Few people know that the choice of a chimney system directly depends on the temperature of the exhaust gases during fuel combustion in the boiler. Ignoring this important point leads to the fact that soon after assembling the chimney, the metal pipe or brick structure crumbles, so repairs and financial costs cannot be avoided. To understand why this happens, you need to understand the operating features of gas boilers.
Important nuances
In solid fuel boilers, fuel burns at a high temperature, so the exiting gases have a high temperature (usually about 300 degrees, although the values may vary up or down). The situation is completely different with gas boilers.
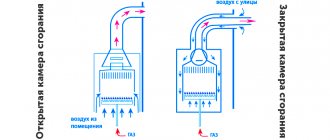
Modern gas equipment used for space heating has an important feature - the temperature of the combustion products leaving does not exceed 120 degrees, and sometimes is significantly lower than this mark. This is due to the desire of manufacturers to increase the efficiency of gas boilers. This desire also has its negative sides. The lower the temperature of the exhaust gases, the more condensate forms inside the system. Condensate contains aggressive substances and therefore has a destructive effect even on stainless steel pipes. In general, unpleasant consequences can be prevented if you take into account several important nuances.
The temperature of the exhaust gases directly depends on the radiator settings. If heating radiators heat up to a temperature of 65 degrees, the combustion products will have a low temperature. When using a heated floor system, in which the water is heated to only 35 degrees, the temperature of the gases will be even lower and there will be more condensation.
Condensation Formation
Under optimal boiler operating conditions (flue gas temperature at the inlet is 120-130°C, at the exit from the mouth of the pipe - 100-110°C) and the chimney is heated, water vapor is carried out along with the flue gases. When the temperature on the inner surface of the chimney is below the dew point temperature of the gases, water vapor cools and settles on the walls in the form of tiny droplets. If this is repeated frequently, the brickwork of the walls of the chimneys and chimneys becomes saturated with moisture and collapses, and black tar deposits appear on the outer surfaces of the chimney. In the presence of condensation, the draft sharply weakens, and a burning smell is felt in the rooms.
As the flue gases cool down in the chimneys, they decrease in volume, and water vapor, without changing in mass, gradually saturates the flue gases with moisture. The temperature at which water vapor completely saturates the volume of exhaust gases, that is, when their relative humidity is 100%, is the dew point temperature: the water vapor contained in the combustion products begins to transform into a liquid state. The dew point temperature of combustion products of various gases is 44 -61°C.
Condensation Formation
If the gases, passing through the smoke channels, are greatly cooled and lower their temperature to 40 - 50 ° C, then water vapor, formed as a result of the evaporation of water from the fuel and the combustion of hydrogen, settles on the walls of the channels and the chimney. The amount of condensate depends on the temperature of the flue gases.
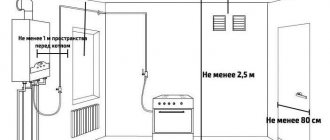
Cracks and holes in the pipe through which cold air penetrates also contribute to the cooling of gases and the formation of condensation. When the cross-section of the pipe or chimney channel is higher than required, flue gases rise through it slowly and cold outside air cools them in the pipe. The surface of the chimney walls also has a great influence on the draft force; the smoother they are, the stronger the draft. Roughness in the pipe helps reduce draft and retain soot. The formation of condensation also depends on the thickness of the chimney walls. Thick walls warm up slowly and retain heat well. Thinner walls heat up faster, but retain heat poorly, which leads to their cooling. The thickness of the brick walls of chimneys running in the internal walls of the building must be at least 120 mm (half a brick), and the thickness of the walls of smoke and ventilation ducts located in the external walls of the building must be 380 mm (one and a half bricks).
The outside air temperature has a great influence on the condensation of water vapor contained in gases. In the summer, when the temperature is relatively high, condensation on the internal surfaces of chimneys is too small, since their walls take a long time to cool, so moisture instantly evaporates from well-heated surfaces of the chimney and condensation does not form. In the winter season, when the outside temperature is negative, the walls of the chimney are greatly cooled and the condensation of water vapor increases. If the chimney is not insulated and is very cool, increased condensation of water vapor occurs on the internal surfaces of the walls of the chimney. Moisture is absorbed into the pipe walls, which causes the masonry to become damp. This poses a particular danger in winter, when frost causes ice plugs to form in the upper sections (at the mouth).
Chimney icing
It is not recommended to connect mounted gas boilers to chimneys of large cross-sections and heights: the draft weakens and increased condensation forms on the internal surfaces. The formation of condensation is also observed when boilers are connected to very high chimneys, since a significant part of the temperature of the flue gases is spent on heating a large heat absorption surface.
When choosing a chimney, consider the boiler power
When choosing a chimney system, it is necessary to take into account the power of the gas boiler . The higher the power, the higher the combustion temperature of the fuel will be. This is sure to be reflected in the escaping gases. The power value helps to choose the correct pipe diameter and length. For example, a 300 kW boiler requires a pipe with a diameter of 150 mm.
Typically, the instructions for use indicate not only the technical characteristics of the heating equipment, but also provide recommendations for the selection and installation of a chimney system. If necessary, seek help from a specialist if you yourself cannot correctly calculate the optimal parameters of the chimney pipe.
Protection of a solid fuel boiler from low-temperature corrosion
In the boiler firing mode at a coolant temperature of less than 55-65 degrees. Condensation falls from the flue gases on the surface of the heat exchanger in the boiler. Condensate mixes with fuel combustion products and gradually clogs the heat exchanger , which reduces the efficiency of the boiler. In addition, deposits contain acid, which accelerates metal corrosion and significantly reduces the service life of the boiler and chimney.
To protect the boiler from low-temperature corrosion, the temperature of the water in the return pipeline, at the entrance to the boiler, during firing, must be raised above 55-65 degrees as quickly as possible and not reduced further.
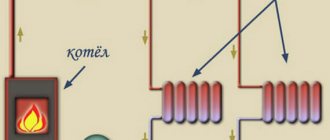
| Scheme for protecting the boiler from low-temperature corrosion. When the boiler is fired up, the coolant circulates only through the boiler circuit KK |
The boiler protection unit against low-temperature corrosion (item 6 on the heating diagram) divides the circuit into two circuits - on the boiler protection diagram, KK - boiler circuit and OK - heating circuit.
When lighting the boiler, a three-way valve directs the circulation of the coolant along the boiler circuit, past the heating devices. As a result, the coolant and boiler quickly warm up.
After the temperature of the coolant in the boiler circuit rises to more than 55-65 degrees, the three-way valve begins to gradually mix and add water from the heating circuit.
Thus, the circulation of coolant in the heating circuit begins only after the boiler circuit has quickly warmed up. The temperature of the water in the return pipeline at the entrance to the boiler, while the fuel in the boiler is burning, always remains above 55-65 degrees.
Which material should you prefer?
Nowadays, stainless steel chimneys are very popular on the market. They are used for boilers of various types, although this approach is fundamentally wrong. If you plan to install a gas boiler , you need to decide what material the chimney should be made of. Don't rush to buy metal pipes. They are excellent for solid fuel boilers, as they can easily withstand high temperatures.
For gas boilers, which are characterized by low temperatures and large amounts of condensate, it is preferable to choose plastic or polymer pipes. Their main advantage is good resistance to moisture. Because of this, they usually last longer than metal chimneys. FuranFlex pipes are excellent for gas boilers, which are characterized by excellent resistance to aggressive substances, strength and durability.
If you use a gas-wood combination boiler , you will have to abandon the use of FuranFlex. The fact is that polymer pipes are produced in two versions - for high and low temperatures (solid fuel and gas boilers, respectively). Polymer stockings cannot be used effectively at high and low temperatures at the same time.
How to calculate chimney sections
When choosing, you need to first measure the existing cross-section of the pipe. It should have the same dimensions. It is desirable that the sizes match. If the diameter is larger, a drop in pressure will occur and the traction force will decrease. It is prohibited to operate two solid fuel boilers with one chimney. Each must be equipped with a separate pipe. With the correct selection of diameter, as well as competent installation, there will always be good traction.
The cross-sectional size (sq. m) is determined by the formula:
volume of fuel consumed (m3/s) / gas velocity.
The chimney can have different cross-sectional shapes:
- Circle.
- Rectangle.
For normal operation, you can use any option, but a round section is still much preferable. When smoke moves inside the pipe, it spirals. Any foreign part in the pipe creates resistance to the movement of the gas flow.
If the inner surface of the pipe is rough, the gas velocity will decrease. When smoke, during circular movements, collides with a right angle, a sharp change in trajectory occurs, and mixing occurs. As a result, soot settles in the corners.
Constant, thorough cleaning will be required.
Features of repair work to restore the chimney
If repair of a gas boiler , or rather its chimney system, is required, the most effective solution would be to use FuranFlex technology. When installing a polymer stocking, there is no need to perform dismantling work. The FuranFlex pipe is inserted into the chimney from the inside, and after hardening it serves as support and protection. It prevents further destruction, while the material itself has excellent performance characteristics. The main thing is to choose the right type of material, but our employees are always ready to help in resolving this issue. They will advise you on all your questions.
Result
Cooling of boiler flue gases using such solutions can be quite deep - up to 30 and even 20 °C from the initial 120-130 °C.
The resulting heat is quite enough to heat water for the needs of chemical water treatment, make-up, hot water supply and even the heating network. In this case, fuel savings can reach 5÷10%, and an increase in the efficiency of the boiler unit can reach 2÷3%.
Thus, the implementation of the described technology allows solving several problems at once. This:
- the most complete and beneficial use of the heat of flue gases (as well as the latent heat of condensation of water vapor),
- reduction of NOx and SOx emissions into the atmosphere,
- obtaining an additional resource - purified water (which can be usefully used in any enterprise, for example, as a feed for heating networks and other water circuits),
- elimination of the smoke plume (it becomes barely visible or disappears completely).
Practice shows that the feasibility of using such solutions primarily depends on:
- the possibility of useful utilization of the available heat from flue gases,
- duration of use of the received thermal energy per year,
- the cost of energy resources at the enterprise,
- the presence of exceeding the maximum permissible concentration of emissions for NOx and SOx (as well as the severity of local environmental legislation),
- a method for neutralizing condensate and options for its further use.
Device and installation
When installing a metal chimney, work starts from the bottom, gradually moving upward. Pipes can be connected in several ways:
- By the movement of smoke.
- For condensate
When the boiler is connected to the chimney according to the first option, installation occurs from the boiler. The second option, on the contrary, goes to the boiler. The metal structure consists of several parts:
- Cup.
- Pipe sandwich.
- Condensate collector.
- Spark arrestor.
- Header.
- Cleaner.
To create a reliable connection, establish:
- Adapters.
- Tees.
The joints are fastened with clamps from the outside.
Temperature measurement techniques
- An ordinary household thermometer on the surface of a heating device.
- A device designed to measure temperature in a non-contact manner. Such a meter is called -.
- Alcohol thermometer.
- A special electrical device.
If you take measurements with an ordinary thermometer, you will need to add a few more degrees to the readings.
The most accurate readings can be obtained using an infrared device - a pyrometer. Its error is no more than 0.5 degrees.
To regularly monitor temperature, use only the safest device - an alcohol thermometer.
For these purposes, it is attached to the radiator using tape and wrapped in thermal insulation material.
How to use the electric version of the thermometer?
You need to take a wire with a thermocouple and attach it to the heating device. This is how the indicators are taken.
If a commission comes to your apartment to measure the temperature of the batteries, they must have a certified device.
You have the right to demand from a representative of the inspecting organization documents confirming that the equipment has passed state verification.
Very serious requirements are placed on the heating system.
The process of delivering hot coolant using circulation pumps (the rules for installation in the heating system are written here) to a residential building and distributing it evenly throughout all apartments is not an easy task.
This issue must be approached responsibly and with an understanding of all technological subtleties.
In order for the heating system to work efficiently, all its elements must function harmoniously.
This applies to all pipes and batteries. in each of the apartments of a multi-storey building.
Therefore, when replacing radiators (read how to install heating radiators in a private house in this article), you need to take into account the features and subtleties of the heating main.
If this is not done, some apartments will experience an excess of heat, while bad times will come for the residents of other apartments (they will have cold radiators).
How can we optimize the heating of urban homes?
Answer: by introducing the following standards:
The safety regulations state that the temperature of the working liquid substance in the heating main must be 20 degrees less than the temperature of self-igniting materials.
For residential multi-apartment buildings, the coolant limit has established standards - 65 - 115 degrees Celsius (this takes into account seasonality);
if the water, for some reason, overheats and reaches the reading of 105 degrees, emergency measures must be taken to prevent it from boiling;
The standard limit for water circulating through batteries is 75 degrees. In case this indicator is exceeded, a restrictive structure must be installed on the battery (about methods of heating distribution in a private house is written here);
in regions located in the middle latitudes of our country, the heating season, as a rule, begins on the fifteenth of October and ends on the fifteenth of April.
In some cases, these standards may be changed.
Service providers should rely on the average daily outdoor temperature.
How does a heating regulator work?
A regulator is a device that provides automatic control and adjustment of the temperature parameters of the coolant circulating in the heating system.
It consists of the following nodes and elements:
- Computing and switching unit;
- Actuator on the coolant supply line;
- An actuator for mixing water from the return line (sometimes a three-way valve is used and then they are combined);
- Boost pump on the “cold bypass” line (not always);
- Booster pump on the supply line;
- Shut-off fittings and valves;
- Coolant supply sensor;
- Return sensor;
- Outside air temperature sensor;
- Sensor (sensors in several places) room temperature;
The last two positions can be used either together or instead of each other, depending on how the heating schedule is set.
Now let's figure out how the control processes actually occur, how the regulator works.
Main elements of the temperature control system
The coolant temperature at the outlet of the heating system (return) depends on the volume of water passing through it, since the load is relatively constant. Therefore, the regulator, covering the water supply, increases the difference between the supply and return to the required value (sensors are embedded in these pipelines), to the required value.
If, on the contrary, it is necessary to increase the flow, then a booster pump is installed into the heating system, which is also controlled by the regulator. To lower the temperature of the incoming flow, the so-called “cold bypass” is used - part of the water circulated through the system is again sent to the inlet.
Thus, by redistributing flows depending on the data collected by the sensors, the regulator ensures a strict temperature schedule for the heating system.
One of the Vailant regulator block models
Often the heating controller is combined with a DHW controller using one computing unit. The hot water regulator is much simpler in terms of control and actuators. Using a sensor on the hot water supply line, the passage of coolant through the boiler is adjusted, and the stable 50 degrees required by the standard is ensured.
How to save money on heating, and what temperature should the room be?
According to regulatory requirements, the air temperature in residential premises should be between 18 and 25 degrees Celsius. Experiment with the settings, switch modes, choose a comfortable temperature just for you.
Remember that the temperature at night is lower than during the day. In this case, it would be ideal to use programmers that will automatically regulate the operation of the gas boiler during temperature changes. This way you will save money without losing comfort.
If your house is connected to a gas main, then install a meter. This way you can accurately control fuel consumption and pay only for the volume consumed, and not according to the standard.
Which boiler to choose?
Chimneys for solid fuel boilers differ in several ways.
- Main (pipe risers standing on a separate foundation, connected to the boiler by an inclined gas duct).
- Mounted (installed directly above the boiler and serve as a continuation of the boiler flue).
- In the form of a channel in the wall (built during the process of laying load-bearing external or internal walls).
Depending on their location, boilers can be external or internal:
- External (mounted outside the building as free-standing or attached to an external wall in a radical design).
- Internal (mounted inside a building in any design).
Note! The operation of two or more solid fuel boilers on a common chimney is not allowed.
- metal (ferrous, galvanized, stainless or sandwich pipes);
- brick (ceramic or fireproof);
- ceramics (ceramic pipes and blocks);
- concrete (prefabricated reinforced concrete panels with special vertical channels of round or oval cross-section);
- asbestos cement (pipes made of asbestos cement);
- glass (special fire-resistant glass).
The most common ones when installing individual boiler rooms with solid fuel boilers are chimneys made of brick, ceramics and steel:
| Brick chimneys | Clay and refractory bricks are traditionally used in the construction of chimneys. Requires special masonry skills. | the ability to build them into an array of walls without taking up useful space in the room. |
Due to partial utilization of useful energy (t = 250-3000), additional heat radiation occurs in the rooms adjacent to the chimneys.
not subject to corrosion,
durability, do not require additional insulation.
Fire safety technology
It is allowed to install a chimney in accordance with the requirements:
SNiP 2.04.05–91U.
DBN B 2.5-20–200.
NAPB A.01.001–2004.
Installation should only be carried out by professionals. The cross-section of the chimney must correspond to the value specified by the manufacturer in the instructions supplied with the boiler.
The required chimney height is usually recommended by the manufacturer, or it must exceed 5 meters.
If there is a horizontal section, its length should not exceed one meter.
The design must provide for the possibility of draining condensate, as well as cleaning the smoke exhaust channel.
How to connect a chimney
All connections of parts to the nozzle of a solid fuel boiler are made with a heat-resistant sealant that can withstand temperatures in the range of 1250-1500 degrees.
When the diameter of the chimney does not match the size of the chimney outlet, an adapter is installed to create a tight joint.
How the parts are assembled
Any single-walled, as well as sandwich, with insulation, are assembled in only one option: “pipe is inserted into pipe.” The connection points of the chimney parts do not require the installation of additional clamps.
If the structure is made of special stainless steel, assembly is carried out only using condensate. In this case, condensate, as well as the resulting tar deposits, will never get out; they will flow along the walls of the pipe directly into the condensate drain.
If a revision is used in the chimney and tees are installed, all parts are assembled “according to the smoke.” The assembly of vertical parts extending from the tee is carried out “using condensate”.
If it is necessary to line the channel, the gap formed between the pipe and the channel must be more than 4 cm. It is necessary when the metal expands when heated.
To ensure that the chimney sandwich parts have a more rigid fastening, rivets are installed or screws are screwed in.
Fixing the chimney
The pipe is attached to the wall only with special materials.
The single-wall structure must be fastened with a fastening step of 1.5 meters on all vertical sections of the pipe.
If the sandwich chimney does not have a supporting structure, it is necessary to secure each element.
If the system uses a 45–87 degree tee or a 45–90 degree elbow, installation is carried out in such a way that the load on the rotating parts of these parts is completely eliminated.
If installation requires additional support, use a floor stand installed under the inspection.
When the chimney pipe is raised above the roof by more than 1.5 meters, a bracket must be installed under the brace.
Passage through floors
To make a passage through the wall of a house or its ceiling, it is necessary to use the building codes that are in force in Ukraine today.
If a sandwich chimney with insulation passes through wooden walls, a liner must be installed and another layer of thermal insulation is applied.
When a chimney pipe is installed through the roof, builders must install a special additional pipe part, the so-called “roof”. Another additional layer is created, consisting of fireproof insulating materials.
The final stage of construction
When a brick chimney is lined, its upper part is covered with an additional part - the end.
Usually the top of the pipe is covered with a baffle or a beautiful fungus.
If the building's roof covering is made of a fire-hazardous material, such as bitumen shingles, a special spark arrestor is mounted on the top of the chimney.
If a gas boiler is installed in the house, installing a deflector is strictly prohibited. According to current regulations, the upper part of the gas device pipe is always kept open.
Pipe height
This size is determined by SNiP, which sets certain parameters:
- If the roof is flat, the chimney should rise 1.2 meters above it.
- If the chimney is located near the ridge, and the distance is less than 1.5 meters, it should rise above the ridge by 0.5 meters or more.
- When the pipe is located in the range of 1.5 - 3 meters to the ridge, it should not be below the ridge line.
- If the location of the chimney from the ridge exceeds 3 meters, its height should be on a line extending from the ridge, maintaining an angle of 10 degrees relative to the horizon line.
To determine the height of the chimney, a large number of indicators are taken into account. The parameters presented above apply only to gas equipment. To make an accurate calculation, you need to use the services of a specialized company.