Heating systems using gas as fuel are highly efficient and reliable. The thermal energy generators in them have impressive efficiency and are safe to use. There are several ways to organize gas heating for a private home.
There are solutions both budget-friendly and more expensive with maximum efficiency and operational stability. We are ready to share with you proven options for installing a gas heating system. Using our recommendations guarantees the construction of a trouble-free and secure network.
The information we provide is based on building regulations. The information offered for review is supplemented by visual photo illustrations, diagrams and video tutorials.
How does an open heating system work?
There is no need to install a pump to start the system. The coolants are constantly in a closed system, so there are no losses. Installation of the heating system is so simple that it does not require special skills.
Open heating system
What are the main parts of the system?
- Gas or solid fuel boiler. The consumer can choose the best option that meets the desired requirements;
- Heating radiators. You can make your choice in favor of either cast iron or steel;
- Expansion tank made of steel;
- Pipes.
How does an open heating system work?
The first step is to heat the water in the boiler. Hot water then flows under pressure into the pipes and reaches the low pressure zone. After the hot water makes a complete whirlpool and gives off heat, it returns to the starting point - the boiler. Due to the fact that water expands under the influence of high temperatures, an expansion tank is required in the system. It acts as a compensator for excess water volume. The tank is an object that is not sealed hermetically. To make it easier to start the heating system, it is necessary to install a mortise tap. With its help, air is removed from the system. The operating principle of an open heating system is divided into two stages:
- "Innings". The water is heated, flows through pipes into radiators and heats the room;
- "Treatment". The cooled water from the radiators is returned through the pipes to the boiler.
Features of the arrangement of an open heating system:
Be sure to place the expansion tank above the level of other heating system devices;
Choose water rather than antifreeze as the coolant; Since water can evaporate when heated, it is important to monitor its level in the boiler and replenish reserves in a timely manner.
Stages of gas heating installation
Selecting and installing a heating system is a multi-stage process. It includes:
- system design - calculating heat losses, choosing a circuit, wiring;
- preparation of equipment - the actual selection of radiators, pipes, boiler, as well as preparation for installation: For example, if autonomous gas equipment needs to be placed in the house, then you will need to build an extension;
- installation of a heating system - installation of radiators and pipes;
- installation and connection of a gas boiler;
- checking and configuring the system.
The last stage involves registering a gas meter and an operating permit from the gas company.
Drafting
The starting point for the project is heat loss calculations. Ideally, this is done using special equipment - thermal imagers. But you can do without them. On average, a house loses 10–15% of heat through the walls, up to 15% through the basement, and up to 30% through the roof. This depends on the level of insulation, the material of walls and roofs, and the design of the building.
On average, it takes 1 kW to heat 10 m² of housing with a ceiling height of no more than 2.5 m. That is, to heat a building with an area of 250 m², a boiler with a capacity of at least 25 kW will be required. It will consume 2.5*24=2.5 m³ of gas per day. This will amount to 1800 cubic meters per month. m. Taking into account the weather in the region, the result is multiplied by the corresponding number of cold months.
Calculate approximately, only to establish some maximum limits. They serve as the basis of the project along with the features of the building.
Design includes:
- dividing the house into zones and determining the required temperature conditions in each of them;
- calculation of the heating network by zones or rooms;
- calculation of the number of sections for heating the zone;
- selection of heating type - wiring, installation diagram;
- calculation of boiler power, equipment and materials.
Valera
The voice of the construction guru
Ask a Question
Power largely depends on the material of the heat exchanger in the boiler itself and the material of the radiators. Bimetallic successfully transfers heat to the room at a water temperature of +35°C. The cast iron battery begins to heat up at a coolant temperature of at least +50°C.
Equipment preparation
Radiators, pipes, and boiler are selected based on the requirements of the project.
- Pipes – for heating, metal-plastic ones are considered the best option. They can withstand high heat, are durable and have a lower coefficient of thermal expansion. This makes installation much easier. It is also possible to take polyethylene ones.
- Radiator - They produce a variety of options. Aluminum batteries heat up very quickly even at low coolant temperatures, are resistant to corrosion and are beautiful. However, the material is soft and cannot withstand water hammer. Cast iron, on the contrary, is resistant to pressure changes and gives off heat for a long time, but it is very heavy and takes a long time to heat up. Bimetallic radiators heat up quickly, retain heat for quite a long time, but are more expensive and not as durable.
- Boiler – its main characteristic is power. You need to buy a boiler with a power reserve of 15%, no less. It is worth considering that if the house is large, and even three-story, you should not install a double-circuit one. Even with high power it will be ineffective.
The rest of the equipment - taps, regulators, fittings - is selected according to the material of the pipes and batteries.
Installation and connection of equipment
Only specialists install gas equipment and connect it to the main line. But some of the related work can be done with your own hands.
- First of all, a room is equipped : at least part of it is finished with fireproof materials, and ventilation is equipped.
- Install the boiler , connect the circulation pump and manifold, if required. Connect the device to the chimney.
- Install all necessary control sensors and regulators .
- Laying pipes . Heating pipes can only be mounted on the wall using brackets. They must be placed at a slope of 5 mm per linear meter.
- Radiators are installed - also on brackets.
- The heating system is filled with water and its operation is checked.
Then the gas boiler . An employee sets up the system, seals the device and the meter.
System testing and technology verification
Pressure testing is carried out after connecting the gas boiler. The algorithm is as follows.
- Fill the system with water slowly to reduce the amount of air in the radiators as much as possible. As soon as the pressure gauge reaches the desired value, the water supply is stopped.
- There is an air vent in the battery connection. If the valve is automatic, air release is performed without human intervention. If there is a Mayevsky tap, you need to manually bleed air from each battery until a stream of water appears.
- Turn on the boiler - set the switch to zero, turn on the gas supply. Follow the instructions, since the activation procedure is different in different models.
- Before starting, you need to bleed the air in the circulation pump . To do this, remove the panel on the device, unscrew the central bolt and turn it in the direction of the arrow. Then pull the air vent cap and release the air. The latter interferes with the rotation of the blades.
During work, you need to monitor the pressure gauge: the pressure must be within normal limits.
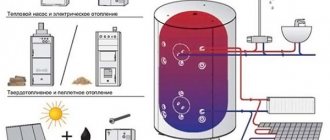
Schemes for water heating in a private house
To heat cottages, heating systems with water as a coolant are installed, consisting of:
- water heating boiler (single-circuit or double-circuit);
- pipelines and fittings (metal or polypropylene);
- bypasses that allow you to disconnect individual heaters from the network;
- batteries (cast iron, aluminum, steel and bimetallic);
- expansion tank.
Gas heating units are equipped with a specific safety system, including a solenoid valve and a thermocouple. The devices are connected to each other by wires. If the heating unit is functioning normally, the thermocouple junction is heated by the igniter. At this time, current flows freely through the winding of the solenoid valve, which ensures the open position of the valve. When the thermocouple cools down, the gas access is blocked by an electromagnetic valve.
According to the battery connection diagram, they are single-pipe and double-pipe. In the first case, water is supplied and discharged from the radiator using one pipe. In the second, the heating device is connected to two separate pipelines (supply and return).
Heating pipes to the radiators can be connected in a bottom, top, side or diagonal pattern
Heating circuits, based on the principle of water movement in pipes, are available with forced and natural circulation. When installing the second option, the coolant circulates in the system due to convection and gravity. And the forced scheme involves the installation of a circulation pump.
To ensure normal operation of a system with two or more circuits connected to the manifold, it provides for the installation of a hydraulic arrow. The hydraulic arrow eliminates pressure drops and the possibility of water hammer.
The expansion tank can be open or closed (divided inside into two parts by a sealed membrane). For gravity heating systems, an open option will be sufficient. A closed tank is designed for forced circulation circuits.
When using an open expansion tank, the water is saturated with air, so that this does not become a problem, the system should be supplemented with an air removal circuit
For small cottages, the natural principle of water movement will be sufficient. However, if a residential building has two or three floors, then you cannot do without a pump. The length of the circulation circuit in the first scheme is limited to 30 meters. The boiler will not be able to “push” water over a greater distance.
With natural circulation of the coolant in the gas heating circuit of a private house, there is no pump. If the boiler is chosen to be non-volatile, then the entire heating system is independent of the power supply. There are simply no elements that consume electricity.
On the one hand, it is more stable in operation, but on the other, the quality of heating in it is lower (the water reaches the radiators farthest from the water heater when it is very cold). The latter especially applies to pipelines and batteries made of steel or cast iron. These materials have high hydraulic resistance, which reduces the coolant current.
In addition to using standard radiators in a country house, you can organize gas heating using “warm floors” (+)
It is also possible to organize a combined heating system. In it, the circulation pump is connected to the main line through a bypass. If it is necessary to quickly warm up the air in the rooms, it is turned on to accelerate the water circulation. In other cases, it is cut off from the main pipe by shut-off valves, while the system continues to function in a natural (gravitational) mode.
Water heating
Undoubtedly, when asked what types of heating there are, it is water heating that first comes to mind. Water heating has the following advantages:
- Not very high surface temperature of various devices and pipes;
- Provides the same temperature in all rooms;
- Fuel is saved;
- Increased service life;
- Quiet operation;
- Easy to maintain and repair.
The main component of a water heating system is the boiler. Such a device is necessary to heat water. Water is the coolant in this type of heating. It circulates through closed pipes, and then the heat is transferred to various heating components, and from them the entire room is heated.
Components of water heating
The simplest option is natural circulation. This circulation is achieved due to the fact that different pressures are observed in the circuit. However, such circulation can also be of a forced nature. For such circulation, water heating options must be equipped with one or more pumps.
After the coolant passes through the entire heating circuit, it is completely cooled and returned back to the boiler. Here it heats up again and thus allows the heating devices to produce heat again.
Classification of water heating systems
Water heating type may vary according to criteria such as:
- water circulation method;
- location of distribution lines;
- structural features of risers and the diagram according to which all heating devices are connected.
In a pump heating system, heating of the coolant can also take place thanks to a hot water boiler room, or thermal water that comes from a thermal power plant. In a heating system, water can even be heated by steam.
Water heating with circulation pump
The disadvantage of direct-flow connection is the dependence of the thermal regime on the “impersonal” temperature of the coolant in the external-type supply heat water.
Features and Benefits
Heating systems differ in the configuration of the expansion tank - a special container that compensates for the thermal expansion of the coolant. An open tank is installed in a gravity system - the liquid moves through the pipes without installing a circulation pump for heating. The coolant moves due to the natural circulation of the medium, which changes density when heated and under the influence of gravity.
A feature of a closed system is the use of a closed expansion tank, which is a sealed container equipped with an elastic membrane inside. This ensures efficient operation under pressure and eliminates contact of liquid with air.
Internal structure of closed expansion tanks
With forced circulation
A closed-type heating system in a private house may include a circulation pump that forces the coolant to actively move, maximally warming up all heating devices or the heated floor circuit.
A closed heating system with forced circulation has a number of advantages
:
Heating of a liquid under pressure occurs faster; the risk of airing of the pipeline and radiators is reduced; evaporation of the coolant (which is especially important when using antifreeze) and the penetration of oxygen into the liquid, which provokes corrosion of the metal elements of the system, are prevented; due to the installation of the membrane tank below next to the boiler, and not at the top point of the circuit, as in open systems, installation and maintenance are simplified; the movement of liquid under low pressure simplifies the calculation and installation of the pipeline - unlike a gravity system, in this option there are no strict requirements for the angle of inclination of the pipes and pipes of smaller diameter can be used; there is no need to use large-diameter pipes and install them in an open manner in order to have access to any part of the system to eliminate air pockets.
Example with an induction boiler
The heating system of a private house with a circulation pump and a membrane expansion tank provides better heating of the premises compared to gravity. But it has one significant drawback - energy dependence. The operation of the pump requires electricity, so this option is not suitable for buildings in remote areas with insufficient power supply or its complete absence.
With natural circulation
The gravity heating system is energy independent, and this is its advantage. Typically this is a heating system with a solid fuel boiler or stove; liquid fuel units are less commonly used.
Heating without a pump is suitable for a home with a relatively small area; it is important to correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes for each part of the system and design their installation scheme, observing the optimal angle of inclination of the pipeline sections. It is necessary to reduce the risk of airing and ensure efficient movement of coolant
A circulation pump can be added to a closed heating system with natural circulation at any time, increasing its efficiency. This is the best option for areas where there are problems with power supply. In this case, if there is a temporary lack of electricity, the house will not be left without heat - a closed-type system in a private house will work like a gravitational one.
Natural circulation
The use of electricity for heating
The use of electricity is one of the ways to create heating for a private house without gas with the installation of a water circuit. Of course, this is an expensive type of heating. In principle, the following electric heating systems for a private home using electricity are possible:
- use of an electric boiler for water heating;
- placement of electric convectors in the premises of the house;
- use of infrared heaters;
- creation of warm floors.
Electric convector
An electric convector is the simplest device for heating air in a living space. The heating device by installing electric convectors impresses with its ease of installation, safety, protection against overheating and environmental friendliness. Infrared heaters are no less convenient for use, and sometimes a combined option of using electric heaters is chosen.
Such devices can be easily combined into one system and ensure its operation in automatic mode. If prices for electric convectors for heating a private home are quite affordable, then the constant increase in electricity tariffs reduces the demand for these convenient heating systems.
Infrared heated floors
One of the most popular options for a country house is infrared heated floors. They are produced in the form of a film, the thickness of which is about 3 mm. Installation of this floor is simple and affordable. The film is laid under any floor covering. Often the film is installed on walls and even on the ceiling. “Heated floors” are most often placed on the ceiling in two-story cottages or in houses with an attic. A large heating area speeds up the heating of the entire room and saves up to 40% of energy.
Electric boiler
Electric boilers are quite a worthy replacement for gas boilers. With their help, it is easy to create home heating alternative to gas heating. Only the price of electricity significantly limits the demand for these convenient and safe devices.
Every 100 m2 requires a power of 10 kW. If you need to install a powerful boiler, you will have to coordinate its installation with Energonadzor. The electrical wiring in the house, as a rule, does not meet the requirements, so an additional line is made from the entrance to the boiler.
According to the principle of operation, boilers that use electricity to heat the coolant are divided into:
- electric boiler with installed heating elements;
- electrode electric boiler;
- induction electric boiler.
All of the above devices have common features that distinguish them from gas and solid fuel boilers. These features, which can be advantages when using boilers for heating country houses:
- high level of security;
- noiselessness;
- simple adjustment of housing temperature, possibility of automation;
- there are no problems with fuel, its transportation and storage;
- do not harm the environment;
- easy to install;
- can be floor-mounted, wall-mounted, three-phase and single-phase.
Electrode boiler
An electrode boiler is the most economical electric boiler for heating a private home, having a small size. Compared to heating element boilers, savings reach 40%. They are characterized by the absence of scale and rapid heating of water.
New heating element
The heating element heats the water in the circuit using tubular heating elements. Its main function is to generate heat. The heating circuit is practically no different from the circuits used for gas or solid fuel boilers. In this case, the correct location of the heating radiators in a private house relative to the windows is necessary. If there are several windows, then radiators are installed under each window.
There are rules and regulations for installing heating batteries:
- the distance between the wall and the battery is at least 2 cm;
- between the window sill and the radiator 8 - 10 cm;
- between the floor and the bottom of the battery 10 - 12 cm;
- In all cases, it is desirable to install a heat shield.
Induction boiler
An induction boiler can be represented as an electromagnetic inductor, or transformer, which has a primary and secondary winding. The secondary winding is the housing, in which the so-called Foucault eddy currents are induced. Since the boiler body is a short-circuited loop, significant currents are induced in it, heating the boiler body, and therefore the coolant. Induction boilers are more economical than heating element boilers and are quite suitable as alternative types of heating for a private home or cottage.
Features of solid fuel boilers
Gas supply and centralized electricity supply are still not available everywhere in Russia. Gas is cheap only in capital cities, and even there it is becoming more expensive. Electricity is expensive everywhere.
Communication networks leave much to be desired: power outages and sudden voltage changes are commonplace outside the city. It is not always possible to connect to the main gas, and purchasing liquefied gas in cylinders is an energy-intensive business.
Heating with a solid fuel boiler has several advantages:
- you can choose the type of fuel that is cheapest in your area - firewood, peat, coal, wood waste, etc.;
- solid fuel boilers are the cheapest in the category. Long-burning models are more expensive, but their thermal efficiency is higher;
- a large assortment. Automation and auxiliary strapping elements can be purchased separately if necessary;
- Unlike gas units, the installation of a solid fuel boiler does not require permission from the local administration.
Now about the cons:
- fire hazard. But both gas and diesel models have this drawback. And in case of problems with wiring - even electrical ones;
- the need to monitor the amount of wood/coal in the firebox. A solid fuel boiler cannot be simply “turned on and forgotten”. It is less often necessary to add fuel to pellet and long-burning boilers, but in this regard they are not very autonomous;
- The combustion process of solid fuel is difficult to control (for other units it is enough to turn off the gas valve or turn off the electricity). The inertia of solid fuel boilers is high, and so is the entire system.
Solid fuel boiler design
https://youtube.com/watch?v=MY-xodMMyDI
Heating scheme
The circulation of water through pipes and radiators occurs due to the upward movement of the heated liquid, as well as from the operation of the circulation pump.
Additional items:
- Shut-off valves (the more taps there are, the easier it will be to maintain and repair heating elements).
- Air vents (oxygen, which gradually accumulates in pipes, is destructive to metals; it must be vented periodically).
- Thermostat (needed to keep the temperature in the rooms at the same level, saves fuel).
Installation of a floor-standing gas boiler in an existing heating system
An expansion tank is a mandatory attribute of any system. It can be closed or open. The closed one is paired with a circulation pump. An open tank is placed as high as possible, for example, in the attic of a house.
Pipe routing
- Single-pipe.
- Two-pipe.
Single-pipe. A pipe extends from the boiler to which radiators are connected in series. The further away the radiator is from the heater, the colder it is. This scheme is the simplest and requires few materials. But it is only suitable for small houses where the coolant will not have time to cool down. In addition, the system cannot be adjusted.
Two-pipe system - all radiators are connected to the supply pipe in parallel. Each one receives the first, hot water. After passing through the battery, the water flows into the return pipe and returns to the boiler. The system is a little more expensive, but all rooms are heated evenly. Suitable for multi-room houses.
Single-circuit or double-circuit boiler - it does not matter when choosing the type of wiring.
Connecting radiators
There are three options for connecting heating radiators:
- Unilateral.
- Lower.
- Diagonal.
They differ not only in location, but also in efficiency.
Let's look at each of these options in more detail:
- One-sided option. The supply and return pipes are located on one side of the radiator. The method saves materials, but is not very effective if the radiator consists of a large number of sections (the coolant simply cools down while it reaches the last section).
- Bottom option. Outdated and ineffective (radiators give off 15–30% less heat than they could). The liquid flows where it is easier - along the bottom of the heating devices, and the upper part remains unused.
- Diagonal option. The most correct. The water enters at the top of one side of the radiator, and, having passed through the entire battery, comes out at the bottom on the other side. This installation is required for long heating appliances. With such a scheme, you can expect that the radiators will give out the passport indicators.
All radiators are universal and have 4 possible connection points. This means that the connection method depends only on your desire.
Chimney
One of the prerequisites: the boiler outlet pipe must exactly match the diameter of the chimney. Other subtleties:
- The chimney from the boiler to the head should not have more than three bends.
- There should be no connections where the pipe passes through the wall or roof.
- The pipe must be insulated in places where it passes through an unheated room.
To check whether the length of the chimney you are planning will be sufficient, perform a simple calculation. Find the volume of the chimney and the volume of the boiler. The boiler must completely “fit” into the chimney. The area S of a round pipe is determined by the formula πR2. To find out the volume, multiply the resulting number by the total length of the pipe.
Conclusion. Having studied all the intricacies and carefully thought through everything, you can proceed to installation work. Remember that connecting the boiler to the gas mains should only be carried out by gas service specialists. They are also conducting a test run of the system.
Selecting the wiring type
Gas heating allows any type of wiring. They choose a scheme based on the area of the house, number of storeys, convenience and possibilities, including financial ones.
The wiring, along with the area, determines the power of the boiler and the need for one or another electrical equipment.
Wiring type
There are 3 options: single-pipe, double-pipe and beam.
- The single-pipe scheme is the simplest. One pipe is sequentially supplied to each radiator along its “path” and returns to the boiler. Here the coolant heats up and the cycle repeats. Suitable for small buildings and technical structures.
- Two-pipe - one pipe goes from battery to battery and carries hot water. The second pipe removes the cooled coolant from the radiators in the opposite direction. This scheme ensures more uniform heating of the entire circuit and can serve a larger area. The use of taps makes adjustments easier. The system is used for heating residential buildings and cottages.
- Radial - here the heated coolant first enters the collector, and from here hot water is supplied to each radiator through an individual pipe. This scheme allows not only to uniformly heat a very large area, but also to heat individual rooms in a random order, heating them to different temperatures. Installation is very expensive, as it requires laying a large number of pipes and very precise settings.
A one- and two-pipe system can be natural, a radial system can only be forced.
Water circulation
In simple systems, it is possible to ensure that water flows by gravity from one battery to another. In this case, the pipes are laid at a certain angle, and an expansion tank is placed at the top point of the system. The latter compensates for the difference in pressure. The scheme requires precise calculations. Not suitable for “warm floors”.
Forced – the movement of the coolant is provided by an electric pump. This is more expensive, but it solves all the problems with a large number of pipes and a complex pipeline configuration.
Vertical and horizontal
This type of wiring is related to the location of the supply pipes.
Horizontal – supply and discharge pipes are located horizontally. In one-story buildings, this option is used, since it is very simple and allows you to do without a pump.
Vertical - heating radiators are divided into some kind of sections, for example, along one wall. A vertical pipe is connected to the section and hot water is supplied through it. It is also discharged through a vertical drain. This scheme is carried out in multi-apartment and multi-storey buildings.
Vertical wiring can only be forced. Here you definitely need a circulation pump to pump water.
Types of single-circuit heating
There are several classifications of single-circuit heating systems depending on various parameters. Initially, the main types of systems should be identified:
- open;
- closed.
Since water has a fairly high coefficient of expansion when heated (0.3% due to an increase in temperature every 10 degrees), it is necessary to compensate for the increasing volume of coolant so that the pipes are not damaged and an accident is avoided. Compensation is usually carried out through an expansion tank into which a polymer membrane is inserted. This membrane is elastic and, under the influence of increasing water volume, fills the tank completely.
The use of such membrane tanks is typical for closed, fully automated systems. Boilers for such systems operate on gas, pellets, and fuel oil. They are safe because when the pressure increases, the system automatically turns off.
Previously, predominantly single-circuit open-type systems were used, which were also called natural circulation heating systems. In such devices, a pipe is installed through which excess pressure and vapor are released into the atmosphere if intensive operation of the boiler causes a significant expansion of the coolant.
Heating installations for a private cottage are also divided into systems with:
- natural circulation;
- forced circulation.
Forced circulation is carried out by including special pumps and other engineering devices for pumping water into the system. This option is considered more modern, does not require the use of pipes, fittings of a larger diameter, and therefore additional labor costs, and is more suitable for multi-storey cottages where it is necessary to supply coolant to the upper floors. The use of pumps is difficult if there are problems with a constant, powerful power supply.
Spider system
The so-called “Spider” system refers to single-circuit natural circulation installations. Today, this principle of constructing a connection between the boiler and the lines leading to the radiator is considered outdated and is used mainly in settlements remote from regional centers, where problems with energy supply may arise. In appearance, the system really resembles a spider (the boiler is installed in the attic, with lines running from it), which is why it received this name among the common people. The installation is carried out with your own hands.
Leningradka system
The most reliable systems, which is also a variant of natural circulation, include Leningradka. "Leningradka" is the optimal price-quality ratio, taking into account the ease of project implementation and efficiency. The classic “Leningradka” is a complex of series-connected radiators along the perimeter of the premises with a single pipeline; the heating source is a boiler. This option is often installed in small two-story cottages using a circulation pump.
Approximate calculation of gas consumption
To provide 1 kW of thermal energy, 0.1 m3 of gas per hour is required. In order to heat a room of 200 m2, you will need a boiler with a capacity of 20 kW. The full power mode of such a boiler consumes: 20 × 0.1 = 2 m3/hour.
So, we divide the heating season into two conditional stages: 3 very cold months and 3 cold ones. For ease of calculation, let’s round the number of days of each period to 100. So for 100 days the boiler will operate at full capacity and the same at half its capacity or even a quarter. The average daily gas consumption for the first period will be: 20×0.1×24=48 m3, and in the second period 24 m3
Often the actual consumption is less than what is stated, since in recent years the winters are not as severe as before and do not require the full power of the boiler. The most profitable heating option is to connect to a natural gas pipeline. But remember that we use gas for both cooking and heating water, so the resulting figure must be adjusted depending on the case and the needs of the residents.
Selection and types of gas boilers
You should know that boilers have several classifications. Each type has its own right to exist and will provide good gas heating for a private home.
Single-circuit and double-circuit boilers
Single-circuit boilers are intended exclusively for heating and do not perform any other functions. Purchased if you do not need to heat hot water directly from a gas boiler.
Such boilers work directly on the heating system. They can also be used to heat an indirect heating boiler, which in turn is used to provide the house with hot water
Double-circuit gas boilers are ideal for both heating rooms and heating water. It should be noted that double-circuit boilers are not always effective for heating water. Usually only enough for one active point. If, for example, you go to the shower and someone decides to wash the dishes, then you will already take a cold shower. You should take this into account when purchasing.
Wall and floor boilers
Wall-mounted boilers are safe and automated, but often operate only on one type of gas - natural. (There are models in which you can change the burner and they will also work on liquefied gas). They can be installed in kitchens, since it is smaller in size compared to floor-mounted ones.
The power of wall-mounted boilers is often limited to 35-40 kW. Therefore, if you want to install gas heating in a large house, you will have to either install two wall-mounted boilers in cascade mode, or install a floor-standing boiler.
Floor-standing boilers are capable of heating large rooms, as they have greater power. They are universal in terms of fuel consumption: natural, liquefied, and main gas are suitable. They can be energy-dependent and independent. Often a cast iron heat exchanger is used. Due to their design, they have an efficiency lower than that of a wall-mounted one, but at the same time a longer service life.
Materials and tools
To build a gas boiler, prepare the following materials and tools:
- electric drill;
- pliers;
- level;
- corner;
- roulette;
- metal pipe;
- steel sheet;
- gas pipe;
- doors for creating a firebox;
- red brick;
- fittings;
- clay;
- galvanized sheet;
- welding tool;
- thermostat;
- automation;
- deflector.
If everything is clear with most of the above, then choosing the right automation, deflector and thermostat is not the easiest task. What to look for when choosing them:
Thermostats can be wired or wireless. The former are slightly cheaper than the latter. Choose programmable models; they make it easier to control and regulate the boiler temperature. Structurally, the thermostat consists of two devices. One is placed in the room, the other on the facade of the boiler. When the room temperature drops, the thermostat starts the heater
Pay attention to domestic device models. They are in no way inferior to expensive foreign analogues; The concept of “automation for gas boilers” includes: flame control module, overheating protection, draft controller, blast valve
These devices are sold separately. For normal operation of the heater, all of the listed devices are needed. Do not choose the cheapest or too expensive models. Stop at the average price; The deflector provides good exhaust. It is installed on top of the chimney pipe. For a homemade gas boiler, a model in the form of a cone-shaped stainless steel umbrella is suitable.
Convection and condensation gas boilers
Gas convection boilers are standard type devices that use only fuel combustion energy. Such units have a simple design and relatively inexpensive cost. The main problem of a convection device is the formation of condensate consisting of water and acids on the heat exchanger. The way to combat dew is to maintain a high temperature in the heat exchanger, and for this, the temperature of the coolant in the return must be at least 60 degrees. For heating devices with boilers of this type, it is allowed to use wall-mounted radiators, registers and convectors. The heated floor system and in-floor appliances cannot be combined with a convection unit, since they will not warm your feet, but burn them.
Condensing units do not always fully utilize their energy, which is produced during the combustion process. They convert the energy of condensation of water vapor into heat
For a condensing boiler, it is important that the heat exchanger has a low temperature, as well as the return. Typically, the gas heat supply scheme in a private house with a heating unit of this type is as follows: radiators are placed under the windows and a heated floor system is installed, for which the return of the heating radiators is used, where the coolant gives off the last heat.
When heating a private house using gas equipment, the following boilers are used:
- with natural circulation
- they take air from the room into an open burner and remove combustion products, directing them to general ventilation. To install them, a separate room with an area of at least 4 “squares” with a wide door and window is required; - with forced circulation
. In this case, in order to maintain combustion, air is taken from the street, and combustion products are also discharged there through a separate air duct. The boiler can be installed even in a residential area.
Practical recommendations
Gas heating installation schemes must be thought out to the smallest detail, so projects must be carried out by professionals.
One example of drawing up a professional heating system plan
When choosing equipment for gas heating, remember that the main indicator is the area of the heated room. The volume of equipment, the number of radiators, the footage of pipes, fittings, valves and valves, and plugs depend on it.
When choosing a method for laying heating pipes and installing them, remember that the cold and hot distribution lines must be laid with a slight slope directly towards the hot water flow.
Experts recommend installing taps on each battery. Thanks to this, it will be possible to control the supply of hot water to a separate room of a private house. If you are using an expansion tank of 20 to 30 liters, then it should be installed at a height of 3 meters above the heating boiler.
Alternative methods of heating a private house
Gas is not the only heat source that can heat your home. There are several other options for keeping the room warm. But are they so beneficial compared to the gas system?
Methods of alternative heating of a private house:
- Electricity. The most common and accessible source of energy, however, it is almost the most expensive. It may simply not be enough to heat a private home, since not every electrical network will be able to transfer the amount of energy required for heating. Problems cannot be ruled out in winter. Not the most economical and practical option.
- Diesel. Diesel fuel has a high price. It tolerates a very unpleasant aroma, which cannot be removed by anything, either at home or on the street. And if you take diesel fuel of insufficiently high quality, the heating system may break down. Not the best option.
- Solid fuels. Coal and wood. They must be supplied to the heating system two to four times a day. Every day it is necessary to remove ash from the heating system. Naturally, heating a house will require a considerable amount of fuel of this kind per year. This requires large amounts of money. You should have a separate warehouse for them; in addition, they are dangerous, as they can emit carbon monoxide. In this regard, gas installations are more economical and safer.
- Pellets. These are special granules that are made from peat and wood waste. Its disadvantages are similar to the negative sides of coal and firewood: you need a room to store a large number of pellets, they do not smell very good and they often need to be loaded into the heating system. The difference is that they are cheaper than all the types of fuel listed above, except gas. And they need to be loaded less often than firewood or coal: no more than once a week. Not a bad option.
Obviously, gas heating wins in many respects: efficiency, ease of operation, minimal heat loss, low cost of the fuel itself. Therefore, if you decide to install a good heating system, then opt for a system with gas heating of the coolant.
No. 2. Heating with main and bottled gas
Gas heating can be realized through:
- main gas pipeline;
- liquefied gas in cylinders and gas holders.
If a dacha or country house is located close to a gas pipeline, then you don’t have to think long about how to organize heating - the choice is obvious. The main gas pipeline allows us to talk about complete autonomy in providing heat, makes it possible to equip a system of heated floors, but it can take a lot of time to coordinate all the necessary documentation.
Even if there is no gas pipeline in the area, it is possible to organize an inexpensive gas heating system, and for this they use liquefied gas cylinders . The costs of setting up such a system pay off within several years. Bottled gas is not capable of providing a completely autonomous heating system, but the problem can be solved by connecting several cylinders. The security of the existing system will need to be checked every one to two weeks.
Gas tanks - large-volume containers located underground near the house - have shown themselves to be excellent From time to time, their gas reserves are replenished with special gas carriers. Despite the fact that the use of liquefied gas is not as convenient as main gas, for areas located far from gas pipelines it is a real salvation. The heating system works the same whether from the main gas or from liquefied gas. Gas tanks are installed on a concrete pad; if necessary, two tanks can be connected into one system if gas needs increase later. Gas tanks are made of steel, and when choosing, pay attention to the wall thickness (the larger the better) and volume (depending on needs).
Heating system installation
Installation of the heating system of a country house is carried out in several stages:
- project development, obtaining permits from the relevant authorities;
- purchase of materials, equipment and preparation of tools;
- insertion into a gas pipeline that runs along the street and through which gas is supplied to residential buildings;
- preparing a place for a gas boiler, laying out pipes;
Installation of gas equipment
boiler installation; filling the system with coolant; diagnostics.
The main criterion by which the amount of materials is calculated and the model of heating equipment is selected is the area of the house. The larger it is, the more powerful the device will be needed. For a small house, a small-sized boiler is suitable, which can be installed in the bathroom or kitchen. For a cottage or two-story mansion, it is better to choose a large, powerful device.
A heating system in a private home installed in accordance with all the rules will function for a long period. Before starting installation work, you should familiarize yourself with the heating diagram and the rules for installing heating equipment.
What to do before installing the boiler
You will have to take into account that without a gas service, it is prohibited by law to connect a gas boiler and operate a heating or water heating system.
Necessary steps before installation:
- All documents and constituent papers are collected to approve the planned project. This is needed for the gas service. She will sign the permit only after a complete review of the project.
- Additionally, you will need an explanation of who will do the installation. The performer must have permission. For their part, gas workers will help supply gas to the required place in the house.
- Gas equipment, consumables and a full list of components are purchased. You can save a little, but you can’t do without the basic elements of the system.
- A connection is made into a centralized gas pipeline to connect to a fuel source.
- You can install a boiler and connect to a pipe system with radiators.
Therefore, it will not be possible to do without the help of the gas service. But you can do some of the work yourself.
Air heating
These types of heating of various premises are considered one of the oldest. For the first time such a system was used before our era. Today, such a heating system has become widespread - both in public buildings and industrial premises.
Air heating of a private house
Heated air is also popular for heating buildings. When recirculated, such air can be supplied to a room, where the process of mixing with indoor air occurs and, thus, the air is cooled to room temperature and heated again.
In air heating systems, the air is heated by air heaters. The primary heater for such components is hot steam or water. In order to warm the air in the room, you can use other heating devices or any heat sources.
Local air heating
When asked what kind of heating there is, local heating is often equated only to industrial premises. Local heating devices are used for rooms that are used only during certain periods, in rooms of an auxiliary nature, in rooms that communicate with external air flows.
The main devices of the local heating system are a fan and a heating device. For air heating, devices and devices such as air heating devices, heat fans or heat guns can be used. Such devices operate on the principle of air recirculation.
Heat gun
Central air heating
Central air heating is done in rooms of any type, if the building has a central ventilation system. These types of heating systems can be organized according to three different schemes: with direct-flow recirculation, with partial or complete recirculation. Full air recirculation can be used mainly during non-working hours for standby types of heating, or to heat the room before the start of the working day.
Central air heating
However, heating according to such a scheme can take place if it does not contradict any fire safety rules or basic hygiene requirements. For such a heating scheme, a supply ventilation system should be used, but the air will be taken not from the street, but from those rooms that are heated. The central air heating system uses such structural types of heating devices as: radiators, fans, filters, air ducts and other devices.
Air curtains
Cold air can come in in large quantities from the street if the entrance doors in the house are opened too often. If you do not do anything to limit the amount of cold air that enters the room, or do not heat it, then it can negatively affect the temperature regime, which should correspond to the norm. To prevent this problem, you can create an air curtain in the open doorway.
Limiting the amount of cold air entering from outside the building takes place thanks to design changes in the entrance to the room.
Electric air curtains
Compact air-thermal curtains have become increasingly popular lately. The most effective curtains are considered to be “shielding” type curtains. Such curtains create a jet air barrier that will protect the open doorway from the penetration of cold air currents. As a comparison of heating types shows, such a curtain can reduce heat loss by almost half.
No. 4. What boiler power is needed?
One of the main characteristics of a boiler is its power. According to this parameter, boilers are divided into devices of low (up to 65 kW), medium (up to 1700 kW) and high power (up to 15000 kW). Low-power boilers are usually used for dachas and country houses; the rest have found application in industry.
The choice of boiler power depends on a lot of parameters:
- room size;
- climatic conditions;
- quality of home insulation;
- the need to heat water for hot water supply.
According to the simplest calculation , for every 10 m2 of heated space you will need 1 kW of boiler power. This formula gives a general idea of the requirements for heating equipment, but to obtain more accurate data it is worth considering other parameters. For houses built according to a standard design with a ceiling height of no more than 3 m, the calculation is simple. For every 10 m2 of area you will need the following boiler power:
- 0.7-0.9 kW for houses in the southern regions;
- 1-1.2 kW for the middle band;
- 1.2-1.5 kW for Moscow and Moscow region;
- 1.5-2 kW for northern regions.
The results of these calculations are valid if the boiler is used only for heating. In the case of double-circuit boilers , which also operate for hot water supply, it is worth adding another 25% of power to the result obtained. If the house uses a forced ventilation system, it is better to add 5% of the power to the obtained value.
If the house is built according to an individual project, then the calculation becomes somewhat more complicated. For this, special calculators are used, but you can approximately calculate the required power using the following scheme:
- We calculate the heat loss of the building using the formula V*Рt*k/860, where V is the volume of the room, Pt is the maximum difference between the external and internal temperatures, and k is the dissipation coefficient, depending on the thermal insulation;
- for well-insulated houses with reliable double-glazed windows k = 0.6-0.9, for buildings with an average level of thermal insulation - 1-1.9, with a low level - 2-2.9, without thermal insulation - 3-4;
- for example, there is a house with an area of 120 m2 and a ceiling height of 3.5 m, it is well insulated, but not enough (k=1), the temperature in the house must be maintained at 210C, and outside it can drop to -200C. Heat loss will be (120*3.5)*41*1 = 17.22 kW;
- The power reserve is 15-20%, so for our house we will need a boiler with a capacity of about 22 kW.
Of course, you don’t have to bother yourself with calculations and take a boiler with a power many times higher than required, because automatic systems can regulate gas flow. But not everything is as simple as it might seem. Firstly, a much more powerful boiler than necessary will cost more, its efficiency will decrease, malfunctions may occur in the operation of the equipment, components will quickly wear out, so it is better to take a boiler that at least approximately meets the requirements of a particular country house or cottage.
If the source of gas is a gas cylinder, then the calculations and setup of the system are approached with special responsibility. Practice suggests that heating and hot water supply to an insulated house with an area of about 130 m2 will require 3-4 cylinders per week, and this is provided that outside temperatures drop to -230C, and in the house they are maintained at +230C.
Condensing boilers help save money and increase productivity , which, in addition to the heat of combustion of fuel, also use the heat of combustion products and water vapor. In conventional boilers, this heat is released outside. The efficiency of such boilers often exceeds 100%. If the performance of one boiler is not enough, then you can connect several boilers “in cascade”.
To save gas, you should also insulate the room, equip the heating system with automation and gas leak detection sensors.