Electric heating boilers are characterized by low cost, greatest comfort and ease of operation, high reliability, but heating using electricity is the most expensive.
The theoretical efficiency of all modern electric boilers is approximately 99%, that is, at maximum load, a boiler producing 9 kW of thermal energy will consume 9.091 kW of electricity. However, the efficiency of, for example, heating element electric boilers depends on the hardness of the water and the formation of scale on the heating element, so over time it can decrease to 90, 80 or even 70%. Then, more electricity will be required to heat the water to the same operating temperature.
Therefore, the efficiency of an electric boiler, first of all, depends on the principle of its operation, as well as the functionality of the control of the electric boiler: modulated power, scheduling modes, the ability to configure operation for periods of cheaper night tariffs.
What are electric energy-saving heating boilers?
Why are they needed and how are they used?
If it is possible to connect to a gas main, you should choose a gas boiler without hesitation. Otherwise, electric boilers can be used as the main heating equipment, or as an additional one, for example, in conjunction with solid fuel or liquid fuel. Then the simplest low-power boilers with a thermal power of 3-6 kW are used. This power is enough to temporarily (up to 2-3 days) retain heat in a house with an area of up to 100-120 m2.
This is what the VIN-3 induction electric boiler looks like. A compact dark case with floor mounting instead of the usual wall-mounted rectangle.
The simplest low-power models cost between 11-13 thousand rubles.
As a main one, even the most economical electric boiler can be used in a private house with an area of up to 100 m2. The best and most effective option is temporary heating of a country house when the owners come only on weekends or during vacation.
The cost of electric boilers is extremely low compared to other types, they are easy to install (there is no need for ventilation or a chimney), electric boilers do not require attention or particularly careful maintenance. The cost of electricity consumed during such irregular use will be covered for a long time by the low initial price of the electric boiler. If the heating system is not drained of coolant, it becomes practically autonomous.
Design and principle of operation
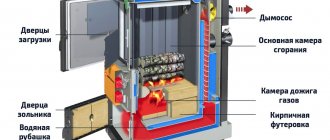
Electric boilers, unlike other types, have a fairly simple design. A heating element (heating element, electrodes or induction coil) is placed in a steel body, which heats the coolant according to the flow principle. The coolant can circulate naturally or forcedly (using a circulation pump).
Let's look at the principle of operation and the effect on energy consumption in more detail for each type:
- Heating elements (rheostatic) electric boilers. Modern models use steel heating elements (tubular electric heaters), most often in pairs for greater power and heating speed. New electric heating boilers are more powerful, have the usual square body with a wall mount, which houses other elements of the heating system: a circulation pump, a safety valve and a pressure sensor, automation and a control panel.
Construction of a standard heating element electric boiler.
They are also equipped with the greatest functionality: modulated power, various operating modes, weekly planning, and the ability to connect a room thermostat. However, serious disadvantages of heating electric boilers are the formation of scale and the dependence of their efficiency on the hardness of the water and the thickness of that same scale. They can only be called economical when using extremely pure soft coolant and the additional presence of softening filters. - Ionic (electrode). Electrodes fixed at a certain distance from each other are used as a heating element. Alternating current changes their polarity (50 times per second at a standard frequency of 50 Hz), as a result of which the water ions between them are in constant motion, their temperature rises.
A visual principle of operation of an electrode heating boiler.
Electrode boilers are increasingly in demand and are the most economical; scale does not form on the heating elements, which has a positive effect on their durability and stable efficiency. In addition, such boilers are absolutely safe and do not require intervention even after power outages, since heating of the liquid between the electrodes begins immediately after electricity is supplied to them.Is it worth using electrode boilers for heating a private house?
- Induction (vortex). An induction coil is used as a heating element, the magnetic field of which heats the core located inside it (most often a steel pipe). Thermal energy from the heated core is transferred to the coolant flowing through it. With this heating method, virtually no scale is formed, and the coolant heats up 1.5-2 times faster.
Operating principle of induction electric boilers.
Typically, induction boilers are equipped with modern advanced automation that can provide the most economical heating mode. However, they are not so in demand due to their high cost, comparable to models of wall-mounted gas boilers.
Are induction electric boilers justified in the heating system of a private home?
conclusions
Electric boilers are considered a good alternative to gas and solid fuel units. The equipment is used as the main or additional source of space heating, and can also provide hot water supply.
When choosing, take into account the characteristics, functions and power of the device in order to purchase the most suitable model. For example, a 1 kW electric boiler can heat 10-12 m².
You may be interested in knowing what an electric boiler is.
Reviews of economical household electric boilers: advantages and disadvantages
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Compact sizes. Models with a steel square case are much smaller than gas models. Electrode boilers can be slightly larger than the main heating system in the house. | High energy consumption and, as a result, the most expensive heating costs. Therefore, even the most energy-saving boilers can hardly be called economical. According to practice and reviews from owners, heating even a small house with an area of 80 m2 with electricity costs 9-12 thousand rubles. per month. To use cheap night rates, you need an appropriate meter. |
| High efficiency and heating rate of coolant | Models with a power of more than 5-6 kW require a three-phase power supply (380 V). |
| Easy to install and operate. You can install an electric boiler without any special skills; moreover, it does not require a chimney, ventilation system, or boiler room. Operation and maintenance require minimal attention. | When used as the main heating equipment, it is completely dependent on power supply. For stable operation in domestic conditions, a stabilizer and a UPS or generator are desirable |
| Electric boilers are absolutely environmentally friendly because, unlike other types, they do not emit any substances during operation | Powerful models create a significant load on the electrical network of the house. Therefore, they require high-quality and serviceable wiring. |
| Absolutely silent operation | |
| Availability of both single-circuit and double-circuit models (providing heating and hot water supply). Many models can be used in underfloor heating systems. | |
| Extremely low cost of most models |
Features of operation
There are no special requirements when servicing boilers. It is enough to monitor the fluid level in the system, replenishing it if necessary (with water or antifreeze). In addition, the pressure in the system is monitored thanks to the built-in thermometer.
However, given that the devices are equipped with modern automation, the units operate automatically, with virtually no human intervention.
If sounds that are not characteristic of the equipment are observed, crackling sounds are heard from the device, or an unpleasant odor appears, it is recommended to contact a specialist after first turning off the power to the device.
How to choose an economical electric boiler
Having decided on the type of electric boiler, it is worth considering all models based on other criteria that affect efficiency.
Single-phase or three-phase power type
This is what a compact and economical full-fledged heating system with an inexpensive electrode boiler looks like.
Low-power models up to 5-6 kW inclusive can operate from a single-phase network (220-230 V). For higher power models, a single-phase network will simply not be enough. This means that the coolant will take longer to heat up to operating temperature, the heating elements will be active for a much longer time, and the economical operating mode of the automation will be disrupted.
Conversely, for low-power electric heating boilers, a single-phase network is quite sufficient; there is no need to specially re-equip the wiring to provide three-phase power.
It is also worth remembering that the installation of models with a power of over 10 kW requires approval from the Energy Supervision Services.
Automation functionality
Compact wall-mounted model Evan Comfort Class Warmos (380 V) with 3-stage power adjustment.
Simpler, less expensive models must have at least a three-stage power switch. Accordingly, more expensive models should have power smoothly modulated by a temperature sensor. Some models have factory-installed economical modes and the ability to program boiler operation by day and hour, which allows you to focus on maximum heating of the coolant at night at reduced electricity rates.
By the way, when using night tariffs, a buffer tank will be especially effective, which will allow you to use the heat accumulated during the night during the day, without turning on the boiler at all during peak and half-peak tariff periods.
The most economical and comfortable operating mode is using a room thermostat. Even the simplest models of room thermostats have many fine settings, and the boiler automation is guided not by the temperature of the coolant, but by the air temperature in the room, which is more correct.
Instructions for selecting and connecting an external thermostat to an electric boiler
Calculation of the minimum required power
To use an energy-saving electric boiler as an auxiliary heat source in houses up to 120-150 m2, models with a power of 3-6 kW are sufficient. For constant use of an electric boiler, the minimum required power must be calculated based on the heat loss of the house.
To put it simply, for an average house with 2 bricks and a ceiling height of up to 2.7 m in the climatic zone of the Moscow region, heat loss is 1 kW per hour. It is also advisable to provide a power reserve of 10-15%, and for electric boilers with heating elements - 20-30% due to scale formation and reduced efficiency.
Total, for example, for a private house with an area of 80 m2, the minimum required electric boiler power is: 8 kW + 20% = 9.6 or 10 kW.
How to calculate the required boiler power Individual calculation, formula and correction factors
Other selection criteria
- Availability of a circulation pump . Normal natural circulation of the coolant is impossible in heating circuits 30 m long or more, so it is necessary to ensure it forcibly. This is done using a circulation pump. Wall-mounted models in rectangular steel cases already come with a pump; for other models it must be purchased separately. In any case, it is important to understand that it consumes an additional 60-150 watts per hour, depending on its power.
- Single or double circuit . Electricity consumption in dual-circuit models is practically the same, since they operate on the principle of DHW priority: as soon as the hot water tap opens, it is heated from the heating circuit (without mixing). Additional power of heating elements for heating DHW is not required.
- Overheat protection . A mandatory and important criterion that ensures the safety of the boiler in case of emergency situations (leakage, automation error, circulation pump failure, etc.).
The best known manufacturers and models: characteristics and prices
heating elements new
| Photo | Manufacturer and model | power, kWt | Mains voltage | Peculiarities | price, rub. |
| Elektromash EVPM-6 | 6 | single-phase/three-phase | One of the most inexpensive heating element electric boilers. For economical reasons, it has 3 power levels. | 1 900 | |
| ZOTA 9 Economy | 9 | three-phase | Well-known and reliable. Has 3 stages of power adjustment. It is possible to connect a room control panel with more precise adjustments. | 10 300 | |
| Protherm Skat 12KR 13 | 12 | three-phase | One of the best heating element energy-saving electric boilers for heating a private home. Equipped with 6-step power control and smart automation, the ability to connect a room thermostat and heated floors. The heat exchanger is additionally thermally insulated. There is auto-diagnosis, overheating protection, frost prevention mode, safety valve, air vent, pump blocking protection. | 34 000 |
Ionic
| Photo | Manufacturer and model | power, kWt | Mains voltage | Peculiarities | price, rub. |
| Galan OCHAG-5 | 5 | single-phase | One of the best energy-saving electric boilers for heating a private home. It has compact dimensions and functional, economical automation. It is possible to connect a room thermostat. | 4 100 | |
| Beryl-12 Ion | 12 | three-phase | Model from a famous Latvian manufacturer. The heating element has low inertia, and modern automation quickly and accurately assesses the degree of heating of the coolant and further prospects, which allows saving up to 20% of electricity. | 8 500 |
Induction
| Photo | Manufacturer and model | power, kWt | Mains voltage | Peculiarities | price, rub. |
| Alternative energy VIN 3 | 3 | single-phase | Today, it is the only worthy candidate among vortex induction electric boilers. The boiler is controlled through a control panel with many fine settings, including temperature. As a coolant, you can use not only water, but also antifreeze, oil, glycerin, and ethylene glycol-based coolants. | 34 000 |
Poll: what type of electric boilers did you choose?
Rating of the TOP 20 best electric boilers
| Place | Name | Price |
| TOP 3 best electric boilers by price, quality and reliability | ||
| 1 | Protherm Skat RAY 12 KE /14 12 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | STOUT SEB-0001-000009 9 kW | Find out the price |
| 3 | Protherm Skat RAY 14 KE /14 14 kW | Find out the price |
| TOP 3 best electric boilers for 220 V (single-phase) | ||
| 1 | EVAN Warmos-IV-3.75 3.75 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | EVAN EXPERT 7.5 | Find out the price |
| 3 | Protherm Skat RAY 9 KE /14 9 kW | Find out the price |
| TOP 3 best electric boilers for 380 V (three-phase) | ||
| 1 | Protherm Skat RAY 18 KE /14 18 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | EVAN EXPERT 9 | Find out the price |
| 3 | EVAN Warmos-IV-12 12 kW | Find out the price |
| TOP 3 best electric boilers per 100 square meters | ||
| 1 | EVAN S2 12 12 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | STOUT SEB-0001-000012 12 kW | Find out the price |
| 3 | Navien EQB 12HW 12 kW | Find out the price |
| TOP 3 best electric boilers for 150 square meters | ||
| 1 | Reko 15P 15 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | STOUT SEB-0001-000014 14 kW | Find out the price |
| 3 | EVAN EPO 18 18 kW | Find out the price |
| TOP 3 best electric boilers for 50 square meters | ||
| 1 | EVAN EPO 6 6 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | EVAN Warmos-IV-5 5.1 kW | Find out the price |
| 3 | Reco 7P 7 kW | Find out the price |
| TOP 2 best double-circuit electric boilers | ||
| 1 | ACV E-Tech S 160 Mono 14.4 kW | Find out the price |
| 2 | Savitr Premium Plus 21 21 kW | Find out the price |