Pipeline depressurization is an extremely undesirable phenomenon that can lead to very serious consequences.
To minimize the risk of such incidents, it is necessary to ensure that the system is sufficiently reliable before putting it into operation.
A special procedure will help you do this - pressure testing of the pipeline.
Pressure testing with air and water - what is it?
The essence of pressure testing is to fill a certain system with a closed volume - a pipeline, container, machine or mechanism - or its isolated section with a medium whose pressure is 2 - 3 times higher than the working one and almost corresponds to the maximum permissible value (the value of the test pressure for each specific case is set by the appropriate norms).
If the object passes this test, it is considered suitable for use.
Otherwise, places where the system has leaked are identified and repaired.
To create the required pressure, either a special pump for pressure testing pipelines, the so-called pressure tester, or a standard one, for example, a circulation pump in a centralized heating system, is used.
Water is usually used as a working medium, but if for one reason or another its penetration outside the tested system is unacceptable, pressure testing is carried out with air. In this case, leak locations are more difficult to detect.
Pressure testing is a fairly serious undertaking and must be carried out by a specially trained, certified employee. For municipal and industrial enterprises this rule is mandatory.
Upon completion of the procedure, a Certificate of hydropneumatic testing of the system (pressure testing of the pipeline) is signed, indicating the date, pressure value, holding time and other information.
As for private housing, the decision here is in the hands of the homeowner. Many people undertake crimping on their own, but it is still better to entrust this work to a professional.
Equipment and test frequency
Pressure testing of centralized systems is carried out by personnel using standard equipment, so it is hardly worth talking about. But not everyone probably knows about the costs of private heating and water supply. These are special pumps. There are two types - manual and electric (automatic). Manual pressure testing pumps are autonomous, the pressure is pumped up using a lever, and the created pressure is controlled using a pressure gauge built into the device. Such pumps can be used for small systems - pumping is quite difficult.
Manual crimping machine
Electric pumps for pressure testing are more complex and expensive equipment. They usually have the ability to create a certain pressure. It is set by the operator, and it is “caught up” automatically. Such equipment is purchased by companies engaged in professional crimping.
According to SNiP, hydraulic testing of heating systems must be carried out annually, before the start of the heating season. This applies to private houses too, but few people comply with this standard. At best, they check it once every 5-7 years. If you are not going to test your heating annually, then there is no point in buying a pressure tester. The cheapest manual one costs about $150, and a good one costs from $250. In principle, you can rent it (usually from companies that sell components for heating systems or from offices that rent equipment). The amount will be small - you need the device for several hours. So this is a good solution.
When is crimping necessary?
Pressure testing is performed in the following cases:
- Before putting the system into operation for the first time.
- After repairing the pipeline or replacing any of its components.
- After a long period of inactivity (a typical example is heating pressure testing after the summer season).
- If a scheduled check of the system status is provided. For example, sewerage from polymer pipelines is subjected to periodic pressure testing in order to check their integrity.
- Also, pressure testing should be carried out after flushing the pipeline, especially if aggressive chemicals that can weaken the walls of pipes and fittings were used. The same applies to sewer cleaning, since during this operation the joints of the pipelines may be damaged.
There is a special type of pressure testing that is applied to water wells. This check allows you to determine whether the perched water is getting into the wellbore from where water is drawn.
Conditions for performing crimping work
Pressure testing of the heating was carried out correctly and in full if all conditions were met during its implementation:
- During testing, no other work is allowed at the site.
- If pressure testing of the heating system and radiators is carried out by a specialist company, it must proceed in accordance with the plan agreed by the lead engineer. The instructions must contain information about the work to be done, their sequence and the equipment used.
- The presence of persons other than specialists conducting tests at the facility, turning it on and off is not allowed.
- If any work is being carried out at adjacent facilities simultaneously with testing, it is important to ensure the safety of its implementation.
A visual assessment of the operation of heating devices during their inspection should be carried out only under operating pressure conditions. Upon completion of the work, a report is drawn up confirming the tightness of the heating system.
Types of tests and timing
Pressure testing of the heated floor is carried out before pouring the concrete.
Leak testing of the heating unit is carried out in the following situations:
- In a private house, an initial check of the system is carried out at the stage of preparing the house for commissioning. Diagnostics of the pipeline in the grooves and the contours of the heated floor is carried out before sealing and pouring the screed. When the mortar has completely dried, it is recommended to conduct additional hydraulic tests to identify and eliminate possible leaks before laying expensive finishing material.
- To prepare the heating supply network for unplanned switching on, a periodic hydraulic test is carried out once a year after the end of the heating season. The check is also carried out immediately before the start of the heating season at positive ambient temperatures.
- One-time extraordinary checks of the strength and tightness of the system follow immediately after the completion of scheduled and unscheduled repair activities.
All of the above measures are diagnostic in nature and allow timely identification of problems with the heating system, leading to its shutdown and repair.
Preparatory measures for crimping
Before starting crimping work, you must perform the following steps:
- The pipeline system under test is inspected for obvious defects (missing elements, rusted areas, etc.). Identified violations are eliminated. If the system is filled with any substance that cannot be used for testing, for example, coolant in a heating system, it must be emptied.
- Next, according to the rules, the pipeline is flushed. This operation will remove scale, rust, and organic and inorganic deposits from the pipes. Flushing can be carried out in various ways, some of which require the use of a compressor. According to the rules, upon completion of this procedure, the quality of its implementation should be checked by cutting out a section 0.5 m long in an arbitrary place of the pipeline and assessing the condition of its internal surface.
- The preparatory stage ends with the installation of a check valve and a pressure gauge, if they are not part of the injection device. A check valve is necessary to retain the working medium in the system.
When testing heating systems of apartment buildings, work on preparing the heating unit is carried out separately from the entire system and after it. This is due to the fact that this unit is tested with a higher pressure value.
Why hydrotest?
As you know, the heating system is a closed circuit operating under excess pressure. Any leaks in the threaded connections of the fittings or at the connection points of radiators will lead to water leakage, flooding of premises, damage to building structures, finishing, etc. And since the system operates in winter under pressure and high temperatures of the coolant, accidents may also occur situations that threaten the life and health of people. The consequences of leaking heating systems can be very expensive and problematic in terms of eliminating them, especially in winter.
Therefore, hydraulic tests of heating and heat supply systems are mandatory measures both at the time of commissioning of the facility and at the stage of preparatory work before the heating season.
In some cases, the absence of an act on testing the building’s heat supply systems is a guaranteed refusal of the heat supply organization to release heat into the building before the start of the heating period. Therefore, the organization operating the building must be aware of the procedure for preparing networks and must have the appropriate qualifications to test heating systems. In addition, pressure testing of heating systems connected to the heating networks of a city or town is part of the heat supply contract.
The main preparatory work and testing of heating systems include the following activities:
- system pressure testing,
- flushing of pipelines.
Crimping machines, pumps for crimping pipes
First of all, the pumps used for pressure testing differ in the design of the discharge mechanism.
On this basis they are divided into the following groups:
- Piston.
- Vane-rotor.
- Membrane.
For crimping systems with a small volume, for example, heating circuits in private homes, you can purchase an inexpensive and easy-to-maintain manual crimping machine.
Using such a device, the operator will be able to pump up to 3 liters of working fluid per minute into the pipeline. For a multi-storey building, this option, of course, will be unacceptable; here you will need a crimping machine with an electric or internal combustion engine drive.
The most popular is the domestically produced manual crimping machine UGO-30, designed for a maximum pressure of 30 atm. The cylinder volume is 36 cubic meters. cm, force on the handle – 2 kg. Equipped with a 16 liter tank.
For more serious tasks, manual two-stage pumps UGO-50 (up to 50 atm) and UGI-450 (up to 450 atm) are intended.
Manual hydraulic crimping machine UGO 30
Among electric crimpers, units from the German company Rothenberger are known, for example, the self-priming model RP PRO II, which develops a pressure of 60 atm and a flow of 8 l/min. The drive power is 1.6 kW.
Ridgid products are also highly rated, for example, model 1460-E. This crimping machine develops pressure up to 40 atm.
The autonomous water supply system will operate uninterruptedly only if the pressure switch for the hydraulic accumulator is correctly configured. Let's consider the principle of operation and the procedure for adjusting the relay.
Read how to make a drainage well with your own hands here.
Who doesn't dream of a swimming pool in their country house? Such a custom-made design will be expensive, but you can save money and build a pool yourself. Here https://aquacomm.ru/vodosnabzenie/zagorodnyie-doma-v/bassejn-na-dache-svoimi-rukami.html you will find instructions for building a concrete reservoir.
Flushing the heating system (cleaning from the inside)
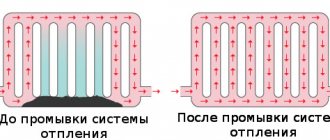
The purpose of flushing the heating is to clean the system of various types of contaminants, deposits and rust.
During operation of the heating system, various deposits arise and accumulate inside it.
This is mainly scale, which is formed due to the precipitation of mineral salts, primarily calcium and magnesium. In addition, small and large particles of rust get into the salt build-up. Over the course of many years, all these various contaminants settle on the walls of the pipeline and other elements of the heating system, reducing its performance and increasing the hydraulic resistance to coolant circulation. They also cause deterioration in heat transfer of heat exchangers, reduce operating efficiency and increase thermal energy consumption, and at the same time, naturally, the cost of servicing heating systems increases. Ultimately, the situation is fraught with an increased risk of failure of the entire heating system. The layer of contaminants and deposits can be up to 50% of the pipe cross-section.
It is not uncommon that in systems where flushing has not been done for more than 10 years, the layer of contaminants and mineral deposits makes up about 50% of the pipe cross-section, significantly reducing the functionality of the system.
Heating systems are usually flushed before pressure testing. The purpose of flushing is to clean the system of various types of contaminants: construction debris, deposits and rust. Flushing should be carried out annually, after the end of the heating season or installation work.
To thoroughly and effectively flush even an old heating system, our specialists use the following methods:
• Chemical flushing of the heating system
When chemically flushing heating, a specialist selects a cleaning agent depending on the type of contamination and pipe material. An acidic, alkaline or gentle neutral base can be used. In addition, anti-corrosion reagents are added. A special flushing liquid with chemically active substances is pumped and circulated through the heating system, dissolving internal contaminants and deposits. Its chemical composition forms a special protective layer on the internal surfaces of pipes and heat exchangers that prevents corrosion and protects against possible contamination in the future.
This method allows you to effectively get rid of scale and rust in hard-to-reach places in the heating system - heat exchangers, pipes, radiators - without disassembling the system. With annual chemical flushing, the heating system can operate for approximately 20 years without major repairs or replacement of elements. Heat consumption is reduced by 30-40%.
Professionals must pay attention to the following points:
— Correct selection of cleaning agent and reagents. Do not use acids or alkalis to flush aluminum radiators. — Taking into account the toxic properties of the flushing liquid. Work in a ventilated area, use personal protective equipment, follow safety rules. — Correct washing duration according to instructions to complete the reaction. — Rinsing with clean water and connecting the system for further operation.
• Hydropneumatic flushing of the heating system
The essence of flushing is to supply water and compressed air to the heating system using a special compressor. The water-air mixture under a pressure of 6 kgf/cm2 passes through the heating system and is discharged into the sewer system using a hose connected to the valve. Flushing is carried out first from the supply point to the return, and then in the opposite direction. The process is repeated until the outlet water is completely clarified. This method is slightly less effective, but also allows you to clean the heating system of foreign matter;
• Flushing the heating system using water hammer
In this case, a special device is connected to the system, which forces the pressure so much that the water speed reaches up to 1.5 km/sec. The resulting hydraulic shock is capable of tearing off foreign fractions and contaminants from the inner surface of the pipes and bringing them out. This method is quite effective only for small systems, since the device is capable of throwing a strong jet up to a maximum of 60 meters.
• Hydraulic flushing of the heating system
Simply, rinse with running water. Typically used in private homes as a gentle and cost-effective cleaning of heating system elements. This washing can remove dirt and pulp, but if there is a large amount of solid deposits, more effective methods will be required.
All of the above methods have their own subtleties and features, knowing which you can further increase the effect of washing. Our company has developed and applies environmentally friendly technologies that allow us to clean the internal surfaces of pipes, boilers, heat exchangers and other heat supply elements from contaminants.
The work performed by the craftsmen and engineers of our company provides guarantees of high quality flushing and confidence that the system will operate flawlessly for all the necessary time, throughout the heating season, providing homes and residents with heat and hot water all year round.
How we are working
Order service
To contents
How it's done?
The general scheme of hydropneumatic tests is as follows:
- The part of the system being tested is isolated by shutting off the shut-off or control valves (the sewer pipes are closed with rubber plugs or wooden plugs wrapped in rags).
- Next, the system is completely filled with water. In the heating system, air is released through air vents installed at the very top.
- A pressure testing pump is connected to the pipeline, which pumps a certain amount of working fluid into the system, creating the pressure required by the test regulations.
- When the required pressure is reached, the pressure tester switches off. In this case, the observer records the readings on the pressure gauge.
- The system remains under pressure for a certain period of time. The exposure time can range from 0.5 hours (for heating systems) to 6 – 8 hours.
- After the appointed time has expired, the observer takes readings from the pressure gauge again. If the pressure differs from the original value, then there is a leak in the system that should be found and repaired. After this, crimping is performed again.
Pressure testing of heating system with air
The following connection points are usually used:
- For heating systems: a special valve on one of the radiators, or a drain valve on the elevator unit (in centralized systems).
- For water supply systems: one of the connections to a cold or hot water tap.
- For the sewerage system: any of the revisions, usually installed in increments of 40 - 50 m.
If the heating system has been tested, the Hydropneumatic Test Report is signed by representatives of the heating network and the organization providing heat supply. Next, the inspector checks the coolant for hardness.
Working and pressure testing in the heating system
During the entire heating season, a certain constant pressure, called working pressure, is maintained in the heating system. During pressure testing, excess pressure is injected into the system, the magnitude of which is determined by SNiP standards.
The pressure test during hydrodynamic tests depends on the type of heating equipment and the number of floors of the building. Failure to comply with established standards can lead to damage to the system, so special attention should be paid to factors such as:
1. Type of building (residential, warehouse, administrative, industrial, etc.; 2. Number of floors; 3. Type of heating radiators used.
Table. Operating and testing pressure in the heating system (approximate data)
| Radiators and convectors | Operating pressure | Crimping |
| cast iron radiators | 9 kg/cm2 | 9 kg/cm2 |
| steel radiators and convectors | 8.5 kg/cm2 | 13 kg/cm2 |
| bimetallic radiators and convectors | 5.5 kg/cm2 | 7 kg/cm2 |
| Building | Operating pressure | Crimping |
| low-rise buildings (no higher than 3 floors) | 1.9 kg/cm2 | 3-4 kg/cm2 |
| low-rise buildings (4-5 floors) | 3-6 kg/cm2 | 6-8 kg/cm2 |
| buildings from 7 floors and above | 7-10 kg/cm2 | up to 12 kg/cm2 |
In low non-residential and residential buildings (no higher than 3 floors), the usual pressure is not higher than 1.9 atmospheres. It is regulated by a special emergency valve located in the boiler room, which is activated, preventing accidents, whenever the pressure exceeds the norm.
To contents
SNiP
Data on the procedure for performing pressure testing of pipelines, technological diagrams of this process and safety precautions are contained in the relevant sections of the following SNiPs:
- SNiP 3.05.01-85 (dedicated to internal sanitary systems).
- SNiP 41-01-2003 (outlines the issues of organizing heating, air conditioning and ventilation systems).
- SNiP 3.05.04-85 (applies to external drainage systems).
The method of pressure testing of pipelines of industrial enterprises is specified in industry standards.
Among other things, these documents establish the value of the test pressure. It depends on the material of the pipeline, the thickness of its walls (the minimum value is taken), the difference in height between the uppermost and lower elements of the system and other factors. Most often, the pressure during hydropneumatic tests is developed to the following values:
- in pressure pipelines (water supply): 10 – 15 atm.;
- cast iron sewerage: 1.5 atm.;
- non-pressure polymer pipes: 1.5 – 2 atm.;
- heating systems in apartment buildings (with cast iron radiators): 2 – 5 atm. (according to SNiP - at least 1.5 working pressure);
- input node (in centralized systems): 10 atm.;
When pressure testing a heating system in private homes, a pressure of up to 2 atm is sufficient. (there is no point in pumping higher: the emergency valve is usually set to this level).
Water hammer in heating networks and its consequences
Timely tests make it possible to identify weak points in communications and prevent a possible accident. The usual operating pressure in the heating main is 12 atmospheres. A sudden increase in permissible pressure causes a situation called water hammer.
What are the consequences of water hammer in a heating network? The moment of occurrence and spread of water hammer cannot be tracked: having suddenly formed in the heating network, it is instantly transmitted to the general heating system, including intra-house communications that are not designed for this pressure. As a result, cracks and leaks occur; in the most serious cases, an accident occurs - a rupture of a weak part in the pipeline, flooding of premises with hot water, which leads to damage to valuable property, furniture, equipment, etc. Subsequently, fungus and mold may spread on the walls and ceiling. Since the pressure in heating systems is high, an area of several tens of meters around can be flooded with boiling water. If a room is flooded with boiling water, people can also be harmed. Regular hydraulic checks and professional maintenance of the heating system help to successfully avoid such unpleasant and dangerous moments.
To contents
Price
The cost of crimping depends on several factors:
- length (internal volume) of the system;
- the age of the system and the condition of its constituent elements (amount of rust and dirt and salt deposits);
- type of equipment used.
Prices from different performers, even within the same city, may differ by 2–3 times. Private teams and craftsmen charge the cheapest for their services.
On average, for flushing and pressure testing the heating system of a building with an area of 400 sq. m (two-story) performers charge from 7 to 15 thousand rubles. As practice has shown, if you know how to bargain, you can agree to complete this amount of work for 4–5 thousand rubles. The work will be completed in 1 – 2 days.
The same work in a building of 5 thousand square meters. m (5 floors) will cost from 30 to 80 thousand rubles.
Some performers indicate prices per unit of volume (150 - 250 rubles / cubic meter) or time (500 - 1000 rubles / hour).
If you want to install the washbasin yourself, be sure to take care of connecting the water seal. Water seal for sewerage: types, purpose and installation features.
You will learn about the types of antiseptics for cesspools in this review.
How much do hydraulic tests cost?
Knowing how to pressurize a heating system, it will not be difficult for the owner of a private house to carry out the work on his own, but this solution is not optimal, especially when launching a new autonomous highway. It is better to contact a specialized company, whose master will show you all the stages of the procedure and tell you the nuances of the work.
The cost depends on the complexity of the process, the length and condition of the heating system. If the procedure is supplemented by washing, replacing metering and measuring instruments and eliminating leaks, then the service will cost more. On average, testing an apartment building will cost from $400 (from 30,000 rubles), a mansion will cost from $200 (15,000 rubles), one apartment on average from $65 (5,000 rubles).
Important! When inviting a master, the owner must receive a contract for the work, an estimate and, upon completion of the crimping, a report drawn up in the form, as well as a guarantee for all types of services provided.
Types of pumps for testing
Test activities are carried out using manual or electric pumps to build up pressure.
Manual models are equipped with pressure control devices, a tap for shutting off incoming water and a shut-off valve for draining water from a rectangular cuvette. A plunger pump is used to pump water under pressure. The main disadvantage of manual equipment is the low download speed and labor-intensive process.
The best choice would be electrical equipment. Its advantage is the high speed of filling the circuits and automatic shutdown when the required pressure is reached.
Limitation of responsibility
First, let's figure out what we will be crimping. There are several options for connecting a building to the heating network. The first, most common option is when inlet valves are installed next to the wall at the entrance from the city. With this option, the boundary of division of responsibility is considered to be the flange of the inlet valve, and the owner of the building is responsible for everything beyond (including the inlet valve). Accordingly, the heating unit and heating system of the building are pressurized.
The second option is when the heating unit is located inside the building, and an internal heating main runs through the building from the input valves to it. With this connection option, you need to clarify where the demarcation line lies. The “Heat Supply Agreement”, which is concluded between the owner and the heat supply company, will help us with this. This agreement has an annex, which indicates where the demarcation line lies.
If the delimitation boundary is considered to be inlet valves, we press three elements of the system: the internal heating main, the heating unit and the heating system. If the boundary of division of responsibility passes through the valves at the heating unit, naturally, we pressurize only the elevator (heating) unit and the heating system.
Equipment washing
It is organized before the water fittings are installed. And here it is assumed that the pipeline is completely filled with water. Next, follow the following sequence of actions.
- Shut off the valve that connects the hot water supply system to external networks.
- Hoses for discharging contaminated water into the sewer system are connected to drain valves responsible for emptying the risers.
But even after such washing there is no guarantee that all debris will be removed. Therefore, specialists are developing equipment that increases the effectiveness of this process.
Video: What is pressure testing of a heating system
What is pressure testing of a heating system?
Any similar device creates a mixture of air and hot water, which is impulsively supplied into the pipeline, which requires cleaning. When the mixture passes through the equipment, it is discharged into the sewer system. The pulsation or feed force can be easily adjusted by lengthening or shortening the time intervals.
Under what conditions is it necessary to carry out hydraulic testing of pipelines?
It is necessary to realize how complex the hydraulic testing of plumbing systems is. The reliability of the structure itself and its quality largely depend on the competence of this procedure. Therefore, the work is trusted only to specialists with the appropriate classification.
The requirements for the test work itself include several items. This is required by any technique.
- All points of use in the riser are switched on simultaneously to check efficiency. But the need at this stage is determined individually, at each enterprise separately.
- The condition of heated towel rails is tested when the hot water supply is checked.
- Temperature measurements take place only at the extreme sections of the system. Water is poured with predetermined characteristics.
- The liquid must be completely drained after completion of all stages of the activity.
- Filling of pipelines begins from the lower floors, gradually moving to the upper ones. Then the air will be properly forced out of the pipes. And there is no danger of air pockets appearing in the pipeline.
- The first stage in filling the water pipeline affects only the main section. Only at the next stages they move on to small local networks and individual risers.
- Outdoors or indoors during work the temperature should not fall below +5 degrees.
How to check for leaks
The initial stage is filling the heating circuit with water whose temperature is not lower than 5°C. Next, the pressure testing process begins - the pressure in the system is raised to the test value (Pwork × 1.5).
Considering that the decentralized system of a private home is being checked, the operating pressure here, as a rule, is no more than 0.1-0.2 MPa. This coolant pressure is provided by most modern heating boilers equipped with circulation pumps.
However, for schemes with centralized connections, the parameters are higher - up to 1.5 MPa.
Based on the operating pressure of the decentralized scheme, a test pressure value of 0.2-0.3 MPa is set. A pressure test pump will help raise the pressure in the heating circuit to such values.
You can use a small electric device, but in private households it is more advisable to use a hand pump.
The choice of such devices is extensive. For example, pressure testing pumps of the HA , RP , TR are inexpensive, simple and convenient designs, equipped with a control pressure gauge. Their market price ranges from 4,000 to 9,000 rubles.
One of the designs of an electric pump for pressure testing. This is a compact, convenient product designed to create a test pressure of up to 50 atm at a liquid supply rate of up to 7 liters per minute. Can also pump technical oil
It is irrational to use electric pumps for pressure testing heating systems assembled by hand due to their high cost. These devices are usually designed for high operating pressures, which is also not necessary when testing a decentralized system in a private home.
The only benefit for the homeowner is that there is no need to put in extra physical effort. Therefore, for those who wish to choose from pumps such as MGF , RP , “Saturn” and others. Price range 17,000 – 65,000 rub.
The priority of choosing a hand pump should also be justified by its design features. This type of equipment provides a smooth increase in pressure, which is important both in terms of safety for the tester and in terms of protecting the heating system from water hammer.
In small systems with heating boilers, water hammer can damage some elements. Therefore, a manual pressure test pump is optimal for testing small heating networks made by yourself.
The heating system pipeline is tested at a pressure exceeding the operating parameters by 0.1 MPa. The minimum pressure indicators must be at least 0.3 MPa. If within 5 min. the drop in pressure indicators does not exceed 0.02 MPa, then the system is considered operational and does not require repair
Subtleties of the testing process
Filling the system with water and subsequent pressure testing is permissible provided the indoor temperature is above zero. Heating boilers and expansion tanks are disconnected from the system during testing.
For control, two pressure gauges installed at different points are required. During pressure testing of the heating system, it is not allowed to try to eliminate defects, twist valve stems, or tap joints.
Using pressure gauges, the pressure created in the circuit is monitored in order to check the tightness of connections and the reliability of all elements. The testing process requires the inclusion of at least two control devices in the circuit
During the pressurization process, care must be taken to effectively remove air from the system. Special devices installed at different points of pipelines – air vents – help to achieve this.
If the heating circuit is not equipped with a device for releasing air, you should raise the pressure to operating pressure and then open for a short time any valve located in the heating circuit at a level higher than the others.
After air is removed, the pressure build-up continues to the test value (not less than 0.2 MPa). For small decentralized heating systems of private households, the test pressure is usually 0.2-0.3 MPa.
The liquid in the system under such pressure must be maintained for a specified time. The minimum exposure time setting is 5 minutes. If during this period there is no pressure drop of more than 0.01-0.02 MPa, in general, do-it-yourself pressure testing of the heating system can be considered successful.
After completing pressure testing of the heating circuit with test pressure, its level is reduced to working level and a visual inspection of all accessible elements of the circuit is carried out
Other important test points
Similar to the process described above, heating is pressurized with a centralized circuit. True, pressure calculations should be made taking into account the operating parameters of just such a system. After pressure testing, relieve the pressure in the heating system to the operating level and carefully check all accessible areas.
In this state, the heating circuit is visually inspected for possible leaks:
- pipelines and fittings are checked;
- installation locations of measuring instruments;
- flange connections of circulation pumps;
- heating boiler valve seals;
- shut-off valves of the expansion tank, etc.
A hydraulic test, based on the results of which no leaks were detected in the area of welds, destruction or deformation of pipelines and equipment elements, tightness violations in threaded connections, leaks in heating devices and fittings, is considered passed.
Shut-off valves (taps, valves, gate valves) are considered to have passed the hydrostatic test for integrity and tightness if, after turning the shut-off valve rod twice, no traces of water appear in the area of the stuffing box.
Pneumatic crimping method
Checking the tightness of the home heating network can be done pneumatically. It is noteworthy that the manometric technique allows testing networks and equipment at low temperatures.
Typically this test method is used to test individual thermal equipment for density. Thus, radiators, boiler heat exchangers, and expansion tanks are checked for leaks using pressurized air.
Pressure testing using the manometric method can be performed with negative thermometer readings. The tests are carried out in two stages. First, the strength of the system is tested with an excess pressure of 0.15 MPa. After eliminating the defects, if they were detected by ear, the system is again filled with a medium with a pressure of 0.10 MPa for testing
The air pressure testing process is carried out in a similar way to the hydraulic pressure testing technique. An air compressor or a conventional automobile air pump is used as a source of working fluid.
High pressures are not used here. To check for density using the manometric method, a small pressure (0.1 -0.15 MPa) is sufficient.
If leaks caused by installation defects are detected under an air pressure of 0.15 MPa, the pressure is released and the defects are eliminated. Then the process is repeated - the heating system is filled with air at a pressure of 0.1 MPa and remains in such conditions for at least 5 minutes.
We recommend: Review of the Breneran long-burning stove with a water circuit: instructions for use
Pressure control in this case allows a pressure drop of no more than 0.01 MPa over a specified period of time. With this result, the system is considered complete and ready for use.
There are often cases of the introduction of specific equipment into the heating system of a private household. It is also not always possible to check equipment using the hydrostatic method, when high pressures are required for pressure testing.
For example, SNiP and GOST provide for testing cast iron or steel radiators with a water pressure of at least 0.9 MPa (9 ATI). However, to perform the same tests using the manometric method (pneumatic), a pressure of 0.1 MPa (1 ATI) is sufficient.
Filling the heating system with air for pressure testing. A conventional air pump is used to inflate car tires.
Convector modules require water pressure testing of at least 1.5 MPa (15 kg/cm2). At the same time, if you resort to pneumatic tests, pressure testing of the convector module in order to confirm its quality guarantees is allowed with air at a pressure of 0.15 MPa.
The testing procedure for such devices is as follows:
- filling devices with air at the specified pressure;
- immersing devices in a container of water;
- check for leaks within 5 minutes.
Some technological elements of the heating circuit have a design that can be checked for integrity using the pneumatic method. You can learn about this from the recommendations for servicing the device.
Typically, instructions on crimping methods are given in the operating instructions that come with any heating equipment.
It must be emphasized: the pneumatic (manometric) method is good specifically for checking density. However, it is recommended to check the strength of a heating system, including one made by yourself, using the hydraulic method. Also, the hydrostatic crimping method is preferable for panel heating systems.
Installation of heating pipelines according to the principle of panel systems assumes that the pipeline is embedded in a panel of walls or ceilings. This requires high-quality crimping to ensure reliable operation in the future.
Checking steam and panel heating systems
Pressure testing of panel heating systems using the hydrostatic method is carried out at the installation stage, subject to full access to components and devices through the installation windows. Conditions for pressure testing, including with your own hands, imply a rise in pressure inside the system to a level of 1 MPa.
The test is carried out for a minimum of 15 minutes. During this period of time, there should not be a decrease in pressure of more than 0.01 MPa.
If the heating circuit is built taking into account the combination of heating panels with other heating devices, the test pressure value is set equal to the parameters of other heating devices.
Pressure testing of heating panel systems using the manometric method is performed under an air pressure of 0.1 MPa. Exposure time 5 minutes. The permissible pressure drop is not more than 0.01 MPa.
Individual test conditions apply to steam system piping and equipment. If steam heating is designed for an operating pressure of 0.07 MPa, the hydraulic test pressure value will be 0.25 MPa.
At operating pressures greater than 0.07 MPa, crimping is carried out under pressure P slave + 0.1 MPa, but not less than 0.3 MPa. The holding time for steam systems is 5 minutes. The permissible minus pressure difference is no more than 0.02 MPa. After completion of the tests, the circuit is additionally checked under operating steam pressure.
If, when carrying out pressure testing using the manometric method, it is difficult to determine the leakage of medium from the heating system by ear, you can lather the connecting nodes and places of possible weakening of the pipeline
Thermal testing of heating systems
In addition to hydraulic and pneumatic tests of residential heating systems, a thermal test is also provided. The essence of this procedure is to check the uniform distribution of the coolant, testing the heating and thermal output of each individual heating device.
The process is carried out under positive ambient temperatures. The coolant temperature is not lower than 60°C.
If a thermal test is possible only in the cold season (for example, due to the lack of coolant), it is performed immediately after the system is started in operating mode. Test at water temperature, which must correspond to the heating temperature schedule, but not lower than 50ºС.
The coolant pressure must correspond to the operating pressure. The thermal test takes at least 7 hours. During this period of time, the uniformity of heating of all available heating devices is periodically checked.
Before filling the grooves selected for the heating device with a solution, in addition to hydraulic or pneumatic pressure testing, thermal tests are mandatory.
How to correctly draw up a pressure test report for a heating system
To draw up an act according to all the rules, it is important to indicate in it the following:
- Test method used.
- The project according to which the installation and installation of the test object was carried out.
- Date and address of testing events.
- List of persons whose signature must be on the document. In most cases, the property owners and representatives of service organizations are indicated.
- Methods for eliminating identified defects.
- Test results.
- Presence of signs of depressurization of the system or violation of threaded connections and welds. It should also be noted that there is condensation on the surface of pipes and fittings.