The reliability and performance of a heating system depends on the efficient operation of all parts included in it.
These include : a boiler for heating the coolant, radiators connected to it and to each other in a certain way, an expansion tank, a circulation pump, shut-off and control valves, and a pipeline of the required diameter.
Creating highly efficient heating system is possible thanks to special knowledge and experience in this field of activity. An important role in the working process of heating a room is played by the return pipeline.
Types of heating schemes
For multi-storey buildings, a single-pipe direct distribution system is often used. It does not have a clear division of pipes into the liquid supply to the radiators and the return, so the complete circuit is conventionally divided into two equal parts. The riser coming out of the boiler is called the supply, and the pipes coming out of the last radiator are called the return. Advantages of this scheme:
- saving time and material costs;
- convenience and simplicity of installation work;
- aesthetic appearance;
- the absence of a return riser and a sequential arrangement of radiators (coolant is supplied to the 1st, then the 2nd, 3rd and so on ).
For a single-pipe system, vertical wiring with a vertical circuit and heat supply from above is common.
With a two-pipe wiring system, it is meant to install two closed, parallel-connected circuits, one of them provides the function of supplying coolant to the heating device (radiator), the second - the function of its outlet (return).
Radiators are connected in several ways:
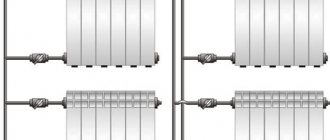
- Lower (or saddle, crescent-shaped). Provides for connection of supply and return to the lower connecting holes of the radiator. A Mayevsky tap and a plug are installed on the upper holes. Used for systems in which pipes are hidden under the floor or baseboard. Suitable for multi-section radiators; with a small number of sections, heat loss reaches up to 15%.
- The lateral method is popular. The pipes are connected to the radiator on one side: coolant supply through the top, return through the bottom. Not suitable for devices with a large number of sections.
Photo 2. Two-pipe heating circuit with a side connection type. The supply and return temperatures are indicated.
- The diagonal (or lateral cross ) method involves supplying hot water from above, connecting the return line from below and on the other side. Suitable for radiators with at least 14 sections.
- The third option for organizing a heating scheme is a hybrid method, based on the simultaneous use of one-pipe and two-pipe systems. For example, a collector circuit involves supplying coolant through a single riser; further on-site wiring is carried out according to an individual plan.
How it works and how to improve productivity
A single circuit does not ensure uniform heating of heating devices; heat transfer decreases with distance from the boiler (the last radiators receive coolant cooler than the first ones). The disadvantage of such a system is the high coolant pressure.
Reference. The performance of a single-pipe system is increased by the presence of a circular pump or bypasses formed on each floor.
Advantages of a two-pipe heating option:
- heating a sufficient number of devices equally, regardless of their distance to the heat source;
- adjusting the temperature regime or carrying out repairs on a separate device does not affect the operation of others.
Flaws:
- complexity of the wiring diagram;
- complexity of installation and connection.
The optimal choice for private construction is the most productive two-pipe system, which is also often chosen for heating luxury housing.
It is advisable to install a two-pipe system with the installation of a circulation pump, which allows the use of pipes of smaller diameter.
After it, in order to protect the recirculation circuit from squeezing, a check valve is installed.
When installing a system without a circular pump, the rule is observed : supply is possible if there is a slope from or to the boiler. A coolant with a higher temperature enters the radiator through the inlet (slope from the boiler to the heating device) and warms it up, and then exits through the return (slope from the radiator to the boiler), but at a lower temperature. Experienced craftsmen often resort to replacing the recirculation pump ring with a system of 3 or 4-way mixers.
Important! With natural circulation, the entire pipeline from the riser to the radiators should not be long.
Peculiarities
Long-term operation of boiler equipment is possible with a properly designed pipe distribution system, which ensures a certain temperature difference between the pipes that discharge and supply the coolant.
Risers and liners
Risers are responsible for the vertical distribution of water in apartments located one above the other. The connections perform the function of distributing liquid through taps and other plumbing fixtures inside the apartment.
In apartments, serial (tee) wiring is traditionally used. The collector type is more material-intensive and requires hidden installation of connections, which greatly complicates their further maintenance.
DHW systems are divided into two types:
- centralized,
- local (decentralized).
In centralized systems, a heating installation in a central heating point (centralized heating point) can serve one or more buildings within a microdistrict or village. Centralized circuits are designed and installed with circulation pipelines for uninterrupted supply of hot water. Without them, in the absence of water supply in the supply pipelines, the water cools down, and the consumer is forced to drain it, which leads to excessive water consumption on the meter. In addition, heated towel rails are installed, which cannot work in the absence of circulation.
Decentralized (local) hot water supply is used in cases where the construction of a centralized scheme is not economically profitable: with a low density of heat loads in rural settlements, etc.
DHW schemes are:
- With a dead-end pipeline, where, with low consumption or no water withdrawal, the water quickly cools down. This scheme is used in low-rise residential buildings with a short network, bath and laundry plants.
- With circulation risers. Similar schemes are used in multi-storey residential buildings and hotel complexes.
Heating pipe temperature table
The heating temperature, including return pipes, directly depends on the readings of street thermometers . The colder the air outside and the higher the wind speed, the higher the cost of heat.
A standard table has been developed that reflects the temperature values at the inlet, supply and outlet of the coolant in the heating system. The indicators presented in the table provide comfortable conditions for a person in a living space:
| Pace. external, °С | +8 | +5 | +1 | -1 | -2 | -5 | -10 | -15 | -20 | -25 | -30 | -35 | |
| Pace. at the entrance | 42 | 47 | 53 | 55 | 56 | 58 | 62 | 69 | 76 | 83 | 90 | 97 | 104 |
| Pace. radiators | 40 | 44 | 50 | 51 | 52 | 54 | 57 | 64 | 70 | 76 | 82 | 88 | 94 |
| Pace. return lines | 34 | 37 | 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 58 | 62 | 67 | 69 |
Important! the difference between the supply and return temperatures depends on the direction of movement of the coolant. If the wiring is from above, the differences are no more than 20°C , if from below - 30°C.
Pressure norm
Effective transfer and uniform distribution of coolant for the performance of the entire system with minimal heat loss is possible at normal operating pressure in the pipe lines.
The coolant pressure in the system is divided according to the method of action into types:
- Static. The force of influence of a stationary coolant per unit area.
- Dynamic. Force of action during movement.
- Maximum pressure. Corresponds to the optimal value of liquid pressure in the pipes and is capable of maintaining the operation of all heating devices at a normal level.
According to SNiP, the optimal indicator is 8-9.5 atm , reducing the pressure to 5-5.5 atm . often leads to heating interruptions.
For each specific home, the normal pressure indicator is individual. Its value is influenced by factors :
- power of the pumping system supplying coolant;
- pipeline diameter;
- remoteness of the room from the boiler equipment;
- wear of parts;
- pressure
Pressure control is possible using pressure gauges mounted directly into the pipeline.
Advantages
- Cost-effective;
- Attractive cost of the equipment itself;
- High performance indicators;
- Excellent heat saving;
- Versatility. Different types of steam boilers can use different types of fuel;
- High efficiency;
- For heating, pipes with a small diameter are used, which has a positive effect on the compactness of the circuit;
- Can be installed for any home, the circuit will remain safe. The main thing is to follow the rules of installation and operation;
- Consumed fuel does not require constant monitoring;
- Low inertia parameters, which ensures faster heating of rooms.
Why doesn't the return work work?
There are many problems associated with return flow in a heating system.
Squeezes feed
The water temperature in the return pipeline is determined by the design of the heating system and corresponds to the value in the temperature chart approved by the service organization.
Often apartment residents are faced with a problem when the return flow squeezes the supply.
A common reason is the transition of hot coolant from the supply line to the return circuit through various parts (for example, jumpers) of the hot water supply pipeline or ventilation. With an automatic control device, as a rule, it is enough to configure it correctly.
The coolant does not drain well
If the circulation of fluid in the heating circuit is disrupted, the water in the return pipes does not drain well. Initially, check that the power of the circulation pump meets the requirements. The reason may be hidden in a banal pipeline leak . The situation with poor circulation is typical for apartment buildings located on the final section of a heating main with insufficient pressure drop .
The return is cold, the pipes are clogged
Low return temperature is a serious problem that prevents indoor comfort. Causes of cold return:
- incorrect heating wiring;
- air bubble in the system or riser;
- insufficient water flow through the network;
- low temperature in underwater pipes;
- increased volumes of heat loss ;
- inefficiency of pumping equipment , result: poor circulation and insufficient temperature difference between heat supply and return;
- low pressure;
- clogged pipes and radiators.
The use of Mayevsky cranes makes it possible to eliminate air pockets that impede the movement of the coolant.
Photo 4. Mayevsky tap installed on a heating radiator. Using it you can bleed excess air from the system.
It is important to bleed air correctly:
- shut-off valves to stop the heat supply;
- open the Mayevsky tap, bleed the coolant with air;
- restore the movement of heat by opening the lock.
The narrow passage of the control valve often explains the low return temperature, this is a reason to replace it with a new one.
Periodically check the pipeline for clogging, which interferes with the movement of the coolant. Dirt and deposits are removed . If pipe patency cannot be restored, the section is replaced with a new pipeline.
Attention! The exact cause determined after checking the entire heating system.
This article lists the main malfunctions that can happen to the heating system of a private home, as well as ways to eliminate them. Troubleshooting heating systems can be divided into two types. Do-it-yourself heating system repairs can be done in the heating system wiring: radiators and fittings. All problems that arise in the boiler room and equipment require special knowledge and experience, so heating system repairs related to equipment to specialists.
Options for solving the return problem
Depending on what is the root cause of the problem, appropriate methods are selected to eliminate it. For example, if the return flow does not work well due to insufficient pressure or water speed, it is recommended to purchase a special pump.
His job will be to push water into the system with a certain force to avoid stagnation and ensure continuous movement of liquid through the batteries.
- If the pipes are clogged, you can use special water mixtures, biological products, or use pneumatic hydraulic shock.
- In the case of biological products, they involve the use of special microbes that are launched into the system and help break down the scale, sediment and other deposits that have stagnated there.
- They are good to use for older systems. The cleaning process will only take a few days. Regarding the use of pneumatic-hydraulic hammer, it helps break through scale and slag deposits without damaging the pipe walls.
The battery does not heat up
If one or more radiators do not heat or heat poorly, then the first thing you need to do is check if there is air in them using air vents. If water flows from the drains, but the radiator still does not heat, then you need to make sure that both taps of this radiator are open (such inattention can often occur). The next step is to check if the radiator is clogged. To do this, other heating radiators that heat and are on the same branch as the non-working one must be shut off so that all the water flows through this radiator. If it starts to warm up, it means it is not clogged. In this case, it is necessary to hydraulically level the branch. In simple terms, it is necessary to cover the remaining radiators on the branch so that the one who is not working gets more. You need to be prepared that leveling will take more than one day, because the heating system may be slow to respond to changes in settings. If the taps in front of the radiator are completely open, and it is cold, then it is clogged (extremely low probability). Basically, the last radiators on the branch may not heat . But this can always be eliminated by hydraulic leveling. If someone tells you that “it’s not pumping there” or “the pump’s power is insufficient,” don’t rush to believe and touch the pump or pipes. In order to prevent the pump from pumping too much, you need to try very hard when installing the heating system. If one or more of the last radiators does not heat up even after working with the taps, then there may be an air lock in the pipes (see circulation disturbance in the heating system).
How to make radiators hot - looking for solutions
If you find that the return is too cold, you should take a number of steps to find the causes and troubleshoot problems. First of all, you need to check that the connection is correct. If the connection is not made correctly, the down pipe will be hot when it should be slightly warm. The pipes should be connected according to the diagram.
To avoid air pockets that impede the flow of coolant, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a Mayevsky valve or bleeder for air removal. Before bleeding the air, you need to turn off the supply, open the tap and let out the air. Then the tap is turned off and the heating valves open.
Often the cause of cold return is the control valve: the cross-section is narrowed. In this case, the tap must be dismantled and the cross-section increased using a special tool. But it is better to buy a new faucet and replace it.
The reason may be clogged pipes. You need to check them for passability, remove dirt and deposits, and clean them well. If passability cannot be restored, the clogged areas should be replaced with new ones.
If the coolant flow rate is insufficient, you need to check whether there is a circulation pump and whether it meets the power requirements. If it is missing, it is advisable to install it, and if there is a lack of power, replace or upgrade it.
Knowing the reasons why heating may not work efficiently, you can independently identify and eliminate malfunctions. Comfort in the house during the cold season depends on the quality of heating. If you carry out the installation and inspection of the heating system yourself, you can save on hiring third-party labor.
No comments yet
If you are already registered on our website, but have forgotten your password or have not received a confirmation email, use the password recovery form.
How much monthly contribution does the company accept for management of houses?
Representatives of the housing inspection department now call 20 residential buildings problematic. Significantly in them.
The house was accepted for management in the current year 2022. The first survey of utility networks showed a lack.
Entering the heating season takes a certain amount of time each year. There are regular and...
Status of connecting houses under management to heat supply as of 10/09/2018.
Status of connecting houses to the heat supply as of 10/04/2018.
The boiler works, but the radiators do not heat: why is there a cold return in the heating system?
The heating system is a complex structure consisting of several elements combined into one circuit and put into operation through a chain reaction.
But it happens that the system fails and the water in the batteries becomes cold. The reason for this may be problems with the return line.
The pressure in the heating system drops
Once again, we emphasize that after startup the heating system must operate for several days or even weeks. Air is dissolved in the system; it gradually comes out using automatic air vents and during manual de-airing of radiators. This leads to a loss of pressure. At first, frequent replenishment of the heating system is normal. If the system has been running for more than a month and the pressure drops, then you can check this version. If the volume of the expansion tank is incorrectly calculated, pressure surges in the heating system may occur, as a result of which the safety valve may be activated and water may be released, resulting in a drop in pressure when cooling. If everything is in order with this, then there is a leak in the system, which is not pleasant, you need to look for a leak.
How to deal with problems
If the boiler goes out and does not light up again, check the quality of ventilation in the room. This is a common cause of problems for atmospheric models “Proterm”, “Navien”, “Ariston”, “Bosch” with an open combustion chamber, because they take combustion air from the room.
What to do:
- Organize high-quality ventilation in the room;
- Install ventilation valves on sealed window packages;
- Open the window in the boiler room for air flow.
Check the presence of draft in the boiler chamber. To do this, light a match and bring it to the control window or chimney outlet. If there is draft, the flame will deviate to the side. If not present, it will burn evenly. In the latter case, a chimney inspection is required.
Problems with the chimney part
This is excess, deficiency or backdraft. All this leads to the fading of the wick and automatic shutdown of the equipment.
Backdraft or blowing out occurs due to weather conditions: strong winds, pressure changes lead to the burner extinguishing. During installation, take into account the requirements for the height of the chimney:
- The height of the pipe on a flat roof is at least 50 cm;
- With a distance from the roof ridge of 1.5 meters - from 50 cm above the ridge;
- At a distance of 1.5–3 meters - level with the ridge.
Compliance with these parameters will help to avoid blowing and backdraft.
Excess air flow occurs with a powerful kitchen hood or ventilation. The solution is to turn off the hood while the boiler is operating.
Lack or absence of traction provokes:
- Blockages. Occurs in stationary chimneys. Clear the mine of leaves, debris, and construction debris. Fixed and coaxial pipes can become covered with ice in winter. Along with combustion products, hot steam escapes into the street, condensation forms, which freezes on surfaces. Insulate the chimney.
- Damage, burnout of the pipe. Only replacing the chimney will help.
Line pressure drop
Does the dual-circuit device “AOGV”, “Beretta” or “Vailant” turn off and not turn on? This is possible when the fuel supply is unstable. For the same reason, the burner does not light the first time. First of all, check:
- Pipes and joints for gas leaks. To do this, lubricate them with soap foam. If bubbles appear, there is a leak. Then turn off the valves, open the window and call the gas workers.
- Counter. If there is a breakdown, the meter readings do not change; noise and crackling are heard. You can’t fix the problem yourself—you need a specialist.
If everything is fine, wait until the gas supply is restored.
Return is hot and supply is cold
Why is the return hot and the supply cold? This is a rare occurrence. It can be observed when the pump is installed in reverse and without a check valve. This is also possible due to the operation of the heated floor pump. When the floor is first started and heats the structure, it operates at full capacity and can, under certain circumstances, change the circulation in the radiator circuit. Once the floor warms up, it may go away on its own. If the pipes are hidden, then you need to check whether the pipes (supply and return) are mixed up. You can do it in different ways: with water or just blow.
What problems arise in the apartment due to cold return
Violation of the return flow entails certain problems and troubles.
Firstly, the batteries in this case do not heat up properly, or even do not work at all. Accordingly, the room itself becomes cold, which is certainly not encouraging.
Secondly, if the functionality of the return flow is impaired, a strong dissonance occurs in the temperatures of the supply and discharge of liquid.
This entails the accumulation of condensate on the walls of the boiler, which begins to react with carbon dioxide released from fuel combustion. The consequence of this process is the formation of acid, which corrodes the walls of the boiler, thereby destroying it.
No circulation or poor circulation in the heating system
The boiler is working, the pump is definitely working, but there is no circulation in the heating system. Again, the first thing we do is check the air in the radiators. Then, we check the shut-off valves (taps), which may have been closed somewhere due to inattention. The next step is to clean the filter in front of the boiler and in other places, if any. This will solve the issue in 90% of cases, even if the heating system has been recently installed. If not, then we check the heating pipes for the possibility of air pockets in the pipes (see installation of the heating system). If there are such areas in the heating distribution, then the problem can be temporarily solved by draining the water from the radiator under pressure. which is located behind the loop, the flow of water will expel the air from the loop. If possible, an automatic air vent should be installed on large hinges. This will eliminate the problem in the future. If, as a result of the above measures, circulation is not restored, then you need to contact a specialist.
Heating system design - what is return?
The heating system consists of an expansion tank, batteries, and a heating boiler. All components are connected to each other in a circuit. A coolant liquid is poured into the system. The liquid used is water or antifreeze. If the installation is done correctly, the liquid is heated in the boiler and begins to rise through the pipes. When heated, the liquid increases in volume, the excess enters the expansion tank.
Since the heating system is completely filled with liquid, the hot coolant displaces the cold coolant, which returns to the boiler, where it is heated. Gradually, the temperature of the coolant increases to the required temperature, heating the radiators. Liquid circulation can be natural, called gravitational, or forced, using a pump.
The return is a coolant that, having passed through all the heating devices included in the circuit, gives up its heat and, cooled, enters the boiler again for the next heating.
Batteries can be connected in three ways:
In the first method, the coolant is supplied and the return is discharged at the bottom of the battery. This method is advisable to use when the pipeline is located under the floor or baseboards. With a diagonal connection, the coolant is supplied from above, the return is discharged from the opposite side from below. This connection is best used for batteries with a large number of sections. The most popular method is side connection. The hot liquid is connected from above, the return is discharged from the bottom of the radiator on the same side where the coolant is supplied.
Heating systems differ in the way pipes are laid. They can be laid in one-pipe or two-pipe ways. The most popular is the single-pipe wiring diagram. Most often it is installed in multi-storey buildings. It has the following advantages:
- a small number of pipes;
- low cost;
- ease of installation;
- serial connection of radiators does not require the organization of a separate riser for liquid drainage.
Disadvantages include the inability to adjust the intensity and heating for a separate radiator, and a decrease in the temperature of the coolant as it moves away from the heating boiler. To increase the efficiency of single-pipe distribution, circular pumps are installed.
To organize individual heating, a two-pipe pipe layout is used. Hot feed is carried out through one pipe. In the second, cooled water or antifreeze flows back into the boiler. This scheme makes it possible to connect radiators in parallel, ensuring uniform heating of all devices. In addition, the two-pipe circuit allows you to regulate the heating temperature of each heating device separately. The disadvantage is the complexity of installation and the high consumption of materials.
Operating principle of a steam boiler
First of all, you need to understand what is called a steam boiler. A steam boiler is a device that generates steam. There are two types of steam produced - saturated and superheated. The saturated temperature is 100 degrees and the pressure is 100 kPa. Superheated steam heats up to 500 degrees, and the pressure can exceed 26 MPa. Saturated steam is used in household units, and superheated steam, due to its characteristics, is applicable only at industrial-scale facilities.
The raw material for creating steam is water, which is processed in a boiler running on any type of fuel. During operation, the generated steam is converted into a coolant that delivers thermal energy to the area where it is used.
Regardless of the design features of a particular device, the general principle of operation of a steam boiler always remains the same:
- First, the water goes through a purification stage and is sent to a reservoir (usually located at the top of the device) using an electric pump;
- The water accumulated in the reservoir flows into pipes leading to the collector located below;
- From the collector, water is directed upward, entering the heating zone;
- In the pipe, water is converted into steam, which escapes upward due to the difference in pressure between the liquid and gas;
- At the top of the structure there is a separator that allows you to separate steam from water and drain excess water into the tank;
- The steam is directed into the pipeline and sent to consumers;
- In steam generators, the heating stage is carried out again to achieve the required steam state.
To understand well how a steam boiler works, you also need to consider the features of its design, which will be discussed further.
Why is the riser hot and the batteries cold?
Sometimes, with a hot supply, the return of the heating battery still remains cold. There are several main reasons for this:
- installation was performed incorrectly;
- the system or one of the risers of a separate radiator is airborne;
- insufficient fluid flow;
- the cross-section of the pipe through which the coolant is supplied has decreased;
- The heating circuit is dirty.
Cold return is a serious problem that must be eliminated. It entails many unpleasant consequences: the temperature in the room does not reach the desired level, the efficiency of radiators decreases, and there is no way to correct the situation with additional devices. As a result, the heating system does not work as it should.
The main trouble with cold return is the large temperature difference that occurs between the supply and return temperatures. In this case, condensation appears on the walls of the boiler, reacting with carbon dioxide, which is released during fuel combustion. As a result, acid is formed, which corrodes the walls of the boiler and shortens its service life.
The role of return and its difference from supply
Sometimes, when carrying out plumbing work on their own, the user does not know how to identify the supply and return pipes when the battery is connected. If you are completely unfamiliar with the design, you can use a thermometer, identifying the supply and return pipelines by the temperature difference, if you know the circuits for discharging coolant to the heating radiators, consider the following options:
- With diagonal and side switching, the supply is always at the top and the outlet at the bottom.
- In the lower connection, the direction of movement of the input and output flows is sometimes indicated by arrows on the supply unit (binoculars).
- In Leningradka, the return pipe is considered to be the one coming from the last radiator in the row.
- In the manifold distribution, the supply combs are equipped with adjustable supply sensors in the form of fittings with transparent caps and indicators placed inside; the shut-off valves of the return comb are closed with threaded plugs. Also, the color marking of the forward feed is red, and the return feed is blue.
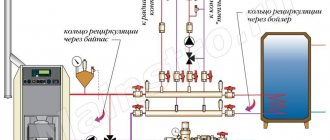
Rice. 3 Organization of heating systems using an open expansion tank
The return line plays no less important role than the direct line for supplying media to heat exchange devices or heated floors, its purpose and installation methods:
In gravity flow structures with an open storage tank. The movement of water in open circuits occurs due to the difference in hydrostatic pressures of the cooled and hot water columns due to the fact that the hot liquid has a lower density.
It follows from this that the greater the temperature difference between the cold and hot water column, the more significant the difference between the supply and return in pressure and, accordingly, the force that pushes the heated flow upward.
Therefore, the return line is designed and installed taking into account the following rules:
- Heat loss in the return must be quite significant to minimize the cooling of the water, that is, the batteries must have significant heat transfer.
- As the distance from the bottom point of the radiators to the boiler inlet pipes increases, the length of the low-temperature column increases and, accordingly, it more effectively displaces the heated coolant. The high location of the boiler from the battery lengthens the section with a cooled return, while simultaneously shortening the section of the high-temperature column - as a result, a large temperature difference shifts the working fluid much further up the circuit and heating occurs more efficiently.
- The upper installation of the boiler is contradicted by the condition under which it must be at a height below the level of the last batteries in the chain for the gravity flow of the carrier into it at an angle. If the boiler is installed low in the basement, to ensure normal circulation during installation, slopes towards the heating unit should be observed (2 - 3 mm per linear meter).
It should be noted that both of the above schemes are working (the latter is used more often) and their choice is related to the convenience of installing boiler equipment in the house.
Rice. 4 Closed heating system - diagram
Perhaps by reading. what is the return of a heating system, it will be interesting to read about Connecting the boiler to the heating system
In closed circuits with an electric pump. In multi-circuit heating with heated floors, circular pumps are installed that create the required pressure in the main; in many cases, two circular pumps are used - one pumps water throughout the system, and the second supplies coolant to the floors or radiator heaters.
With collector wiring, the return temperature relative to the supply plays an important role; the difference should not exceed 10º C, standard differences are 55 - 45, 50 - 40, 45 - 35, 40 - 30 degrees. To achieve these parameters, the cooled coolant from the return manifold is partially mixed with the hot coolant coming from the boiler, and then supplied to the heated floors.
In boiler piping. When the boilers are put into operation, the initial difference between the supply and return temperatures is quite significant - this leads to the formation of condensation on the walls of the heating chamber and chimney pipes, which, entering into a chemical reaction with carbon dioxide and other combustion products, causes accelerated corrosion of their surface.
To prevent these negative consequences, a small circuit is created with an adjustable check valve, in which the temperatures of the coolant entering the boiler and the heated fluid are quickly equalized. After reaching the specified temperature threshold, the thermal valve automatically opens and the entire system line is connected to the small heating circuit.
Sometimes, to equalize the temperature parameters of the supply and return, a bypass jumper of small diameter is installed between them; the width of its passage channel can be adjusted with screw valves (ball valves are used only for completely closing and opening passages).