To prepare hot water for household needs, each manufacturer of gas heating systems offers modifications with an additional circuit. When purchasing a water heating unit for your home, it will be useful to understand the scheme by which a double-circuit gas boiler operates. This will help you choose the right one for your needs and operating conditions.
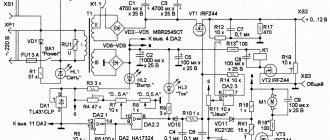
Navien double-circuit boiler design
The principle of operation of a double-circuit gas boiler
The gas boiler is designed in such a way that it can operate in two modes: heating and hot water supply.
When heating a room, a heat exchanger with coolant is heated in the boiler body. It can be heated to temperatures ranging from 35 to 80° depending on the result you need. To turn on the heating mode, the gas boiler is equipped with a thermostat that responds to a decrease in room temperature. At the same time, it transmits a signal to the system, as a result of which the pump starts, creating a vacuum in the coolant return pipeline. As a result, the heated coolant enters the heating system. If the pressure in the system reaches 0.45 bar or rises above this mark, the relay contacts close and the burner begins to operate. The launch of these processes is controlled by a microprocessor.
Diagram of a gas boiler with a fan.
The first time after startup, the gas boiler operates at minimum power, which gradually increases to maximum. If, during the process of increasing power, the coolant is heated to the required temperature, then the power does not increase further and the operation of the device goes into modulation mode. If immediately after startup the operating power of the device is too high, the burner is switched off electronically. It can be re-ignited no earlier than after 3 minutes.
The burner occupies the lower part of the combustion chamber, which is a metal container with good thermal insulation. A heat exchanger is located above it. The burner starts working at the moment when, in order to continue the correct operation of the system, it is necessary to heat the water, which in this case is used as a coolant. Simultaneously with the operation of the burner, the operation of the circulation pump begins, which ensures the movement of coolant through the pipeline of the heating system.
When the default boiler operating parameters are reached, the gas supply will be reduced and the boiler will go into standby mode. When the temperature drops again, the temperature sensor will give a signal, which will lead to an intensive supply of gas, causing the burner to ignite.
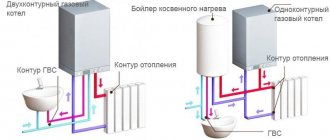
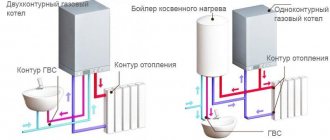
Water from the heating circuit does not enter the hot water supply circuit thanks to the three-way valve. The coolant enters the heating system pipeline through the supply pipes and returns through the return pipes. That is, in the first heat exchanger, water moves in a closed circle. Thanks to this, a minimum amount of plaque forms on the inner surface of the pipes. Water is supplied to the second circuit from the water supply; as a rule, it contains much more impurities, which increases the likelihood of circuit failure. If this happens, the boiler can be used as a single-circuit boiler, that is, for heating only.
Single-circuit
Gas-fired heating boilers are divided according to functionality. Depending on the method of heating the coolant, equipment is of two types: single-circuit and double-circuit.
Designs with one circuit are capable of heating the coolant, which will only be used in the heating system of the house. Therefore, such equipment is best used in small private homes.
The main advantage of a single-circuit boiler is that it costs an order of magnitude cheaper than its double-circuit counterparts.
Double-circuit gas boiler: principle of operation
As noted above, the device can operate in several modes. If a single-circuit boiler is intended only for heating a room, then a 2-circuit boiler can also heat water, but this has already been said. If you need to heat a room, then the principle of operation is as follows: the carrier, in our case it is water, enters the heat exchanger, which heats it to a certain temperature. Today the range hovers around 35-85 degrees Celsius. The thermostat starts heating mode automatically. This is done when the temperature in the system drops below normal. As a result, the circulation pump starts working and supplies water from the heat exchanger (preheated) to the system. The pressure in the system is also taken into account, which should not fall below 0.5-0.7 Bar. If necessary, the microprocessor sends a signal to the burner, which heats the media to the desired temperature.
Similarities with other designs
Although the design of a double-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler is far from simple, upon closer examination of the operation of its components, everything turns out to be not so scary. Equipment of this type resembles a gas instantaneous water heater (especially the presence of a burner and heat exchanger). All other parts are borrowed from a single-circuit wall-mounted boiler. A significant positive role is played by the built-in piping, consisting of an expansion tank, a circulation pump and a safety group.
When studying the principle of operation of a gas double-circuit boiler, it is important to keep in mind that mixing water from the hot water system with the coolant should not be allowed under any circumstances. To pour liquid into the heating system there is a separate pipe, which is part of the circuit
To prepare hot water, a certain volume of coolant is used, which moves inside the secondary heat exchanger.
Use a recirculation pump
The best option is that the water heater is located in close proximity to the hot water intake points. The closer it is, the faster the hot water enters the tap, the more efficiently it is used. If this option for installing a water heater is not possible, then it is recommended to install a recirculation pump.
The pump is installed in the section between the water heater and the hot water intake points, ensuring the slow movement of hot water through the pipes. In addition, if you install a heated towel rail in this section, it will perform its direct function at any time of the year, regardless of the operation of the heating circuit of the boiler.
Operating principle of a gas heating boiler: heating circuit
The main function of heating equipment is to heat the coolant by direct transfer of thermal energy that is generated during the combustion of a gaseous substance. For clarity, the process of operation of a single-circuit device that is unable to provide heating of water for consumer needs is considered below.
Gas supplied under a certain pressure from the main network enters a special chamber, where it ignites
It is important that this process is completely safe. The combustion power is controlled using various sensors and an automation system
When a flame appears, a significant amount of heat is released. It is transferred to the heating system directly through the heat exchanger, inside which the working fluid circulates. Heating is carried out externally. The heat exchanger is exposed to a jet of burning gas. The material used for this element is cast iron, steel or copper.
The principle of operation of a double-circuit gas boiler
Now we will begin to analyze the principle of operation of a gas double-circuit boiler. We have found out the purpose of individual components and modules, now this knowledge will help us understand how all this equipment works. We will consider the principle of operation in two modes:
- In heating mode;
- In hot water generation mode.
In heating mode, the boiler provides your home with heat.
Let us immediately note the fact that operation in two modes at once is impossible - for this purpose, double-circuit boilers are equipped with a three-way valve that directs part of the coolant to the DHW circuit. Let's look at the principle of operation when heating, and then find out how the equipment works in hot water supply mode.
In heating mode, a double-circuit boiler operates in the same way as a regular flow-through heater. When first turned on, the burner works for quite a long time, raising the temperature in the heating circuit to the set point. As soon as the required temperature is reached, the gas supply will be turned off. If an air temperature sensor is installed in the house, the automation will take its readings into account.
The operation of the gas burner in double-circuit boilers can also be affected by weather-dependent automation that controls the temperature of the outside air.
The heat from the operating burner heats the coolant, which is driven through the heating system in forced mode. The three-way valve is positioned to ensure normal water flow through the main heat exchanger. Combustion products are removed in two ways - independently or using a special fan located in the upper part of the double-circuit boiler. The DHW system is in a switched off state.
Operation in hot water mode
As for the hot water supply circuit, it starts the moment we turn the handle of the water tap. The resulting water flow triggers the three-way valve, which turns off the heating system. At the same time, the gas burner is ignited (if it was turned off at that time). After a few seconds, hot water starts flowing from the tap.
When switching to hot water supply mode, the heating circuit is completely turned off.
Let's look at the principle of operation of the DHW circuit. As we have already said, turning it on turns off the heating operation - only one thing can work here, either the hot water supply or the heating system. A three-way valve controls it all.
It directs part of the hot coolant to the secondary heat exchanger - note that there is no flame on the secondary. Under the influence of the coolant, the heat exchanger begins to heat the water flowing through it
The scheme is somewhat complicated, since it involves a small circle of coolant circulation. This operating principle cannot be called the most optimal, but double-circuit gas boilers with separate heat exchangers can boast of normal maintainability. What are the features of boilers with combined heat exchangers?
- Simpler design;
- There is a high probability of scale formation;
- Higher efficiency of DHW.
As we see, the disadvantages are closely intertwined with the advantages, but separate heat exchangers are more valuable. The design is somewhat more complicated, but there is no scale here
Please note that when the DHW is operating, the flow of coolant through the heating circuit stops. That is, its long-term operation can disrupt the thermal balance in the premises
As soon as we close the tap, the three-way valve is activated, and the double-circuit boiler goes into standby mode (or the heating of the slightly cooled coolant immediately starts). The equipment will remain in this mode until we open the tap again. The productivity of some models reaches up to 15-17 l/min, which depends on the power of the boilers used.
Having understood the principle of operation of a gas double-circuit boiler, you will be able to understand the purpose of individual components and will even be able to independently understand repair issues. At first glance, the device seems very complex, and the dense internal layout evokes respect - after all, the developers managed to create almost ideal heating equipment. Double-circuit boilers from companies such as Vaillant. are actively used for heating buildings for various purposes and for generating hot water, replacing two devices at once. And their compactness allows you to save space and eliminate the need to purchase a floor-standing boiler.
How is it calculated
A control method is selected, then a calculation is made
The calculated winter and reverse order of water supply, the amount of outside air, and the order at the break point of the diagram are taken into account. There are two diagrams: one of them considers only heating, the second considers heating with hot water consumption
For an example of calculation, we will use the methodological development of Roskommunenergo.
The input data for the heat generating station will be:
- Tnv – the value of outside air.
- TV - indoor air.
- T1 – coolant from the source.
- T2 – reverse flow of water.
- T3 – entrance to the building.
We will look at several heat supply options with values of 150, 130 and 115 degrees.
At the same time, at the exit they will have 70°C.
The results obtained are compiled into a single table for subsequent construction of the curve:
So, we have three different schemes that can be used as a basis. It would be more correct to calculate the diagram individually for each system. Here we examined the recommended values, without taking into account the climatic features of the region and the characteristics of the building.
To reduce energy consumption, it is enough to select a low temperature setting of 70 degrees and uniform heat distribution throughout the heating circuit will be ensured. The boiler should be taken with a power reserve so that the system load does not affect the quality operation of the unit.
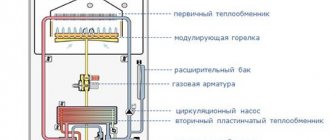
Construction of a double-circuit gas boiler
In order to understand the principle of operation of a gas double-circuit boiler, it is necessary to understand its structure. It consists of many individual modules that heat the coolant in the heating circuit and switch to the DHW circuit. The coordinated work of all components allows you to count on trouble-free operation of the equipment. Knowing the structure of a double-circuit boiler, you can understand its operating principle.
We will not consider the design of double-circuit boilers with precision down to the screw, since it is enough for us to understand the purpose of the main components. Inside the boiler we will find:
Design of models with two circuits: heating and DHW circuit.
- The burner, located in an open or closed combustion chamber, is the heart of any heating boiler. It heats the coolant and generates heat for the operation of the DHW circuit. To ensure accurate support of the set temperature, it is equipped with an electronic flame modulation system;
- Combustion chamber - the above burner is located in it. It can be open or closed. In a closed combustion chamber (or rather, above it) we will find a fan responsible for pumping air and removing combustion products. It is this that is the source of quiet noise when the boiler is turned on;
- Circulation pump – ensures forced circulation of coolant through the heating system and during operation of the DHW circuit. Unlike the combustion chamber fan, the pump is not a source of noise and operates as silently as possible;
- Three-way valve - this is the thing that is responsible for switching the system to hot water generation mode;
- The main heat exchanger - in a double-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler, it is located above the burner, in the combustion chamber. Here the coolant used in the heating circuit or in the DHW circuit for heating water is heated;
- Secondary heat exchanger - this is where hot water is prepared;
- Automation - it controls the operating parameters of the equipment, checks the temperature of the coolant and hot water, controls modulation, turns on and off various components, monitors the presence of flame, records errors and performs other useful functions.
At the bottom of the buildings there are pipes for connecting the heating system, cold water pipes, hot water pipes and gas pipes.
Some models of gas double-circuit boilers use dual heat exchangers. But the operating principle remains almost the same.
You may notice that the design of the geyser differs only in the absence of a heating circuit.
We found out the structure of a double-circuit wall-mounted gas boiler - it seems a little complicated, but if you understand the purpose of certain components, the difficulties will disappear. Here we can note the similarity with a gas instantaneous water heater, from which a burner with a heat exchanger remains here. Everything else is taken from wall-mounted single-circuit boilers. An undoubted advantage is the presence of a built-in piping - this is an expansion tank, a circulation pump and a safety group.
When analyzing the operating principle and design of a gas double-circuit boiler, it should be noted that water from the DHW circuit is never mixed with the coolant. The coolant is poured into the heating system through a separate pipe connected to the heating. Hot water is prepared using part of the coolant circulating through the secondary heat exchanger. However, we will talk about this a little later.
Varieties of such boilers
Among the many models of such boilers, we can distinguish:
- flow-through. Suitable for providing those who use more than fourteen liters of water at a time;
- equipped with an additional boiler. Provide a large amount of hot water.
It is also customary to divide the design of double-circuit gas boilers into floor-mounted and wall-mounted models.
Wall-mounted boilers are much cheaper than floor-mounted ones, which is their main advantage. In addition, such devices are quite easy to install, which allows you to save on installation costs. Connoisseurs of aesthetics are attracted to such devices by the ability to fit them into almost any room interior. Wall-mounted boilers are more compact than floor-mounted ones, which is also their undeniable advantage.
If we talk about the advantages of floor-standing boiler options, the first thing worth noting is incredible power. One such gas boiler can heat a large house. Unlike wall-mounted ones, floor-mounted ones do not need to be connected to electricity.
Also, such devices are more durable because their heat exchangers are always made of cast iron, which is not subject to corrosion. Floor-standing boilers can have different types of burners. The most popular type of burners is atmospheric. They are distinguished by a more affordable price, simple design and almost zero noise level. Fan burners are more powerful, but at the same time their cost is much more expensive than atmospheric burners.
Volatile and independent models
It is also worth making a choice in favor of a non-volatile or electricity-dependent boiler. In the first case, even a power outage will not affect your heating system. But such floor-standing boilers are not equipped with powerful automation. You will have to do all the adjustments manually, and this is sometimes difficult and unsafe.
If your equipment is equipped with powerful and reliable automation, then servicing it will be easy. But in this case, your house must be connected to a reliable source of electricity, because if there is no current, the boiler will turn off, which means the house may get colder.
Design of a dual-circuit device
The design of a double-circuit gas boiler (Fig. 4) consists of three main components, which are found in all types of appliance:
Also, an invariable part of a gas heating unit is a housing with a layer of thermal insulation.
Rice. 4 Design of a double-circuit gas boiler
The gas burner is a structure with perforations along the entire body, and there are nozzles inside. Nozzles supply and distribute gas for an even flame. The burner can be of several types:
- Single-stage - this burner is designed so that it cannot be adjusted, it operates in one mode;
- Two-stage - this device has 2 power adjustment positions;
- Modulated - the power of such a burner can be adjusted, due to this the boilers use fuel more economically.
Heat exchanger. Dual-circuit gas appliances have 2 heat exchangers:
- Primary - it heats the coolant for the heating circuit. Made from steel or cast iron;
- The secondary is a heat exchanger in which water is heated for the hot water supply circuit. It is usually affected by a slightly lower temperature than the primary, so it can be made from materials such as copper, stainless steel, etc.
Rice. 5 Primary heat exchanger for a dual-circuit gas appliance
Automation is a unit that controls the operation of a gas device. It includes an electronic circuit and a sensor system. Sensors provide readings of the operation of a double-circuit boiler to an electronic circuit, which sets the operating mode or turns off the device.
Circulation pump - this device is needed for a heating system with forced circulation. This is a component part for a volatile system. Such a pump provides the required pressure.
The combustion product exhaust system can be equipped with:
- natural traction. In this case, combustion products are discharged into the chimney, which must rise above the roof by at least 1 meter;
- forced draft. Boilers with such a system have a fan in their design to remove combustion products into a coaxial chimney (pipe within a pipe). Such boilers are called turbocharged.
Expansion tank. When the coolant heats up to a high temperature, it expands and its excess temporarily enters the expansion tank. The volume of the tank can be different, it depends on the volume of coolant in the system and the power of the boiler.
The combustion chamber looks like a metal container with thermal insulation. It is above it that the primary heat exchanger is located, and at its bottom there is a burner. The combustion chamber of a gas device can be:
A gas dual-circuit appliance with an open chamber is a device that can be non-volatile, since it takes combustion air directly from the room in which it is installed. It is recommended to install such units in separate rooms – boiler rooms. They must be arranged according to all the rules, namely have good ventilation and a window. If a double-circuit boiler with an open combustion chamber does not have enough air, it will emit carbon dioxide.
A gas double-circuit appliance with a closed chamber is a device that takes combustion air from the street through a coaxial chimney. The principle of the coaxial gas exhaust system lies in its special design - “pipe in pipe” (Fig. 6). That is, a pipe with a smaller diameter is located in a pipe with a larger diameter. Combustion products exit through a small pipe, and air is taken into the gas boiler through a large pipe. The advantage of a coaxial chimney is that it can be installed both horizontally and vertically.
Rice. 6 Pipe for coaxial chimney (pipe in pipe)
Heating system water temperature
- In the corner room +20°C;
- In the kitchen +18°C;
- In the bathroom +25°C;
- In corridors and stairwells +16°C;
- In the elevator +5°C;
- In the basement +4°C;
- In the attic +4°C.
It should be taken into account that these temperature standards refer to the heating season and do not apply to the rest of the time. Also, it will be useful information that hot water should be from +50°C to +70°C, according to SNiP-u 2.08.01.89 “Residential buildings”. There are several types of heating systems: Contents
- 1 With natural circulation
- 2 With forced circulation
- 3 Calculation of the optimal temperature of the heating device 3.1 Cast iron radiators
- 3.2 Aluminum radiators
- 3.3 Steel radiators
- 3.4 Warm floor
With natural circulation The coolant circulates without interruption.
One of the leaders in popularity is Lemax. Description of the boiler Premium 16N V
When choosing equipment for heating and hot water supply, you should pay attention to models from. Among the company’s other offers, “Premium 16N B” should be highlighted
This device has an acceptable cost - about 25,000 rubles. The boiler is equipped with a durable casing made of 2 mm steel. The equipment can be used for autonomous heating.
The heat exchanger is reliably protected from corrosion by an enamel coating. Inhibiting compounds provide protection against aggressive factors. Such double-circuit floor-standing gas boilers for home heating provide the consumer with the ability to connect equipment to liquefied gas. You can use the soft start option. The control panel consists of a thermometer and temperature controller. Using the first one, you can monitor the heating temperature of the coolant.
This device has a power of 16 kW. The maximum natural gas flow rate is 0.95 m3/h. Heating temperature – 90 °C. These double-circuit Lemax floor-standing boilers weigh 60 kg. They have many advantages, for example:
- ease of maintenance;
- advanced security protection system;
- increase in primary and secondary air flow;
- boiler compliance with all environmental and safety requirements;
- the ability to connect a room thermometer, with which the consumer will be able to adjust the temperature of the unit taking into account the temperature inside the room.
Typical diagram of a double-circuit gas heating boiler
Let's consider a typical boiler diagram using the example of a double-circuit gas heating boiler Saunier Duval Themaclassic F 30:
Boiler Saunier Duval Themaclassic F 30 (diagram)
1. Fan. 2. Traction sensor - manostat. 3. Primary heat exchanger. 4. Temperature sensor (emergency). 5. Gas combustion chamber. 6. Expansion tank. 7. Flame detection electrode. 8. Burner. 9. Ignition electrode. 10.Circulation pump. 11. Coolant temperature sensor. 12. Ignition block. 13. Bypass. 14. Gas unit. 15. Water pressure sensor in the heating system. 16. DHW heat exchanger. 17. Three-way valve. 18. DHW flow sensor. 19. DHW filter. 20. Device for water replenishment of the heating system. 21. Heating system safety valve. 22. Water drain tap. 23. Heating filter.
A - Water inlet from the heating system. B - Cold water. C - Water outlet to the heating system. D - DHW output. E- Gas.
The operating principle of a double-circuit heating boiler with two heat exchangers
When a double-circuit gas heating boiler operates in the “heating” mode, the following processes occur in it.
- The gas burner heats the primary heat exchanger,
- The heat exchanger transfers thermal energy to the coolant circulating (due to the pump) in it
- The three-way valve is in a position that prevents coolant from entering the secondary heat exchanger.
- All the coolant “goes” into the heating system, gives off energy to the radiators there and returns to the boiler through the return line.
Schemes of boiler operation in heating and hot water modes
Operation of a double-circuit gas boiler in a domestic hot water supply system (hot water supply)
- Gas burner heats the primary heat exchanger,
- The heat exchanger transfers thermal energy to the coolant circulating (due to the pump) in it
- The three-way valve is in a position that prevents coolant from entering the external circuit of the heating system.
- The coolant circulates through the secondary heat exchanger, heating it.
- Tap cold water, passing through the secondary heat exchanger, heats up and “goes” into the hot water supply line.
Advantages of heating boilers with separate heat exchangers:
- The primary heat exchanger is less susceptible to corrosion and the formation of plaque (scale) on it, since the coolant circulates in a closed circuit and does not constantly and significantly change its chemical composition.
- The secondary heat exchanger is more susceptible to “attack” by “aggressive” tap water. The salts included in its composition clog it over time, and the heat exchanger fails.
Disadvantages of heating boilers with various heat exchangers: higher cost compared to bithermal ones.
The principle of operation of a double-circuit gas heating boiler with a bithermal heat exchanger
Scheme of a double-circuit boiler with a bithermal heat exchanger
When the boiler operates in hot water supply mode, the gas burner heats the coolant located in the external circuit. And from it the running tap water located in the inner pipe of the heat exchanger is heated.
Advantages of boilers with bithermal heat exchangers: lower cost than boilers with separate heat exchangers.
Disadvantages: increased thermal “load” on the heat exchanger (heating the coolant and hot water).