Here you will learn:
- General tips for connecting a radiator
- Possible radiator connection diagrams
- Diagrams for inserting a radiator into the system
- Approximate sequence of installation of a heating radiator
Existing heating systems are divided into three groups - single-pipe, two-pipe and collector. The cheapest option to implement is the first option. However, a single-pipe system is the least effective in terms of adjustability of heat transfer in rooms and thermal energy consumption.
The maximum effect in terms of these indicators is achieved by a circuit with a heating manifold. But it will also cost the most to create. An analogue with two pipes occupies a certain middle ground between them in cost and performance characteristics.
A two-pipe system is much more efficient than a one-pipe system, and with proper design, installation costs only 10–25 percent more than it does.
In a heating system with two independent pipelines, through one of them the coolant, most often water, is supplied to the radiator, and through the other it is discharged. As a result, each battery in the circuit receives almost the same amount of heat to transfer it to the room.
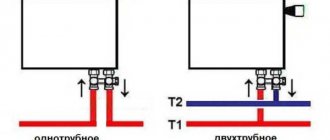
In a single-pipe analogue, the coolant is supplied to the radiator and discharged through one common heating pipeline. In this case, the first room heater from the boiler (boiler) receives much more thermal energy than the last one in the chain. And it turns out that the room farthest from the water heater is always cool, and the room closest to it is too hot.
The basic visual difference between these systems is the presence of a bypass in the single-pipe distribution next to the battery. This jumper ensures uninterrupted coolant circulation when one of the radiators needs to be completely or partially disconnected from heating. In a heating circuit with two pipes it is simply not needed.
Among the main advantages of using a two-pipe system:
- accuracy of heat transfer adjustment in individual rooms;
- versatility - suitable for any home;
- independent operation of individual radiators from the rest;
- possibility of quick installation of additional batteries.
However, efficiency comes at the cost of increased length of heating pipes. Each radiator in such a system is supplied with a pair of pipelines with coolant from the boiler - one for supplying heated water, the second for return.
A common mistake when choosing between one-pipe and two-pipe schemes is that the second option is estimated to be one and a half to two times more expensive than the first, which is absolutely not true
If there is only one pipe, then in the project it is laid out wider in cross-section than with a two-pipe distribution. As a result, the total cost of these two options in terms of materials does not differ so much.
But the volume of installation work actually doubles. If you do the installation yourself, then this point is not so relevant. However, if you order the assembly of the system externally, you will have to pay a little more for a circuit with two pipelines. But it will definitely not be twice as expensive.
Place of radiators in the heating system
The use of radiators in heating residential premises plays a key role today.
Not all residential properties, especially apartments in multi-storey buildings, can be converted to underfloor heating. Therefore, the main work of heating internal living spaces is performed by radiators or the good old batteries that are familiar to us. Radiators transfer thermal energy from the coolant to the surrounding space. Heat transfer is carried out due to the large heating surface of the heating device. Modern models have a number of technical improvements, thanks to which it has become possible to connect in a variety of options and with any wiring diagram.
in old cast iron and steel batteries there was only one upper and one lower pipe, through which hot water is supplied and the return is released.
In modern models, in addition to the main supply and outlet pipes, there are built-in air vents. This design of batteries radically changed the quality of functionality of the heating system. If there are air pockets in heating devices, it is enough to open the drain valve and bleed the air.
In many ways, thanks to modern models of heating batteries, it has become possible to choose the most convenient connection scheme and install heating devices in those areas of the living room in which they are most effective. The quality of operation of the heating water circuit depends on correctly installed piping. The process is necessary if you are using a pipeline made from polypropylene pipes.
Important! If there are metal risers, the piping is made from other consumables. It can be metal copper pipes or metal-plastic
The use of polypropylene pipes in this case is strictly prohibited.
The reason for the incompatibility of metal pipes with polypropylene products is the presence of a threaded connection. Considering the fact that propylene pipes have a high coefficient of thermal expansion, when hot coolant is supplied, the threaded connection will lose its tightness and stability. Therefore, if you want to connect a heating radiator made of polypropylene pipes, try to use fittings, adapters and couplings made from similar materials.
the difference in diameters of pipes made of different materials should be taken into account
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
Radiators with bottom connection
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the bottom connection. There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, coolant is supplied to the radiator on one side and removed from the other.
Bottom connection of heating radiators for single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply and where the return is connected is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
Heating radiators with side connection
With a lateral connection, there are many more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected into two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
Option #1. Diagonal connection
This connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard and this is how manufacturers test their heating devices and the data in the thermal power passport for such a connection. All other connection types transfer heat less efficiently.
Diagonal diagram for connecting heating radiators with a two-pipe and one-pipe system
This is because when the batteries are connected diagonally, the hot coolant is supplied to the upper inlet on one side, passes through the entire radiator and exits from the opposite, lower side.
Option #2. Unilateral
As the name implies, pipelines are connected on one side - supply from above, return from below. This option is convenient when the riser runs on the side of the heating device, which often happens in apartments, because this type of connection usually predominates. When the coolant is supplied from below, this scheme is used infrequently - it is not very convenient to position the pipes.
Lateral connection for two-pipe and one-pipe systems
With this connection of radiators, the heating efficiency is only slightly lower - by 2%. But this is only if there are few sections in the radiators - no more than 10. With a longer battery, its farthest edge will not heat up well or will remain cold at all. In panel radiators, to solve the problem, flow extenders are installed - tubes that bring the coolant a little further than the middle. The same devices can be installed in aluminum or bimetallic radiators, thereby improving heat transfer.
Option #3. Bottom or saddle connection
Of all the options, saddle connections for heating radiators are the least effective. Losses are approximately 12-14%. But this option is the most inconspicuous - pipes are usually laid on the floor or under it, and this method is the most optimal from an aesthetic point of view. And so that losses do not affect the temperature in the room, you can take a radiator a little more powerful than required.
Saddle connection of heating radiators
In systems with natural circulation, this type of connection should not be made, but if there is a pump, it works well. In some cases, it’s not even worse than the side one. It’s just that at a certain speed of movement of the coolant, vortex flows arise, the entire surface heats up, and heat transfer increases. These phenomena have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not yet possible to predict the behavior of the coolant.
Why do you need to make adjustments?
Setting the optimal temperature of the heating radiators allows you to create the most comfortable living conditions indoors. In addition, adjustment allows:
- Remove the effect of air in the batteries, allow the coolant to move freely through the pipeline of the heating system, effectively transferring its heat to the interior of the room.
- Reduce heat consumption costs by up to 25%.
- Do not keep windows constantly open if the air in the room is excessively overheated.
It is advisable to set up heating and adjust batteries before the start of the heating season. This is necessary so that later you do not experience discomfort in the apartment and do not adjust the heating temperature of the batteries in emergency mode. Before setting up and adjusting the radiators, initially in the summer you need to thermally insulate all windows. In addition, you need to take into account the specific location of the apartment:
- In the middle or corner of the house.
- Lower or upper floor.
After analyzing the situation, it is advisable to use energy-saving technologies to maximize heat conservation inside the apartment:
- Insulate walls, corners, floors.
- Carry out hydro and thermal insulation of the seams between the concrete joints of the panel house.
Without this work, it will be useless to regulate the temperature of the radiators, since the lion's share of the heat will heat the street.
Heating in the house
At the first stage, you should decide on the types of radiators and options for their connection, since buildings should be prepared in advance for the selected type of heating. A modern space heating system includes several components.
These include:
Do-it-yourself polypropylene heating wiring without a soldering iron
You can find different versions of them in large quantities in our markets.
General instructions for installing batteries look like this:
- First select a place to place them;
- bring pipes to them;
- connect them together;
- perform a test run, and if everything is in order, turn on the heating at full power.
How to install heating radiators with polypropylene pipes with a jumper for quick shutdown
Tying polypropylene pipes instructions
Radiator piping can be done using a variety of pipes, but experts recommend using polypropylene pipes. Ball valves for piping are also purchased in polypropylene; they can be straight or angular; this option is the simplest and most inexpensive. Brass fittings are more expensive, and their installation is more difficult.
Polypropylene strapping is done as follows:
- the coupling with a union nut is inserted into the multiflex, which easily connects to any outlet;
- The pipes themselves are attached to the walls at a convenient height; they should not fit tightly to the surface; it is better to leave a gap of 2-3 cm. The pipes are secured using special brackets, which are fixed to the wall with nails or self-tapping screws.
Polypropylene piping to radiators can also be carried out when laying pipes in the wall, in which case they come to the surface only at the connection points.
Radiator piping can be done using a variety of pipes, but experts recommend using polypropylene pipes.
Battery fasteners can be very different, most often it is a pin connection that is fixed to the wall surface. Corner brackets can also be used, which also allow radiators to be suspended at the required height. For panel batteries, fasteners are supplied included; for sectional batteries, they must be purchased separately. Typically, two brackets or pins are sufficient for one section.
The taps are connected as follows:
- the tap is disassembled, the fitting and union nut are screwed into the radiator;
- Use a special wrench to tighten the nut tightly.
As you can see, this process is extremely simple. To perform such work, you only need to purchase a special plumbing wrench for American women, without which it is unlikely that you will be able to simply install a faucet.
To install batteries and tie them, the following materials and tools are required:
- a set of special keys;
- seals for threaded connections;
- tow and thread paste;
- threads for carving.
Features of connecting radiators
Heating installation has some features:
- It is necessary to maintain a distance of 100 mm from the radiator to the window sill. If the gap between the batteries and the bottom of the window sill is different, then the heat flow is disrupted and the effect of the heating system will be low.
- The distance from the floor surface to the battery should be 120-150 mm, otherwise a sharp temperature change will occur.
- In order for the heat transfer of the equipment to be correct, the distance from the wall must be at least 20 mm.
At the same time, we take into account that the installation and efficiency of heating radiators is greatly influenced by the installation method: under an open window sill the efficiency of the heating system is maximum - 96-97%, in an open niche - up to 93%, in a partially closed form - 88-93 %, completely closed - 75-80%.
The heating radiator can be installed using a variety of methods; its piping is done with metal, polyethylene, polypropylene pipes
During installation, it is important to correctly position not only the pipes, but also the batteries themselves, and make the connection in accordance with all recommendations and standards. In this case, the heating system will work very efficiently and will not require repair work.
Share a useful article:
How to add sections
After you have experimentally determined that the reason for the cool temperature in the house is not a clogged radiator, you should find a store near your home (so that you don’t have to travel far away and thereby waste your time) that sells heating equipment. You need to buy the same sections that your radiator is equipped with - made of cast iron, aluminum, or bimetallic.
It should not happen that you select inappropriate sections - because of such an error, you simply will not be able to add them, that is, the money spent will be thrown away, so be careful. The procedure for increasing sections is carried out in the same sequence of actions for all types of heating radiators.
To join sections, you need a connecting nut - nipple
Let's proceed directly to increasing the number of sections. The first step is to unscrew the fitting using a radiator wrench on the side to which you plan to add one or more elements. After you have unscrewed the fitting, a nipple (connecting nut) is placed in the area where the sections join. The following important feature must be taken into account: the threads at different ends of the nipple are different, and in order to correctly install new sections you must follow the following rules:
- The right side of the nipple should be directed towards the direction where the connection to the new element will be made;
- Accordingly, the left one is towards the already present sections of the heating radiator.
In order to prevent further leakage of the battery, you should put intersection gaskets on the nipple (they can be rubber, paranitic, or gel)
At the same time, they must be put on carefully and carefully - this will guarantee that the gasket will be positioned as evenly as possible, without unwanted distortions. Next you need to tighten the thread. This action should also be carried out without sudden movements, in a leisurely rhythm, and carefully
If you want to build a high-quality heating radiator, then there can be no rush
This action should also be carried out without sudden movements, in a leisurely rhythm, and carefully. If you want to build a high-quality heating radiator, then there can be no rush.
To prevent leakage, an intersection gasket is required
Damage to metal threads is extremely undesirable - this may result in not the most harmless problems, the solution of which will require you to additionally spend your own time and financial resources.
The enlarged radiator must be placed back on the bracket and the connection to the central heating pipe restored. To do this, you need to arm yourself with a wrench of the appropriate diameter and tow, which is necessary for wrapping the pipe threads when screwing the radiator.
It’s not difficult to add sections to a heating radiator; you don’t need to work in a team of heating installers for 10 years. But this process cannot be done without a serious approach, the availability of basic tools and the removal of your personal time. However, you can resort to the second option for solving the problem of insufficient heating of the room - becoming a client of a company providing such services, whose employees will do everything themselves, quickly and efficiently.
Types of heating systems
The amount of heat that the heating radiator will emit depends not least on the type of heating system and the selected type of connection. To choose the best option, you must first understand what kind of heating systems there are and how they differ.
Monotube
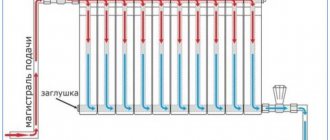
A single-pipe heating system is the most economical option in terms of installation costs. Therefore, this type of wiring is preferred in multi-storey buildings, although in private buildings such a system is far from uncommon. With this scheme, the radiators are connected to the main line in series and the coolant first passes through one heating outlet, then enters the input of the second, and so on. The output of the last radiator is connected to the input of the heating boiler or to the riser in high-rise buildings.
Example of a one-pipe system
The disadvantage of this wiring method is the impossibility of adjusting the heat transfer of radiators. By installing a regulator on any of the radiators, you will regulate the rest of the system. The second significant drawback is the different coolant temperatures on different radiators. Those that are closer to the boiler heat up very well, those that are further away become increasingly colder. This is a consequence of the serial connection of heating radiators.
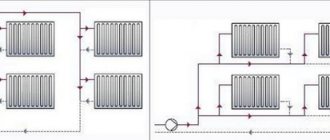
Two-pipe wiring
A two-pipe heating system is distinguished by the fact that it has two pipelines - supply and return. Each radiator is connected to both, that is, it turns out that all radiators are connected to the system in parallel. This is good because the coolant of the same temperature enters the input of each of them. The second positive point is that you can install a thermostat on each of the radiators and use it to change the amount of heat it emits.
The disadvantage of such a system is that the number of pipes when laying out the system is almost twice as large. But the system can be easily balanced.
What kind of piping can be made from polypropylene pipes
The piping for a home heating system can be very different. The thing is that the consumer is always trying to reduce the amount of consumables, while simultaneously trying to install radiators in all heated rooms.
It should be said right away that these are relics of the past. Unlike expensive metal pipes, polypropylene consumables are much cheaper and easier to install. therefore, it is not worth saving on the length of the pipeline. Choose the type of harness that will bring maximum benefit in your case. The only reasons that may influence the choice of type of harness are the following factors:
- what heating circuit is used (one-pipe system or two-pipe);
- what type of radiator connection you have chosen (diagonal, side or bottom).
As a rule, when using any heating scheme: single-pipe or two-pipe, you can use any type of heating radiator connection.
According to experts, pipeline laying must minimize the number of bends. A smooth highway remains resistant to hydrodynamic loads. The number of zones in which air can accumulate will be reduced in the pipeline.
There are specific features for piping a single-circuit and double-circuit heating system using polypropylene pipes.
- Typically, such a system uses a series connection of radiators;
- A bypass is always installed in front of the battery, connecting the supply pipe and return pipe. During normal operation of the heating system, the bypass is not activated. When carrying out maintenance work or in the event of an emergency, the water supply to the radiator is stopped. The coolant circulates freely through the bypass.
- Both parallel and serial connections of batteries are used;
- Both radiator hoses are connected to different pipes. The upper one is connected to the supply pipe, the lower pipe is connected to the return pipe. Typically, radiators are connected in parallel in two pipe systems, so installing bypasses is not required.
Tying polypropylene pipes with radiators is done in two ways: soldering and using fittings. Radiators are installed and connected using a soldering iron and American-style plumbing wrenches.
Conditions for efficient heat transfer of batteries
Two-pipe heating system
The correct choice of heating devices ensures energy savings. Among the many offers on the market, they differ:
- shape;
- material;
- heat transfer level;
- connection type.
For each room in which the heating system is installed, the number of radiators will be different. This depends on the following parameters:
- heated volume;
- room area;
- wall insulation;
- radiator thermal power;
- the presence of window openings;
- air temperature outside during the cold season;
- the presence of adjacent rooms and an attic.
To ensure maximum heat transfer between the heating device and the wall, it is recommended to install a special heat-reflecting film. When installing radiators, you must adhere to the following rules:
- batteries must be placed on the same level;
- The radiator fins must be positioned in a strictly vertical position;
- the center of the heating equipment must coincide with the center of the window;
- The radiator length must be at least 75% of the opening length.
When performing work on installing a heating system, you need to take into account the type of material from which the communications are made. For example, connecting plastic pipes to cast iron radiators can cause a lot of trouble and ruin the heating system.
The use of polypropylene pipes in the heating system
Polypropylene heating pipes
The most popular material for coolant communications is polypropylene. Pipes made of this material provide maximum resistance to aggressive environments.
No plaque forms on their interior, and solid particles do not settle in the system. Installation of polypropylene pipes is carried out using special equipment. If they are used, you can be sure that the heating radiator piping will prevent coolant leakage.
The advantage of polypropylene pipes is the ability to create a heating circuit of any configuration. However, in this case, it must be taken into account that the longer and more complex the pipeline, the higher the heat loss.
Pipe connections can be made by soldering and using fittings (special parts for fixing). This method is less reliable than soldering, because it does not exclude the possibility of communications leakage.
Modern polypropylene pipes have a long service life (up to 40 years). They easily withstand internal pressure, and exposure to a heated coolant does not cause deformation.
There are some restrictions when installing plastic communications. They cannot be used near the boiler, and the gas supply pipe to the heating device must have a rigid connection.
During installation, do not use tow, tapes, or rubber gaskets. These warnings are for safety reasons. Before turning on the system, you must carefully check all connections.
The peculiarity of the boiler - the main element of the system - is taken into account when installing and choosing the type of communications for heating the premises. To increase the effect of its operation, various types of additional elements are used, including a circulation pump, an expansion tank and a device for regulating pressure.
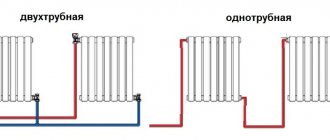
Advantages and disadvantages of single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
The main difference between the two heating schemes is that the two-pipe connection system is more efficient in operation due to the parallel arrangement of two pipes, one of which supplies the heated coolant to the radiator, and the other removes the cooled liquid.
The single-pipe system circuit is a sequential type wiring, due to which the first connected radiator receives the maximum amount of thermal energy, and each subsequent one heats up less and less.
However, efficiency is an important, but not the only criterion that you need to rely on when deciding to choose one scheme or another. Let's consider all the pros and cons of both options.
Single pipe heating system
- ease of design and installation;
- savings in materials due to the installation of only one line;
- natural circulation of coolant, possible due to high pressure.
- complex calculation of thermal and hydraulic parameters of the network;
- the difficulty of eliminating errors made during design;
- all network elements are interdependent; if one section of the network malfunctions, the entire circuit stops working;
- the number of radiators on one riser is limited;
- it is impossible to regulate the flow of coolant into a separate battery;
- high heat loss coefficient.
Two-pipe heating system
- possibility of installing a thermostat on each radiator;
- independence of operation of network elements;
- the ability to insert additional batteries into an already assembled line;
- ease of eliminating errors made at the design stage;
- to increase the volume of coolant in heating devices, there is no need to add additional sections;
- no restrictions on the length of the contour;
- coolant with the required temperature is supplied throughout the entire pipeline ring, regardless of the heating parameters.
- complex connection diagram compared to a single-pipe;
- higher consumption of materials;
- installation requires a lot of time and labor.
Thus, a two-pipe heating system is preferable in all respects. Why do the owners of apartments and houses refuse it in favor of a single-pipe scheme? Most likely, this is due to the high cost of installation and the high consumption of materials required to lay two highways at once. However, one should take into account the fact that a two-pipe system involves the use of pipes of a smaller diameter, which are cheaper, so the total cost of installing a two-pipe option will not be much more than a single-pipe one.
Owners of apartments in new buildings are lucky: in new buildings, unlike residential buildings of Soviet construction, a more efficient two-pipe heating system is increasingly used.
Choosing a location and method of installing a radiator
Options for connecting heating radiators depend on the general heating scheme in the house, the design features of heating devices and the method of laying pipes. The following methods of connecting heating radiators are common:
- Lateral (unilateral). The inlet and outlet pipes are connected on one side, with the supply located at the top. The standard method for multi-storey buildings, when the supply is made from a riser pipe. In terms of efficiency, this method is not inferior to the diagonal one.
- Lower. In this way, bimetallic radiators with a bottom connection or a steel radiator with a bottom connection are connected. The supply and return pipes are supplied from below on the left or right side of the device and are connected through the lower radiator connection unit with union nuts and shut-off valves. The union nut is screwed onto the lower radiator pipe. The advantage of this method is that the main pipes are hidden in the floor, and heating radiators with bottom connections fit harmoniously into the interior and can be installed in narrow niches.
- Diagonal. The coolant enters through the upper inlet, and the return is connected from the opposite side to the lower outlet. The optimal type of connection ensures uniform heating of the entire battery area. In this way, correctly connect a heating battery whose length exceeds 1 meter. Heat loss does not exceed 2%.
- Saddle. The supply and return are connected to the lower holes located on opposite sides. It is used primarily in single-pipe systems when no other method is possible. Heat loss as a result of poor coolant circulation in the upper part of the device reaches 15%.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=olrD9qxCAhM
WATCH THE VIDEO
When choosing a location for installation, several factors are taken into account to ensure the correct operation of heating devices. Installation is carried out in places least protected from the penetration of cold air, under window openings. It is recommended to install a battery under each window. The minimum distance from the wall is 3-5 cm, from the floor and window sill - 10-15 cm. With smaller gaps, convection worsens and the battery power drops.
Typical mistakes when choosing an installation location:
- The place for installing control valves has not been taken into account.
- A small distance to the floor and window sill prevents full air circulation, as a result of which heat transfer is reduced and the room is not heated to the set temperature.
- Instead of several batteries located under each window and creating a thermal curtain, one long radiator is chosen.
- Installation of decorative grilles and panels that prevent the normal spread of heat.
Coolant circulation methods
Coolant circulation through pipelines occurs naturally or forcedly. The natural (gravity) method does not involve the use of additional equipment. The coolant moves due to changes in the characteristics of the liquid as a result of heating. The hot coolant entering the battery, cooling, acquires greater density and mass, after which it sinks down, and a hotter coolant takes its place. Cold water from the return flow flows by gravity into the boiler and displaces the already heated liquid. For normal operation, the pipeline is installed at a slope of at least 0.5 cm per linear meter.
Scheme of coolant circulation in the system using pumping equipment
For forced supply of coolant, the installation of one or more circulation pumps is required. The pump is installed on the return pipe in front of the boiler. The heating operation in this case depends on electrical power, but has significant advantages:
- The use of small diameter pipes is allowed.
- The line can be installed in any position, vertically or horizontally.
- Requires less coolant volume.
Selection of the optimal option
The choice of the appropriate method for connecting a heating radiator in a private home directly determines the uniformity of heating, so this issue should be taken seriously. Each type of connection has its own disadvantages and advantages:
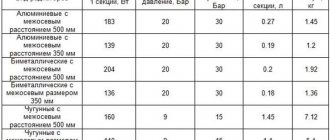
Diagonal connection of a heating radiator - the input is connected to the top hole of the battery, and the return - to the opposite bottom. This scheme most effectively ensures that heat is evenly distributed throughout the radiator. It can be used when it is planned to install equipment with a significant number of sections. The level is 2%.
One-way - the input is connected to the hole located at the top, and the return - to the bottom, located on the same side. This option is suitable for apartments, but is rare in private houses. The pipeline there, as a rule, is single-pipe, located in one of the corners, and only one battery needs to be connected. This method is aesthetic and can be used to save material.
Saddle - the supply pipe is connected to the lower hole, and the outlet pipe is connected to the lower one, located on the opposite side. This scheme for installing heating radiators in private homes is not very common, since it has low efficiency. The level of heat loss in this case is about 15%. It is usually used when the pipeline is hidden in the thickness of the wall. Then you have to remove the bends and connect them to the pipes.
Bottom - entry and exit are performed at one point. This option is optimal when the pipes are hidden under baseboards, hidden in the wall or located in the floor. This heating radiator connection scheme is only suitable for panel or steel devices in private homes. In principle, bimetallic units that are monolithic can also be connected in this way. But it also has a significant drawback - significant heat loss, amounting to about 20%.
Video instruction with advice from a specialist
Hello! I have the following problems with heat: 1) In the corner apartment in the children's room there are two supply and return pipes. The supply pipe is fiery and the return pipe is several times colder. The radiators are connected to the return line, is this correct or not? Can I connect radiators in addition to the supply and run them along a cold street wall? 2) There is no radiator or pipe in the toilet at all, although the wall is also cold (outdoor). 3) In the bedroom there is only a pipe (return) with a radiator battery connected to it, and through the wall in our kitchen there is a supply. Is it possible to somehow combine two rooms and install them in two rooms with a supply pipe?
In our 9-story building, the heating system is built like this: one supply pipe goes from bottom to top. Radiators are connected to it on all floors in parallel with jumpers. The coolant enters the radiator from below, and the upper outlet from the radiator is connected to the same pipe. Only part of the radiator warms up. How to properly connect a radiator so that it warms up completely?
Good afternoon. The nine-story building has a two-pipe heating system in every room. In one room, the heating supply pipe runs upstairs past all the radiators. Accordingly, all the radiators from the ninth floor are connected to the return line, and my battery on the second floor is generally almost cold. Tell me whether this connection is natural, or is it just a mistake made by the mechanics?
Hello! Please tell me how correct your data is in determining an effective method for connecting a radiator? And what sources can you refer to to obtain the above data? Thanks in advance everyone!
Embed the valve into the jumper (which is not entirely legal if there are valves on the radiator) or reconnect the radiator in a diagonal pattern. On propylene it is simple and fast, compact and quite aesthetically pleasing. The top insert (outlet) is transferred instead of the top plug opposite. Do not forget that the thread direction of the plugs is mutually opposite.
Obviously, you have a single-pipe heating system in your house, in which some rooms are connected to the pressure line, and other rooms are on the return line. This is a moronic Soviet system - the return water is already cooled and cannot heat the room. But you may be fined for installing additional batteries, because... such alteration of the project is not permitted
Selection of materials
The popularity that polypropylene pipes have gained. associated with a number of their positive qualities:
- Their price is significantly lower than their metal counterparts.
- High durability due to the fact that the plastic does not rust, and there is practically no sediment deposited on it.
- Does not need painting.
However, it should be taken into account that not all types of polypropylene pipes are suitable for heating systems. The fact is that they must have a reinforcing layer that prevents significant thermal expansion of the pipeline.
Reinforced polypropylene pipe
Moreover, it is desirable that the reinforcement layer be aluminum, since fiberglass reinforcement leads to saturation of the coolant with oxygen. This in turn causes rusting of the metal surfaces of boilers and other heating supply elements. Pipes that have aluminum reinforcement and are suitable for heat supply systems are marked PN25.
Note! When choosing pipes, you should pay attention to the uniformity of their wall thickness. To do this you need to look at their cut
As for the diameter, the optimal parameter is 25 mm.
In this case, it is also necessary to purchase fittings, which include:
Single-pipe and two-pipe radiator connection diagram
Restrictions on use
Welding table for polypropylene pipelines.
With all their positive qualities, polypropylene pipes are not ideal - this must be taken into account when planning the installation of heating systems. This also applies to the choice of polymer raw materials and their qualities. According to standards, pipes can be made from several grades of polypropylene - the grade is indicated on the outer walls of the products.
To compare the properties of polypropylene pipes, a special gradation of types of polypropylene and areas of its application was introduced. It looks like this:
- PN 10 - thin-walled pipes for cold water supply and heated floors (working temperature up to 45°C, working pressure 1 MPa.
- PN 16 - for cold water supply with high pressure and central heating supply with low pressure.
- PN 20 - for hot and cold water supply pipelines (operating temperature up to 80°C, pressure 2 MPa.
- PN 25 - for central heating and hot water supply (up to 95°C), operating pressure 2.5 MPa, three-layer pipes reinforced with aluminum foil.
Installation diagram of polypropylene pipes with upper distribution circulation.
Polypropylene has a high coefficient of linear expansion: when exposed to high temperatures, pipes stretch and increase in diameter.
Scheme of a polypropylene pipeline with temperature compensators.
If the pipeline is designed for cold liquid, the effect is not visible. At temperatures up to 45°C - also. However, at high temperatures and there is no room for expansion, the pipe may rupture or damage the outer lining. This must also be remembered when installing pipelines outdoors - in winter, pipes can shrink, which will lead to their ruptures and damage to fittings.
There is one reliable method of preventing such consequences - the implementation of compensation loops. You can make them yourself by creating loose U-shaped sections of pipes (their frequency and size are indicated in the specifications). Many companies offer ready-made shaped products in the form of loops.
A few words need to be said about the methods of installing polypropylene. Such products can be installed in any of the following ways: hidden laying of the pipeline, open laying, laying in shafts, boxes or soil. Pipelines for water at elevated temperatures must be secured with the possibility of subsequent longitudinal displacement.
There is one reliable method of preventing such consequences - the implementation of compensation loops. You can make them yourself by creating loose U-shaped sections of pipes (their frequency and size are indicated in the specifications). Many companies offer ready-made shaped products in the form of loops.
Where to put radiators
Traditionally, heating radiators are placed under windows, and this is no accident. The rising flow of warm air cuts off the cold air that comes from the windows. In addition, warm air heats the glass, preventing condensation from forming on it. Only for this it is necessary that the radiator occupies at least 70% of the width of the window opening. This is the only way the window will not fog up. Therefore, when choosing the power of radiators, select it so that the width of the entire heating battery is not less than the specified value.
How to place a radiator under a window
In addition, it is necessary to correctly select the height of the radiator and the location for its placement under the window. It must be placed so that the distance to the floor is around 8-12 cm. If you lower it lower, it will be inconvenient to clean, if you raise it higher, your feet will be cold. The distance to the window sill is also regulated - it should be 10-12 cm. In this case, warm air will freely go around the obstacle - the window sill - and rise along the window glass.
And the last distance that must be maintained when connecting heating radiators is the distance to the wall. It should be 3-5 cm. In this case, rising currents of warm air will rise along the back wall of the radiator, and the rate of heating the room will improve.
Installation
Conventionally, several stages of work can be distinguished. First, the type of heating is determined. If gas is supplied to the house, then the most ideal option would be to install two boilers: one gas, the second a spare, solid fuel or electric.
Next, you should agree on the installation of the heating system in the project documentation and begin purchasing the necessary materials, devices, and preparing tools.
Stages
Briefly, installation consists of the following points:
- a supply pipe is led upward from the boiler and connected to a compensating tank;
- a pipe from the upper line is removed from the tank, which goes to all radiators;
- a bypass (if provided) and a pump are installed;
- the return line is drawn parallel to the supply line, it is also connected to the radiators and cut into the boiler.
Boiler
For a two-pipe system, the boiler is installed first, for which a mini-boiler room is created. In most cases, this is a basement (ideally a separate room). The main requirement is good ventilation. The boiler must have free access and be located at some distance from the walls.
The floor and walls around it are lined with fire-resistant material, and the chimney is vented to the street. If necessary, a circulation pump, distribution manifold, control and measuring instruments are installed near the boiler.
Radiators
They are installed last. They are located under the windows and fixed with brackets. The recommended height from the floor is 10–12 cm, from the walls – 2-5 cm, from the window sills – 10 cm. The inlet and outlet of the battery is fixed with shut-off and control devices.
It is advisable to install temperature sensors - with their help you can monitor temperature indicators and regulate them.
We connect the heating radiator to polypropylene pipes
In the private sector, in old housing stock and in new buildings, work is currently underway to re-equip heating systems. Old heating equipment, steel and cast iron heating radiators are replaced with new devices. Modern industry produces bimetallic, steel heating devices with improved parameters and characteristics. Accordingly, in parallel, the old steel pipelines through which the coolant circulates are being replaced with new consumables. Today, polypropylene pipes are taking the lead in creating a heating circuit.
Accordingly, in view of such a large-scale modernization of heating systems, reasonable questions arise. How is a polypropylene water circuit installed at home? What does it look like to connect a heating system radiator to polypropylene reinforced pipes. Let's look in detail and consider what it means to connect polypropylene consumables to heating sources in detail.