Among thermal insulation materials, basalt mineral wool occupies a leading place. It is used to insulate facades, roofs, floors and utility networks of residential and industrial premises, soundproof walls in residential premises and recording studios, and provide fire protection for wooden structures from highly heated building elements, for example, a chimney.
Let's try to figure out why in industrial and residential construction they are increasingly using cotton wool based on basalt fibers for thermal insulation and whether it is worth buying this type of insulation when building a private house or renovating an apartment.
Description of material
For many visitors to the StroyGuru website it will seem surprising, but the history of using basalt wool for home insulation goes back several centuries. At the same time, there are no special mysteries: during the eruption of one of the volcanoes on the Hawaiian Islands, lava erupted in the form of a fountain, and a strong air flow turned part of the molten basalt into long, strong threads.
Local residents found them and began using them to insulate their homes. Europeans learned about this and tried to repeat the natural process artificially. In the end, the search was crowned with success, as a result of which basalt wool insulation appeared on the building materials market. Over time, they began to melt one of the types of granite - gabbro.
Cotton wool is obtained from stone using a simple technology consisting of several stages:
- basalt or gabbro is crushed;
- the crushed mixture is loaded into the oven and heated to 1500oC;
- the molten mass is fed onto rotating drums, which are blown with a strong air flow, resulting in the formation of stone threads;
- plasticizers are fed into the resulting fibers (formaldehyde resin, and from leading manufacturers - arbolo-urea resin);
- the fibers are cooled to a temperature of +200oC to start the polymerization process on the surface of the fibers of the thinnest layer of resin;
- on a special conveyor belt, the fibers are compressed (pressed) to a certain density;
- continuous tape is cut into sheets or tapes for rolls;
- the resulting insulation, if necessary, is reinforced or foil-coated.
A product produced using this technology has its advantages and disadvantages, which we will consider.
Advantages and disadvantages
Stone wool for insulation stands out among its competitors with its strengths:
- durability - manufacturers indicate a service life of more than 50 years. In practice, there have been cases of material service life of 70-75 years without significant loss of heat-saving properties;
- resistance to heat - destruction of fibers begins at +1100oC and above;
- almost zero hygroscopicity - within a day, cotton wool completely immersed in water absorbs only 0.095% of moisture;
- very high thermal insulation properties;
- good soundproofing properties - absorbs up to 57 dB of airborne noise (cotton wool is powerless against structural and impact noise);
- excellent resistance to fungi and mold - microorganisms do not multiply on basalt fibers;
- versatility - used for insulating walls outside and inside the building, floors, ceilings, roofs, metal entrance doors, etc.;
- convenient transportation - easy to transport and carry;
- simple installation - installation can be done with your own hands;
- resistance to alkalis, acids and salt solutions;
- good elasticity - shapes and sizes are maintained throughout the service life;
- environmentally friendly - all components do not belong to the group of allergens and do not emit harmful substances when heated.
Attention: in insulation you can find two types of resins: arbolo-urea and formaldehyde. The first is absolutely harmless to humans, the second emits so few harmful substances when heated that the human body practically does not notice them.
In addition, two more features of stone wool should be noted:
- The ability of the material to resist rodents - they do not make passages and nests.
- When performing thermal insulation of walls from the outside and inside, decorative plaster can be applied directly over basalt wool.
Among the disadvantages, consumers note:
- high price;
- the presence of seams through which heat is lost;
- dust - is formed during cutting and laying, which requires the presence of a respirator (a new product has appeared on sale - dust-free stone insulation).
Comparison
All materials have their own pros and cons, so when comparing it is more important to consider what problems need to be solved. Basalt wool has some similarities with ecowool: thermal insulation properties depend on density, the materials are resistant to rotting and burning. Ecowool does not have a strong structure, so independent installation is difficult.
When compared with mineral wool, it should be noted the superiority of the basalt-based material in terms of thermal insulation parameters.
Slag wool, like basalt, is made in the form of slabs. High hygroscopicity does not allow the use of slag wool in residential construction. These are just some of the similar and distinctive parameters of the materials; others are presented here.
Characteristics and properties
Each type of insulation is characterized by a large number of indicators. However, the following characteristics of basalt wool are of practical importance:
- linear dimensions of products;
- fiber size;
- insulating properties;
- specific gravity (density);
- hygroscopicity;
- vapor permeability;
- strength;
- fire-resistant properties;
- environmental cleanliness.
Linear dimensions of insulation
European and Russian standards do not impose any specific requirements for the sizes of rolls and sheets. The width of the slabs can be 50-60 cm, the rolls - 100 cm. The length: slabs - 100-120 cm, rolls - 200-600 cm. The thickness ranges from 2 to 24 cm. The specific dimensions depend on the type and geometry of the insulated surface.
Fiber size
Several important parameters of insulation depend on the size of the fiber: thermal conductivity coefficient, specific gravity, elasticity and strength. On the packaging these sizes are marked: BTV (fine-fiber basalt) and BSTV (basalt with ultra-fine fiber).
For BTV, the fiber diameter is 5-15 microns, the length is 15-50 mm. The designation BSTV includes fibers with a diameter of 1 to 3 microns and a length of 50 to 70 mm.
In addition to the fiber parameters given above, thick-fiber materials are used in industrial construction, where the diameter of the threads is 25-150 microns and coarse-fiber materials with a thickness of 150-500 microns.
Thermal insulation properties
The ability of a material to retain heat is characterized by its thermal conductivity coefficient: the lower it is, the better the thermal insulation characteristics. For wool made from basalt fibers, this indicator ranges from 0.035 to 0.042 W/(m×°K). To understand how good the insulation is, let's give a simple example. Thus, a basalt mat only 5 cm thick retains heat in the same way as:
- wood 13-15 cm thick;
- brickwork made of red brick 70-80 cm thick;
- sand-lime brick and cellular concrete 1 m thick.
When compared with insulation materials, basalt wool is inferior only to polyurethane foam and has similar performance to cork, foam rubber and polystyrene foam.
The variability of the indicator is explained by the influence of the fiber diameter and the density of insulating mats on the thermal insulation characteristics. After all, it is not the fibers themselves that retain heat, but the air chambers located in the fibrous structure of the material. As a result, the more air inside the insulation, the lower the thermal conductivity of stone wool.
However, do not rush to buy loose insulation labeled BSTV. It has one problem: low strength, due to which the heat insulator cakes on horizontal planes and settles on vertical surfaces. In both cases, the thermal insulation properties of basalt wool are lost to a significant extent.
Insulation weight
The weight of the insulation depends on its density, which is associated with the weight load on the insulated structures. However, this is a one-sided approach to the problem. The strength (rigidity) of the mats also depends on the indicator, which in many cases is the determining criterion when choosing a thermal insulation material, and its thermal conductivity.
The density of basalt slabs used for insulation ranges from 30 to 300 kg/m3, which allows you to choose your own type of insulation for a specific situation. Among the main brands that take into account the density of insulation:
- PT-250, PT-220, PT-300 (hard mats) with a specific gravity of 220-300 kg/m3;
- PPZh-160, PPZh-180, PPZh-200 (slabs with increased rigidity) - the density indicator reaches 160-210 kg/m3;
- PM-50, PM-40 - the most popular sheets with a density of 30-55 kg/m3;
- PZh-120, PZh-100, PZh-140 - rigid insulation with a specific gravity from 100 to 150 kg/m3;
- PP-80, PP-70, PP-60 - semi-rigid mats weighing 60-90 kg/m3.
Hygroscopicity
The problem with insulation materials is always their hygroscopicity - wet insulation materials deteriorate their thermal insulation properties. Basalt fibers have virtually zero moisture absorption.
So, when conducting an experiment to determine the wettability of a basalt mat, it was immersed in water for 24 hours. As a result, the following data was obtained:
- only 0.095% of water was absorbed;
- the inside of the cut mat was absolutely dry.
If you are constantly in a damp room, moisture absorption does not exceed 1-2%, which allows you to use cotton wool for thermal insulation of baths, saunas and foundations.
Vapor permeability
The presence or absence of vapor permeability of any finishing material determines whether the walls will “breathe” or not. To find out, let's do a little experiment. Place a container of water on the stove and bring it to a boil, then cover the boiling water with a piece of basalt-based insulation. After 1-2 minutes we observe the effect: steam begins to pass freely through the insulation. The result of the experiment: the vapor permeability of the insulation is 0.25-0.35 mg/m2 x h x Pa.
Strength
The strength of the material is characterized by a number of indicators:
- compressive strength - 8-60 kPa;
- for layer separation - 80 kPa;
- bending - 0.15 MPa.
To understand what this means in practice, here are two examples.
1. A car drove onto the mat, creating a pressure of 100 kPa. There were no visible traces left - the fibers completely restored their previous shape after removing the load.
2.Plates were glued to the top and bottom of the slab and tried to tear the layers of insulation. As can be seen in the photo, the efforts will be crowned with success only after applying forces of more than 80 kPa.
Fireproof properties
Basalt wool refers to fire-resistant materials (not to be confused with fire resistance - these are different terms). The experiment shows that when the insulation is heated with autogenous heat to +700-800oC, nothing happens to the fiber: it does not ignite or collapse.
If you touch the heated area with your bare palm from the back, you will not feel any sensations of the heated surface - only 15-25oC, which corresponds to natural heating from the environment. This experience confirms not only the fire resistance of the material, but also the excellent thermal insulation properties of basalt wool.
Kinds
To perform certain work, to insulate specific structural elements of buildings, it is necessary to use basalt wool with one or another set of properties. Basalt-based products are divided into several types according to individual characteristics.
Foil, with foil
Foil-coated basalt products are heat-resistant, waterproof materials, covered on one or both sides with thin aluminum foil. The products have heat-reflecting characteristics; slabs (or other forms of release) can be installed without vapor barrier. Foil materials are used to insulate walls, ceilings and partitions in baths and saunas. Features of stone wool with foil are:
- moisture-repellent properties , foil does not allow moisture and steam to penetrate inside the insulation, which increases its service life;
- increased efficiency , foil wool reflects thermal energy, preventing it from escaping through the walls, as a result, heat is retained in the room longer than when using standard materials;
- ease of installation , materials are installed with the foil side inward, joints are taped with aluminum tape.
Foil wool is also used for thermal insulation of household water supply and ventilation systems and pipelines. In industry, insulation is used to insulate technological equipment, elements of production lines, containers in which it is necessary to maintain certain temperatures, and refrigeration chambers. The products are actively used in frame construction.
In rolls, cylinders, mats and so on
The classification of basalt insulation is carried out in accordance with the form of release. Materials are produced in plates, rolls, cylinders, granules. The slabs, in turn, are soft, semi-rigid and hard. Rigidity determines the scope of application of products; the higher the indicator, the greater the mechanical loads the material can withstand.
Soft, with maximum insulating properties, not intended for significant impact, sold in mats and rolls. Semi-rigid ones are most often produced in slabs and cylinders, they are excellent for performing construction work for private and industrial purposes, suitable for insulating ventilated facades, protecting air ducts from fire in the event of a fire. Rigid ones can withstand heavy loads without deforming or losing their properties; they are produced in slabs and are intended for outdoor work and floor insulation.
Basalt insulation ISOBOX ExtraLight-31 in slabs. Stroylandia Photos
Rolls and slabs are in demand among private buyers. For large facilities, it is more practical to use granulated wool, which is blown into the walls with pneumatic devices, like ecowool. Cylindrical ones are used for working with pipelines and gas pipelines.
Dimensions
The dimensions of basalt products are indicated on the packaging - length x width x thickness. The most in demand are slabs whose standard dimensions are 1200x600 mm . Length indicators for slabs are 1000-1200 mm, width - 600, thickness - 20-240, materials with a thickness of 50 and 100 mm are in particular demand. Rolled cotton wool has the following average dimensions: length - 3000-10000 mm, width - 600-1200, thickness - 50-100. In addition to products of standard sizes, customers have the opportunity to purchase thermal insulation materials of non-standard dimensions.
Thickness: 50, 100 mm. and not only
The thickness of basalt insulation is an important parameter that directly influences the choice, since for solving various problems there are certain recommended values for the thickness of the thermal insulation layer. For example, to insulate sloping roofs, the value must be at least 150 mm, for external walls - over 100. To calculate the optimal value, you need to know two parameters:
- R – thermal resistance, measured in sq.m. per K/W;
- λB – thermal conductivity, which is indicated on the packaging, the average value is 0.45 W/sq.m x K.
Basalt insulation ROCKLIGHT-30, 50 mm thick. Stroylandia Photos
The indicators must be multiplied (R x λB), as a result it is possible to obtain optimal indicators for the thickness of the insulating layer for various structural elements, for example, for the roof it is 220 mm, for walls - 150 mm.
Is basalt wool harmful?
Many experts believe that basalt wool is harmful to health. They explain their point of view by the presence of formaldehyde resin, which releases harmful substances when heated. However, it is difficult to agree with this for two reasons.
- Leading manufacturers of stone wool have switched to arbolo-urea resins, which are harmless to human health.
- Indeed, when formaldehyde resin is heated, hazardous substances are released into the surrounding space. But their size is so small that they do not harm the human body (the insulation contains only 3% resin, and the resin, in turn, releases about 3% of harmful substances when burned). It should not be forgotten that doctors prescribe medications containing 0.5% formaldehyde to patients, considering this dose to be safe.
Valuable advantages of ready-made basalt insulation
The modern Russian market offers a wide variety of insulating materials for home improvement, both high-quality and not so good. But if you have basalt thermal insulation from a trusted manufacturer, then you don’t have to worry about many things. It is quite easy to install and fireproof, unlike many other types of thermal insulation.
For example, stone wool fibers can withstand a melting temperature of more than 1000 degrees Celsius - this is reached after no less than 2 hours of a strong fire. At the same time, foam products not only cannot withstand such heat, but also spread the fire themselves.
Here is an interesting promotional video that clearly demonstrates all these points:
Basalt wool really has such valuable properties as fire resistance, moisture resistance and resistance to deformation:
This kind of insulation seems unrealistically ideal, wouldn’t you agree? Considering that a lot of effort is spent on it and rocks are melted, why not.
Application area
Basalt wool is used in various sectors of the national economy. It can be found in fine and coarse water purification filters, in the composition of soil for drip irrigation, pipeline transport, etc. However, the main area of application is industrial and residential construction. Here the material is used for insulation:
- flat roofs;
- attic space;
- floor bases;
- interfloor floors and ceilings;
- external and internal walls;
- foundation from inside the building;
- walls with multi-layer masonry;
- frame houses made of sandwich panels.
In addition, such material properties as fire resistance, fire resistance and the ability to absorb airborne noise are used. Therefore, on sale you can find:
- basalt wool for the chimney - protects flammable elements of the building from contact with an overheated chimney;
- soundproofing mats for recording studios;
- rigid slabs for constructing a “wet” facade, on which you can immediately plaster.
Which one is better to choose?
Basalt insulation ISOVER Frame house. photo source here
First, before purchasing insulation, you should decide on several initial data:
- which structural element is to be insulated , then choose either a material specially designed for this work, or pay attention to universal products;
- budget calculation , high-quality products from leading enterprises are sold at appropriate prices, basalt products of well-known brands should be purchased from trusted suppliers in order to minimize the likelihood of purchasing a counterfeit;
- necessary characteristics , the most important parameters when choosing are thickness, dimensions and density, the first two were discussed earlier, so some recommendations on the third parameter should be noted: insulation with a density of up to 35 kg/cub.m. It is recommended to use for heat and sound insulation of non-load-bearing pitched roofs, attics and attics, for insulation of frame walls and ceilings;
- 35-50 — for insulation of ventilated facades and external walls of low-rise buildings;
- 50-75 — for insulation of floors, concrete and wooden ceilings, in multi-layer internal partitions;
- 75-100 — for insulation of external walls;
- 100-125 — for insulation of reinforced concrete structures;
- 125-150 — increasing the sound insulation properties of floors and walls;
- over 150 - for screeded floors.
For convenience, you should decide on several lines of materials suitable for their characteristics, from which you need to choose the best option.
Manufacturers and prices
An analysis of the preferences of Russians showed that the best manufacturers of basalt slabs are:
Rockwool. The Danish company (“Rockwool”) has many factories in Russia and the CIS countries, which allows it to offer European quality products at affordable prices on the building materials market (the price does not include transportation costs, customs clearance and higher wages for foreign workers).
Basalt mats are characterized by:
- fire resistance - one of the few enterprises whose wool can withstand heating up to +1000oC (for European consumers the norm is +600oC);
- durability - not only linear dimensions are preserved, but also insulating properties;
- environmental friendliness, as confirmed by the “EcoMaterial Green” certificate;
- good noise and heat protection properties.
Price for 1 m3 is about 7,000 rubles.
Paroc. There is practically not a single construction forum dedicated to thermal insulation where Finnish products (Parok) are not discussed. The company's products:
- high heat-saving properties, allowing you to save on heating the room;
- good acoustic insulation - basalt wool is used to protect recording studios from extraneous noise;
- excellent fireproof characteristics.
But, before choosing Parok products, it’s still worth looking at how much stone wool from Finland costs. After all, the price is quite high and amounts to 9,400-10,750 rubles/m3.
IZOVOL. IZOVOL is a Russian manufacturer of insulation made from basalt fibers. Affordable products are in good demand for insulating walls, roofs and ventilated facades.
The line of brands for thermal insulation of pitched roofs and attics is especially popular. Technical and operational characteristics of the product comply with European and Russian standards:
- the insulation has a low thermal conductivity coefficient - 0.035 W/(m×°K);
- standard indicators of durability, sound insulation, etc.
The downside is a slight shedding during the work process, which greatly affects the rating. You can buy “IZOVOL” for 3,999-4,900 rubles/m3.
TechnoNIKOL. Another manufacturer of basalt insulation from Russia is. The brand's products are produced in Lithuania, Belarus, England, the Czech Republic and other countries. Cotton wool is distinguished by good quality and affordable price. For the first time in the world, the company's enterprises began to produce dust-free wool (Rocklight brand), which simplifies the insulation process.
In terms of production volume, the holding is among the TOP 5 largest producers of mineral wool. Prices vary in the range of 2,350-3,780 rubles/m3.
Isover. Isover, a French multinational company producing basalt insulation, has built its enterprises in Russia. The products have the best balance between price and quality, which allows the brand to be a sales leader in most countries of the world.
The price for 1 m3 ranges from 3,999 to 5,240 rubles.
What is it, composition
Basalt (alternative names: stone and mineral ) wool is pressed into different shapes, randomly intertwined fibers of mineral origin, hence one of the names. Externally, stone wool is a mass of needle-shaped fibers , the diameter of which is measured in microns, and the length is about 5 cm, the color is beige or gray . Rocks of the gabbro-basalt group and metamorphic rocks similar in chemical composition are used as raw materials for the production of materials:
- silicon dioxide (SiO2) - 45-65%;
- aluminum oxide (Al2O3) - 10-20%;
- calcium oxide (CaO) - 5-15%;
- magnesium oxide (MgO) - 5-10%;
- iron oxide (Fe2O3 + FeO) - 5-15%;
- sodium oxide + potassium oxide (Na2O + K2O) - 1-3%.
TeploKNAUF mineral wool for roofing. Photo Pilomaterialy.rf
There are three types of mineral fiber insulation, each of which has its own raw materials and production technology:
- glass wool produced from molten glass, as well as sand, soda, limestone, dolomite;
- slag wool made from melted blast furnace slag waste;
- basalt, produced mainly from the melt of basalt and gabbro rocks.
Basalt wool insulation technology
When working with basalt insulation, the technology of thermal insulation of various building elements has its own nuances that need to be taken into account.
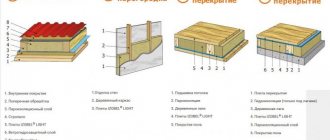
Roof insulation
When insulating the roof, it is necessary to take into account that here the probability of condensation formation is the highest. Therefore, all work must be performed in the following sequence:
- the bottom of the rafters is filled with lathing, on which the insulation will be laid;
- a vapor barrier film made of polyethylene 0.5-0.1 mm thick is overlapped over the sheathing and rafter system so that moist air from the room does not enter the insulation layer;
- joints are glued with construction tape or masking tape;
- 18-20 cm thick basalt mats are laid on the film between the rafters (ideally, the thickness of the mat should correspond to the width of the timber in the rafter system);
- A vapor barrier (sometimes they write and say - windproof) class B membrane (for a pitched roof) is attached to the insulating layer. In this case, it is necessary to lay it with the smooth side to the insulating layer, the rough side to the roof;
- the counter-lattice is stuffed;
- boards are nailed to the rafters to secure the roofing material and create a ventilation gap between the roof and the insulation;
- roofing material is attached.
If there is an attic under the roof, then instead of lathing, OSB or plywood sheets are attached to the rafters below.
Floor insulation
Having high compressive strength, rigid mats made of basalt fibers can be used for floor insulation using the “floating” screed principle. Here the work is performed in the following order:
- the base of the floor is repaired and then thoroughly removed from debris;
- waterproofing work is carried out to prevent moisture from entering the insulation from below;
- Thermal insulation mats are laid. It is advisable to seal the connecting seams with tape or masking tape;
- a reinforcing film is laid on top of the insulation;
- the screed is poured.
In practice, basalt insulation is mainly laid directly under the finishing floor covering. In this case, the work algorithm is as follows:
- A polyethylene film with a thickness of about 200-500 microns is laid over the screed;
- a sheathing with a height of 20-50 mm is arranged (it is advisable to make the cells a few millimeters smaller than the size of the mats);
- insulation is installed in the sheathing;
- a wooden floor or rough plywood or OSB flooring under laminate, tile, parquet, etc. is laid over the lathing.
Wall insulation
Stone wool insulation is attached differently to the walls inside and outside the building. The indoor work algorithm is as follows:
- the wall is cleared of old finishing, after which it is inspected and, if necessary, repaired;
- removes dirty and greasy stains;
- a layer of penetrating primer is applied;
- a vertical frame is mounted in increments equal to the width of the mat;
- Insulation is laid between the vertical posts. At the same time, the slightest cracks and gaps are not allowed - they will conduct cold;
- the resulting gaps between the slats and the cotton wool are foamed with polyurethane foam;
- the lathing is covered with sheets of plasterboard.
Facade insulation
To insulate the facade, it is best to use specialized facade insulation made from basalt. In this case, thermal insulation work is carried out using three different technologies:
- “well” system;
- with a ventilated facade;
- "wet" method.
"Well" system
A feature of this method of insulation is the presence of 2 walls: load-bearing and decorative, between which the insulation is laid. In this case, the supporting structure is laid first, then the façade is insulated, and only after that a wall of facing bricks is laid out: the schematic diagram is shown in the photo.
With ventilated facade
The installation of a ventilated facade is carried out as follows:
- a frame is placed on the wall with a distance between vertical posts equal to the width of the slabs. Horizontal slats are attached at intervals that are a multiple of the length of the insulating mats. The width of the beam should be slightly larger than the thickness of the insulating mats - this way a small ventilation gap is formed between the heat-insulating layer and the facade cladding;
- sheets of insulation are placed in the cells of the sheathing, after which they are fastened with special screws to the wall or staples to the slats;
- a windproof (vapor barrier) membrane is attached on top of the insulation;
- the counter-lattice is attached;
- the façade is covered.
"Wet" method
When constructing private houses, the most common method is the “wet” method of insulating facades. Its essence is that first the basalt slabs are very rigidly fixed to the wall using glue and 5 special dowels, after which a reinforcing mesh is attached to the wool. The technical process is completed by applying a layer of decorative plaster.
Recommendations for selecting thermal insulation density for walls and ceilings
In private, country and cottage construction, flexible roll coverings and panel varieties of basalt insulation are mainly used.
- Material for interior work, with a density of 110-140 kg/m3, is selected taking into account the installation technology and the properties of the protective and decorative cladding. Coatings of lower density on vertical structures are prone to deformation sagging.
- Technologies for arranging suspended and panel-plaster facade insulation are based on the use of two-layer panels with double densities of 90 and 140 kg/s2. The elastic backing perfectly copies the unevenness of the microrelief and provides a dense coating and adherence to the insulated surface.
A denser front covering is responsible for maintaining shape, resistance to mechanical and other adverse effects, and compatibility with different types of plaster decor. In particular, windproof membrane components are not required in installation technologies for suspended insulation systems.