Autonomous heating of a house using a radiator system or underfloor heating requires the installation of a boiler unit and equipment connected to it. Usually, a special room is allocated for this purpose inside the building, an additional extension or a separate structure is erected. For safety reasons, a boiler room in a private house must comply with the current requirements of SNiP; in addition, this ensures ease of operation of heating equipment. If a gas boiler is chosen as a heat source, then the design of a boiler room for a private house requires approval.
What are the requirements for installing a boiler room?
Types of boiler houses
One of the most important functional components of any building is the heating system. A properly selected and calculated boiler room is a prerequisite for a comfortable life. Below, Kotel52 specialists will provide a complete overview of current issues related to boiler houses.
What kind of boiler rooms are there? How to equip a boiler room? Let us dwell only on the most commonly used types.
By type of fuel:
- Gas boiler houses, the main advantage of which is environmental friendliness and relative efficiency. They are quite simple to design and maintain and, importantly, are autonomous for a long time.
- Liquid fuel boiler houses. Their usual fuels are fuel oil, diesel fuel and waste oil. They are also easy to maintain and can be put into operation quickly and easily. They can automate everything possible, and they are highly productive. The only difficult point with this type of boiler room is that it must be a separate boiler room, equipped with excellent ventilation, fire extinguishing and fuel tanks.
- Solid fuel boiler houses. They work on coal, wood, peat, and waste from the forestry industry. That is, fuel is universally available and relatively inexpensive. At the same time, for their installation and commissioning, fuel supply systems and slag and ash removal systems are required.
- Hot water. These are boiler rooms to which we are all accustomed and which are usually used in heating and hot water supply systems of small buildings. As the name suggests, water is used as a coolant here. It can be heated up to +110°C;
- Steam. They use steam, and such boiler rooms can more often be found in industrial enterprises. They use steam in production processes.
- Combined. They combine the parameters of the first two types, and are also usually found in industrial enterprises.
- Oily. A rare type of boiler house that uses special oil and other liquids as a coolant that can heat up to +300°C.
Types of boiler houses according to the method of maintenance:
- Automated. Boiler rooms that do not require intervention during operation;
- Mechanized. Equipped with the simplest mechanized elements for fuel preparation, fuel supply and cleaning, which facilitates the work and maintenance process;
- Boiler rooms with manual operation. The entire maintenance process is carried out manually.
Standard list of requirements for a boiler room
As a complex technological element of the heating system of a building or complex of buildings, the boiler room has many requirements for itself. Let's list the main ones.
- The area of the room must be at least 10 m2. It is recommended to have at least 15 m2. Additionally, for each kilowatt of power, 0.2 m3 should be added to the boiler room area. Ceilings in solid fuel boiler rooms must be at least 250 centimeters high.
- The boiler room must have a separate entrance, and, of course, should not be residential. It is also prohibited to place heating rooms under the attic.
- A mandatory element of the boiler room is a window. Its area is calculated as 0.03 m2 for each cubic meter of space. This follows from the consideration of the priority of natural lighting over electric lighting. If natural lighting is not enough, then it is allowed to have artificial lighting, as well as emergency lighting.
- If the boiler room is designed as an extension to the main building, then it must be adjacent to the blank wall of the main building. The minimum permissible distance from windows and doors should be at least a meter.
- The room is made of heat-resistant materials. The best solution for boiler rooms is brick or ceramic tiles. If this is not possible, plaster is allowed. If the room is wooden, then fire-resistant impregnation and lining with fire-resistant sheets are required. Solid fuel pyrolysis boilers can only be placed on the floor.
- The supply air ventilation duct must be made with a cross-section larger than the cross-section of the chimney. These channels must be kept open at all times. The best solution would be to do them at the bottom of the door. The volume of supply air is the sum of the volume required for combustion and the volume of exhaust air. Be sure to check the quality of traction!
Rules for placing a boiler room in a house
Boiler room design
It is better to entrust the development of a boiler room project to specialists. In addition to SNiP standards, there are many additional restrictions on the size of the room and its arrangement relating to fire safety, air exchange rate requirements, and operating features.
The choice of room is influenced by the heater power:
- If the power of a gas boiler does not exceed 30 kW, it can be installed anywhere, including the kitchen and hallway.
- Equipment with a power of up to 60 kW can also be placed in the kitchen or in the hall, but compensate for the insufficient air exchange with a supply duct with a minimum diameter of 15 cm.
- The device, with a power of 60 to 150 kW, is installed only in a specially prepared room.
- Even more powerful units are installed only in a separate building.
If in a special building everything is arranged for the correct placement of the boiler, then in the utility compartments or in the basement it is necessary to take into account the installation and design features of different systems. The gas boiler is mounted on the floor or on the wall. At the same time, in the kitchen it is allowed to mount an appliance up to 60 kW on the wall, and in the hallway - only up to 35 kW.
A single-circuit boiler only works to heat the house, a double-circuit boiler supplies hot water. This option is chosen if a small volume of hot water is used. Then the boiler room replaces the boiler room.
Premises requirements
The floor, walls and ceiling are sheathed with non-combustible materials.
The room for a gas boiler must fulfill a number of the following conditions.
- There should be a window in the stoker. It can be either plastic or wood. Its area is calculated from the proportion - 0.03 m² of glass per 1 m³ of room. Therefore, they build a boiler room in the basement only if the utility unit belongs to the semi-basement.
- Ventilation is mandatory. The power and type of system depends on the parameters of the boiler.
- Water and sewer pipes, gas pipes, control systems, and electrical wiring are connected to the unit. The equipment must be placed so that free access to the boiler and any heating element is maintained.
- Walls, floors, and ceilings can only be sheathed with non-combustible materials. For walls and floors, tiles are usually used; plastering is allowed.
- No more than 2 devices are allowed to be installed in the boiler room.
- The weight of the boiler is taken into account. If it exceeds 200 kg, a reinforced concrete pad or slab foundation is built under it.
- All openings must be finished with non-combustible materials, the doors must open outwards.
- All elements of the heating system must remain freely accessible.
It is preferable to install boiler rooms in the northern or eastern part of the house. They are usually combined with a bathroom, boiler room, and kitchen.
Requirements for a boiler room attached to a house
Sometimes a separate module is allocated for the boiler room.
A separate module can be built for the stoker room. This option is rarely resorted to, since usually an extension distorts the appearance of the building. However, if the equipment being installed has high power, there is no other choice.
There are a number of special requirements for the extension:
- The foundation of the structure is not connected to the foundation of the building; a gap is left between them, and is often additionally waterproofed.
- Gas appliances get very hot, so the walls, floor and ceiling are made and finished only with non-combustible materials.
- The foundation for the extension is a slab with a height of at least 20 cm.
- A special foundation will be required for the chimney pipe.
A separate or attached boiler room, like a room in the house, is equipped with its own hood. Windows are required.
The construction of attached and roof-mounted boiler houses is permitted if the standards for water pressure and temperature are met.
Equipment for a boiler room or how a boiler room works
Heating boiler (solid fuel)
In our boilers, wood is burned using pyrolysis. This requires one combustion chamber to burn the wood gas produced by pyrolysis in the second chamber.
Boiler
The boiler is a tank with a spiral-shaped tube located inside. In this coil there is constant circulation of water using a circulation pump. This ensures water heating for hot water supply. Thermoregulation is performed via a thermostat. The boiler usually has two pipes. The water heated in the boiler enters the boiler through the inlet pipe, and from the boiler through the outlet pipe into the heating circuits. The exact scheme depends on the heating scheme.
Expansion tanks
Expansion tanks are designed to periodically release air, which is always contained in the heating system and hot water supply system. These tanks are always installed at the highest point of the system.
Control devices
Boiler rooms require a control system responsible for controlling the elements of the boiler room. Such devices are manual and automatic.
Manual devices have a protective temperature limiter to turn off the system in case of overheating of the boiler, a simple regulator and a temperature indicator.
A protective temperature limiter is present in any control device and is a sensor set to a certain temperature.
All automatic control devices are linked to the outside temperature. Such automation has a set of curves depending on the temperature of the water in the heating system and the temperature of the outside air. Depending on the weather outside, a curve with an optimal steepness is selected, at which a comfortable temperature inside is achieved with the least fuel consumption. There is also an additional adjustment that allows you to adjust the boiler temperature if the outside conditions change suddenly. Automation will also help to correct the indicators if the temperature is selected incorrectly.
Automation can provide several modes of boiler operation. For example, an economical mode, when the boiler automatically reduces the coolant temperature. Or frost protection mode, which ensures only a minimum water temperature to prevent it from freezing. The parameters can be changed within specified limits by Kotel52 specialists, but there is always the possibility of resetting to factory settings.
Circulation pump
The circulation pump creates the necessary pressure in the heating system. Of course, it requires electricity to operate. This may create some inconvenience, but in the long term it increases the overall efficiency of the system and helps improve its energy efficiency.
Pipelines for piping boiler equipment.
Properly executed piping distributes heat evenly throughout the circuits, helps prevent boiler overheating and provides the building with hot water. Simple piping is provided for complicated and expensive boilers, which already include a technological list of devices. Complex piping can be done independently after purchasing a simple boiler.
Modern piping is made from polypropylene pipes, usually with fiberglass reinforcement. These are cast monolithic pipes that do not need to be cleaned at all before installation. This solution allows them to be quickly installed and operated reliably.
The gravity scheme is based on the difference in pressure between the water in the boiler and the water in the circuit. In this scheme, a circulation pump is dispensed with. However, even if there is a pump, the heating system should be checked so that it can function without it (in the event of a power outage).
The operation of the circulation pump creates a forced circuit. The pump helps to increase the efficiency of the heating system and reduce fuel costs.
Shut-off valves
Most often, a simple ball valve can be found as a shut-off device. It has only two working positions - “open” or “closed”. This is a simple device with a brass body, which has a built-in element in the form of a ball with a hole. Such devices are used to separate radiators from the system for maintenance, to disconnect circuits, and to empty and fill the system. Check valves are also used. They serve to pass water in one direction and tightly block its movement in the opposite direction. They are usually installed in boiler piping. The balancing valve provides the set water flow, which in turn is regulated using radiator thermostats.
The thermostatic valve regulates the flow of water through the radiator depending on the room temperature. It is usually installed in conjunction with a remote thermostat to control water flow.
If it is necessary to regulate the temperature by mixing two streams of different heating levels, then it is necessary to provide a three-way valve. This is a brass body with three pipes with a controlled stem, controlled by a thermostatic actuator.
Elements for connecting the heating boiler to the chimney.
Taking into account the high gas temperatures at the boiler outlet, it is recommended to use steel or ceramic chimneys.
When operating a brick chimney, you may encounter many problems, primarily associated with the formation of condensation and difficult cleaning. Therefore, recently you can increasingly find stainless steel. Such chimneys are lightweight, easy to install and maintain, and do not require a foundation.
Chimneys can be divided into single-walled (they also form condensation on the inner surface, so in severe frosts the chimney can freeze) and double-walled (a pipe in a pipe, and thermal insulation between them, which eliminates the formation of condensation and increases the cost)
It is necessary to select the correct length and diameter of the chimney. This is critical for the correct operation of the entire boiler installation. This can be easily determined at the design stage with the help of Kotel52 specialists. Their recommendations are below
Table 1 - Dependence of chimney dimensions on boiler power
| power, kWt | Diameter, mm | Height, m |
| 18 | 130 | 7 |
| 28 | 150 | 8 |
| 45 | 150 | 9 |
| 65 | 200 | 10 |
| 90 | 250 | 11-13 |
In general, chimneys consist of the following elements:
- Cup.
- Pipe sandwich.
- Condensate collector.
- Spark arrestor.
- Header.
- Cleaner.
A pocket is required at the base of the chimney to remove soot. Fastening to supporting structures is carried out using brackets. To prevent the formation of condensation, it is necessary to provide additional insulation. A tee is used to drain condensate.
Additional items
At this point we stop considering the boiler itself - the main reason for re-equipping the building. But there are also some related factors that need to be paid attention to. They are also subject to a number of conditions that must be observed. The main mistake of many cottage owners is often that they concentrate their attention on the dimensions of the room and forget that the inspection may well issue a fine for more prosaic reasons. Next, we will focus on the details that must be taken into account.
Ventilation
The ventilation system is connected to the smoke outlet. This saves space and resources during construction.
The boiler room must be ventilated, even if the dimensions of the gas boiler for a private home are minimal. The limit of three complete indoor air cycles every hour must still be reached. That is, complete air exchange should take place within a time range of 20 minutes.
The only way to avoid such a need is to install electrical equipment.
Chimney
Installed if combustion products are present. All norms are quite standard. The diameter of the chimney itself must exceed the pipe. It is important that the chimney outlet is above the roof. That is, this is the highest point. The internal structure does not matter: brick, metal or modular pipe.
Doors
As already noted, there should be two of them. One leads to a residential building, the second to the street. Street can be almost anything. There are requirements only for dimensions, but this already depends on the opening. The tenant can even make it out of wood.
But a fire-resistant door should lead into the living area, which can easily withstand direct flame for at least 10-20 minutes. Therefore, only one material is suitable for this task - metal.
How to calculate boiler power
In general, the boiler power can be determined as Wbot = S*Wud/10
Where S is the area of the heated room
Wsp – specific boiler power (for every 10 m2):
- for northern cities 1.5-2 kW;
- for southern cities – 0.7-0.9 kilowatts;
- for cities of the Moscow region - 1.2-1.5 kilowatts.
This calculation is based on a ceiling of 2.5 m. If the height differs from that accepted in the calculation, then correction factors should be applied up or down (read below).
It is imperative to take into account the heat loss coefficients of the building. Simplified, you can take the maximum losses with a coefficient of 1.5. Such data can be used, for example, for wooden doors, walls made of concrete or one brick, wooden windows, or if the house is not properly insulated.
If there is high-quality insulation and modern double-glazed windows, double doors with a vestibule, then a coefficient of 1.15 can be applied.
A preliminary calculation by Kotel52 experts will help you avoid inflated costs when operating your heating system. If the system is already installed, they will be able to check the boiler room.
Additional power should also be provided if a hot water supply system is to be installed. In this case, for an average-sized house, an additional 10 kW is added.
Table 2 – Selection of boiler power and average fuel consumption
| Area, m2 | power, kWt | Fuel consumption | ||
| Solid fuel | Diesel fuel | |||
| Ordinary | Boiler52 | |||
| 100 | 10 | 3 | 1,5 | 1 |
| 130 | 13 | 4,5 | 3 | 1,3 |
| 160 | 16 | 6 | 3 | 1,6 |
| 200 | 20 | 7,5 | 4 | 2 |
| 250 | 25 | 9 | 5 | 2,5 |
This is the easiest way to select a heating boiler by power. When analyzing many ready-made calculations, an average figure was derived: heating 10 square meters of area requires 1 kW of heat.
To make it clearer, we give an example of calculating the power of a heating boiler by area. There is a one-story house 12*14 m. Find its area. To do this, multiply its length and width: 12 m * 14 m = 168 m2. According to the method, we divide the area by 10 and get the required number of kilowatts: 168 / 10 = 16.8 kW. For ease of use, the figure can be rounded: the required heating boiler power is 17 kW.
Taking ceiling heights into account
In houses, ceilings can be higher than 2.5 m. If the difference is only 10-15 cm, it can be ignored, but if the ceiling height is more than 2.9 m, a recalculation will have to be made. To do this, find a correction factor (dividing the actual height by the standard 2.6 m) and multiply the found figure by it.
Example of correction for ceiling heights. The building's ceiling height is 3.2 meters. It is necessary to recalculate the power of the heating boiler for these conditions:
- We calculate the coefficient. 3.2 m / 2.6 m = 1.23.
- Let's correct the result: 17 kW * 1.23 = 20.91 kW.
- Round up, we get 21 kW required for heating
As you can see, the difference is quite significant. If you do not take it into account, there is no guarantee that the house will be warm even at average winter temperatures, let alone severe frosts.
Ventilation arrangement
When organizing a boiler room in a private house, the ventilation requirements should be fully met, since the safety and efficiency of the heating unit depends on this.
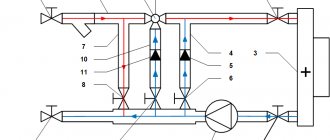
Boiler room ventilation diagram
Natural ventilation may not be enough, so it is worth considering installing a system for forced air supply into the furnace room.
Poor ventilation contributes to
:
- settling of soot on the walls and ceiling of the boiler room,
- reduction of draft in an open firebox (this is associated with excessive energy consumption and the accumulation of soot in the chimney of a solid fuel unit),
- accumulation of carbon monoxide indoors.
Creating natural ventilation
If the house is heated by a boiler with a power of up to 30 kW, in home boiler rooms it is enough to ensure air flow by creating a channel at the bottom of the wall or door. They serve as a hole in the wall with a diameter of 10-15 cm.
How to create a channel at the bottom of a wall or door:
- a piece of plastic or asbestos cement pipe is inserted into the hole;
- a protective mesh is attached to it from the outside, protecting against the penetration of insects and dust;
- It is advisable to install a reverse draft valve on the inside of the channel;
- air flow is ensured through the lower part of the street door covered with a grille;
- the exhaust duct is discharged through the roof. It is a pipe of the same diameter, which in the upper part is equipped with a protective mesh and an umbrella that prevents precipitation;
- It is recommended to place the inlet opening near the firebox, at the bottom of the wall. In this case, the air will enter the combustion chamber directly without raising dust in the room;
- the location of the hood is also “tied” to the heating unit. Since combustion products rise, the exhaust duct is installed near the chimney.
Ventilation device in the boiler room
Creating forced ventilation
Natural ventilation in a boiler room with a powerful heating unit may not be sufficient. Its operation is unstable because it depends on weather factors, and control of air flow into the combustion chamber becomes impossible.
Installing a fan on an exhaust pipe will ensure the required air flow intensity and protect the boiler room from the accumulation of volatile combustion products. The fan power is selected in accordance with the maximum needs of the boiler - 30% is added to the parameter indicated in the passport.
Refined calculation of boiler power
In general, the formula for a refined calculation of boiler power is as follows:
Wcat = Qt*Kzap
Where:
- Qt – heat loss of the object, kW.
- Kzap is a safety factor by the amount of which it is recommended to increase the design capacity of the facility. As a rule, its value is in the range of 1.15...1.20 (15-20%).
Predicted heat losses are determined by the formulas:
Qt = V*ΔT*Kp/860, V = S*H;
Where:
- V – volume of the room, cubic meters;
- ΔT – difference between external and internal air temperatures, °C;
- Kr – dissipation coefficient, depending on the degree of thermal insulation of the object.
The dissipation coefficient is selected based on the type of building and the degree of its thermal insulation.
- Objects without thermal insulation: hangars, wooden barracks, structures made of corrugated iron, etc. – Kr = 3.0...4.0.
- Buildings with a low level of thermal insulation: single brick walls, wooden windows, slate or iron roof - Kp is taken to be within the range of 2.0...2.9.
- Houses with an average degree of thermal insulation: two-brick walls, a small number of windows, a standard roof, etc. - Kr is 1.0...1.9.
- Modern, well-insulated buildings: heated floors, double-glazed windows, etc. – Kp is in the range of 0.6...0.9.
As a rule, such calculation is carried out according to the following data:
- average value of outside air temperature in the coldest week in the winter season;
- air temperature inside the object;
- presence or absence of hot water supply;
- data on the thickness of external walls and ceilings;
- materials from which floors and external walls are made;
- ceiling height;
- geometric dimensions of all external walls;
- number of windows, their sizes and detailed description;
- information about the presence or absence of forced ventilation.
An example of calculating a line of boilers designed for heating houses of different sizes is given in the table:
Note to column 11: Hc – wall-mounted atmospheric boiler, A – floor-standing boiler, Nd – wall-mounted turbocharged boiler.
Calculation by volume
In the case of determining the power of a heating boiler for an apartment, you can use another method, which is based on SNiP standards. They stipulate standards for heating buildings:
- heating one cubic meter in a panel house requires 41 W of heat;
- to compensate for heat loss in a brick building - 34 W.
To use this method, you need to know the total volume of the premises. In principle, this approach is more correct, since it immediately takes into account the height of the ceilings. A slight difficulty may arise here: usually we know the area of our apartment. The volume will have to be calculated. To do this, we multiply the total heated area by the height of the ceilings. We get the required volume.
An example of calculating the power of a boiler for heating an apartment. Let the apartment be on the third floor of a five-story brick building. Its total area is 87 sq. m, ceiling height 2.8 m.
- Finding the volume. 87 * 2.7 = 234.9 cu. m.
- Round up - 235 cubic meters. m.
- We calculate the required power: 235 cubic meters. m * 34 W = 7990 W or 7.99 kW.
- Round up, we get 8 kW.
- Since there are heated apartments at the top and bottom, we apply a coefficient of 0.7. 8 kW * 0.7 = 5.6 kW.
- Round up: 6 kW.
- The boiler will also heat water for domestic needs. We will give a reserve of 25% for this. 6 kW * 1.25 = 7.5 kW.
- The windows in the apartment have not been replaced; they are old, wooden. Therefore, we use a multiplying factor of 1.2: 7.5 kW * 1.2 = 9 kW.
- Two walls in the apartment are external, so once again we multiply the found figure by 1.2: 9 kW * 1.2 = 10.8 kW.
- Round up: 11 kW.
The technique can also be used to calculate the power of a boiler for a brick house.
Heating calculation - heat loss and power
A simplified formula for calculating the required thermal power for heating one room looks like this:
Thermal power required to heat one room = Reserve coefficient * Number of watts for heating one meter of room * Room area * Heat loss coefficient through windows * Window area ratio coefficient * Heat loss coefficient through walls * Winter air temperature coefficient * External wall coefficient * Ceiling coefficient * Ceiling height coefficient * DHW coefficient
Accordingly, to determine the total thermal power required to heat a house, it is necessary to add up the calculated thermal power indicators of individual rooms.
The reserve coefficient is necessary to ensure a reserve of power in case of severe frosts, during which the heating system will have to work with increased power to maintain a comfortable temperature in the house. As a rule, this coefficient is taken equal to 1.2 when calculating.
The number of watts to heat one meter of room depends on the type of room and its purpose. The standard heating requirement for 1 m2 is 100 watts. If the room is planned to be non-residential (storage room, laundry room, etc.), this value can be reduced. For bathrooms, children's rooms and any other rooms where the air temperature is slightly higher than in other rooms, this figure should be increased.
The coefficient of heat loss through windows depends on the format and quality of double-glazed windows installed in the house. For the simplest single-chamber windows, this calculation coefficient is equal to 1.27, for a two-chamber double-glazed window - 1, for a three-chamber double-glazed window - 0.85.
The ratio of window area is determined by the ratio of the area of windows in the room to the area of the room (by floor) and is, depending on the ratio:
- at a ratio of 10% - 0.8
- 20% — 1,0
- 30% — 1,2
- 40% — 1,4
- 50% — 1,5
This coefficient clearly shows how the thermal power of the heating system of a house with ordinary windows can differ from a house with panoramic glazing.
The coefficient of heat loss through the walls depends on the material from which the walls of the house are made and the presence of thermal insulation in the walls. For the most common wall materials, this heating calculation coefficient will be as follows:
- brick walls (two bricks) with 150 mm insulation – 0.85
- brick walls (two bricks) without insulation – 1.1
- foam concrete blocks – 1
- logs (log house) – 1.25
- ordinary concrete without insulation – 1.5
The winter air temperature coefficient corresponds to the average negative temperature of the coldest month (usually January or February)
- for -15°C it is 0.9
- for -20°С – 1
- for -25°С – 1.1
The coefficient of external walls depends on how many walls of the room are external, i.e. not adjacent to other rooms.
- if there is only one wall in the room that is external, the coefficient will be equal to 1
- for two walls – 1.2
- for three – 1.22
The ceiling coefficient is taken into account in heating calculations as follows:
- if there is an unheated room above the room (attic, attic) – 1
- if there is an insulated attic above the room - 0.9
- if there is a heated room above the room - 0.82
The ceiling height coefficient determines in the calculation the dependence of the heating system power required according to thermal calculations on the volume of air in the room, determined by the ceiling height. The higher the ceilings, the greater the amount of thermal power required for heating.
- for rooms with a standard ceiling height of 2.5 meters this coefficient will be equal to 1
- for ceilings 3 meters – 1.05
- for ceilings 5 meters – 1.1
DHW coefficient
To live in a house, in addition to heating, you also need a hot water supply system. The easiest and most profitable way to organize it is not with separate water heating elements, but with the help of a combination of a heating boiler and an indirect heating boiler. With this scheme, the water will be heated by passing the heating system coolant through the boiler, which will require an increase in the power of the heating equipment. When organizing hot water supply from a heating boiler, the DHW coefficient for the calculation formula will be from 1.2 to 1.3 (depending on the number of hot water consumers living in the house).
Regulations
To install boiler equipment in a private home, you must rely on a number of rules. Until mid-2003, some standards were in force, and from mid-2003 other standards began to apply (SNiP 42-01-2002), so this document should be followed.
A boiler room in a private house must meet a lot of requirements
It is advisable to familiarize yourself with these standards, although specialized organizations are involved in design documentation. After reading the documents, you can decide in advance what equipment can be installed and what cannot be installed in a private home. In this case, you can also decide what preparatory work will have to be done so that the equipment can be installed without delaying the entire process. If any difficulties arise, you must contact the design department for help, since they know exactly all the intricacies of installing this type of equipment, depending on the specific plan of the residential building.
What happens if you incorrectly calculate the required power
If the power of a solid fuel heating boiler is selected less than the calculated one, then the boiler will operate at the limit of its capabilities. And of course, this will inevitably lead to premature wear. In this case, you should also expect extremely slow heating of the heating system, as well as temperatures in living areas below comfortable.
Boiler power higher than the calculated one leads to the rapid formation of soot in the chimney. This is fraught with the formation of condensation in the chimney, and as a result, even more intense soot deposition. In such cases, it is necessary to solve the problem with the help of various distributors and heat accumulators, which is not a cheap undertaking. Therefore, the correct choice of power will help to correctly determine the cost of the boiler room at the initial stages. If you buy a solid fuel pyrolysis boiler from the Kotel52 company, then all the main heating issues for your home will be resolved in advance.
Boiler room volume for different boilers
If the total heat generation is up to 30 kW, then it is required to install the boiler in a room of at least 7.5 m3. We are talking about combining the boiler room with the kitchen or integrating it into the home space. If the device emits from 30 to 60 kW of heat, then the minimum volume level is 13.5 m3. It is allowed to use extensions or separate areas on any level of the building. Finally, if the device power exceeds 60 kW but is limited to 200 kW, then a minimum of 15 m3 of free space is required.
In the latter case, the boiler room is located at the owner’s choice, taking into account engineering recommendations in:
- extension;
- any of the rooms on the first floor;
- autonomous structure;
- plinth;
- dungeon.