As in previous years (for example, in 2022), the standard for heating hot water in the current 2022 is determined by sanitary and epidemiological requirements and is clearly outlined in SanPiN (Sanitary Rules and Norms), which in the Russian Federation have the status of a regulatory document. They establish both hygienic requirements for the quality of water supplied to citizens’ homes and temperature standards.
Boiler
Calculation procedure when calculating heat consumption
In the absence of such a device as a hot water meter, the formula for calculating heat for heating should be as follows: Q = V * (T1 - T2) / 1000. The variables in this case display values such as:
- Q in this case is the total amount of heat energy;
- V is the indicator of hot water consumption, which is measured either in tons or in cubic meters;
- T1 – temperature parameter of hot water (measured in standard degrees Celsius). In this case, it would be more appropriate to take into account the temperature that is characteristic of a certain operating pressure. This indicator has a special name - enthalpy. But in the absence of the required sensor, you can take as a basis the temperature that will be as close as possible to the enthalpy. As a rule, its average varies between 60 and 65°C;
- T2 in this formula is the temperature indicator of cold water, which is also measured in degrees Celsius. Due to the fact that getting to the pipeline with cold water is very problematic, such values are determined by constant values, which differ depending on the weather conditions outside the home. For example, in the winter season, that is, at the height of the heating season, this value is 5°C, and in the summer, when the heating circuit is turned off, it is 15°C;
- 1000 is a common coefficient that can be used to get the result in gigacalories, which is more accurate, rather than in regular calories.
Example No. 2
There is one common appliance installed in the house, and there are also individual appliances in some residential or non-residential premises. Payment for heating in the apartment will be made according to formulas No. 1 and No. 2.
Autonomous heating in the apartment
According to formula No. 1, the calculation will be made using the following method:
1.5 * 1400 = 2100 rubles
- 1.5 is the volume of heat in Gcal, which was taken from what the individual device shows;
- 1400 rubles is the tariff for payment of 1 Gcal of heat;
According to formula No. 2, the calculation is carried out in the following way:
0.025 * 75 * 1400 = 2625 rubles
- the number 75 is the area of the apartment;
- 0.025 Gcal – norm of heat consumption per 1 sq.m.
How to calculate the heating in an apartment, in this case, will depend on whether the apartment has an individual device for metering the heat consumed. The second component of the receipt will be calculated using formulas 10 and 13. The first component will be used to calculate the amount of payment for heat, and the second component will be the volume of services.
(250 – 10 -5000 * 0.25 – 8 -30) * 75 / 6000 = 0.9625 Gcal
Some unknown indicators include:
- 10 Gcal – the volume of thermal energy that was consumed in non-residential premises;
- 5000 sq. m. – total area of all apartments;
- 8 Gcal is the amount of heat that was consumed in the apartments. Data is taken from individual devices.
- 30 Gcal is the amount of heat that is needed for hot water supply if there is no centralized heating distribution in the apartment.
To calculate the cost of payment in rubles, we multiply the volume by the established heat tariff:
0.9625 * 1,400 = 1,347.50 rub.
The full payment for heating the apartment will be calculated using this method:
2,100 + 1347.50 = 3,447.50 – if the apartment’s heating system has an individual device;
2,625 + 1,347.50 = 3,972.50 rubles. – if there is no device in the apartment.
Installing a heat meter in an apartment
Example No. 1
One common device is installed in a residential building, and there are no individual devices in the premises. When deciding how to calculate heating in an apartment, we note that the payment for heating in a residential premises is carried out according to formula No. 3 of the Rules based on the readings of the individual heating meter installed in the apartment, or the heat consumption standard established for heating in residential premises type. All device readings are taken into account in Gcal.
- The volume of heat according to the data of the common house appliance was 250 Gcal.
- The total area of the house, which includes all apartments, as well as non-residential premises, is 7000 sq. m. meters.
- Apartment area – 75 sq.m. meters.
- The tariff for heat energy is 1,400 rubles. for 1 Gcal.
Heating calculations based on the area of the apartment will be made using the following scheme:
250 * 75 / 7000 * 1400 = 3750 rubles
This was the calculation of the first component of the receipt; the second component will be calculated using formulas No. 10 and No. 14. The first formula calculates the volume of the service, and the second formula calculates the amount of the fee in rubles. To determine the volume, you need to take into account the area of non-residential premises and apartments. For example, the size of the area is 6000 sq. meters.
The amount of heat will be produced by the following calculation:
250 * (1-6000 / 7000) * 75 / 6000 = 0.446428571 Gcal.
After these calculations, you can calculate the heating fee:
3750 + 625 = 4375 rub.
Installation of a heat meter in the basement of an apartment building
How to calculate how many gigalories per cubic meter. meter as an example
Measures of energy and volume are different quantities. Simple calculations will help you compare them.
Example: The coolant temperature in an apartment building should be at least 55 ⁰C, the cold water temperature should be approximately 5 ⁰C.
To heat a cubic meter you will need:
(55-5)×0.001=0.05 Gcal.
Heat losses due to imperfect thermal insulation are inevitable; losses of 20% are included in the calculations . This means that actually heating will require 0.06 Gcal.
This ratio allows the heat meter to determine the consumption of heated water.
Example: in a 100-apartment residential building, the heat meter showed 150 Gcal in the summer, when only coolant for domestic needs is consumed. In 20 apartments, hot water consumption is determined by individual meters; the total consumption for these apartments was 400 m³.
The whole house consumes: 150÷0.06=2500 m³. This means that the remaining apartments account for: 2500-400 = 2100 m³. Next, 2100 m³ is divided by the actual number of residents.
This technique allows you to convert thermal energy values into volumetric coolant flow rates and vice versa.
In houses with an open heating system, the difference in water meter readings on the supply and return pipes will indicate the amount of coolant consumed for heating and, after recalculation, the heat energy consumption.
The calculations are for reference only and serve to control the consumption of heat and water supply.
How to convert kW to Gcal/h
Key indicator for converting data from kilowatts to calories:
1 kW = 0.00086 Gcal/hour
To find out how many Gcal is obtained, you need to multiply the available number of kW by a constant value, 0.00086.
Let's look at an example. Suppose you need to convert 250 kW into calories.
250 kW x 0.00086 = 0.215 Gcal/hour.
(More accurate online calculators will show 0.214961).
To ensure 100% reliability of the heating system, a good solution would be to install an electric boiler along with a solid fuel boiler. It is quite possible to assemble such a structure with your own hands and thereby save money.
Instructions for assembling an electrolyzer with your own hands are presented here.
The heating season has arrived, but the radiators are still cold? Don’t look for ways to warm yourself, demand respect for your rights. Follow the link for information on where to call and what to do if there is no heating.
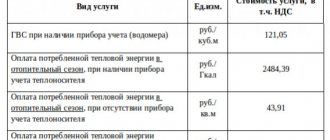
Standard thermal energy consumption for water heating
In Russia, a separate tariff has been adopted for cold water supply and hot water supply. Thermal energy consumption for heating must be paid for. The amount of payment is set in the constituent entities of the federation, because the country is large, and the cost of heating water in different regions may be different. There are certain restrictions established by the federal authorities that local governments have no right to exceed.
Thermal energy consumption rate per cubic meter
DHW (hot water supply) is paid for on several counts - the cost of a cubic meter of cold water, chemicals for cleaning, transportation to the recipient of the resource, plus the cost of wages and maintenance of the property of the supplier company. After all, the manufacturer of the product must maintain the building and equipment in order and pay employees.
Gcal standard for heating 1 m3 of water
The purpose of introducing a two-component tariff is a gradual transition to world standards, according to which calculations cannot be made for 1 m3 of hot water as the final product of production. This method of calculation is still in use, but by 2022 the cubic meter will be used according to a meter or consumption standard to account for the total volume of water used.
Using cold and hot water
The amount of heat to heat the cube is measured in Gcal (gigacalories). Calorie is the unit required to heat 1 g of water by 1 °C, under natural conditions - at normal atmospheric pressure.
To understand the value of Gcal as a unit of measurement, it is enough to understand that this volume of thermal energy for heating is enough to increase the temperature of a thousand tons of water by one degree.
The calculation of the standard for heating hot water in Gcal is legally stipulated by the “Rules for the accounting of thermal energy and coolant”, published and developed by the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of Russia back in 1995. Cold water consumption is carried out according to the meter, in cubic meters.
Standards for heating in the Tver region
The volume of thermal energy consumption is obtained by multiplying the norm established in the region for heating the cube by the water used by the consumer. Its quantity is determined by the installed meter or by regional standards.
In regions where a system of payment for hot water based on two components has not yet been introduced (for example, in the Chelyabinsk region), in 2022 they must develop a regulatory framework and switch to a generally accepted payment system. Such a measure will lead, albeit not very significant, to an increase in tariffs for hot water supplies.
Standards for heating in the Krasnoyarsk Territory
To prevent this from hitting the population’s pockets, certain measures have been taken in advance:
- In some regions of the federation, the introduction of the system was postponed, but in some places they have already come into effect on July 1, 2022.
- Average coefficients have been established for all regional entities. This is the maximum cost above which you cannot charge for hot water. They can be found in Executive Order No. 1347, dated November 12, 2022.
- There are limits that limit the powers of local governments. They are indicated in the order of the Government of the Russian Federation.
Standards in the Volgograd region
The size of the increase in tariffs for water heating varies. For example, the Government of St. Petersburg did not consider it necessary to use the figure of 6%, which is indicated in the order. 3.5% was considered a sufficient measure, which amounted to 59.45 rubles. Moscow will feel the rise in prices in different ways: Mosenergo will charge 130.27 rubles from the second half of the year. per cubic meter, and other companies - 163.36 rubles. per cube of heated water.