Physicists often use the following words: body, interaction, connection, system.
When we solve problems, we consider in them events, processes, bodies of interest to us with the bodies surrounding them, as some kind of systems.
In a broad sense, a system is something connected by a specific purpose. It consists of individual elements and connections between these elements.
The Greek “Systema” is a whole, a compound consisting of parts, a set of elements naturally connected to each other and connections between them (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Elements of the system are symbolically indicated by numbered circles, connections between elements are indicated by arrows
Open and closed OS
All modern digital devices run on a specific operating system.
For example, for a computer it could be Windows or Linux, and for smartphones and tablets it could be Android and iOS. Operating systems come in open and closed types. The term “open operating system” means an open source system. This code is open for editing, and any user can change it (of course, within the framework of the license and the law). And a closed operating system does not allow you to “dig” into its source code.
Open OSs are usually free, develop very quickly, and can be customized in detail for any device. And all because any user who understands this at least a little can correct errors in the system, write drivers, etc. Errors in closed operating systems are corrected only by service packs produced by the official developers of the OS.
Consequently, the strength of any closed communication system is determined by the degree of secrecy of the key used in it.
However, this key must be known to other network users so that they can freely exchange encrypted messages. In this sense, cryptographic systems also help solve the problem of authentication (establishing the authenticity) of received information, since an eavesdropper passively intercepting a message will only deal with the ciphertext. At the same time, the true recipient, having received these messages, closed with a key known to him and the sender, will be reliably protected from possible misinformation. [p.246] The largest joint venture in Russia with foreign companies is developing the Ardalinskoye oil field in the Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The process of oil and gas production is fully automated, the technological system is closed. The extracted liquid comes from oil fields to the fractional separation unit of oil, water, and gas. At the collection point, the prepared commercial oil is measured and transferred to the main pipeline system. [p.103]
The banking system is a closed system. In the full sense, it cannot be called closed, since it interacts with the external environment, with other systems. In addition, the system is replenished with new elements corresponding to its properties. Nevertheless, it is closed, since, despite the exchange of information between banks and the publication by central banks of special statistical collections, information directories, and bulletins, banking secrecy exists. By law, banks do not have the right to provide information about account balances and their movements. [p.289]
When selling almost all goods and services by private firms to government agencies at various levels, a closed bidding system is used. Most business connections between firms also involve more or less formally expressed trades. It is extremely important for the buyer to maintain uncertainty among the bidders and thereby achieve a price that is closest to the actual costs of completing the contract. This chapter examines the question of what price a firm should charge for a contract in the face of this and other sources of uncertainty. [p.168]
Video materials and closed-circuit television systems [p.199]
The mechanistic model of the organization allows us to establish technical and economic connections and dependencies of various factors of production. Organizational management is focused on operational management. In this model, the organization is a closed system. A closed system has rigid, fixed boundaries; its actions are relatively independent of the environment surrounding the system. In this case, a company is considered as a system in a situation where its activities depend only to a small extent on the influence of environmental factors (political, economic, demographic, etc.). At the same time, it does not sufficiently take into account the role of the human factor in the effective operation of the organization. [p.34]
A closed system is characterized by the fact that any element of such a system has connections only with elements of this system. It has no connections with the external environment; its elements interact with each other only within the system. Closed systems are an abstraction and such systems do not exist in reality. But this concept is very useful when studying the behavior of systems that have lost external connections. [p.15]
Generally, the minting of good and bad coins differs between the two types of money. High-grade coins are characterized by the practice of free coinage, while inferior coins are characterized by a system of closed coinage - the state mints them exclusively from metal located in the state treasury. [p.752]
The banking system has the following characteristics: 1) includes elements subordinated to a certain unity, meeting common goals 2) has specific properties 3) is capable of interchangeability of elements 4) is a dynamic system 5) acts as a closed type system 6) has the character of a self-regulating system 7) is controlling my system. [p.88]
The banking system is a closed system, as there is banking secrecy. Banks do not have the right to provide information about cash balances in accounts or their movements. [p.88]
Speech modules (system of tales, persuasion for Clients, Partners) System of closed seminars Branded [p.95]
The essence of the banking system is characterized by 1) the peculiarities of the interaction of its constituent elements 2) as a single holistic formation 3) a constant dynamic state 4) as a closed type system 5) has the character of a self-regulating system 6) as a controlled system. [p.114]
One of the significant advances in organization science is the distinction between closed and open systems. A closed system does not depend on the environment, it is autonomous, does not interact with the environment and is clearly separated from it. Although completely closed systems do not actually exist, early research on organizations focused on closed systems. Early management concepts such as scientific management, leadership style, and industrial systems design were approaches that viewed the organization as a closed system because it took the environment for granted and assumed that organizational performance could be improved through internal change. It is quite easy to manage a closed system when the environment is stable, predictable, does not interfere with our affairs and does not create problems for us. If such conditions had actually existed, early management research would have succeeded in its task. [p.22]
Gasoline and diesel fuel from oil supply bases and tank trucks should only be accepted in a closed manner through the risers of the loading system, and a small amount of them through special dispensing devices. [p.134]
If the thermostat in the cooling system is not working, engine warming up slows down and self-regulation of fluid temperature is eliminated. Fears of possible overcooling of the radiator, when with the thermostat valve closed, insufficiently heated coolant will circulate only in the engine system, bypassing the radiator, are fair. To monitor this, a temperature indicator is installed on the instrument panel in the car cabin. A decrease in temperature indicates the need to take timely measures to prevent overcooling of the engine and its radiator, for example, closing the blinds or installing a shield. Then its temperature regime will be restored and will again be automatically maintained by the thermostat. [p.164]
A prototype of such an AKO device passed industrial tests for the first time at JSC Kauchuk. It is proposed to test devices with intensive electron-ion technology in systems for purifying reaction gases of lime kilns for the production of soda ash or smelting ferroalloys in closed furnaces, as well as for purifying contact gases in dehydrogenation units or oil catalytic cracking units. The use of such devices eliminates water consumption and reduces the energy intensity of production while simultaneously improving the environmental situation in industrial regions, and in the conditions of ferroalloy production it provides better parameters of reaction gases for their use in energy fuels. [p.76]
OPEN AND CLOSED SYSTEMS. There are two main types of systems: closed and open. A closed system has rigid, fixed boundaries; its actions are relatively independent of the environment surrounding the system. A clock is a familiar example of a closed system. The interdependent parts of the watch move continuously and very precisely once the watch is wound or the battery is inserted. And as long as the watch has a source of stored energy, its system is independent of the environment. [p.79]
Distinguish between open and closed systems. [p.85]
In the critical path method and the PERT method, projects are viewed as networks of individual events and activities. Work on these systems is any element of a project that requires time to complete and may delay the start of other work. Let us pay attention to the fact that work may not always imply the performance of some real action, i.e. be fictitious (artificially closed to display connections. - Ed.). The main difference between the two methods is the different approach to the duration of operations. The critical path method assumes that the duration of activities can be estimated with a fairly high degree of accuracy and certainty. The PERT method allows for uncertainty in the duration of activities and analyzes the impact of this uncertainty on the duration of the project as a whole. Currently, the critical path method is more widely used, rather than the evaluation and revision method [p.632]
Closed system as a shelter. The Japanese human resource management system encourages employees to view their place of work as a refuge from their surroundings. When managed internally, research departments become a haven for employees when there is a tendency within and outside the company to interfere with R&D activities. [p.188]
If the total number of mines being liquidated in the region turns out to be so large that it is impossible to immediately employ the laid-off workers in new jobs, we can allow the option of some stretching out the process of closing a group of mines for 2-3 years in order to avoid “peak overloads” of the social system. [p.212]
Oil preparation and pumping. Oil and gas coming from wells are collected through a closed system that ensures oil collection and movement from the well to the delivery point in a sealed environment. [p.104]
The block tap serves to protect the water heater from unsoldering when the water supply is cut off. When the water valve is open, water flows into the block tap. Entering the lower water chamber, it passes through the radiator, filling the upper water chamber, and stops, reaching the closed collapsible hot water tap. In still water, the pressure, based on the principle of communicating vessels, is the same at all points of the tubular system, therefore, the membrane will experience the same pressure from above and below, equal to the water pressure in the water supply system, i.e. through the stem to the valve [p.219]
Oil and gas coming from the well are collected in a closed system. The oil collection system ensures the separation of gas, water and sand from it, measurement of flow rate for each well (oil, gas, water), in-field transportation of oil, preparation of it for processing, measurement of general field production and delivery of oil. [p.142]
In world practice there are examples of effectively working systems of this kind. The most successful of them are the Chinese (combining a liberal regime and export orientation of rapidly growing free zones with strict regulation and closed domestic market) and Indian (linking the self-organization of the domestic market with its closedness to foreign competitors with an active policy of stimulating the economy based on state institutions). The economies of China and India are growing steadily at a rate of more than 6% per year, even in the context of the global financial crisis. Until recently, there was sustainable and rapid development in the countries of Southeast Asia, which synthesized an active development policy based on state regulatory institutions with the gradual liberalization of the domestic market. When this process of liberalization, accelerated under the pressure of international finance capital and the IMF, went beyond the limits ensuring the internal integrity of the relevant systems, the latter lost their stability and collapsed under the influence of waves of speculative capital. The situation was also the same in Japan: the forced liberalization of its economic system (active development policy, export orientation and closed domestic market) led to its disorganization and loss of stability. [p.16]
In May 1994, at the third congress of the Russian Union of Rectors, in a resolution addressed to the Government, certain demands were put forward for the protection and support of higher education during times of crisis; acts of educational law need to be discussed locally; for 10 years, state educational institutions of higher education should be excluded from the privatization program professional education, their scientific, clinical and production bases, during the reorganization, do not allow the unreasonable closure of existing universities, as well as the transfer of federal and departmental universities to the category of regional and municipal without introducing mechanisms for the formation of their budgets. A number of economic demands were formulated. Starting this year, in order to socially support the higher education system, additional payments and bonuses have been established for higher education employees for academic degrees and titles. [p.120]
Oil and gas coming from the well are collected in a closed system. [p.174]
BILLON COIN (from the French billon - low-grade silver), bargaining inferior metallic. a coin whose face value exceeds the value of the metal it contains and the cost of minting. Bank money cannot play the role of a measure of the value of goods; it acts only as a means of circulation and a means of payment. Billion coins are signs (representatives) of full-fledged money. They are minted from cheaper metals (silver, copper, nickel and other metals and their alloys) to serve small-scale turnover. The amount of banknotes in circulation is usually determined by the center, the bank of the country, taking into account the needs of turnover according to the established rules. standards (usually a certain amount per capita). The coinage is characterized by a closed minting system, in contrast to the free minting established for full-fledged coins. This means that coins can be minted by the state only from metal that belongs to it, which limits the issue of inferior coins, increasing their relative value over the actual one. the value of the metal contained in them, and ensures that the state receives coin income. The state establishes different procedures for the circulation of high-grade and inferior coins. While the power of full-chain coins as a means of payment is not limited, banknotes are endowed with the power of legal tender only to a limited extent, that is, sellers and creditors are obliged to accept them only to a certain extent. amount. For example, in Russia there are silver coins in denominations of 25 kopecks or more. up to 1 rub. could be accepted in amounts up to 25 rubles. with each payment, smaller silver coins, as well as copper coins - in the amount of up to 3 rubles. Along with this, the issue of silver coins was limited to 3 rubles. per capita. [p.156]
It is believed that the banking system acts as a closed system. Despite the exchange of information between banks and the publication by central banks of special statistical bulletins, information ifavsgshnkdb, banking secrecy exists. [p.104]
While Chandler gave us a historical background, James D. Thompson provided a theoretical framework for understanding the relationship between environment and organizational structure. In his book Organizations in Action [227], Thompson showed the difference between closed and open organizational systems. A closed system strives for certainty and includes those factors that are associated with achieving a goal, while an open system explicitly recognizes the interdependence of organizational structures and their environment. An open system tries to achieve stabilization in its relations with external environmental factors. [p.190]
Route II. Walking around, observing the operation and taking readings from instruments of auxiliary equipment and compressor plant structures located outside the machine room of the compressor shop (starting air compressors, circulation pump equipment of the open and closed cycle cooling system of the mining and metallurgical complex, gas purification units, cooling tower dust collectors, air intake filters MMC, etc.). [p.156]
Recently, a number of companies have begun to more clearly communicate the corporation's technical philosophy. In its formulation, research laboratories played a significant role. This does not mean that a corporation's technology policy is now normatively derived from the corporation's top-down technical philosophy. Mitsubishi Electric has chosen the formula "Mitsubishi Electric" creates the future as its technical philosophy. But this does not mean that the corporation's laboratories are constantly guided by the corporation's policies. The organizational structure of laboratories is directly open to the public without a strictly unified filter (Fig. 10.5 and 10.6). According to the chief head of the corporation's research and development work, laboratories are an open system. Thus, from the point of view of internal problems, laboratories are a closed system. But from the point of view of its role in the formation of technical philosophy or strategic [p.192]
Examples of open and closed operating systems
An example of an open operating system for smartphones and tablets is Google Android. This OS allows the user to do whatever he wants - rewrite some drivers, add support for new functions, etc. But the Windows Phone operating system is considered closed and does not give users any right to intervene. They can only periodically install service packs, buy programs or use free ones.
There are also conditionally open operating systems – iOS and Symbian. You can’t change anything in such OSs either, but you can write programs for them using special software provided by the developers. The most popular operating systems for smartphones are Google Android and iOS. For an ordinary user who is not creating new programs, the difference between these operating systems will only be in the interface.
When it comes to computer operating systems, Windows is considered a closed operating system, while Linux is considered an open operating system. Naturally, you can only customize Linux. There is another operating system - Mac OS, which is very similar in architecture to Linux, but it is considered a closed OS.
As for the choice of OS to use, each user decides for himself. For example, in closed operating systems the probability of catching a virus is much higher, and in this case you will have to wait until the developers fix the hole in the system with the next service pack. In addition, Windows and Mac OS are paid operating systems, while Linux is freely available to everyone.
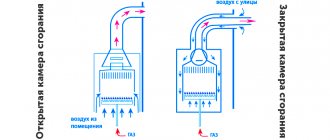
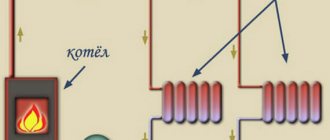
Open heating systems
In an open system, water is constantly supplied from the heating plant and this compensates for its consumption even if it is completely dismantled. In Soviet times, approximately 50% of heating networks operated according to this principle, which was explained by efficiency and minimization of heating and hot water costs.
But an open heat supply system has a number of disadvantages. The purity of water in the pipelines does not meet the requirements of sanitary and hygienic standards. As the liquid moves through long pipes, it becomes a different color and acquires unpleasant odors. Often, when sanitary and epidemiological station workers take water samples from such pipelines, harmful bacteria are found in it.
The desire to purify the liquid entering through an open system leads to a decrease in the efficiency of heat supply. Even the most modern methods of eliminating water pollution are not able to overcome this significant drawback. Since the length of the networks is considerable, costs increase, but the cleaning efficiency remains the same.
An open heat supply circuit operates on the basis of the laws of thermodynamics: hot water rises, due to which high pressure is created at the outlet of the boiler, and a slight vacuum is created at the entrance to the heat generator. Next, the liquid is directed from a zone of high pressure to a zone of lower pressure, resulting in natural circulation of the coolant.
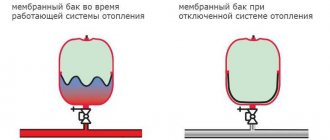
Being in a heated state, water tends to increase in volume, so this type of heating system requires an open expansion tank, such as in the photo - this device is completely leaky and is directly connected to the atmosphere. Therefore, this heat supply received the appropriate name - an open water heat supply system.
In the open type, water is heated to 65 degrees and then supplied to water taps, from where it is supplied to consumers. This heat supply option allows you to use cheap mixers instead of expensive heat exchange equipment. Since the distribution of heated water is uneven, for this reason the supply lines to the end consumer are calculated taking into account maximum consumption.
Saving resources
The dependent type of closed system provides that water flows to the consumer without passing through heating points. In this case, there is no need to install circulation pumps, devices for regulating heat exchange and automatic control. But there is also a minus - the inability to regulate the temperature in the system.
Independent closed heating systems save energy resources in the amount of 10-40% per year. They allow you to regulate the amount of heat supplied, the temperature of the coolant and improve its quality characteristics, which leads to reliable operation of heating equipment.
An example of an open heating system in the video:
Myth 2: according to the type of connection of the building to heating networks
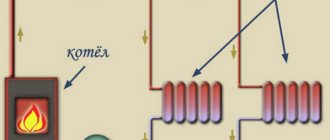
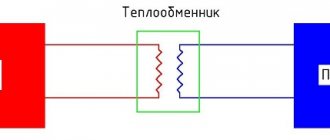
Closed systems (meant in this context) are building heating systems that are connected to external heating networks through a heat exchanger. That is, the consumer’s heating system is not connected in any way to external networks, hence the name “Closed”.
In fact, this type of connection is correctly called Independent (Fig. 3).
Fig.3. Scheme of independent connection of the heating system to heating networks
With this connection, the coolant from the source (CHP) circulates through the heat exchanger, giving off heat.
When designing the entire heating system of an object, for example, a residential apartment building, it becomes clear what type of heat exchangers is suitable: shell-and-tube, shell-plate, or it is necessary to buy a plate heat exchanger.
The heat exchanger is installed in the building’s individual heating unit (IHP).
Currently, this type of connection is replacing the outdated one - Dependent .
Open systems are heating systems connected directly to heating networks or through an elevator. In this case, the coolant comes from external heating networks to the end consumer, having previously passed through an elevator to lower the temperature.
The supply temperature in heating networks is 110-150 °C; such a hot coolant cannot be used in heating systems, as burns from radiators and pipelines will be possible.
The elevator, in addition to lowering the temperature of the coolant, performs one more function - it creates the pressure that is necessary for the movement of the coolant in the intra-house system (Fig. 4).
Fig.4 Diagram of dependent connection of the heating system
It would be correct to call such a connection – Dependent .