If everything is very clear with the common heating element models of electric boilers, then not everyone has an understanding of the operating principle, advantages and disadvantages of electrode heating boilers. This is due to inflated statements by marketers claiming incredible savings and, conversely, with reviews from owners who are convinced that this is not entirely true.
In fact, electrode boilers are ordinary electric boilers, slightly different in operating principle, compact size and lower cost. But whether it is worth using them for heating a private house and how true all existing opinions are, we will find out by analyzing the principle of operation and the differences from standard heating element electric boilers.
What are electrode heating boilers?
Compact heating system using an electrode boiler (in the gray metal housing on the left).
Automation and controls are located in the electronics. shield on the right. Electrode boilers are compact in size; low-power single-phase models barely exceed the diameter of the heating system lines and do not require space around them, so they can be installed absolutely anywhere. But it is worth considering that they are just a heat exchanger, unlike heating elements models in a monoblock housing, they require the separate purchase of an expansion tank, circulation pump, safety group and other elements of the heating system.
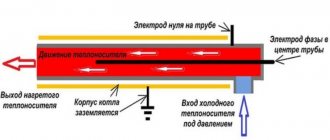
Design and principle of operation
A visual principle of operation of an electrode heating boiler.
The operation of boilers is based on direct heating through electrolysis. Electrodes are located in the housing at a certain distance from each other: cathodes, which attract positively charged water ions when direct current is applied, and anodes, which attract negatively charged ions. But when alternating current is applied to the electrodes, they change polarity 50 times per second (standard current frequency 50 Hz), which causes constant movement of water ions. Due to the high resistance of the medium, the kinetic energy of moving ions is converted into heat and the coolant quickly heats up.
In the technical literature, electrode boilers are also called direct heating electric boilers, since the coolant is heated directly by passing current through it, and not through heating the heating element, which then heats the water.
On the one hand, this heating principle does not imply the formation of scale and the efficiency of ion electric boilers remains unchanged throughout their entire service, while the efficiency of heating elements models due to scale formation when using hard water as a coolant decreases over time to 90 or even 80% (from the original 99%). On the other hand, the effect of electric current enhances the corrosion process of all metal elements of the water circuit of the heating system.
For the operation of electrode boilers, an undistilled and unfiltered coolant is required, which will act as an electrolyte. This can be regular tap water, propylene glycol or ethylene glycol. Almost all manufacturers of ion electric boilers produce their own coolants and recommend using them (there is often a catch here, because using a different coolant will void the warranty; this is stated in the passport of most models).
The use of distilled water, antifreeze or oil as a coolant is unacceptable.
The principle of operation of antifreeze
Water at 0°C abruptly and abruptly turns into ice, expanding by 11%. The pipes cannot withstand such a load. The heating system has to be dismantled, including the boiler and all radiators. Water is a good solvent, so even a small amount of antifreeze greatly shifts the crystallization point of water, and abrupt transformation into ice does not occur.
At subzero temperatures, water with the addition of antifreeze slowly thickens, and the liquid expands slightly, so the heating system remains safe and sound.
For example, the crystallization of water with 30% antifreeze liquid (propylene glycol) is so slow that there is no need to dilute the coolant to -30°C; it is enough to add antifreeze to the design temperature of -12-15°C. As the temperature drops below the calculated value, such a mixture will slowly but surely harden, and only at -30°C can it freeze completely.
Should they be used for heating a private home: we analyze known statements and misconceptions
- An electrode boiler is much simpler and cheaper to install, since there is no need for a chimney or ventilation. In addition, its installation does not require approval.
This is true, however, any electric boiler does not require a separate room for the boiler room, special wall covering, chimney organization, supply and exhaust ventilation. The process of organizing a heating system with an ion-type boiler is indeed simpler, but not as much as when using heating element analogues, which already have in their housing all the necessary components of the heating system (it is enough to connect only the supply and return).
Another example of a complete heating system with an inexpensive electrode boiler.
Regarding coordination, it all depends on power. Any electric boilers with a power of more than 10 kW require mandatory approval from the Energonadzor services. It is also important to understand that any electric boilers with a power over 6 kW must be connected to a three-phase power supply.
- Electrode boilers have a higher efficiency, they are economical and consume 30-50% less electricity.
The efficiency of all modern electric boilers is more than 99%, so such statements are just a marketing technique or a comparison with extremely old models that have not been on sale for at least several years.
However, there is also some truth in the statement, since due to the formation of scale when using hard water as a coolant, the efficiency of heating element models decreases over time to 90 or 80%: heating the coolant through a layer of scale requires more time and energy consumption. The efficiency of ion boilers remains stable for a long time.
Also, the functionality of the automation seriously affects the efficiency. The automation of ion models is simpler and inferior to heating elements, where models in the mid-price segment and above have energy-saving night modes, the ability to program the operating mode for a week in advance, etc. The problem can be solved using a room thermostat costing 2,000-4,000 thousand rubles, but again, these are additional costs that offset the main advantage of electrode boilers - low cost.
Wall-mounted room thermostat for electric boiler.
- The reliability and service life of electrode models is higher.
With proper operation that meets the requirements, this is partly true, since electrode boilers have the simplest possible design and any malfunction in the first 12-15 years of operation is rare.
At the same time, the only vulnerable part of heating element models is the heating element itself - the heating element. When using low-quality coolant, it must be replaced after 3-5 years, when using prepared, purified and softened coolant - up to 8-10 years.
- Ion-type electric boilers are safer.
In an emergency, this is indeed justified by the principle of operation, since in the event of a coolant leak or power outage, the electrodes will simply stop working. When power is applied, they resume operation again without human intervention. Heating element models without overheating protection will not stop working if the coolant leaks, which will lead to destruction.
But the fact is that today even many budget heating electric boilers have protection against overheating, a mode to prevent freezing, and protection against blocking the circulation pump. Therefore, this is an extremely controversial statement.
Efficiency and selection criteria for energy-saving electric heating boilers
- Price
Most electrode models cost between 4-9 thousand rubles, while the cost of heating elements ranges from 19 to 29 thousand for the most common models in the middle price segment.
The low price of ion-type boilers is indeed a significant advantage, but is often overestimated by the buyer. It is worth considering that to organize the system, you will have to separately purchase an expansion tank, a safety group, a circulation pump and other components already present in the housing of models with a tubular electric heater. And this is another 5-10 thousand rubles. To achieve greater comfort and savings, a functional electronic thermostat is also needed - another 2-4 thousand rubles.
Difficulties in operation
Branded coolant from the manufacturer Galan. At the time of writing, the cost of such a canister is about 2,200 rubles.
- Proper operation in accordance with the requirements implies the use of high-quality coolant with a balanced chemical composition and all the qualities of the electrolyte. Manufacturers recommend using liquids specially prepared for these purposes that have good ionization, sufficient heat capacity and anti-corrosion properties. It is possible to pour ordinary tap water into the heating system, but this usually leads to a decrease in efficiency and rapid corrosion of all metal lines of the heating system. In addition, over time, any coolant loses its properties and requires replacement after 3-4 years, which also causes additional hassle and expense.
- As we have already mentioned, the effect of electric current on ferrous metals and stainless steel significantly accelerates the corrosion process, which reduces the life of the heating system. Therefore, in conjunction with electrode boilers, it is generally not recommended to install steel or cast iron radiators - only aluminum or bimetallic ones. Otherwise, the lifespan of radiators is literally reduced several times.
- The phases of the electrical network are connected to the electrodes, and zero is connected to the body of the electric boiler, so reliable universal grounding is required and it is not recommended to limit yourself to installing an RCD. If the grounding is poor, dangerous potentials may appear on pipes and batteries. In addition, it is necessary to ensure the quality of the wiring in the house, since high-power equipment creates a serious load on the electrical network and causes voltage fluctuations. However, this is not a feature of ion electric boilers, but in general of any electrical equipment with a power of 4-6 kW.
To summarize: if you are not ready for additional installation work and operating features of electrode boilers, it is better to pay an additional 20-30% of the cost and choose a heating element electric boiler, which is what we recommend doing. Today they occupy about 90% of the electric boiler market. But with a competent approach, there is also a choice in favor of ion-type boilers, the advantages and disadvantages of which are summarized below.
Types and properties of heat-carrying liquids
The working fluid of any water system - the coolant - is a liquid that takes a certain amount of energy from the boiler and transfers it through pipes to heating devices - radiators or underfloor heating circuits. Conclusion: the efficiency of heating depends on the physical properties of the liquid mediator - heat capacity, density, fluidity, and so on.
In 95% of private houses, ordinary or treated water is used with a heat capacity of 4.18 kJ/kg•°C (in other units - 1.16 W/kg•°C, 1 kcal/kg•°C), which freezes at a temperature of about zero degrees. The advantages of traditional heating fluid are availability and low price, the main disadvantage is the increase in volume when frozen.
Crystallization of water is accompanied by expansion; cast iron radiators and metal-plastic pipelines are equally destroyed by ice pressure
The ice that forms in the cold literally splits pipes, boiler heat exchangers and radiators. To prevent the destruction of expensive equipment due to defrosting, 3 types of antifreeze made on the basis of polyhydric alcohols are poured into the system:
- Glycerin solution is the oldest type of non-freezing coolant. Pure glycerin is a transparent liquid of high viscosity, the density of the substance is 1261 kg/m³.
- An aqueous solution of ethylene glycol - dihydric alcohol with a density of 1113 kg/m³. The starting liquid is colorless and is inferior in viscosity to glycerin. The substance is toxic, the lethal dose of dissolved glycol when taken orally is about 100 ml.
- The same, based on propylene glycol - a transparent liquid with a density of 1036 kg/m³.
- Compositions based on the natural mineral - bischofite. We will analyze the characteristics and features of this chemical separately (below in the text).
Reference. Any non-freezing heating fluid contains a dye that gives the chemical a distinctive color. Poisonous ethylene glycol is usually colored red or yellow, propylene glycol is green (less often blue). Glycerin antifreeze is given a pink tint or left transparent. This classification is not mandatory and is not always observed.
Anti-freeze products are sold in two forms: ready-made solutions designed for a certain subzero temperature (usually -30 ° C), or concentrates, which the user dilutes with water himself. Let us list the properties of glycol antifreezes that affect the operation of heating networks:
- Low crystallization temperature. Depending on the concentration of polyhydric alcohol in an aqueous solution, the liquid begins to freeze at a temperature of minus 10...40 degrees. The concentrate crystallizes at 65 °C below zero.
- High kinematic viscosity. Example: for water this parameter is 0.01012 cm²/s, for propylene glycol - 0.054 cm²/s, the difference is 5 times.
- Increased fluidity and penetrating ability.
- The heat capacity of non-freezing solutions lies in the range of 0.8...0.9 kcal/kg °C (depending on concentration). On average, this parameter is 15% lower than that of water.
- Aggressiveness towards some metals, such as zinc.
- The substance foams when heated and quickly decomposes when boiling.
Propylene glycol antifreezes are usually painted green, and the prefix “ECO” is added to the marking.
In order for antifreezes to meet operational requirements, manufacturers add additive packages to glycol solutions - corrosion inhibitors and other elements that maintain the stability of the antifreeze and reduce foaming.
Reviews of household ion-type electric boilers: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Consistently high efficiency over a long period of time | All elements of the heating system must be purchased separately |
| Low cost, 20-30% lower taking into account all the elements necessary for organizing a heating system and 50-60% lower when comparing the boilers themselves | Mediocre automation, inferior in functionality to heating elements models in the middle price segment and above |
| Absence of any malfunctions due to the simplest and most reliable device | Additional difficulties in operation: choice of coolant and the need for its regular change, limited choice of heating radiators, need for reliable grounding |
| Easy to install | Use exclusively in closed heating systems |
| Most compact sizes | |
| 30-40% faster heating of coolant |
Ion boiler "Beryl" with a seven-stage block
More expensive models, with automatic control and regulation of power at each specific moment in time, are equipped with a special seven-voltage unit (pictured) and a PID system - electronic temperature control. It is believed that the PID controller, which consists of an amplifier, integrator and differentiator, most quickly and accurately estimates the heating level taking into account the immediate future and generates control signals that allow saving up to 20% of energy.
Line of boilers EOU (Energy Saving Heating Installation)
This is also a Russian-made product. Simple in design, relatively inexpensive, but quite easy to use, the boilers cover a power range from 2 to 120 kW. They can be produced for single- and three-phase current networks, differing in size.
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
Galan
The most common Russian manufacturer of electrode boilers. It has the widest model range and power options: from low-power 2-3 kW models for heating small rooms to powerful 36 kW ion boilers. Electric boilers have some of the most affordable prices, fast heating, and silent operation. Among the disadvantages are stepwise power adjustment and an expensive coolant recommended by the manufacturer (about 2,200 rubles for 20 liters).
The model range is represented not only by the compact “Ochag”, “Geyser” and “Vulcan”, but also by the monoblock “Galax”, the body of which is already equipped with an expansion tank, a circulation pump, a safety valve, an air vent and a pressure gauge.
Cost: 4,000-13,000 rubles. for compact and 29,000-30,000 for monoblock models.
EOU
Another Russian manufacturer, the abbreviation stands for “Energy-saving heating installations.”
The model range is represented by electric boilers with a power from 1 to 36 kW. Electrode EOUs are distinguished by their durability (the service life declared by the manufacturer is 30 years) and function better than ordinary tap water. The disadvantages are mediocre automation, higher prices and mediocre availability, since the manufacturer is represented in the smallest part of the heating equipment market stores.
Cost: 4,600-15,000 rubles.
Beril
Well-known Latvian manufacturer SIA “BERIL”. Despite their higher cost, Beril electrode boilers are among the best for heating a private home, as they are characterized by high reliability, build quality and, most importantly, multifunctional, economical automation. There is a smooth degree-by-degree power adjustment, several economical operating modes, the ability to connect external temperature sensors or a GSM module, and electricity consumption statistics.
There are also protection against overheating and a frost prevention mode typical for heating elements.
Cost: 4,450-25,000 rubles.
Coterm
Another Russian manufacturer of heating equipment. The most successful model is considered to be the Coterm “Dachnik M”, characterized by its most compact dimensions, build quality, reliability, and fast heating of the coolant. Known disadvantages are mediocre automation with only 3-step power control and limited functionality, as well as the need to use exclusively branded Coterm Eco coolant.
Cost: 8,800-11,000 rubles.
Which coolant is suitable for an ion boiler
An ion electric boiler is very demanding on the quality of the coolant. Distilled water and antifreeze liquid are not suitable for it. As a coolant, you need to use ordinary tap water that has undergone special preparation. The heater's data sheet indicates how much salt should be contained in the coolant.
To “set up” the coolant for ion heating boilers, according to reviews, you need to spend a lot of time. For example, if the water resistance is insufficient, then it needs to be salted. Regular table salt is suitable. You only need to sprinkle a little bit of it, literally on the tip of a teaspoon. Then the salted liquid is passed through the system and the resistance is measured. If it has reached the required level specified in the passport, then you can leave everything as is. If necessary, add more salt to the coolant or dilute it with distilled water.
Installation features
To install an energy-saving boiler, it is necessary to install a safety valve, pressure gauge and automatic air vent. The horizontal position of the equipment is unacceptable; install it only vertically, without displacement.
The insertion into the thermal circuit is made so that the zero terminal is at the bottom. Wires connected to the boiler must have a cross-section of at least 4 mm². Connect only through machines, in accordance with all rules of the PUE.
For installation in a new main, only a used boiler is treated with inhibitors. Follow the recommendations for using cleaning products. Ignoring this point will lead to difficulties when setting the ohmic indicators of the liquid in the system.
For heating, the choice of radiators is important. Cast iron samples are not acceptable as they are prone to increased scale formation and other contaminants. It is better to select small radiator batteries, made of lightweight materials (aluminum), so that 1 kW of energy is consumed per 8 liters.
Parallel connection - power amplification
When choosing batteries, it is preferable to choose primary-type aluminum structures, since they contain significantly fewer impurities - this will reduce the overall resistance.
"Galan" Vulcan 36
was one of the first to begin developing such a family of heating devices, using developments in the military space industry and patented engineering solutions. For a quarter of a century, even the first line of devices has not failed and continues to function.
"Galan" Vulcan 36
Model power 36 kW, suitable only for three-phase network. The maximum current for three phases is 27.3 A. The control is mechanical; the boiler is installed only on the floor.
This model “Vulcan” 36 has many advantages, let’s highlight the main ones:
- ease of maintenance and operation.
- safety and reliability - if an electric short circuit occurs, the current supply wires overheat, the set temperature is exceeded, or a coolant leak occurs, the boiler turns off.
- the coolant volume is 600 liters, the volume of the heated room is 1700 cubic meters.
- affordable cost - the average price is 11,000 rubles.
These boilers have been certified by the Customs Union
The table shows technical data and the average price level for boilers operating on a 220 volt network, as the most popular in domestic conditions:
| Technical data | Unit | Single-phase modifications | |||||||||
| 1/2 | 1/3 | 1/4 | 1/5 | 1/6 | 1/7 | 1/8 | 1/9 | 1/10 | 1/12 | ||
| Operating voltage | Volt | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 | ~220 |
| Power consumption | kW | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 12 |
| Heated room volume | m³ | 120 | 180 | 240 | 300 | 360 | 420 | 480 | 540 | 600 | 750 |
| Heated area | m² | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 250 |
| Electricity consumption per day | kW | 2-16 | 3-24 | 4-32 | 5-40 | 6-48 | 7-56 | 8-64 | 9-72 | 10-80 | 12-96 |
| Raising water in a water system (without pump) | m | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 |
| Weight, no more | kg | 3 | |||||||||
| Price of the device, without control panel | rub. | 4200 | 4300 | 4400 | 4500 | 4600 | 4700 | 4800 | 4900 | 5000 | 5100 |
| Price of a set of components for the control panel | rub. | 1410 | 1990 | 1990 | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 | 2540 | 2540 | 2540 | 2540 |
Despite the unpretentious design of EOU boilers, the manufacturer gives them a factory warranty of at least 10 years, and the total service life is estimated at 30 years.
Imported electrode boilers
In addition to Russian-made boilers, models produced in some neighboring countries are in demand.
Ukrainian-designed and produced Forsazh boilers are interesting in that they are equipped with a special casing - a casing, which increases the operational safety of the installation and still makes its appearance more attractive.