditions, such radiators do not work particularly well, therefore they are inferior in comparison with cast ones and are gradually being forced out of the market. But their price is much lower.
Anodized aluminum radiators
In this case, after the radiator sections are cast, they go through oxidation with an anode, hence the name. This is done in order to increase the resistance of radiators to corrosion.
Anodized radiators have smoother channels inside, and the coolant passes through them unhindered, due to which all sections are heated to the maximum and completely evenly.
Anodized aluminum radiators
Such radiators can withstand pressures up to 75 bar and temperatures up to 130°C. However, such advantages are worth the money. Anodized radiators are collapsible, their sections can be increased in number or simply replaced with serviceable ones.
Anodized radiators can be installed in a wide variety of heating systems; there are no restrictions on coolants.
Advantages and features of aluminum radiators
- Aluminum radiators have high heat transfer.
- They weigh little and are easy to transport, drag and install.
- They look quite stylish and come in many different sizes, so they can be installed in a variety of places.
- They are advantageous to use with thermostats due to their good heat inertia.
However, do not forget what we already mentioned at the beginning of the article. Aluminum radiators are best used in private homes, with a separate heating system. Due to the coolants used in heating conventional apartment buildings, they can eventually fail.
Why don't they warm up?
It is extremely unpleasant at the height of the winter season to face the fact that either the whole or part of the heating system is cold. To figure out why the heating radiator in the apartment does not heat, the reasons need to be looked for in what is preventing the flow of coolant into the system.
There are only a few of them:
You can eliminate some of the reasons yourself, for example, remove the air lock.
The heating battery in the apartment has burst - what to do:
- If there is a circulation pump, it must be turned off
to relieve excess pressure on the system. - Open the Mayevsky tap
, and if there is none, then
remove the plugs from the battery
. - These actions will cause air to escape from the system
, which occurs with a characteristic hissing sound. - After water flows from an open tap, turn it off.
It is necessary to prepare containers for the coolant in advance and wait until the whistling from the system stops completely. After some time, you can check the radiators for the presence of heat - if they are hot, then everything is done correctly.
If the reason that the radiators do not heat is a lack of coolant, then such work should not be carried out independently, without having the appropriate experience. When water enters the system, air pockets can form. If the system is clogged, it should also be entrusted to the experts, since this will require removing it for cleaning or completely replacing its damaged areas.
Aluminum radiators Rifar
Aluminum radiators manufactured by Rifar, which have the most advanced performance among their analogues, also have remarkable design features. The structure of the vertical channel and the 2.8 mm thick wall allow them to withstand pressures of up to 20 atmospheres. This is their main difference from other brands of aluminum radiators.
Aluminum radiators Rifar
For free flow of coolant, they have reduced hydraulic resistance. With such radiators, even non-freezing liquids can be used as a coolant. A yellow sticker is placed on such radiators, which lists the main types of coolants suitable for use. The service life of Rifar aluminum radiators ranges from 10 to 25 years.
Bimetallic radiators
Bimetallic radiators are so called because they are made from two types of alloys. To ensure that the coolant flows freely through the internal channels, they are made of stainless steel. On the outside, the radiators are “wrapped” in an aluminum casing, which is famous for its good heat transfer and aesthetic appearance.
Due to the steel alloy and aluminum body, bimetallic radiators have excellent heat transfer and reliability. Steel channels cope well with the alkaline environment and acidity of coolants in heating systems of apartment buildings. It is for this reason that bimetallic radiators most often find their application there.
Bimetallic heating radiators
The coolant with high acidity and alkalinity circulates well through the steel channels, without touching the outer aluminum casing. And that, in turn, due to its smoothness and convection, produces good heat in the room. And in general, as mentioned above, the aluminum body looks more than stylish.
Speaking of stylish. The enamel coating provides this very stylish look to the aluminum body. In addition to decorative functions, it also performs a practical one - it reliably protects the aluminum body from corrosion. So it always looks almost like new and retains its performance characteristics for a long time.
If you decide to use bimetallic radiators in private houses with autonomous heating, we recommend that you integrate a special pump into the heating system to increase the pressure in the system. It may not be enough for the normal operation of a bimetal radiator.
Thanks to steel channels, bimetallic radiators have increased resistance to water hammer and high pressure in the pipes of the heating system. Radiators can be supplied either in separate sections or in the form of non-separable blocks. The last option is the most reliable.
Additional sections or blocks can also be attached to blocks. Installation is carried out on threaded connections with rubber gaskets to withstand high and low temperatures and high pressure.
How to calculate thermal power and determine the number of batteries
After the homeowner has chosen the desired radiator option, it is necessary to calculate the thermal power, which depends on the following indicators:
- wall material: brick or concrete panels;
- room area;
- type of windows: plastic or wooden;
- the number of window openings and external walls of the home.
The choice of one or another type of heating radiator for an apartment, based on the calculation of thermal power, is carried out for a conditional room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m and window sizes in the range of 1.5-1.8 m.
A simplified calculation, subject to satisfactory thermal insulation of the external walls, suggests using one section of the heating radiator per 1.5-2 m² of room.
The types of heating devices available for sale are capable of delivering different thermal power:
- one – 190 W;
- separate part of the bimetallic battery – 200 W;
- solid steel device - 450-5700 W;
- one section of cast iron radiator – 80-150 W.
As a rule, the manufacturer indicates the power of a solid or sectional heating battery in the passport for its products. The values described above, which determine the amount of thermal energy, are calculated for a coolant with a temperature of 70 ° C.
According to experts, regardless of the choice of unit, when creating a system it is important to pay special attention to such points as the prestige of the manufacturer of heating devices and the individual characteristics of the heating system. As a rule, the best radiators are manufactured by large rating companies
Advantages and features of bimetallic radiators
- Aluminum conducts heat well and allows you to warm up rooms in a short time.
- Radiator channels are resistant to corrosion upon contact with coolant. This significantly extends the service life of bimetal radiators.
- In addition to protecting against corrosion, the enamel coating of the aluminum body also gives the radiators a stylish look. Can be installed in any room.
- Due to the fact that bimetal radiators tolerate high pressure and temperature well, they “get along” well in any heating systems, especially in apartment buildings with central heating.
- Such radiators weigh little, they are easy to transport and install, and do it yourself.
pros
- Reliability and durability. Cast iron is unpretentious to the coolant; it will not be damaged even by large fractions or aggressive chemical impurities, often contained in water from Russian thermal power plants. The maximum permissible coolant temperature reaches 130-150 degrees. With regular cleaning, the service life of such a battery can be decades.
- High heat capacity and thermal inertia. Such batteries give off heat for a long time, which after switching off can remain in them up to one third of the original volume. However, this same feature of the material is also its disadvantage - more about this in the corresponding section.
Sectional bimetallic radiators Rifar
Structurally, such radiators are sections with a silicone gasket. This series is produced with center distances of 200, 300 and 500 mm. Moreover, the model with a distance of up to 500 mm is one of the most powerful models of the entire line.
By design, the section of Rifar bimetallic radiators is a stainless steel pipe filled with an aluminum alloy, and the filling took place under high pressure. Due to this, each section of such radiators is durable and has excellent heat transfer.
It should be noted that for bimetallic radiators Rifar it is allowed to use only special water in accordance with paragraph 4.8 SO 153-34.20.51 - 2003 from the “Rules for the technical operation of power plants and networks of the Russian Federation”. The service life of radiators of this model ranges from 10 to 25 years.
Bimetallic radiators Rifar