Heating systems for country cottages with a height of 2 or more floors are usually designed by heating engineers. But owners of houses with a simple layout with an area of up to 200 m² do not have to turn to specialists - they can think through and organize the heating of the building themselves. The purpose of this publication is to explain which heating scheme for a two-story house is best combined with specific operating conditions, boiler equipment and radiators. We invite you to consider the existing options and choose the best one.
Types of heating systems
Practice shows that most homeowners put forward 3 basic requirements for the heating system of a two-story house:
- The house should always be warm.
- Minimum energy consumption - natural gas, firewood, electricity, and so on.
- Beauty. It is advisable to remove pipes, fittings and heating devices from view so as not to spoil the interior.
The requirements are listed in order of importance from the users' point of view. We will talk about installation costs when reviewing the systems.
The wishes are quite understandable, but they should be linked to technical capabilities. For example, in remote regions there are power outages or there is no main gas supply. Hence the advice: first determine the main fuel and backup energy carrier, select a boiler and heating devices. Reflect your wishes on paper - sketch out a rough draft with your own hands.
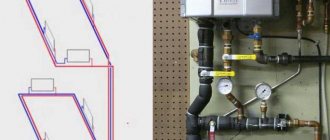
It is not always possible for the owner of a house to arrange utility networks himself - to develop diagrams, install equipment and pipes. In this case, it makes sense to contact the specialists of an engineering company that deals with the listed work. For example, in the central region of the Russian Federation, services for installing boilers and installing heating systems are provided.
Such a thorough approach will allow you to install a heating circuit for a two-story house, which will not have to be redone later. There are 5 system options to choose from:
- gravity (also known as gravitational and convection);
- single-pipe;
- two-pipe;
- radial (otherwise known as collector);
- water underfloor heating circuits called underfloor heating.
Note. The first scheme involves natural circulation of coolant through pipes and an expansion tank communicating with the atmosphere. The rest implement the principle of forced circulation using a pump and work under pressure (a closed membrane tank is used).
An example of a draft heating project for a 2-story mansion.
The indicated systems can be combined with each other. For example, make heated floors on the first floor, and assemble a radial circuit on the second. Now let's take a closer look at each option separately.
Natural circulation scheme
To understand the principle of operation of the gravity system, study the typical diagram used in two-story private houses. Combined wiring is implemented here: the supply and return of coolant occurs through two horizontal lines, connected by single-pipe vertical risers with radiators.
Reference. There are other ways to organize gravity flow on two floors, for example, by dividing the risers directly from the expansion tank with pipes of a smaller diameter. The circuit is material-intensive, looks like a spider, and installation will cause a lot of trouble.
How gravity heating of a two-story house works:
- The specific gravity of the water heated by the boiler becomes smaller. The colder and heavier coolant begins to displace hot water upward and take its place in the heat exchanger.
- The heated coolant moves along a vertical collector and is distributed along horizontal lines laid with a slope towards the radiators. The current speed is low - about 0.1-0.2 m/s.
- Dividing through the risers, the water enters the radiators, where it successfully releases heat and cools. Under the influence of gravity, it returns to the boiler through a return manifold, which collects coolant from the remaining risers.
- The increase in water volume is compensated by an expansion tank installed at the highest point. Typically, the insulated container is located in the attic of the building.
Schematic diagram of gravity distribution with a circulation pump.
In modern designs, gravity systems are equipped with pumps that accelerate circulation and heating of rooms. The pumping unit is placed on a bypass parallel to the supply line and operates when electricity is available. When the light is turned off, the pump is inactive, and the coolant circulates due to gravity.
Scope of application and disadvantages of gravity feeding
The purpose of the gravity circuit is to supply heat to homes without connection to electricity, which is important in remote regions with frequent power outages. The network of gravity pipelines and batteries can work together with any energy-independent boiler or stove (previously they said steam) heating.
Let's look at the negative aspects of using gravity:
- due to the low flow rate, it is necessary to increase the coolant flow by using large-diameter pipes, otherwise the radiators will not warm up;
- in order to “spur” natural circulation, horizontal sections are laid with a slope of 2-3 mm per 1 m of the highway;
- healthy pipes running under the ceiling of the second floor and above the floor of the first floor spoil the appearance of the rooms, which is noticeable in the photo;
Due to the too large distance from the ceilings, it is very difficult to hide the pipe behind the cladding - automatic control of air temperature is difficult - for batteries you need to buy only full-bore thermostatic valves that do not interfere with the convective circulation of the coolant;
- the scheme is unable to work with heated floors in a 3-story building;
- An increased volume of water in the heating network implies prolonged heating and high fuel consumption.
Comment. The last negative point does not play a special role - the energy spent on heat production will not go anywhere. It will return as the pipelines cool.
To fulfill requirement No. 1 (see the first section) in conditions of unreliable power supply, the owner of a two-story private house will have to bear the costs of materials - pipes of increased diameter and cladding for the manufacture of decorative boxes. The remaining disadvantages are not critical - slow heating is eliminated by installing a circulation pump, lack of efficiency - by installing special thermal heads on radiators and insulating pipes.
Design Tips
If you have taken the development of a gravity heating scheme into your own hands, be sure to consider the following recommendations:
- The minimum diameter of the vertical section coming from the boiler is 50 mm (meaning the internal size of the nominal diameter of the pipe).
- The horizontal distributing and collecting manifold can be reduced to 40 mm, before the last batteries - to 32 mm.
- A slope of 2-3 mm per 1 linear line of the pipeline is made towards the radiators on the supply and the boiler on the return.
Even large pipes can be laid hidden (pictured on the right). On the left is a typical installation with open communications - The inlet pipe of the heat generator should be located below the radiators on the first floor, taking into account the slope of the return line. It may be necessary to make a small pit in the boiler room to install a heat source.
- On the connections to heating devices on the second floor, it is better to install a direct bypass of small diameter (15 mm).
- Try to place the upper distribution manifold in the attic so as not to run under the ceilings of the rooms.
- Use an open-type expansion tank with an overflow pipe leading outside and not into the sewer. This makes it easier to monitor when the container is overfilled. The system will not work with a membrane tank.
Important point. Don’t forget to carefully insulate all elements of the gravity circuit located in the attic of a two-story house so as not to heat up the cold roof.
The calculation and design of gravity heating in a cottage with a complex layout should be entrusted to specialists. And lastly: lines Ø50 mm or more will have to be made of steel pipes, copper or cross-linked polyethylene. The maximum size of metal-plastic is 40 mm, and the diameter of polypropylene will be simply menacing due to the thickness of the walls.
Design features
For a gravity system to work effectively, the following requirements must be met:
- the heat source is any non-volatile heat generator with outlet pipes with a diameter of 40-50 mm;
- at the outlet of a boiler or stove with a water circuit, an accelerating riser is immediately installed - a vertical pipe through which the heated coolant rises;
- the riser ends with an open-type expansion tank installed in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floor (depending on the type of wiring and the design of the private house);
- tank capacity – 10% of the coolant volume;
- by gravity, it is advisable to choose heating devices with large internal channels - cast iron, aluminum, bimetallic;
- for better heat transfer, heating radiators are connected according to a versatile pattern - bottom or diagonal;
- special full-bore valves with thermal heads (supply) and balancing valves (return) are installed on the radiator connections;
- It is better to equip batteries with manual air vents - Mayevsky taps;
- replenishment of the heating network is organized at the lowest point - near the boiler;
- all horizontal sections of pipes are laid with slopes, the minimum is 2 mm per linear meter, the average is 5 mm/1 m.
On the left in the photo is the coolant supply riser from a floor-standing boiler with a bypass pump, on the right is the return line connection.
Gravity heating systems are made open and operated at atmospheric pressure. But will gravity flow work in a closed circuit with a membrane tank? We answer: yes, natural circulation will continue, but the speed of the coolant will decrease and efficiency will drop.
It is not difficult to substantiate the answer; it is enough to mention the change in the physical properties of liquids under excess pressure. With a pressure in the system of 1.5 Bar, the boiling point of water will shift to 110 °C, and its density will also increase. The circulation will slow down due to the small difference in the masses of the hot and cooled flow.
Simplified gravity flow diagrams with an open and membrane expansion tank
Pros and cons of a single-pipe scheme
A single-pipe heating system for a two-story private house can function normally only with forced circulation from a pump. The design is as follows: one main line runs along the perimeter of the floor, where all the batteries are connected. That is, the collector simultaneously plays the role of supply and return.
The Leningradka system is compact and works perfectly with a small number of heating devices
The operation of the single-pipe circuit, called “Leningradka”, is quite complex:
- If the pipelines are calculated correctly, then approximately 1/3 of the hot water flows into each radiator. The remaining 2/3 of the volume moves further along the highway.
- The coolant that has passed through the battery gets rid of the heat and returns back to the collector, lowering the flow temperature by 1-2 °C.
- The cooled water flows to the next radiator, where the process of separation and merging of flows is repeated. The temperature of the coolant in the collector drops again. How many batteries are connected to the ring main, the number of times the water will cool.
- Having passed the last heating device, the cold coolant returns to the boiler.
An important condition for the normal operation of the system: the diameter of the main line must be sufficient to supply heat to all batteries. In fact, pipes measuring 25–32 mm (DN 20–25) are used with radiator inlets Ø15 mm (internal diameter DN10).
Supporters of the “Leningradka” call its main advantage the low cost of materials and installation. We agree with the statement, but with a caveat: if the assembly is made with cheap polypropylene.
Single-pipe wiring is easier to install in building structures
A one-pipe heating circuit made in a two-story house from metal-plastic, cross-linked polyethylene or metal will cost more than a two-pipe one due to the price of fittings. Our expert Vladimir Sukhorukov will provide the exact calculation in the video below.
The disadvantages of the Leningradka look like this:
- since each subsequent radiator receives cooler coolant, it is necessary to increase the number of sections to heat distant rooms;
- in order not to select the number of sections at random, you need to calculate the cooling of the water;
- the maximum number of efficiently operating batteries on one branch is 5-6 pieces, otherwise the diameter of the distribution pipe will have to be increased to 40-50 mm;
- a looped highway is more difficult to route through the house - doorways get in the way, especially on the second floor;
- heating devices influence each other, which makes it difficult to organize automatic control.
Example. Imagine that all radiators have thermal heads installed. If the air in the first room has warmed up to the set temperature, the thermostat will close the coolant passage into the battery. Then hotter water will flow to the remaining appliances, which will force the remaining radiator valves to operate.
A small plus of single-pipe wiring: it is easier to hide one branch in a wall or under the floors than two. The heating network can be easily combined with other types of forced circulation systems.
Heating pipes
And a little about pipes and other devices. Today there is no need to complain about their lack of diversity. Until recently, only steel analogues were used, which have already lost their relevance due to high prices, difficulty in installation and rapid failure due to corrosion. They were replaced by copper and metal-plastic pipes with high performance characteristics. And if copper pipes are still used less frequently due to their high cost, then plastic is in great demand today.
Mayevsky crane
We also note that for better operation of the heating system, various devices began to be used:
- Mayevsky valve - it is usually installed on radiators and allows air to be released from the system.
- Shut-off valves - with its help you can shut off the coolant supply to each radiator. This makes it possible to repair it without shutting down the entire system.
- Control valves - they allow you to reduce or increase the supply of hot water.
- All kinds of sensors that control various processes in the heating system.
All these devices serve only one purpose - the efficient operation of the heating system. Of course, all this costs money, but quality always requires expense. True, you will have to invest only once, and then reap the benefits.
Two-pipe wiring - simple and reliable
There is no need to describe the algorithm of operation of the two-pipe circuit, since it is outrageously simple. 2 pipelines are laid past all heating devices - supply and return. According to the first, the hot coolant enters the batteries, where it is cooled and returned to the boiler through the second. The connection is appropriate - one connection is embedded in the supply, the second - in the return.
Classic dead-end wiring. Shown here is 1 shoulder on each floor; if necessary, their number can be increased to 2-3
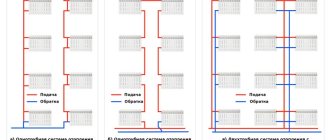
In two-story country houses, 2 types of two-pipe systems are used:
- Deadlock or shoulder. The supply and return lines end at the last radiator; in fact, the coolant changes direction and flows back to the boiler.
- Passing (ring, Tichelman loop). The supply pipe ends at the last battery, and the return pipe starts from the very first radiator, passes through the remaining heaters and returns to the heat source. The direction of water movement does not change, hence the name.
Note. Both systems are powered by a pump and in the vast majority of cases operate under a pressure of 1-2.5 Bar. There is no point in making them open; it is easier and more convenient to install a membrane expansion tank next to the boiler.
In the Tichelman loop, water does not turn around after leaving the battery, but flows in the same direction (classical hitchhiking).
Two-pipe schemes are almost flawless, so let's start by listing the disadvantages:
- extended branches with a large number of heating devices require deep balancing, but when the number of batteries is 5-6 pcs. there will be no problems;
- the pipelines of the Tichelman loop inevitably encounter doorways that have to be rounded in different ways;
- a heating network assembled from polypropylene will cost more than a similar single-pipe system;
- All.
There are really few downsides to two-pipe schemes: they are reliable, stable in operation, easy to automatically adjust and function equally well with heated floors, radiators and other types of heaters. Dead-end wiring arms can be made of different lengths and loads according to the number of batteries, and the Tichelman loop is an example of hydraulic balance that does not require balancing.
For reference. In a country cottage with an area of up to 200 m², it will be possible to get by with pipe diameters of 10-20 mm (internal), no more.
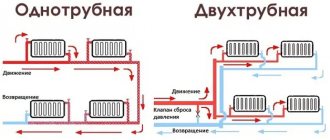
Main differences
Heating systems using liquid coolant are divided into 2 main types - single-pipe and double-pipe. The differences between these schemes lie in the method of connecting the heat-releasing radiators to the main line. The main line of a one-pipe heating system is a closed circular circuit. The heating main is laid from the heating device, the batteries are connected to it in series and pulled back to the boiler. A heating system with one pipeline is easy to install and does not have a large number of components, so it makes it possible to save a lot on installation.
Single-pipe heating structures with natural movement of coolant are built only with overhead wiring. A distinctive feature is that the diagrams have risers for the supply line, but there are no risers for the return pipe. The movement of coolant in a double-circuit heating system is carried out along 2 lines. The first is intended to deliver hot coolant from the heating device to the heat-releasing circuits, the second is to remove cooled coolant to the boiler.
Heating radiators are connected in parallel - the heated coolant enters each of them directly from the supply circuit, thanks to which it has an almost equal temperature. In the battery, the water releases energy and, when cooled, is sent to the outlet pipe - the “return”. Such a system requires double the number of pipes, fittings and fittings, however, it makes it possible to organize complex branched structures and reduce heating costs thanks to individual regulation of batteries. The double-circuit system highly efficiently heats large rooms and multi-storey buildings. In low-rise buildings (1-2 floors) and houses with an area of less than 150 m², it is more rational to build a single-circuit heat supply from both a financial and aesthetic point of view.
The principle of collector distribution of coolant
The beam circuit is a modern type of two-pipe distribution that satisfies all new and old requirements: efficiency, cost-effectiveness due to automated control, completely hidden pipe laying, and so on. What are the features of the system:
- The coolant from the boiler is directed to the main distribution unit - the collector.
- The radiators are connected by DN10-15 connections to the comb according to a two-pipe circuit, each to its own pair of fittings on the supply and return manifolds. There are no highways.
- The supply pipes are insulated and laid hidden along any convenient route - under the floor covering, behind suspended ceilings or in the walls.
- With the help of manifold flow meters (rotameters), manual adjustment of the amount of water directed to the battery is available. If the comb is equipped with servo drives connected to the room thermostat, the coolant flow will be controlled automatically.
The perfection of collector heating schemes for two-story houses is somewhat overshadowed by the high price of materials. Combs with rotameters, pipe insulation, servos - all of these elements cost a lot of money. The second disadvantage: such a system is difficult to assemble in residential premises without making repairs. To hide a bundle of pipelines, you will have to dismantle the floors or remove the ceiling lining.
Do-it-yourself installation of a two-pipe heating system in a private house
The manufacturing of the structure takes place in several stages.
Calculation
Before proceeding with installation, it is necessary to draw up a clear plan, for which specialists always carry out hydraulic calculations. During this process the following results are achieved:
- the number of heating devices is determined;
- the sizes and quantities of circumferential risers are calculated;
- future losses are determined.
Attention! The calculation is made in strict accordance with the heating scheme. Hydraulic calculation gives an understanding of the operating resistances, provides information about water flow rates and the temperature of each individual section
Installation
- First, a heating boiler is installed in a separate ventilated room. Its location should be away from the walls and it should be accessible. The walls themselves, as well as the floors in the room, should be finished with fire-resistant material.
- After this, you need to install a pump, a hydraulic distribution manifold, and measuring instruments/meters at the boiler.
- From the boiler room, straight through the walls, a pipeline is led to the radiators.
Connection
The final stage is connecting the radiators. The batteries are mounted on brackets under the window. In addition, it is recommended to install temperature sensors. With their help, water flows and its temperature are regulated.
Underfloor heating circuits
Like the collector circuit, a water-heated floor is installed during the construction or renovation of a two-story house. There are 2 ways to install underfloor heating:
- embedding pipe coils in a cement-sand screed;
- layout of heating circuit pipes in heat-distributing metal plates without pouring screed.
For reference. Concreting of pipelines is usually done on the first floors of residential buildings. The second method is used for laying inside wooden floors.
The ends of pipes Ø16 x 2 mm, laid with a snake or snail, are connected to the comb, which was mentioned above and described in detail in a separate publication. A manifold with a mixing unit or RTL thermal heads ensures the supply of coolant to the circuits with a temperature not exceeding 50 °C.
The advantages of heated floors are obvious - real energy savings of 15-20% due to heating the surface to a temperature of 20-25 ° C and comfort for those living in the house. Now about the negative points:
- Installing a heated floor in a two-story home is not a cheap undertaking. In terms of the cost of materials and installation, this is the most expensive option for space heating.
- Heating circuits, especially in cement screeds, are very inert in terms of adjustment. Imagine, a cold monolith reaches operating mode within 24 hours. To prevent the room from overheating, a third of the required heating power should be supplied by batteries that quickly respond to changes in air temperature.
- In the event of a malfunction or water leak in the circuit, the concrete screed will have to be broken.
A method for installing heated floors without a cement screed
Despite the problems listed above, heated floors are being used by homeowners more and more often - the heating is too comfortable and the fuel savings are noticeable. Unlike other heating systems, heating circuits do not spoil the interior of the premises at all.
Choosing a suitable scheme
After familiarizing yourself with the heating systems used in two-story houses, it’s time to return to your draft project, where the types of radiators and boiler are selected, the arrangement of this equipment is determined, and wishes are listed. Next, select a scheme in accordance with the recommendations:
- If there are frequent power outages, the choice is small - you need a gravity system. If the house is heated with a brick stove, you should use it as a heat source and not buy a boiler.
- If you still don’t understand what you want, feel free to assemble a closed-type two-pipe dead-end circuit. It can be easily adapted to different conditions and equipment. Subsequently, install a solid fuel, gas or electric boiler - there is no difference, the heating will work.
- If you have increased requirements for interior design, start with manifold wiring. In order not to make a mistake with the size of the pipes, pull the diameter of 32 mm to the comb, and make connections to the batteries Ø16 x 2 mm (outer).
Joint connection of a radiator network and underfloor heating circuits controlled by room thermostats - Warm floors are installed if there are funds and desire. It is better to combine them with any system other than gravity.
Advice. Underfloor heating without a radiator network is not suitable for everyone. To warm a room with a warm floor, its surface will have to be brought to 30 °C or more. A long stay in such a room causes a feeling of stuffiness and discomfort for many.
In a small country house with 2 floors, it is worth making a one-pipe system from PPR pipes. With 3-4 batteries on each branch it will work flawlessly. We do not recommend using Leningradka in a large cottage. For more information about choosing a wiring, watch the video from an expert:
About compatibility with various boilers
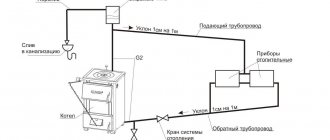
When choosing a heating scheme for a two-story house, you need to take into account the type of heat source. For example, all systems except gravity can work with a wall-mounted gas boiler. If there is a power outage, the heat generator will simply stop. The best option for gravity feeding is a non-volatile floor unit or a brick oven with a water circuit (tank - boiler, but not a coil!).
Direct connection of gravity wiring to a solid fuel boiler is extremely undesirable, although homeowners do it anyway.
Due to the low speed of movement and slow heat extraction, the heating unit will overheat and boil, and sooner or later an accident will occur. A buffer tank is definitely needed, taking away excess energy, and connected according to all the rules of gravity flow - with large diameters and with slopes. The structure will be bulky and ugly.
Closed systems of two-story houses are compatible with any boilers, including double-circuit ones. The only recommendation: when connecting to solid fuel units, it is better to use a heat accumulator, which will prevent the coolant from boiling and prevent an accident.