General calculations
It is necessary to determine the total heating capacity so that the power of the heating boiler is sufficient for high-quality heating of all rooms. Exceeding the permissible volume can lead to increased wear of the heating device, as well as significant energy consumption.
Boiler
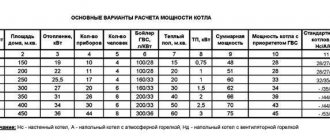
Calculating the power of the heating unit allows you to determine the boiler capacity indicator. To do this, it is enough to take as a basis the ratio in which 1 kW of thermal energy is enough to effectively heat 10 m2 of living space. This ratio is fair in the presence of ceilings whose height is no more than 3 meters.
As soon as the boiler power indicator becomes known, it is enough to find a suitable unit in a specialized store. Each manufacturer indicates the volume of equipment in the passport data.
Therefore, if the correct power calculation is performed, there will be no problems with determining the required volume.
Pipes
To determine the sufficient volume of water in the pipes, it is necessary to calculate the cross-section of the pipeline according to the formula - S = π × R2, where:
- S – cross section;
- π is a constant equal to 3.14;
- R is the inner radius of the pipes.
Expansion tank
You can determine what capacity the expansion tank should have by having data on the coefficient of thermal expansion of the coolant. For water this indicator is 0.034 when heated to 85 °C.
When performing the calculation, it is enough to use the formula: V-tank = (V system × K) / D, where:
- V-tank - the required volume of the expansion tank;
- V-syst - the total volume of liquid in the remaining elements of the heating system;
- K – expansion coefficient;
- D – efficiency of the expansion tank (indicated in the technical documentation).
Radiators
Currently, there is a wide variety of individual types of radiators for heating systems. In addition to functional differences, they all have different heights.
To calculate the volume of working fluid in radiators, you must first count their number. Then multiply this amount by the volume of one section.
You can find out the volume of one radiator using the data from the product technical data sheet. In the absence of such information, you can navigate according to average parameters:
- cast iron - 1.5 liters per section;
- bimetallic - 0.2-0.3 l per section;
- aluminum - 0.4 l per section.
The following example will help you understand how to correctly calculate the value. Let's say there are 5 radiators made of aluminum. Each heating element contains 6 sections. We make the calculation: 5 × 6 × 0.4 = 12 liters.
Specific calculations
Let's say you need to make a calculation for a household with an area of 150 square meters. m. If we assume that 100 watts of heat are lost per 1 square meter, we get: 150x100 = 15 kW of heat loss.
How does this value relate to the circulation pump? With heat losses, there is a constant consumption of thermal energy. To maintain the temperature in the room, more energy is required than to compensate for it.
To calculate a circulation pump for a heating system, you should understand what its functions are. This device performs the following tasks:
- create a water pressure sufficient to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the system components;
- pump through pipes and radiators the volume of hot water required to effectively warm up the household.
That is, in order for the system to work, you need to adjust the thermal energy to the radiator. And this function is performed by the circulation pump. It is this that stimulates the supply of coolant to heating devices.
The next task: how much water, heated to the required temperature, must be delivered to the radiators over a certain period of time, while compensating for all heat loss? The answer is expressed in the amount of coolant pumped per unit time. This will be called the power that the circulation pump has. And vice versa: you can determine the approximate coolant flow rate based on the pump power.
Data needed for this:
- The amount of thermal energy required to compensate for heat loss. For this household with an area of 150 sq. meters this figure is 15 kW.
- The specific heat capacity of water, which acts as a coolant, is 4200 J per 1 kilogram of water, for every degree of temperature.
- Temperature delta between the water supply from the boiler and the last section of the return pipeline.
It is believed that under normal conditions this last value does not exceed 20 degrees. On average they take 15 degrees.
The formula for calculating the pump is as follows: G/(cx(T1-T2))= Q
- Q is the coolant consumption in the heating system. So much liquid at a certain temperature must be delivered to the circulation pump to the heating devices per unit of time in order for heat loss to be compensated. It is not advisable to purchase a device that has more power. This will only lead to increased electricity consumption.
- G - heat loss at home;
- T2 is the temperature of the coolant flowing from the boiler heat exchanger. This is exactly the temperature level that is needed to heat the room (about 80 degrees);
- T1 - temperature of the coolant in the return pipeline at the entrance to the boiler (most often 60 degrees);
- c is the specific heat capacity of water (4200 Joules per kg).
When calculated using the above formula, the figure is 2.4 kg/s.
Now we need to translate this indicator into the language of circulation pump manufacturers.
1 kilogram of water corresponds to 1 cubic decimeter. One cubic meter is equal to 1000 cubic decimeters.
It turns out that the pump pumps the following volume of water per second:
2.4/1000=0.0024 cubic meters m.
Next you need to convert seconds to hours:
0.0024x3600=8.64 cubic meters m/h.
How to calculate the cost of heating in an apartment?
The calculation algorithm is completely determined by the method of heating the house and the available heating devices. Options for equipping buildings with accounting devices can be completely different:
- Only one meter is installed for the entire house, and individual apartments and non-residential premises are not equipped with metering devices.
- There is a common meter, but some apartments and premises are also equipped with individual devices.
- There is no meter in the house, but some apartments have metering devices.
Before you begin calculating heating, you need to find out which method of metering gas consumption is used in the house. Without this information, further actions are simply impossible.
How to calculate the heating fee in an apartment using a meter common to the entire house?
In order for our calculations to be clear, it is necessary to take some data as an example. Let's say that the meter in the house showed consumption of 300 Gcal. The area of the multi-storey building itself is 8500 m². The apartment taken into account has an area of 80 m². Let’s take the tariff for consumed electricity to be 1,500 rubles/1 Gcal.
First, we’ll find out how to calculate heating based on the area of an apartment; for this we’ll use the following scheme: (300*80/8500)*1500 =4235 rubles
. This amount will appear first on the receipt, since it is the payment for heating in the apartment.
However, let’s not forget about non-residential premises, the heating costs of which are distributed among the residents. Let's assume that the living area is 7000 m². Then the calculations will be as follows: 300*(1-7000/8500)*80/7000=0.6051 Gcal
.
Convert into monetary equivalent: 0.6051*1500=908 rubles.
The total amount of the receipt in this case will be: 4235+908=5143 rubles.
How to calculate heating according to the meter in an apartment?
Let's imagine that some apartments, as well as non-residential premises, are equipped with meters. According to available metering devices, 15 Gcal were spent on heating non-residential areas, and 10 Gcal for other apartments. The needs of hot water supply accounted for 40 Gcal.
First, let's find out how much heat fell on our square meters:
- If you have a meter, take readings and multiply by the current tariff: 2*1500=3000 rubles.
- in the absence of a meter, the rate of heat consumption per 1 m² is taken into account, which is 0.03 Gcal: 0.03 * 80 * 1500 = 3600 rubles.
Now you need to find out what amount will be added. The following scheme will help us with this: ( 300-15-7000*0.03-10-40)*80/7000=0.2857 Gcal.
Convert to rubles:
0.2857*1500=429 rubles.
- 3000+429=3429 rub.
- 3600+429=4029 rub.
How to correctly calculate heating in an apartment without a common meter?
In this case, the presence of a metering device in the home is also of great importance. The first step is still to determine the cost of heating the apartment:
- with counter: 2*1500=3000 rub.
- without meter: 0.03*80*1500=3600 rub.
Now we need to know the amount for the needs of the house, and this requires information about the area of the common property. Let's say it is 200 m², then the calculation will be as follows: 0.03*200*80/7000=0.0686 Gcal
.
In money: 0.0686*1500=103 rubles.
The total amount of the receipt will be:
- if you have an individual device: 3000+103=3103 rub.
- in the absence of a meter in the apartment: 3600+103=3703 rubles.
As you can see from the calculations, an apartment meter significantly reduces the payment for thermal energy, so it’s worth thinking about installing an individual meter. This will not only save you money, but will also allow you to fully control the accrual process.
Dynamic parameters of the coolant
We move on to the next stage of calculations - analysis of coolant consumption. In most cases, the heating system of an apartment differs from other systems - this is due to the number of heating panels and the length of the pipeline. Pressure is used as an additional “driving force” for flow vertically through the system.
In private one- and multi-story buildings, old panel apartment buildings, high-pressure heating systems are used, which makes it possible to transport the heat-releasing substance to all sections of the branched, multi-ring heating system and raise water to the entire height (up to the 14th floor) of the building.
On the contrary, an ordinary 2- or 3-room apartment with autonomous heating does not have such a variety of rings and branches of the system; it includes no more than three circuits.
This means that the coolant is transported using the natural process of water flow. But you can also use circulation pumps; heating is provided by a gas/electric boiler.
We recommend using a circulation pump for heating rooms larger than 100 m2. The pump can be installed either before or after the boiler, but usually it is installed on the “return” - lower fluid temperature, less airiness, longer pump life
Specialists in the field of design and installation of heating systems define two main approaches in terms of calculating the volume of coolant:
- According to the actual capacity of the system. Without exception, all volumes of cavities where the flow of hot water will flow are summed up: the sum of individual sections of pipes, sections of radiators, etc. But this is a rather labor-intensive option.
- According to boiler power. Here the opinions of experts differ greatly, some say 10, others 15 liters per unit of boiler power.
From a pragmatic point of view, you need to take into account the fact that probably the heating system will not only supply hot water for the room, but also heat water for the bath/shower, washbasin, sink and dryer, and maybe for a hydromassage or jacuzzi. This option is simpler.
Therefore, in this case, we recommend setting 13.5 liters per unit of power. Multiplying this number by the boiler power (8.08 kW) we obtain the estimated volume of water mass - 109.08 liters.
The calculated coolant velocity in the system is precisely the parameter that allows you to select a certain pipe diameter for the heating system.
It is calculated using the following formula:
V = (0.86*W*k)/t-to,
Where:
- W – boiler power;
- t – temperature of the supplied water;
- to – water temperature in the return circuit;
- k – boiler efficiency (0.95 for a gas boiler).
Substituting the calculated data into the formula, we have: (0.86 * 8080 * 0.95)/80-60 = 6601.36/20 = 330 kg/h. Thus, in one hour, 330 liters of coolant (water) move through the system, and the system capacity is about 110 liters.
Initial data for designing a heating system
To calculate heat consumption for heating, you first need a house design.
The house plan allows you to obtain almost all the initial data that is needed to determine heat loss and load on the heating system
It must contain the internal and external dimensions of each room, windows, and external doorways. Internal doors are ignored because they have no effect on heat loss.
Secondly, you will need data on the location of the house in relation to the cardinal directions and the construction area - each region has its own climatic conditions, and what is suitable for Sochi cannot be applied to Anadyr.
Thirdly, we collect information about the composition and height of the external walls and the materials from which the floor (from the room to the ground) and the ceiling (from the rooms and out) are made.
After collecting all the data, you can start working. Calculation of heat for heating can be done using formulas in one to two hours. You can, of course, use a special program from Valtec.
To calculate the heat loss of heated premises, the load on the heating system and heat transfer from heating devices, it is enough to enter only the initial data into the program. A huge number of functions make it an indispensable assistant for both the foreman and the private developer
It greatly simplifies everything and allows you to obtain all the data on heat losses and hydraulic calculations of the heating system.
How to choose a circulation pump
You can’t call your home cozy if it’s cold inside.
And it doesn’t matter what furniture, decoration or overall appearance is in the house. It all starts with heat, and it is impossible without creating a heating system.
It is not enough to buy a “sophisticated” heating unit and modern expensive radiators - first you need to think through and plan in detail a system that will maintain the optimal temperature in the room
And it doesn’t matter whether this refers to a house where people constantly live, or whether it’s a large country house, a small dacha. Without heat, the living space will not be habitable and it will not be comfortable to be in it.
To achieve a good result, you need to understand what and how to do, what nuances there are in the heating system, and how they will affect the quality of heating.
When installing an individual heating system, it is necessary to provide for all possible details of its operation. It should look like a single balanced organism, requiring a minimum of human intervention. There are no small details here - the parameter of each device is important. This may be the power of the boiler or the diameter and type of pipeline, the type and connection diagram of heating devices.
Today, not a single modern heating system can do without a circulation pump.
There are two parameters by which this device is selected:
- Q is the coolant flow rate for 60 minutes, expressed in cubic meters.
- N is the pressure indicator, which is expressed in meters.
Many technical articles and regulations, as well as device manufacturers, use the designation Q.