Today, gas boilers are the best solution for heating almost any private house or apartment, both in terms of reliability and practicality, and in terms of purchase cost and operating costs.
Every year, one can more and more clearly observe a trend towards a preference for wall-mounted models: less universal, exclusively energy-dependent, but more efficient, compact and, in practice, according to statistics of service calls, almost as reliable.
In the article we will look at how to wisely choose an even more interesting option - double-circuit wall-mounted gas boilers, which allow, with the same size and efficiency, to provide the house with hot water.
What are wall-mounted double-circuit gas boilers?
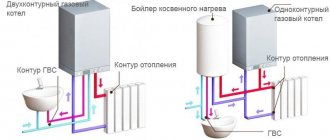
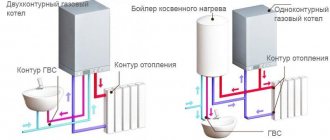
Gas mounted double-circuit models with the same dimensions and heating technical characteristics combine the functionality of two devices at once - the boiler itself and a flow-through (less often storage) water heater. The coolant from the heating circuit in dual-circuit models does not mix with sanitary water from the hot water supply (DHW) circuit.
It is advisable to install wall-mounted double-circuit models in small and medium-sized residential buildings with an area of up to 350-400 m2, in which the distance from the boiler to the points of consumption is not too large (7-10 m). Otherwise, preparing and heating running water will take too much time, 20 seconds or more, which negatively affects not only comfort, but also water and fuel consumption.
Another important point is the number of people living in the house, or rather the number of points of simultaneous consumption of hot water. Most dual-circuit models operate on the principle of DHW priority, i.e. when the consumption point opens, the heating circuit is preheated.
Less often, usually in more expensive models, where the distribution of performance is implemented using a three-way valve, the heating of the heating circuit does not stop completely, but the performance is still reduced.
In practice, this means that if you use several hot water consumption points at the same time, the performance of the DHW circuit may not be enough, not to mention the heating circuit. Therefore, the total number of rooms with hot water consumption points (bathroom, guest bathroom, kitchen, etc.) should not exceed three.
Design and principle of operation
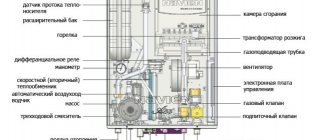
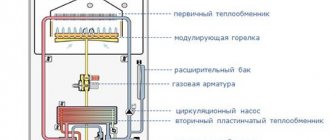
Double-circuit wall-mounted boilers differ from single-circuit boilers only in the presence of an additional heat exchanger and devices for distributing productivity between the circuits. The technical device may vary from model to model, but the standard design is simple and clear: a burner to which gas is supplied and its igniters → a primary heat exchanger, inside of which there is a heating circuit coolant and a secondary heat exchanger, inside of which sanitary water from the DHW circuit circulates → product removal system combustion into the chimney.
All well-known and common models are already equipped from the factory with all the elements and components necessary for the heating system: expansion tank, circulation pump, automatic air vent, safety valve, pressure gauge, set of sensors, etc. This means that for a standard heating scheme it is enough to just connect the supply and return lines to the boiler, as well as a water source for the DHW circuit (for example, a water supply).
To clearly understand the operating principle of dual-circuit models, let’s consider the functionality of each circuit separately:
- heating - a basic circuit in which the coolant continuously circulates, heating up in the heat exchanger and releasing heat through radiators in heated rooms;
- water heating - activated only when the hot water consumption point is opened, redirects all or a certain part of the heating circuit coolant to water heating.
After closing the consumption tap, the boiler switches back to the heating circuit and heats it up if the coolant has cooled down, or goes into standby mode (background heating) if everything is fine with the temperature.
Traditional double-circuit boilers are always characterized by a delay in the supply of already heated water (from 5 to 15 seconds), but there are models without such a delay, with a built-in boiler, operating on the principle of a storage heater, which we will talk about when describing the selection criteria.
In any case, there is also a delay in the supply of hot water, independent of the boiler, associated with the length of the pipeline between the boiler and the point of consumption, where the cooled water is located.
Baxi Nuvola-3 Comfort 240 Fi
The Italian-assembled model has a lot of positive aspects, including:
- wall mount;
- the area of a residential building or apartment allowed for heating is up to 220 m2;
- presence of a display;
- possibility of removing the control panel;
- operation on natural gas supplied through a main pipe or from a cylinder in a liquefied state;
- closed combustion chamber type.
In terms of overall dimensions, a gas boiler of this brand is considered quite large and heavy. After all, its weight is 70 kg, its height is close to a meter, its depth is half a meter, and its width reaches 60 cm.
A special feature of the model is 2 separated heat exchangers: the primary one is made of copper, and the secondary one is made of stainless steel. The temperature of the heating system is regulated by the Baxi boiler from 40 to 85 degrees. Net power starts from 10 kW and can increase by 2.4 times.
Since heating equipment from this manufacturer has a high price, buyers usually ask for clarification of the advantages of this product over others. In this case, experts note:
- Adaptation of the model to pressure surges in a gas pipe.
- Convenient ignition.
- Availability of storage boiler and expansion tank.
- Complete with an energy-saving circulation pump.
- Setting up operating parameters for a weekly period.
- The presence of automation that connects to an external temperature sensor and regulates parameters.
Type of combustion products exhaust system
Boilers are divided into two large subgroups - with an open combustion chamber and with a closed one. Accordingly, they are spilled into systems for supplying the air necessary for gas combustion and for removing combustion products into the atmosphere.
Chimney boilers with an open combustion chamber
An open combustion chamber assumes that air enters the burners naturally, from the room in which the boiler is located. The combustion products, also naturally rising upward, are redirected to the pipe to which the chimney pipe is connected. In a word, the effect of natural draft is used, based on the difference in the density of cold and heated gases.
pros
The operation does not require a special fan. This means the absence of noise and lower power consumption of the boiler.
The contraction does not have complex air injection and control elements (pneumatic relays), therefore, the overall reliability of the device is higher.
A chimney assembled in accordance with all the rules solves the problem of condensation formation.
Chimney boilers are cheaper than turbocharged boilers.
Minuses
Air enters the combustion chamber directly from the room. This means that the issues of constant supply ventilation should be considered. And this very often leads to excessive heat loss in the premises and the appearance of drafts.
There are special, fairly strict rules for the design and installation of a chimney. This often leads to large-scale repair and construction work and serious expenses - otherwise you will not be able to obtain permission to install the boiler.
Installing a chimney is not possible in principle in all buildings.
Flueless boilers with a closed combustion chamber.
Such boilers are often called turbocharged. The air for them is supplied from the street forcibly, using a special fan-turbine; accordingly, combustion products are also thrown out into the street by the created pressure.
The chamber itself is completely closed, and exhaust gases cannot enter the room.
The supply of air and the emission of combustion products can be carried out through two separate pipes, but the vast majority of modern boilers of this type provide for the installation of a coaxial system - a “pipe in a pipe”, which is discharged through the wall to the outside.
Inside the outer pipe, usually 100 mm in diameter, a second pipe with a diameter of 60 mm is located coaxially. Through the space between the outer wall and the inner pipe, air is forcedly drawn in from the street. The internal channel serves for the exit of combustion products.
pros
There are practically no significant restrictions on its installation.
There is no need to provide fresh ventilation in the room.
The cost of such boilers is slightly higher, but it is fully justified by the absence of large-scale work on the design and construction of the chimney.
Minuses
A significant temperature difference in the outer and inner pipes is accompanied by the formation of condensation. In severe frosts, this can lead to icing, impairing the permeability of the chimney and, accordingly, insufficient vacuum in the chamber for the automation to operate.
Mandatory elements of the system are a pneumatic relay, a fan and a fan switch relay. All of them have a certain resource, and failure of any of them leads to failure of the boiler.
The fan creates noise when operating. In addition, this is an additional energy consumption.
A boiler with an open combustion chamber and a conventional chimney looks more reliable in operation. But turbocharged boilers are easier to install and have no special restrictions on the installation location.
Controls, automation, protection levels
The boiler must be fairly easy to use, have clear controls, be equipped with the necessary functions to optimize operation and several degrees of protection against emergency circumstances.
Leading manufacturing companies are constantly improving their models, thereby creating competition between brands, so new developments are constantly appearing.
Thus, modern boilers can be equipped with the following options:
- Flame modulation in heating and water heating modes. The flame level is electronically regulated, ensuring smooth starts, which is especially important for models with instantaneous heating of DHW water. The automation independently selects the height of the flames depending on the set temperature and the specific current water flow. In some models, the last 5 degrees to the set heating temperature of the heating system are gained at a reduced combustion intensity. This allows you to make the operation of the device smoother, reduce the number of starts, and therefore increase the service life of the equipment.
- The smooth electronic ignition system pursues similar goals. When, after the minimum flame appears on the burners, it gradually grows to the specified combustion intensity within 30 - 40 seconds. When the boiler operates as a water heater, this option does not apply - what is important here, on the contrary, is the speed of heating the water to a given level.
- Weather-compensated boiler automation. This innovation, when installing an external street sensor, allows the equipment to monitor the level of external temperature and make adjustments to maintain an optimal microclimate in the apartment. More advanced equipment of this type also has an automatic self-adaptation function. Electronics not only compares graphs of changes in external and internal temperatures, but also conducts an analysis, making adjustments to the operation of the boiler, which leads to maximum comfort and significant gas savings.
- Pump post-circulation. A useful function that, when a room thermostat is installed, can significantly reduce energy consumption. Once the required heating temperature has been reached in the heating system, the boiler turns off and the pump continues to operate for another three minutes. When it is necessary to resume operation, both the boiler and the pump are started simultaneously.
- Naturally, all modern electronically controlled boilers allow you to accurately set the temperature in both the heating circuit and the DHW. In addition, some models provide two switchable ranges in heating mode - for conventional radiators and for heated floors.
- The electronics allow programming of the boiler operation for a certain period of time, with the programs being stored in memory for reuse.
- Any gas equipment has several degrees of protection - in case of insufficient draft, in case of heater extinguishing, in the absence or insufficient water pressure in the circuits, etc. In addition, modern models are equipped with other safety functions. So, if the temperature in the circuits drops to +5 degrees, the boiler will start on its own to bring the heating level of the coolant and water to a safe value, in order to avoid freezing. In addition, some control systems also monitor the condition of the boiler elements. If the device has not been used for more than a day, the processor will turn on the pump for a short time or switch the position of the three-way valve back and forth. This allows you to avoid blocking or “sticking” of these units and extends their service life.
- Control panels can have push-button, touch or electromechanical control, and are equipped with dial or digital indicators of temperature and pressure in the system.
Installation instructions
Instructions for installing a double-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler, problems associated with installation are of concern to all buyers, and also whether it is possible to install the equipment yourself. In this section we will understand the sequence of this process.
Installing a wall-mounted boiler is much simpler, unlike a floor-mounted one, since you don’t have to find a place to place it and prepare it. As for the connection, all the steps are the same. The main thing to remember is that you can install the boiler yourself, but the development and connection to the gas main must be carried out by specialists from the relevant department.
Sequence of work
- Determining the location and fasteners for fixation in accordance with the quality of the wall.
- Installation of circuit heating (piping outlets and inlets). It is advisable to install a filter that will purify the water from impurities and dirt.
- Connection of the boiler to the gas pipeline. This work is performed by employees of this structure, after which they install the meter.
- Installation of a coaxial pipe for waste disposal.
- Electrical connection. It is advisable to use a voltage stabilizer.
- Filling the heating system with water.
- Carrying out diagnostics and the first launch, which must be carried out by a specialist.
To avoid problems and breakdowns, you should immediately seek help from professionals who will set up the operation of the boiler in accordance with the requirements and standards.
How to choose a wall-mounted double-circuit gas boiler for a private home
Convection or condensation
The first thing you need to decide is the type of boiler, which affects the principle of its operation and, accordingly, efficiency:
- convection - a traditional boiler that accumulates thermal energy exclusively from the combustion of gas in the combustion chamber, while some of the heat goes into the chimney along with the combustion products;
- condensing - a more advanced, efficient and expensive design with another additional heat exchanger that accumulates the heat of condensate formed from exhaust gases. The temperature of the exhaust gases with this operating principle is 30-50 degrees or more lower, and the thermal energy accumulated by the additional heat exchanger is directed to heating the return line.
Of course, in the second case, the efficiency of the installation is much higher; fuel savings, depending on the design, can reach 15-20%. The real element of condensing boilers is a low-temperature heating system (large radiators, constant burning at low power, coolant temperature up to 50°C), in which case the higher costs pay off after 3-5 years of operation. Otherwise, in modern Russian conditions, the payback period for condensing models is from 7 to 12 years.
The cost of condensing models starts from 50 thousand rubles, but more often it is 65 thousand rubles or more, with the exception of Korean and Chinese models costing about 30 thousand rubles. Such a high price is explained by the high requirements for the materials of the additional heat exchanger, which must be resistant to the acidic effects of condensate. Another disadvantage of condenser units is the need to dispose of condensate, which is not ordinary water.
If you do not plan to organize a low-temperature heating system, we do not recommend bothering with condensing models; today, for now, it is enough to choose a traditional convection boiler.
Structural design and material of the heat exchanger
Double-circuit boilers have two heat exchangers, which can be combined or separated:
- bithermal heat exchanger is a heating circuit and a domestic hot water circuit combined into one inseparable structure; they are combined according to a “pipe-in-pipe” scheme, in which sanitary hot water is located in the inner pipe, and the heating circuit coolant is in the gap between the walls of the inner and outer pipes
- monothermic heat exchangers are two separate traditional heat exchangers, in one (primary) the coolant of the heating circuit circulates, in the other - sanitary water of the DHW circuit.
If in the case of a heating system, even the hardest, but not replaced water practically does not form scale that impedes circulation, although such cases do exist. Then in the DHW circuit the water is constantly changing, and when heated in the heat exchanger, it settles on the walls in the form of scale, significantly narrows the diameter of the coil, and over time completely clogs it.
But if two separate heat exchangers can be cleaned without problems even mechanically, then a bithermic (dual) heat exchanger is almost impossible to clean and if it becomes clogged with scale, it must be replaced. However, models with a single design are more compact and cheaper to manufacture than more reliable and durable boilers with two separate heat exchangers.
No less important, affecting durability and reliability, is the material from which the heat exchanger is made:
- steel – steel heat exchangers are inexpensive to produce, lightweight and flexible, and are not afraid of sudden thermal changes, but they are highly susceptible to corrosion, even despite good anti-corrosion coatings. Their service life is usually 10-14 years;
- copper - copper heat exchangers are more expensive, but also more thermally conductive, more resistant to corrosion, their service life is about 14-17 years.
Availability of a storage tank
Modern mounted boilers can have various methods of preparing hot water:
- flow-through – the previously described principle in which water begins to heat up when the point of consumption is opened;
- storage – the principle in which a certain volume of heated hot water is constantly available in the built-in storage tank of the boiler.
If you use hot water intensively, we recommend choosing a boiler with a storage tank, the capacity of which can be from 30 to 60 liters. A storage tank means eliminating the 5-10 second delay in preparation, a certain supply of already heated water, and a more uniform temperature. Please note that formally such boilers are usually called “single-circuit boilers with a built-in boiler”; when searching in the product catalog of an online store, they may be located in this category.
Minimum required power
It is reasonable to select the power after deciding on the model, since all modern models have a wide selection of versions with different heating capacities (usually the range is from 12 to 35 kW and wider).
For an average uninsulated or poorly insulated house in the climatic zone of the Moscow region, with 2 bricks and a ceiling height of 2.7 m, the minimum required power of heating equipment is calculated based on the rule: 1 kW for every 10 m2 of heated area. We also recommend setting aside a power reserve of 15-20%, and in the case of a double-circuit boiler - 25-30%.
In non-standard cases, if panoramic windows are used and the glazing area is much larger, the ceilings are high, the house is well insulated, and is located in the extreme southern or northern point of the country, correction factors are taken into account that can change the result by 15-30% up or down. You can make a detailed calculation using the calculator below.
Which heat exchanger to choose?
When choosing a double-circuit heating boiler, you have to decide whether to buy a boiler with a bithermic heat exchanger or with separate heat exchangers. You will have to decide, because there is no clear answer. Here are the criteria:
- With bithermic, water for hot water heats up faster, since heating comes directly from the burner flame. That is, you spend less water while it heats up, and less gas and electricity is wasted.
- Since the heating is direct, the temperature is maintained more accurately.
Deciding on a heat exchanger is not so easy - For models with separate heat exchangers, they are less likely to clog. In addition, it is possible to replace only one of the heat exchangers.
- If the bithermic “flies”, both heating and hot water supply do not work. In a boiler with separate heat exchangers, if the secondary one fails, the heating will continue to operate.
- As practice shows, it can be very difficult to flush a “neglected” bithermal heat exchanger. Plate-type ones, after washing, may be inoperative (the plates are at a distance of 2-3 mm from one another). But if the heat exchanger is of a collapsible type, it can be disassembled, cleaned and put back together. So problems can only arise with brazed plate heat exchangers. We recommend reading the article on how to clean a heat exchanger.
- Bithermic ones have less throughput - the pipe is divided into sections. To ensure the same water consumption, it is necessary to take more expensive models (due to the greater consumption of expensive metals for more efficient heat exchangers).
- In summer mode (without heating), a bithermic heat exchanger is more economical.
- As a rule, a bithermal heat exchanger costs more than two separate ones.
Opinion of the site editors . We recommend purchasing heating boilers with separate heat exchangers.
Now you not only know how a double-circuit boiler works, but also what heat exchangers can be installed in it.