An infrared heater refers to equipment that emits electromagnetic waves. Users unfamiliar with how such devices operate express concern about whether they have a negative impact on health. Marketers, in turn, present this type of heating as convenient, environmentally friendly and completely safe. If you follow the rules for using the equipment, there will be no harm to your health from the infrared heater.
Operating principle
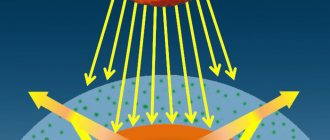
Infrared (IR) or thermal radiation has a different wavelength from other types. This figure ranges from 0.78 to 1 micron. The frequency range is from 106 to 500 x 106 MHz. IR waves are completely inaccessible to human visual perception, but receptors on the skin can perceive them as thermal radiation.
IR radiation is also called thermal radiation. In nature, the most famous sources of such waves are the Sun (the most powerful) and humans.
Types of infrared wave bands:
- near - 0.8–2.5 µm;
- medium - 2.5–25 microns;
- far - 25–1000 microns.
The general rule of wavelength is that it is inversely proportional to its ability to pass through tissue, that is, a shorter wave is able to penetrate tissue structures faster. Infrared radiation is characterized by deep heating and penetration into objects.
IR waves are long, so they can be freely absorbed even in a room that is too cold and very windy. Heating of the room begins almost immediately after connecting the infrared device to the network. The speed of heating is explained by the fact that the radiation flow is directed to a specific area that needs to be heated.
The operating principle of an IR heater is similar to the interaction between the sun and the atmosphere. The sun's rays penetrate the surface, which absorbs heat, heats up, and then releases this energy.
The body of the IR device is made of steel, and powder paint is applied to the surface. Inside it is an aluminum reflector to which a heating element is attached. Externally, the device is similar to a heating panel or lamp, inside which a beam of infrared rays is concentrated, the action of which does not depend on the speed of movement and direction of cooled and warm air masses.
Possible painful symptoms from IR heaters
What symptoms can people experience when exposed to infrared heaters?
Standing in front of infrared heaters for a long time can cause headaches.
- A headache is a clear sign that it’s time to temporarily turn off the heater or sit away from it.
- A numb or cottony feeling in the head is another sign of adverse effects. Perhaps you incorrectly calculated the power of the equipment you are using or did not ensure that recommendations for its placement in the rooms are followed.
- A feeling of dry skin – a similar sensation occurs after sitting near a fire for a long time. The skin seems to dry out, tighten, and feels overheated. If you feel this effect, sit away from heaters.
Thus, all harm is associated only with improper operation - being close to people, incorrect selection of power, staying in front of the heater for too long, incorrect selection of wavelength . If you follow the rules of operation of such devices, then you will receive only benefit from them, but not harm.
Why is it harmful to the body?
Some experts claim that radiation has a negative effect on the human body; they claim that the waves cause diseases of the eyes, skin, as well as the nervous system and blood. Other experts say that infrared heat is good for health: it has a positive effect on metabolism, skin and muscles. However, there are independent studies that show that the waves emitted by emitters are harmful.
In case of prolonged exposure to infrared, the eyes become more susceptible to harmful radiation, and headaches may begin. In extreme cases, with extremely prolonged exposure, cataracts can occur as a result of the initiation of chemical processes in the white of the eye. It is worth noting that infrared radiation with short waves, quickly penetrating through tissue, reaches the structures of the eye faster.
Far infrared light is used to heat rooms in which people are located. This is radiation that is easily absorbed by particles of liquid that are present in the human body. Therefore, cells (especially skin) are heated in a certain sense directly and quite quickly. But the power emitted by the heater is small. This range is considered completely safe, as confirmed by studies presented by the manufacturers.
According to scientific research, only long-wave infrared devices have a positive effect on the human body. But this process should be short-term. Otherwise (with prolonged directed heating), according to professionals, the skin will be overheated and dry out, which will have a bad effect on its condition. In addition, it is possible to burn the retina and lens of the eye, so experts do not recommend looking at the heater coil for a long time.
Film
This type of heater is ideal for organizing a warm corner somewhere on a loggia or veranda. It is used for zonal heating, although no one bothers to cover the apartment with “warm films” over the entire area.
In film infrared heating, the main material is a thin layer of graphite, which is applied to a thermoplastic film. Instead of graphite, a carbon thread can be used - when heated, it creates a heat flow. Note that film heaters create a single integral system, but it consists of separate modules. If some section fails, it is not difficult to replace it with a new one without compromising its integrity.
These panels do not have high power, so their efficiency is low. For this reason, they are used for local heating and are rarely installed along the entire perimeter of the apartment.
Is there any benefit
We can say that one of the undoubted advantages of infrared heating is its positive effect on the human body, as well as on the condition of buildings.
The benefits are as follows:
- The rays do not cause air or dust movement. This may be especially important for people with allergies.
- The heat emitted by the device is absorbed by the floor, walls, and ceiling, as a result there are no problems with high humidity in the room, and the risk of mold or mildew is reduced.
Panel
When organizing infrared heating of a private house or apartment, panels are more often used, and films are less often used. Flat panel equipment allows you to save room space, as it does not involve changing the height of the room. This is a relevant solution for rooms with low walls.
They consist of:
- Heating element - heating element. It is made from one of three materials: quartz, ceramics, tungsten.
- A special panel that receives heat and transfers it to objects in the room.
- Insulation on the back side. It reflects heat waves from the back of the device and eliminates heat loss.
- Cases.
Infrared panels can be built into the ceiling or hung. Built-in ones are more popular and aesthetically pleasing. In this case we are talking about infrared plasterboard heating with special thermal insulation and graphite thread. They are also built into the walls around the perimeter of the room. Each panel has an average power of 150–200 W.
Types of devices
Devices that emit infrared rays require certain power sources to operate.
There are the following types of infrared devices based on the type of heating element:
- Electric. This heater, when reaching a higher temperature (about 2200 °C), emits short infrared rays IR-A with a wavelength of about 1.2 microns. They are not visible to people, but their radiation is felt as a thermal impression, that is, an increase in temperature. The heater is a radiant/infrared filament which is made of a gold plated glass tube with a tungsten filament. The entire radiator is filled with gas. 92% of the energy consumed by a radiator is reflected in the form of noticeable heat. The service life is 7000 hours. The number of starts and stops does not negatively affect the emitter.
- Gas. These devices have a significantly greater heat capacity and impressive dimensions; their height can reach 15-20 meters. The models work on the same principle as electric ones, but use gas as an energy source.
- Diesel, kerosene. They are used in the construction of large facilities and are involved in the technological process of drying wood. The power of such devices is comparable to gas models, but they are more compact and can be reconfigured to work in any conditions.
- Ceramic. Equipped with a ceramic plate that does not emit visible light. The mid-wave infrared (IR) radiation emitted by these devices has a wavelength of 2 to 10 microns. The source temperature, depending on the power, ranges from 272 to 726 °C. The power of one emitter ranges from 150 W to 1000 W. It provides heat directly to the person and all objects within the range of the heating element.
Most often, electric and ceramic models are chosen for apartments and private houses.
There are three types of IR heaters based on heating level:
- Emitting long waves. This type of device is installed in private households, offices and small industrial premises.
- Average. Used in buildings with high ceilings - more than 3 m.
- Short. The equipment is used exclusively in industrial workshops, large halls with high ceilings, or outdoors. The models are not suitable for home use, since their radiation is the strongest.
Infrared radiation - what is it?
Conclusions about the harmfulness of this radiation can only be drawn if you understand what it is. In principle, any heating device emits infrared rays, but the wavelengths, as well as the intensity, are different. Therefore, it would be incorrect to compare the IR radiation of a conventional cast iron battery and an infrared heater.
Infrared radiation refers to electromagnetic radiation. Its natural source is the Sun. It's nice to feel the warmth of the sun on your skin, but being exposed to it for too long can be harmful. In principle, the negative and positive effects of this radiation are determined by the degree to which it penetrates deep into the skin.
One of the main advantages of infrared heaters is that they transmit energy to its destination with virtually no losses. The surface of objects exposed to infrared radiation heats up the more strongly, the higher the temperature of the heater itself. Indeed, as it heats up, more and more short waves appear in the spectrum. Namely, they heat up the surfaces that face them the most. And if the heater produces predominantly only short-wave radiation during operation, then we have to talk not about the benefits, but only about the harm of infrared heaters.
Depending on the wavelength and the temperature to which the heating element is heated, infrared heaters are divided into three types:
- Heaters emitting long waves (from 50 to 200 microns) heat up to 300 degrees Celsius.
- Heaters emitting medium waves (from 2.5 to 50 microns) heat up to 600 degrees.
- Heaters emitting short waves (from 0.7 to 2.5 microns) heat up the most - over 800 degrees.
Depending on the degree of penetration into the depths of human skin, the entire range of the infrared wave spectrum can be divided into three parts:
- IR-A – waves with a length from 0.76 to 1.5 microns. They are able to penetrate deep enough into the skin - up to four centimeters.
- IR-B is a wavelength range from 1.5 to 3 microns. Their degree of penetration under the skin is average.
- IR-C - waves longer than 3 microns. They do not pass further than the uppermost layers of the skin (from 0.1 to 0.2 microns), being completely absorbed by them.
The radiation from the heating element consists of short, long and medium waves. It’s just that there are more of them in the spectrum, and less of others. The higher the heating temperature, the more short waves appear in this spectrum. But not all manufacturers of infrared heaters talk about this. Here is an example of the dependence of wavelengths on the temperature of the heating element given by one of the honest manufacturers of infrared heaters.
Source temperature, 0Wavelength, µmPower, W/m2
| 255 | 6,80 | 150 |
| 354 | 5,40 | 250 |
| 354 | 4,90 | 300 |
| 452 | 4,50 | 400 |
| 468 | 4,15 | 500 |
| 553 | 3,85 | 650 |
| 602 | 3,60 | 750 |
| 685 | 3,15 | 1000 |
Let's take for example the human body, which has a temperature of 36.6 degrees. The maximum energy it emits comes from waves with a length of 9.6 microns. An infrared heater with a ceramic element emits maximum radiation at a wavelength of 3.6 microns and a temperature of 600 degrees. The sun has the greatest radiation in the visible part of the spectrum at a wavelength of 0.5 microns.
From this it becomes clear that our body can easily perceive heat waves with a length of more than 9.6 microns. By looking at the passport of a heater produced by a reliable company, you can find the range of emitted waves in it. Typically it is either 2 (or 3) to 10 microns.
The main advantage of IR heaters - instant energy transfer - is due precisely to the influence of short and medium waves. The more the emitter heats up, the more short waves appear in the spectrum. As a result, the surface that needs to be heated will become warm much faster than when using, for example, a convector-type heating device, which should heat all the air in the room.
The operating principle of a convector heater.
If you have had a fireplace or electric reflector, then you know that it is warm to sit next to them, but you also need to move close enough to the device. And the heat from them goes only in one direction. It's like sitting around a fire. If you gape and overheat, you may end up with harm instead of benefit from infrared heaters. Therefore, manufacturers of these devices try to soften the radiation.
The emissivity, also called the degree of emissivity, determines its intensity. If you heat up a completely black object very much, the radiation from it will be the hardest. The intensity of the rays from the element located in the ceramic housing is slightly reduced. The radiation is softened by reflectors mounted in the device.
So: based on the influence of infrared rays, it is possible to make an excellent device that will not have a negative effect on the human body and a very mediocre one.
How to choose a good one
IR heaters operate on a principle that can be compared to sunlight. While oil and convection heaters heat the air in the immediate vicinity, IR heaters fire rays that raise the temperature of objects they encounter along the way. Only the heat of solid objects heated in this way increases the air temperature.
In the case of infrared heating using panels, objects and people again reflect the accumulated heat, thereby ensuring comfort throughout the entire room with an even temperature distribution.
According to the installation method, heaters are distinguished:
- ceiling;
- floor, baseboard;
- wall-mounted
Blocks that are attached to the ceiling are most in demand today, as they completely eliminate the effect of convection and do not tolerate dust. In addition, the mounted device does not require much space; it is mounted in a suspended ceiling or attached to a conventional one using brackets.
Floor-standing electrical appliances are less efficient than ceiling-mounted ones, because their radiation flow is not directed directly, thereby making heating more difficult. For home use, it is best to choose progressive carbon devices. Their heating elements are made in the form of a quartz tube with a carbon spiral inside. Although during operation they emit a reddish glow that is not very pleasant for the visual organs. The ceramic element does not glow as well, but is inferior in quality.
Some IR wall heaters consume less electricity than other devices. They heat semi-closed rooms and open areas well.
Portable models are compact in size, but can heat a much smaller area than stationary ones.
Modern infrared devices are of the following types:
- Quartz. They are the safest for use (the temperature of the heated elements is 450–500 ºС). Quartz glass serves as a radiation filter.
- Halogen. Not recommended for use in residential buildings, suitable only for large spaces (elements temperature is 2000 degrees). Gas is pumped inside the flask; if it is damaged, the substance can be hazardous to health.
- Carbonaceous. Devices with a spiral are considered reliable and durable, resistant to elevated temperatures (carbon elements are heated to 600–700 degrees).
- Micathermic. These new products are characterized by the highest efficiency and safety. Covered with a mica plate, the element is heated to 60–80 degrees. The reliability of this type of heating equipment for the home has been tested in practice.
- Ceramic. Thin wall panels come in a variety of shades. The model can be matched to any interior. They are installed in apartments and houses after renovation, where it is necessary to carefully install the heating system without spoiling the finish.
- Steel. Such devices use a metal radiating panel. Outwardly, they resemble fluorescent lamps. Their main advantage is their small thickness.
- Film. The most original and beautiful models. Produced in the form of unfolding pictures. They look great and are suitable for temporary heating.
If you are already planning to purchase a heating device, it is recommended to choose devices with long-wave radiation. Such models do not pose a danger to people during operation.
general characteristics
Any heater is a source of infrared radiation. In nature, such waves are generated by the sun.
Infrared radiation has a thermal effect and penetrates into the deep layers of tissue. The operating principle of household heaters is quite simple. Infrared rays leave the device, reach objects and heat them. When objects heat up, they release heat into the atmosphere.
The energy from the devices reaches objects and people, and the air around them warms up. The effect of infrared radiation is local. Objects outside the reach of waves do not heat up and remain cold.
Unlike convective heating, warm air does not collect in the ceiling area. Therefore, infrared heaters are economical and heat the required area of the room. The main heating can be reduced; thanks to the device, a person will feel warm in the required areas of the room.
Like the article: “ Electromagnetic radiation from a computer