Despite the variety of heating equipment, solid fuel boilers are still in great demand, especially in places where gas supply is difficult, there are difficulties in organizing the storage of liquid fuel, and power outages often occur. Let's consider the principle of operation and piping diagrams of solid fuel boilers.
Connection diagram of a solid fuel boiler with a heating system
Features of solid fuel boiler operation
This heating system generates heat by burning solid fuel (wood, coal, peat, pellets). It is distinguished by its features, which directly affect its effectiveness and safety:
- Inertia. A solid fuel boiler cannot be stopped immediately. After the oxygen supply is stopped, the system continues to operate until the oxygen inside the firebox runs out, or until the fuel burns out. This can lead to overheating of the coolant and the formation of a large amount of steam. The result is destruction of the boiler body or parts of the heating system.
- Condensate. Appears when the boiler is connected directly, low-temperature coolant passes through the boiler tank. Leads to corrosion of the steel walls of the fuel tank. At the same time, when mixed with ash, it turns into a sticky mass that is difficult to clean off.
To eliminate the problems listed above, it is necessary to properly organize the boiler piping with the obligatory inclusion of a safety group in it. Let's take a closer look at why the piping of a solid fuel heating boiler is needed and the basic installation diagrams.
General installation instructions
Before purchasing a heating unit, you need to determine where it will be installed. The furnace room is designed for this, but often there is not enough free space in it, since it is occupied by an existing gas or other heater. Then the installation of a solid fuel boiler in a private house can be done behind the wall of the furnace room, in an extension. A frame made of metal structures is installed and covered with sandwich panels or profiled sheets with insulation. This option is convenient for those who plan to burn with coal; there will be no dirt inside the house.
All inexpensive solid fuel boilers for low-power homes can be placed directly on the rough floor screed. They are light in weight and do not exert vibration loads on the base, since they are not equipped with a fan or screw conveyor for feeding pellets. For units with a power of over 50 kW, it is recommended to build a concrete foundation, which should rest on the ground and compacted crushed stone bedding. The foundation is made 80-100 mm above the level of the screed, and it should not be connected to it. Foundation devices also require long-burning boilers, which have a mechanism for lifting and lowering heavy loads.
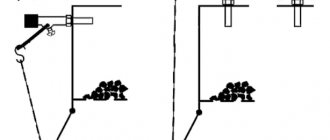
Projects for private houses usually provide for the installation of a chimney shaft in the thickness of the wall with a pipe exiting through the roof. If the shaft is missing or occupied by an existing gas heater, you will need to install a chimney for a solid fuel boiler. To do this, it is better to use metal double-walled chimneys with insulation. They are lightweight, assembled from sections of the required length and are easily attached to the wall of the house. For turns and branches, the same double-walled tees and bends are made. Methods for installing chimneys with and without an exhaust shaft can be seen in the figure.
Chimney installation
The furnace room must have natural exhaust ventilation. When heating boilers are installed in a private house, the exhaust is provided through a shaft in the wall. The shaft is parallel to the chimney, only with a smaller cross-section. If it is not available, a transfer grille is installed in the outer wall; it should be located under the ceiling of the room. The role of the hood is as follows:
- A vacuum is created in the furnace room, as a result of which fresh air from other rooms is sucked in and used for combustion. Boiler systems with a power of 50 kW and above require the organization of separate supply ventilation.
- Removing combustion products that accidentally entered the room.
The approximate layout of the equipment and the installation diagram of a solid fuel heating boiler are shown in the figure.
Solid fuel boiler installation diagram
Often in boiler rooms of country houses there is no sewerage outlet. This is not entirely correct, since sometimes it is necessary to empty the system or the water jacket of the boiler. The safety valve discharge is directed into the same drain.
Installation procedure
To perform the work, the following instructions for installing solid fuel boilers are proposed:
- Release the product from its original packaging.
- If there is not enough space in the furnace room, then it is better to assemble the product outside. Install all doors and ash pan drawer, as well as other elements supplied separately. There is no need to install a fan and automation devices; this is done after installing the boiler.
- Move the unit indoors and install it on the foundation or floor so that the gas outlet pipe is on the same axis with the chimney pipe. At home, installing a solid fuel boiler yourself must be done with an assistant; the weight of the equipment is rarely less than 50 kg.
- Secure the boiler to the foundation or screed so that there are no distortions.
- Connect the chimney, install a fan with a control unit and a safety group.
- Connect the boiler to the heating system according to the selected scheme.
Piping of a solid fuel heating boiler. Purpose. Elements
The most important purpose of the piping is to ensure efficient, safe, economical operation of the boiler. This means:
- protect equipment from overheating, sudden pressure changes, maintain the most acceptable temperature;
- control the amount of coolant in the system, remove excess liquid, excess steam;
- remove air from the system;
- distribution function - to divide the coolant between all heat consumers in the system.
The piping elements of a solid fuel boiler and their correct installation in one way or another work to ensure the safety of heating equipment. The main ones include:
- safety group (pressure gauge, air vent, safety valve);
- expansion tank;
- heat accumulator;
- three-way mixing valve.
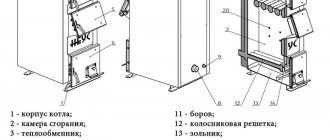
Heating boiler
Piping rules that must be followed when independently connecting a solid fuel heating system:
- to avoid the appearance of condensation, the temperature difference between the supply and return should not exceed 20 ⁰C;
- protective devices should be installed that will regulate the coolant pressure throughout the entire circuit;
- It is also recommended to include automatic devices in the piping that are responsible for regulating power and fluid temperature in the system.
These rules work best in systems with forced coolant movement. Let's briefly look at the wiring diagrams for solid fuel boilers. But before that, a few words about the safety group in the heating system.
Which boiler model is ultimately better to choose?
If you have chosen Tis boilers, the most versatile and common is Tis Pro DR. In our opinion, this is the best offer in terms of price-quality ratio. In general, there are no unsuccessful or overly prominent models in the lineup. The choice depends primarily on the budget, as well as the type of fuel and its fragmentation.
The main thing in choosing is to determine the required boiler power. For an average house in the climatic zone of the Moscow region, with a masonry of 2 bricks and a ceiling height of 2.7 m, the minimum required power of heating equipment is calculated from a simple rule: 1 kW for every 10 m2 of area. We also recommend setting aside a small margin of 15-25%.
For example, having the above-described house with an area of 150 m2, the minimum required power is 150/10 * 1.2 (20% reserve) = 18 kW.
If the house is well insulated (for example, polystyrene foam 10 cm thick) or is located in the extreme southern point of a country with a warm climate, the result can be adjusted downward by 5-30%.
How to calculate the required boiler power Individual calculation, formula and correction factors
Security group
Includes elements:
- pressure gauge (shows the pressure level in the system) - safety valve (automatically relieves pressure if it exceeds the permissible value of 2 Bar, usually triggers at 3 Bar), - automatic air vent (removes air from the coolant).
Heating scheme
It is installed on the supply pipe of the boiler itself, immediately at the outlet. It is important to remember that no locking mechanisms should be installed between the safety group and the boiler. These devices must be installed in any heating system piping circuit.
Open type with natural circulation
The simplest wiring with a minimum number of devices, complete independence from electricity. The movement of fluid through the system occurs naturally due to the general arrangement of the pipes at a slight slope. The boiler is installed half a meter below the level of the radiators. Minimum number of locking mechanisms, control devices, etc.
This type of piping is effective for a small house with a small number of heat consumers. An open type expansion tank is installed as high as possible, in the attic, for example.
In this case, the coolant temperature cannot be adjusted. And air often enters through an open expansion tank, which has a detrimental effect on the inner surface of the pipes.
Heat accumulator calculation
A container for storing thermal energy can be either purchased ready-made or made independently. But a logical question arises: how big should the tank be? After all, a small tank will not give the desired effect, and too large will cost a pretty penny. The answer to this question will help you find the calculation of the heat accumulator, but first you need to determine the initial parameters for the calculations:
- heat loss of the house or its square footage;
- duration of inactivity of the main heat source.
Let us determine the capacity of the storage tank using the example of a standard house with an area of 100 m2, which requires an amount of heat of 10 kW to heat. Let’s assume that the boiler’s net downtime is 6 hours, and the average coolant temperature in the system is 60 °C. Logically, during the period of time while the heating unit is inactive, the battery should supply 10 kW to the system every hour, for a total of 10 x 6 = 60 kW. This is the amount of energy that should be accumulated.
Since the temperature in the tank should be as high as possible, for calculations we will take a value of 90 ° C; household boilers are still incapable of anything more. The required capacity of a heat accumulator, expressed in mass of water, is calculated as follows:
- Q is the amount of accumulated thermal energy, for us it is 60 kW;
- 0.0012 kW / kg ºС is the specific heat capacity of water, in more conventional units of measurement - 4.187 kJ / kg ºС;
- Δt – difference between the maximum temperature of the coolant in the tank and the heating system, ºС.
So, the water accumulator should hold 60 / 0.0012 (90 – 60) = 1667 kg of water, which is approximately 1.7 m3 in volume. But there is one point: the calculation is made at the lowest temperature outside, which happens infrequently, excluding the northern regions. In addition, after 6 hours, the water in the tank will only cool down to 60 ºС, which means that in the absence of cold weather, the battery can be “discharged” further until the temperature drops to 40 ºС. Hence the conclusion: for a house with an area of 100 m2, a storage tank with a volume of 1.5 m3 will be enough if the boiler is inactive for 6 hours.
Closed type with natural circulation
It is also a fairly simple piping scheme with a small number of heat consumers. The scheme is very similar to the open type. It is distinguished by the inclusion of a closed expansion tank with a membrane, which is installed on the return pipe. In addition, do not forget about the security group. Some models are already equipped with it in production.
The expansion tank is designed for a volume of more than 10% of the total coolant volume.
There are several important points when lining a heating boiler with polypropylene. The pipe from the heat generator to the safety group is made of metal, then it is laid from polypropylene. Also, the section of the return pipe with an installed three-way valve and sensor is made of metal. Polypropylene has low thermal conductivity. If you install a three-way valve on it, it will respond with a delay to an increase in temperature, and the sensor will provide information incorrectly.
In general, the polypropylene piping system for a heating boiler is beneficial and quite practical.
Closed type with forced circulation
A simple circuit with a circulation pump that moves coolant throughout the system. The slope as such is no longer required to be observed. The pump, as well as a temperature sensor (controls the operation of the pump) are installed on the return line (between the expansion tank and the boiler) and connected to the electrical network.
Closed heating circuit with forced circulation
This harness is characterized by greater productivity due to the use of a temperature control device. Can be used where the power supply is stable. Otherwise, if there is a power outage, the heating system will stop.
Manifold piping with forced circulation
Circulation pump + collectors. This is a characteristic difference between the manifold piping system.
The pump moves liquid through the pipes. Collectors (so-called combs) are connected to the heating system. They are pipes with a large cross-section. They have one common input and several outputs for connecting the required number of heating elements (for example, radiators, underfloor heating system, heated towel rail). Connect to the supply and return pipes of the system.
Heating wiring diagrams
The specificity of such a connection is characterized by a separate supply of coolant to each element of the system with the same temperature and pressure. It features more efficient regulation of the heating system.
It should be taken into account that such piping will take a lot of time, effort, and material costs (high pipe consumption, financial expenses).
Harness with hydraulic arrow
The piping system uses a vertical pipe with a large cross-section - a hydraulic arrow. This element is connected to the boiler by supply and return pipes. It is installed in the same place as the collectors: after the expansion tank, in front of the heating elements (radiators, heated towel rail, etc.).
Diagram of a heating system with a hydraulic arrow
It differs from collectors in that it can be connected to the hydraulic arrow at different heights. This directly affects the temperature of the coolant, and with it the temperature of each heating element in the house. Thus, using a harness with a hydraulic arrow, you can create an optimal thermal regime for each device separately.
Do you need “holes, not a drill” - the ultimate quality solution for home heating systems?
With us, our clients comfortably implement the wisdom of “trust and verify” – without “buts”. Those executors of your plan who share your concerns and worries in such a global issue of home heating create conditions for you to comfortably control all the steps and details, so that you do not have to trust in everything, and trust grows with each stage.
You can entrust your home heating to us - we have experience and recommendations from our clients. And we are already with you – now – at the moment of searching for information. After all, it was for this step of yours that we made this site and wrote these articles for you from our experience.
Take the next step in heating installation with us - call or write to us.
Connecting a solid fuel boiler with a heat accumulator
For equipment operating on solid fuel, it is recommended to install a heat accumulator. It is a buffer tank for accumulating and then storing the heat generated by the boiler.
A very profitable device, because it allows you to increase the efficiency of solid fuel equipment and at the same time save heating material.
The wiring diagram for a solid fuel boiler with a buffer tank is as follows. The inlet and outlet pipes from the heat generator are connected to the heat accumulator, and from it to the heating elements. Now two contours are formed at once:
- between the heat buffer and the boiler;
- between the buffer and the heating devices of the house.
As the coolant passes through the heating system, it fills the buffer tank. In this case, cooled liquid from the heating elements passes below, and hot liquid from the boiler passes above. The buffer accumulates heat when the firebox is operating at full power. After the fuel burns out, the accumulated heat from the tank is released through the heating system for a certain period of time. After the storage buffer, a pump and a three-way valve are installed to adjust the temperature of the heating fluid.
The wiring diagram of a solid fuel boiler with a battery tank saves fuel, allowing you to add coal and firewood much less frequently. It must be taken into account that with such piping, the boiler power should be sufficient for heating and warming up the buffer tank.
Recommendations for choosing and connecting radiators
An ordinary homeowner, going to a heating equipment store and seeing a wide selection of different radiators there, can conclude that choosing batteries for his home is not so easy. But this is the first impression; in fact, there are not so many varieties of them:
- aluminum;
- bimetallic;
- steel panel and tubular;
- cast iron
Sectional batteries made of aluminum alloy have the best heat transfer rates; bimetallic heaters are not far behind them. The difference between the two is that the former are made entirely of alloy, while the latter have a tubular steel frame inside. This was done for the purpose of using the devices in centralized heat supply systems of high-rise buildings, where the pressure can be quite high. Therefore, installing bimetallic radiators in a private cottage makes no sense at all.
It should be noted that heating installation in a private home will be cheaper if you purchase steel panel radiators. Yes, their heat transfer rates are lower than those of aluminum ones, but in practice you are unlikely to feel the difference. As for reliability and durability, the devices will successfully serve you for at least 20 years, or even more. In turn, tubular batteries are much more expensive, in this respect they are closer to designer ones.
Steel and aluminum heating devices have one useful quality in common: they lend themselves well to automatic control using thermostatic valves. The same cannot be said about massive cast iron batteries, on which it is pointless to install such valves. This is due to the ability of cast iron to heat up for a long time and then retain heat for some time. Also because of this, the rate of heating of the premises is reduced.
If we touch on the issue of appearance aesthetics, then the cast-iron retro radiators currently offered are much more beautiful than any other batteries. But they also cost incredible amounts of money, and inexpensive Soviet-style accordions MS-140 are only suitable for a one-story country house. From the above, the conclusion suggests itself:
Wiring a solid fuel and gas boiler (electric boiler)
This harness is relevant and in demand among residents of country houses. It allows you to organize year-round comfort in the house, including several heating sources in the overall system. As a rule, steam from a gas heating boiler with a solid fuel device is installed, as well as solid fuel equipment with an electric boiler.
Solid fuel boiler+electric
The wiring diagram for gas and electric devices with wood is the same , it is quite simple, because it uses a heat accumulator at the same time as a hydraulic arrow. This allows you to efficiently supply heat to a large number of heating points at once (radiators, heated floors, boiler, heated towel rail, etc.). In this case, the heat from the gas heating boiler (electric) and wood-burning boiler charges the buffer tank, and then it supplies thermal energy to the heating end points.
There is also another option for connecting a gas heating boiler (electric boiler) and a solid fuel boiler together, without using a buffer tank, because this is quite expensive. Here the main source of heating is a wood-burning boiler, with a gas boiler as an auxiliary one.
Operating principle. After solid fuel burns out, the air temperature decreases. This detects the sensor installed in the room and immediately starts the gas boiler. When the main boiler cools down, it switches off automatically. The gas one operates until the wood-burning unit begins to process the next portion of fuel. Now, in reverse order, the room temperature sensor turns off the gas heating device.
The scheme with such a harness is simple, you can install it yourself.
Piping with connection of an indirect water heater
The wiring diagram for a solid fuel boiler with a boiler is quite common due to its cost-effectiveness and efficient operation. This is especially relevant during the heating season, when you can save a significant amount on electricity.
This piping is designed in such a way that the heated liquid is supplied simultaneously to the boiler and radiators. In this case, the boiler circuit is connected to the heat exchanger of the water heater, which heats the water indirectly.
Often, an additional method of heating liquid (gas, heating element) is installed in the boiler in case the heating is turned off (warm season).
The considered piping can be used with all heating devices with both natural and forced circulation of liquid.
Prices: summary table
| Model | Available power, kW | Peculiarities | price, rub. |
| Small | 12, 16, 20 | Reduced, lightweight, compact model, 4 mm steel | 42 000-47 500 |
| Pro DR | 17, 22, 27 | Standard model with 5 mm steel, installation of a control panel possible | 58 500-72 000 |
| Plus DR | 17, 22, 27 | Pre-installed control panel | 82 000-108 000 |
| UNI | 15, 25, 35, 45, 55, 65, 75, 85, 95 | Full-fledged automation (controller and fan) is preinstalled, a large selection of powers | 82 500-220 000 |
BoilersReviewBoiler ManufacturersSolid Fuel Boilers