When designing and building a private house, it is necessary to correctly select and subsequently install the heating system. In apartment buildings, residents do not have problems with this issue. Since the heating system in the apartment is centralized, all manipulations are performed by the appropriate services.
But private sector developers have to decide for themselves which heating system to choose. And you should find out how to properly configure the heating system of a private house or cottage. As a rule, many criteria are taken into account and the most optimal heating system is selected.
What is a heating system
A heating system is a whole complex of various equipment that is designed to generate and transfer heat to the end user, that is, the resident of the house. The heating system includes a heat source, pipes through which this heat will be transferred, and heating radiators.
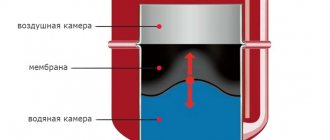
The heat source, as a rule, is either gas, electricity, or diesel or other fuel. The coolant that is transferred through the pipes is usually water or antifreeze. Accumulator tanks for heating systems act as thermal energy storage; they are built into the system circuit. A similar storage tank for heating allows you to accumulate heat for subsequent supply.
Modern automated heating systems also use faucets. They mix hot water and chilled water from the return line into the heating system. When choosing the type of heating system, you need to start by deciding what will act as a heat source. In other words, you need to know whether the water will be heated using electricity, gas or ordinary wood. Next, you should select the appropriate boiler. Then the type of pipes is selected, or an option without pipes is selected, that is, the water flows directly into the radiator.
One of the popular types of heating systems today is still boiler rooms.
In our country, the heating season, as a rule, lasts about two hundred days a year. When choosing a heating system, do not forget about this. The heating system is cleaned at the end of the season, and before the heating season it is washed and cleaned again.
Today's heating systems are regulated completely differently than their predecessors. Heating systems now are systems that maintain the desired thermal characteristics in real time. Therefore, in such systems a fundamentally new hydraulics of the heating system is used, in which there is a constantly changing mode. To maintain the appropriate temperature in the heating system, an overhead thermometer for heating systems is used, which is built in separately.
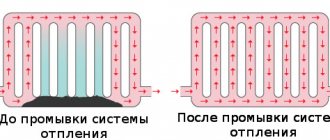
After the heating system is installed, the pipes are checked and then water is poured into the system. Or the heating system is supplied with water in a different way in order to test the new system. Thus, the heating system is being adjusted, which is being started for the first time. The heating system must be flushed within three hours. And the water after washing should be clean.
This procedure is necessary to remove construction debris that may have appeared there during installation of the system. Next, the second batch of water is heated to a boil. Boiling water also helps get rid of oily debris. Any heating system must be flushed twice a year. Some owners of private houses are interested in how to pump water into the heating system to flush it. But first you need to consider how to prepare the water for rinsing.
New mineral coolants
We decided to highlight the description of these liquids, since they are made based on the natural mineral - bischofite. The substance is a magnesium salt of hydrochloric acid, the full name is magnesium chloride hexahydrate. The manufacturer declares the following characteristics of the finished antifreeze, designed for a minimum temperature of minus 30 degrees:
- the color of the aqueous solution is light yellow, the density is 1117...1250 kg/m³;
- boiling threshold - 116 °C, freezing point - minus 30 °C;
- specific heat capacity - 0.77 kcal/kg •°С (3.23 kJ/kg•°С);
- thanks to the additives, there is no foaming and no aggressive effect on various seals - silicone, paronite, EPDM and BMS rubber;
- the substance is not toxic;
- In terms of viscosity and fluidity, the drug is very close to glycol chemicals.
Reference. The product appeared on the market after 2010. The price of liquid as of 2022 is about 1 USD. e. per liter of finished coolant (-30 ° C).
Compared to traditional glycol analogues, mineral antifreeze benefits due to its high boiling point, cost and health safety. The negative point is the increased density and low heat capacity, 23% worse than that of water.
The practical use of the coolant has revealed a number of shortcomings, as evidenced by reviews from homeowners:
- The fluidity of the solution is extremely high. There have been cases where antifreeze penetrated through the soldered joint of polypropylene pipes.
- Upon contact with air, the liquid fraction quickly evaporates, leaving a noticeable salt build-up. Similar phenomena are observed in heat exchangers and pipelines where air bubbles have penetrated.
- The substance reacts with bare metal on welds. Stalactites of iron and salt form inside the system, reducing the flow area and clogging the mud traps.
- In case of overheating, antifreeze turns into a liquid of unknown color, as shown in the photo.
User responses about this type of “anti-freeze” can be read on the well-known construction forum: https://www.stroimdom.com.ua/forum/showthread.php?t=157650
Taking into account the experience of users, we do not dare to recommend mineral antifreezes for use in heating systems of private houses. Perhaps over time, manufacturers will eliminate the above problems and the magnesium chloride solution will be able to compete on equal terms with glycols.
How to properly prepare water?
So, in order for the heating system to last for many years, it is necessary to flush it at least twice a year. Since the system is flushed exclusively with water, there must be special requirements for water. What are the requirements for the water used to flush the heating system? And how is water prepared for the heating system at this time? Next, we will consider the question of how to prepare water for the heating system yourself. Why are there stringent requirements for water?
Using untreated water to flush the heating system can lead to:
- to the destruction of pipes;
- to scale formation;
- to the breakdown of heating radiators;
- to reduce the permeability of pipes, the amount of water in the heating radiator is thus reduced;
- to a decrease in coolant velocity;
- to excessive fuel consumption and unplanned and unreasonable material costs.
As can be seen from the evidence above, the speed of water in the heating system will decrease significantly, and the batteries will no longer warm us as much in the winter.
How to soften water?
This is why it is so important to prepare water for flushing pipes. The first requirement for the water used to flush the heating system is its softness. Therefore, they try to soften the water. There is more than one water softener for heating systems on the market today. Next, the water is purified from various impurities, then settled and purified from harmful microbes and bacteria. This is an example of water treatment for a heating system for flushing the heating system.
If we consider the process of water purification and preparation, then briefly this process will look like this. In order to soften water, various devices are used, for example AquaShield. Such devices not only make the water softer, but also clean the inside of the equipment from scale. Previously, cationic resins were used to soften water. Water can also be softened with various chemicals.
Summing up and useful tips
People use water every day for cooking, bathing, washing and other purposes. If you think about it, ordinary tap water is not even suitable for watering flowers. There are many ways to soften it, but how to figure out how to purify the water, for example, for fish in an aquarium?
- To water the plants, you can use ordinary tap water, which has been left in an open container for several days, or you can add natural alkali to the liquid: ash, peat.
- For bathing adults, soda, flax seeds, and almond flakes will help soften the liquid. For washing it is better to use cool melted water. The skin of young children is very sensitive to hard water, so it is better to bathe them with a small amount of soda added (a teaspoon per bath), or use filtered, boiled water or thawed ice.
- To wash your hair, you can use water acidified with vinegar or lemon juice.
- You can wash dishes and clothes with the addition of soda ash or laundry soap, but it is much easier to install at least a magnetic filter on the water pipes.
- Boiled, melted, distilled or purified with multi-stage filters are added to the aquarium. The liquid is replaced by no more than a third, so as not to disturb the microclimate.
- Air humidifiers use only well-purified or distilled water.
- It is recommended to use bottled, melted or purified water with modern filters as drinking water.
What kind of water can I use?
The chemical composition of water and its suitability for flushing a heating system can be determined using various tests. Such tests are done in specialized chemical laboratories. Having received the test results, there is no doubt about the reliability of the results and their high accuracy.
If taking water samples to a specialized laboratory is expensive and troublesome, then you can use various water analysis kits at home. Such express kits allow you to determine water hardness and its ph level. Using these tests, you can also determine various impurities in water, such as iron, various sulfides, nitrites, nitrates, etc.
After determining the composition of water at home or after receiving analysis results from the laboratory, it is necessary to bring the water parameters back to normal. It is believed that dissolved oxygen should be present in water at about 0.05 mg/cub.m. The acidity level of the water should be between 8.0 - 9.5. The iron content in water should be no more than 0.5-1 mg/l. The water hardness indicator should be within 7-9 mg eq/l.
Such analyzes must be carried out twice a year.
Various microbes and microorganisms contained in water naturally greatly deteriorate its quality. Thanks to these pathogenic microbes, a mucous film can form on the walls of the pipes.
Why you need to use a softener to reduce water hardness
A filter can be used as a water softener. What dangers may await owners of a heating system who do not use special filters to reduce the hardness of the coolant? Firstly, calcium and magnesium salts, which are found in large amounts of hard water, transform over time into limescale deposits.
Secondly, these insoluble deposits attach to the walls of the pipes and reduce their permeability. This does not allow the use of means of monitoring and recording water consumption. The pipes are gradually failing. The worst thing about this situation is that the process of deposition of insoluble residues and scale formation is a long process. It is invisible to system consumers. Therefore, water softener filters are required.
Chemical compounds in the heating system - as a means of water softening
An alternative to using filters would be chemical reagents. But they did not become a worthy replacement. Polyphosphates are used among chemical compounds and reagents. Polyphosphates prevent scale particles from connecting with each other. But in this case, these chemicals must be constantly present in the heating system. And another disadvantage of chemical reagents is that they do not adapt to the new level of water hardness.
The second type of chemical reagents that are used to soften water hardness are reagents for prevention or for purifying water after its use. You can use a heating concentrate that is compatible with antifreeze. It is used for corrosion protection. Now you can return to the question of how to pump water into the heating system yourself.
Creation of a surfactant film
One of the methods for creating a protective barrier against the effects of corrosion and scale formation on the surfaces of SCT elements is the creation of a film of surfactants (surfactants). Surfactants are part of a complex of chemicals used to modify feedwater.
Their addition serves several purposes. The addition of surfactants to solutions of phosphates and phosphonates should stabilize the products of their interaction with hardness salts—suspensions—in water. They should also prevent the accelerated appearance of repeated deposits after washing. But the use of surfactants to achieve these goals is of an auxiliary nature.
The well-known properties of surfactants force us to search among their large range for those that will allow us to simultaneously wash out old deposits and form a protective film that prevents corrosion and scale formation. Surfactants have a prolonged effect and washing of residual deposits continues even after the end of the main process during boiler operation.
Conclusions from experiments
Further experiments led to the conclusion that it is possible to clean the boiler without stopping it if you simply add a certain amount of surfactant to the water.
Depending on the thickness of the deposits, they are completely washed off within one or two months. Observation of the hydraulic resistance of the washed boilers during the next heating season showed that it remained quite stable.
The increase in hydraulic resistance began only in the middle of the second (after flushing) heating season. Visual inspections of the internal heating surfaces after the completion of the heating seasons showed that they were free of deposits after the season when a one-time introduction of a surfactant was made (up to 2% of the volume of water in the system).
New deposits appeared during the next heating season. The system was not subject to thermal deaeration or chemical degassing during all three heating seasons during which the experiment was conducted. Research has also shown that a thin (up to 50 microns) durable gray film appears on the surface, which has dielectric properties.
Considering the electrochemical nature of the corrosion reaction, we can assume that this is what determines its anti-corrosion properties and at the same time prevents the appearance of scale formation centers.
How to add water to the heating system
There are two types of heating systems. These are a closed type heating system and an open type heating system. In an open system, water comes into contact with air. This happens through the tank, which is located at the highest point of the heating system. In a closed system, water does not come into contact with air.
To add water to a closed heating system, you must:
- Have a pump for drawing water from a well or reservoir. Using a hose that is connected to the pump and to the drain pipe, pump up water. All taps open to full capacity. It is important to prevent overflow in the heating system, so you need to constantly regulate the water supply.
- Particular attention should be paid to the pressure with which the pump supplies water, and adjust the pressure required for the heating system. And this is 1.5 atm.
- To calculate the volume of the heating system, you need to know how many liters are in the radiator and one linear meter of pipe.
Modification of surfaces of elements in SCT
There are other known methods for preventing corrosion and scale formation associated with modifying the surfaces of elements in the SCT that are in contact with water. It is possible to use alloy steels for the manufacture of elements of heat exchangers and boilers. This allows you to get rid of corrosion, but the price of SCT elements increases significantly.
Despite the increase in equipment costs, there are such examples. These are pre-insulated pipes for heating networks, or condensing water heating boilers and Viessmann. Or water heating sectional boilers made of aluminum alloys and Bosch-Buderus. IN
It is also possible to use plastics for the manufacture of pipes for heating networks, but only for coolant temperatures not exceeding 95°C. There are known designs of air heaters for boilers made from glass pipes or plastic. All these technologies are still quite expensive and are not widely implemented.