Ventilation in the boiler room is a mandatory requirement for the safe use of gas heating appliances. Failure to comply is associated with a number of problems, both administrative and an increased likelihood of an emergency.
Since the accumulation of carbon monoxide and other combustion products poses a danger not only to the direct owner of the gas boiler, the compliance of the ventilation system with SNiP standards is carefully checked by gas services at the stage of equipment acceptance.
In turn, using a boiler without the appropriate permission can lead not only to administrative, but in some cases to criminal liability.
Carbon monoxide is very dangerous, so the ventilation system of a gas boiler room in a private house must work flawlessly Source tula.sm-news.ru
Types of ventilation
There are only two main types of ventilation: forced and natural, and in some cases combined ventilation is used, which is sometimes classified as a separate category.
As the names indicate, the first type of ventilation uses forced air supply, for which air pumps or fans are used. In the second case, the air flow occurs due to the difference in its temperature and pressure - inside and outside the room. To ensure air exchange, it is enough to position the ventilation holes correctly. Also, some of the air can enter the room through natural openings - for example, cracks under doors.
If there is such a possibility, then it is most profitable to use a combined system - while natural ventilation copes with air exchange, forced ventilation is in standby mode.
Natural ventilation
If the air volume changes three times per hour, then in a standard six-meter (in height) room you can get by with natural air exchange.
For reference! The standards were developed for all boiler houses - industrial and domestic, so the standard was taken to be a room large enough for a private home.
When the ceiling is lowered by every meter, you will have to increase the air circulation by at least 25%. Plus, in any case, you should design the air exchange with some margin.
Scheme of operation of the ventilation system in the boiler room of a private house Source pew.ledikycora.ru.net
The scheme is extremely simple - opposite the boiler, in the door or wall, there is a ventilation inlet (the diameter depends on the power of the boiler), which is located no higher than its working area. The second, the exhaust hole is arranged above the boiler; usually an air duct with a check valve is attached to it (so that the hood only works in one direction) and an “umbrella” on the outside (so that the pipe does not flood).
The distance between the “input” and “exit” of air in the room should be as large as possible to ensure better draft.
Disadvantages of natural ventilation:
- Dependence on weather conditions . It is necessary to protect air ducts from external environmental influences.
- Difficulty in accurately calculating air conditioning. Depending on the direction and strength of the wind, different volumes of air can enter the room.
- It is very difficult to design one ventilation system for several rooms - so that one pipe passes through all the rooms. Mostly, the exit from each room is made directly to the street.
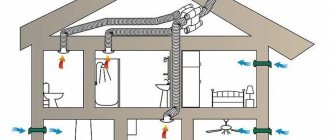
Forced ventilation system or, more simply, an exhaust hood for a boiler in a private house Source m.yukle.mobi
See also: Contacts of companies that specialize in ventilation and air conditioning.
Forced ventilation
Forced air supply is carried out by so-called “mechanical devices”, that is, fans. This type of air exchange arrangement is convenient for two reasons :
- It becomes possible to install climate control equipment , with heaters and filters, which will clean and heat the incoming air;
- It also becomes possible to turn on the system only at the necessary moments , which will save energy by turning it on, for example, only when the boiler is operating.
The disadvantages of forced ventilation are as follows:
- Cost - first of all, such a system will cost more than natural ventilation;
- In some cases, noise – for example, when installing climate control equipment with air conditioning;
- Choosing equipment without proper preparation can be fraught with a safety violation: in particular, for gas boiler houses it is important to have fire-resistant equipment.
The heating system is a rather complex set of equipment, so its selection and adjustment should be carried out by professionals Source stroimdom.com.ua
Fire hazard of industrial premises
The premises of single-apartment and multi-apartment buildings have been dealt with. Now let's talk about heat generators for industrial and warehouse purposes. According to Federal Law No. 123 TR on fire safety requirements.
The designation helps determine what and in what cases is necessary to ensure the safety of people and their property in buildings in the event of an emergency. For example, equipping a building with a fire alarm, a fire extinguishing system, the degree of fire resistance of finishing materials, the type of emergency evacuation, and so on.
To determine the degree of explosion/fire hazard of an object, division into classes and categories is used.
According to PP No. 390, a gas boiler house is classified as a hazardous production facility and belongs to category F5. According to the standards, premises of this type are standardized to a fire hazard category from the most dangerous under the letter A to the least dangerous, designated by the letter D:
- Increased fire/explosion hazard is A.
- Explosion and fire hazard - B.
- Fire hazard falls into category B - from B1 to B4.
- Moderate fire hazard - under the letter G.
- For a reduced fire hazard, to which it is difficult to classify such a gas installation, the symbol is D.
As a rule, it is difficult to coordinate the design of a gas facility with the D-subclass, so we will consider boiler houses from A to D.
You can't just go ahead and define a specific subclass. To do this, the necessary research and calculations should be carried out with the help of specialists with experience in designing gas-fired heat generators.
The subclass should be calculated based on:
- Type of fuel used.
- According to the degree of fire resistance (I, II, III, IV and V).
- The equipment that is installed indoors.
- Design features of the boiler room itself (hazard class according to the design of the gas boiler room C0, C1, C2 and C3). Determined by Article 87 of Federal Law No. 123.
- Characteristics of the processes being carried out.
The subclass is also conditionally determined on the basis of SP 12.13130.2009, NPB 105-03, SP 89.13330.2011, Federal Law No. 123. In principle, it is not necessary to determine which hazard class a particular gas boiler house belongs to, if the task is simply to determine whether it is a hazardous production facility.
The boiler room, in any case, is a gas consumption network. OPO is determined by the following criteria:
- The presence of boilers that are under excess pressure or temperature indicators of the working environment above 115 degrees.
- If the gas boiler house contains gas pipelines with a pressure of 0.005 MPa or more.
- A boiler house is a centralized system or installation that serves socially significant segments of the population.
The fire hazard class according to all criteria is determined by design specialists.
What requirements must be met?
After the stage of construction or creation of the boiler room, they move directly to its design, and here again SNiP standards come to the fore. There are quite a lot of them, so we will consider only the most important ones that directly affect cost and design:
- for each boiler , if there are several of them, it is necessary to equip its own ventilation system;
- a gas boiler requires a separate room if it is more powerful than 30 kW, otherwise installation in another room (for example, a kitchen) is allowed, but its area should not be less than 15 m and the ceiling should not be lower than 2.5 m;
- if the boiler room is equipped in a separate extension , then the latter should stand on the foundation;
- it is necessary to provide conditions for convenient cleaning of the hood;
- the vent (ventilation hole) for each kW of power should be 8 cm2 in the case of intake from the street, or 30 cm2 if the ventilation takes air from other rooms;
- the hood for a boiler in a private house must be located on top ;
It is advisable to supplement the ventilation system with an extractor hood for a gas boiler in a private house Source tigerrupakix.tumblr.com
The need for air circulation in the boiler room
Even with the use of high-tech equipment, the number of poisonings and deaths does not decrease. The first sign of poor ventilation is the appearance of weakness and headache.
If there is insufficient ventilation, heating equipment does not operate normally. Because in the absence of a constant flow of oxygen, which ensures proper operation of the boiler, incomplete combustion of the fuel occurs, which means the heating output will be at a minimum.
A very important fact is that with poor ventilation, soot forms inside the boiler. This leads to a decrease in the flow capacity of the air duct and flue gases can flow from the chimney back into the boiler room and other rooms of the house.
If the heat supply scheme provides for a separate boiler room building, then the boilers will use only the air that is inside for operation.
When installing ordinary windows and wooden or metal doors, outside air will enter the room, but plastic structures are highly airtight and air from the street will not penetrate. This means that over time the boiler will consume oxygen in the boiler room and the air will be discharged. The next step may be carbon monoxide entering the boiler room. To avoid such situations, a ventilation system is designed.
Chimney of a gas boiler for a private house
You should know that liquefied gas boiler rooms cannot be located in the basement of buildings or basements. This requirement is determined by common sense: in the event of a leak, fuel of this type can accumulate in the lower layers of air and “drain” down. Otherwise, such a boiler room, according to the standards, can be located in a separate building or an extension to the house, or in the attic. But, at the same time, ventilation in a private house for a gas boiler imposes a number of mandatory requirements :
- Ventilation in the boiler room of a private house in this case should use two horizontal channels , with one for the ventilation chimney located at its level, and the second about a quarter of a meter lower, used for cleaning;
- The boiler must be at least 0.1 m ;
- The chimney should not make more than three bends.
Safety regulations
During any construction, established standards must be followed. It is thanks to compliance with these standards that people gain confidence in the safety of their homes or their stay at industrial facilities. For example, gas supply regulations give instructions on where to lay the pipeline to houses, its distance from the ground or underground.
The rules must be followed when installing gas equipment, as well as operating the facility. Gas supply will be installed in residential buildings only when construction standards are met during their construction.
All components must meet certain requirements. For example, steel pipes installed indoors must be different from those installed outside the home. Rubber or rubber-fabric hoses may be used if they are sufficiently resistant to passing gas. The pipes are connected by welding. A threaded connection can also be used, but then a shut-off valve is installed.
To ensure the safety of gas supply, special rules have been developed for the design, construction and operation of supply systems, as well as the release and use of equipment. According to them, the requirements are established:
How is ventilation calculated?
When calculating the ventilation system, it is worth considering that small-power gas boilers (up to 30 kW), according to the law, are calculated using a slightly different formula, because a number of requirements according to SNiP are different.
So, for natural ventilation of a room measuring 3 by 5 m, with a ceiling height of 3 m, you must first calculate the volume: in this case it will be 45 m3 (we multiply all the parameters). Now the air exchange: 6 (the height that should be) – 3 m (our ceiling) should be multiplied by the “penalty” coefficient of 0.25 and add 3 meters. The result will be 3.75. Now you need to understand what the value of air circulation is: for this, the air exchange rate is multiplied by the square footage of the room, in the example the result is 168.75 m3 - this is the value that you then need to look at in a special table to determine the diameter of the air duct. In our case it will be 225 mm.
Heating system with gas boiler Source radio.enjob.ru
In the case of a gas boiler, the 0.01 m2/10 kW scheme is used for the supply lines - that is, if the boiler has a power of 30 kW, then the ventilation of the boiler room should provide an air flow of about 0.03 m3/sec, plus, it is advisable to include a 30% reserve. The hood, according to SNiP, must have a cross-section of at least 130 mm. If the supply ventilation hole does not provide proper air exchange, then forced supply ventilation is installed.
Selection and installation of equipment
The selection of equipment will depend primarily on the following factors :
- area ;
- Permissible distance to combustible devices;
- Type of room (separate room, free-standing room or existing one - for example, a kitchen or attic);
- Budget (for example, monoblock ventilation is significantly quieter than other types, but it will cost more)
The boilers themselves are:
- Gas;
- Solid fuel;
- Pellet (pellet-based, essentially solid fuel boilers);
- Diesel;
- Electrical;
- Combined (using several methods).
Combination boilers are an excellent option in a home where there are interruptions in electricity or gas supply Source brjansk.buyreklama.com
Currently, gas boilers are most often used in private homes, and we are talking about low-power boilers. This is due to the relatively low price of gas in gasified areas, and the convenience of using this heating method (the combustion temperature is lower, which allows the use of cheaper materials in production). To install it you will need permits. In addition, the boiler can be installed simultaneously with water heating (with a boiler) only for rooms up to 200 m2.
How to choose material for the hood
The hood can be constructed from various materials. Below is a list of the main ones.
- Brick – used for exhaust hood in solid fuel boiler houses. It is quite difficult to clean, but it lasts a long time in the case of solid fuel boilers. For gas and other boilers, this type will not be a good choice, because they have a lower temperature - condensation forms in the pipe, and the surface of the brick quickly collapses;
Brick air duct Source en.yenni.biz
- Ceramics can be different; for solid fuel boilers, ceramics are used that can withstand temperatures of more than 650°C. It is also necessary to ensure that soot does not ignite in the chimney. For liquid fuel (and gas) you can use a ceramic hood using a lower temperature range, but with condensate removal. Insulation of the pipe should be provided (most often it is insulated with mineral wool);
- Steel is a good choice for solid fuel heaters, and if ventilation is used in a boiler room with a gas boiler. In the case of a higher temperature (solid fuel), you should simply choose a thicker pipe, up to 1 mm, in others - 0.6 mm. The steel must be heat resistant. The only negative is that such pipes cannot be called cheap, and their service life is shorter than, for example, brick.
The choice of a specific material depends on the combination of corrosion resistance parameters and resistance to soot (its accumulation). In addition, the hood is selected according to the draft pressure (forced ventilation implies excess pressure), according to the degree of condensation formation from the fuel, and according to the smoke temperature. It is worth knowing that the hood can be reconstructed - for example, the hood for a gas boiler in a private house, if there is already a brick pipe, is organized by inserting a steel pipe into a brick chimney, subject to other conditions.
Why choose metal air ducts
It is necessary to determine not only the cross-sectional diameter, but also the material from which the ventilation pipe consists. Air ducts are:
- metal;
- metal-plastic;
- non-metallic.
For boiler room ventilation, it is better to use metal ventilation ducts. They meet all fire safety requirements. Such pipes are made of aluminum, steel or galvanized. The main requirement for such ventilation ducts is resistance to corrosion.
Air ducts made of metal can withstand both static and shock loads. Therefore, the risk of destruction of the ventilation structure is minimal. Some pipes are flexible, so you can bend them with your own hands at any angle. High structural strength - allows you to withstand maximum internal pressure.
The only disadvantage of metal pipes is that they cannot withstand condensation and become rusty over time. Only 2 types of metal are definitely resistant to moisture - aluminum and stainless steel. When installing such pipes, you must also take care of the fasteners. Choose ones that can withstand the load. Therefore, the installation process may be delayed. The price for such pipes is also higher than for air ducts made of other materials.