I welcome my dear reader and bring to your attention an article on how to correctly calculate the chimney in your home.
The main component of comfort in the home is warmth. The owner of the house has to solve heating problems in a private house. For heating, small units are used that can be installed independently (except for gas ones), including chimneys.
To ensure complete removal of flue gases from the room, good draft and prevent draft overturning, it is necessary to comply with the requirements of regulatory documentation.
Why do you need to know the diameter?
Beginners do not understand the importance of the chimney cross-section for a stove and why it is so important to correctly calculate not only the internal size, but also the height of the pipe. When developing an individual project for an autonomous heating system for a residential or industrial premises, the level of traction and performance of the unit depends on the accuracy of the data.
Inexperienced builders can make a pipe with a large or insufficient cross-section. In any such option, the operation of the heating device is disrupted, and you are simply throwing money away. For optimal operation of the home heating system, it is important to carry out an accurate calculation and familiarize yourself with the recommendations of regulatory documents.
Important! Fire safety at home, work productivity, comfortable temperature - the solution to all these issues depends on the correct determination of the size and length of the chimney.
A couple of tips
When the house has alternative heating, it also requires a chimney. But it is unprofitable to produce different smoke exhaust systems. It is easier to combine them into one, which will connect all the channels made taking into account such parameters as equipment power, amount of smoke and type of fuel. Such structures have a number of advantageous qualities:
- they save living space;
- all systems work stably;
- time, money and labor are saved.
But only specialists can calculate such structures.
What should be the diameter of the chimney for a stove?
The size of the chimney can be calculated in several ways. The simplest one is to determine the cross-section of the chimney depending on the size of the combustion compartment. Solid fuel consumption is determined by this characteristic, and based on these data, the volume of exhaust gases can be determined.
If you have an open firebox and the chimney is made of a round steel pipe, these values should be in a ratio of 10 to 1. For example, the dimensions of the combustion chamber are 50/40. Such a stove must be equipped with a chimney with a cross-section of 180 mm.
If we make a pipe from brick, its internal size should exceed the size of the ash pan or ash door by one and a half times. The minimum size of a square cavity for gas removal is 140/140 mm.
How to calculate the cross-sectional area of a chimney?
There are several methods for calculating the optimal cross-section. For example, on the size of the combustion chamber of the hearth or on the area of the furnace blower window. But in this publication, attention will be focused on the methodology, which is based on assessing the volume of flue gases generated during the combustion process.
The combustion of wood and other solid fuels is always accompanied by very significant smoke formation. And the chimney pipe must be able to discharge these volumes outside in a timely manner.
Based on calculations and experiments, experts have long compiled tables from which information can be obtained on specific smoke production for different types of solid fuel. That is, what volume of combustion products is formed when burning, say, one kilogram of firewood, coal, peat, etc.
We will also present such a table (in an abbreviated version). In addition to the specific smoke formation, it shows the calorie content of the fuel (the amount of heat released when burning one kilogram) and the approximate temperature of the combustion products at the exit from the chimney. The first of these characteristics does not particularly interest us at a given moment - it simply gives a general idea of fuel efficiency. But the temperature, yes, will be needed for calculations.
Fuel typeSpecific caloric content of fuel, kcal/kg, averageSpecific volume of combustion products released from combustion of 1 kg, m³Recommended temperature at the chimney outlet, °C
| Firewood with an average humidity level - 25% | 3300 | 10 | 150 |
| Lump peat (in bulk), air-dried, with an average moisture level of no higher than 30% | 3000 | 10 | 130 |
| Peat - briquettes | 4000 | 11 | 130 |
| Brown coal | 4700 | 12 | 120 |
| Coal | 5200 | 17 | 110 |
| Anthracite | 7000 | 17 | 110 |
| Pellets or wood briquettes | 4800 | 9 | 150 |
As you can see, the volumes are impressive. Even types of fuel that produce minimal smoke are already about 10 cubic meters for every kilogram burned. This means, simply for reasons of physics and geometry, the cross-section of the chimney duct must be able to constantly drain these considerable volumes out.
This is why we “dance” when calculating.
Calculation methods
Exact method + formula
Calculating a chimney for a stove is not a task for beginners. It is better to entrust such work to professionals. But if you decide to calculate this parameter yourself, you will need knowledge of basic data and several formulas:
- To determine the volume of exhaust gases, it is important to know the power of the heating unit. For calculations we use the formula:, where:
- B is the combustion rate coefficient of solid fuel. This value is determined based on the data in table No. 10 of GOST 2127;
- V – level of volume of fuel burned. This value is indicated on the tag of the industrial device;
- T – heating level of exhaust gases at the exit point from the chimney. For wood stoves – 1500.
- The total area of the chimney. It is calculated based on the ratio of gas volumes, this value is designated “Vr”, and the speed of their movement in the pipeline. For a household wood-burning stove, this number is 2 m/sec.
- The diameter of a round pipe is calculated using the formula – d² = (4 * Vr) / (π * W), where W is the speed of gas movement. It is better to perform all calculations on a calculator and carefully enter all values.
Calculating the optimal amount of thrust
This operation is performed to control the calculations of the optimal height and cross-section of the chimney. This calculation can be carried out using 2 formulas. We will present the basic, but complex formula in this chapter, and we will present the basic, simple formula when performing a trial data calculation:
, Where:
- C is a constant coefficient equal to 0.034 for wood-burning stoves;
- The letter “a” is the value of atmospheric pressure. The value of natural pressure in the chimney is 4 Pa;
- The height of the chimney is indicated by the letter “h”.
- Т0 – average level of atmospheric temperatures;
- Ti is the amount of heating of the exhaust gases as they exit the pipe.
Example of calculating the cross-section of a chimney
We take as a basis:
- the potbelly stove runs on solid fuel;
- within 60 minutes, up to 10 kg of hardwood firewood burns in the stove;
- fuel moisture level – up to 25%.
Let's look at the basic formula again:
The calculation is carried out in several stages:
- We perform the action in brackets – 1+150/273. After calculations we get the number 1.55.
- We determine the cubic capacity of the exhaust gases - Vr = (10*10*1.55)/3600. After calculations, we obtain a volume equal to 0.043 m3/sec.
- The area of the chimney pipe is (4*0.043)/3.14*2. The calculation gives a value of 0.027 m2.
- We take the square root of the chimney area and calculate its diameter. It is equal to 165 mm.
Now we determine the amount of thrust using a simple formula:
- Using the formula for calculating power, we calculate this value - 10 * 3300 * 1.16. this value is equal to 32.28 kW.
- We calculate the level of heat loss for each meter of pipe. 0.34*0.196=1.730.
- The level of gas heating at the exit from the pipe. 150-(1.73*3)=144.80.
- Atmospheric gas pressure in the chimney. 3*(1.2932-0.8452)=1.34 m/sec.
Important! Using the data from your furnace, you can perform the calculation yourself, but to be on the safe side, it is better to consult with specialists. The safety of your home and the economical operation of heating devices depend on the correctness of the calculation.
Swedish calculation method
The size of a chimney for a stove can be done using this method, but the main purpose of the Swedish method is to calculate the chimneys of fireplaces with an open firebox.
In this calculation method, the size of the combustion compartment and the volume of air in it are not used. To determine the correctness of the calculation, use the following graph:
What is important here is the correspondence between the area of the combustion chamber (“F”) and the opening of the chimney (“f”). For example:
- firebox dimensions 770/350 mm. We calculate the area of the compartment - 7.7 * 3.5 = 26.95 cm2;
- chimney size 260/130 mm, pipe area – 2.6*1.3=3.38 m2;
- We calculate the ratio. (338/2695)*100=12.5%.
- We look at the value 12.5 at the bottom of the table and see that the calculation of length and diameter was made correctly. For our stove it is necessary to build a chimney 5 m high.
Let's look at another example of calculation:
- firebox 800/500 mm, its area is 40 cm2;
- chimney cross-section 200/200 mm, area 4 cm2;
- We calculate the ratio (400/4000)*100=10%.
- Using the table, we determine the length of the chimney. In our case, for a round sandwich pipe it should be 7 m.
Chimney design depending on heating configuration
Go ahead. What chimneys are installed most often today? These are brick, ceramic and insulated and non-insulated steel.
And first of all, when designing a chimney, its minimum throughput indicators are calculated. If mistakes are made here, flue gases will begin to accumulate inside the pipe and cause a lot of problems.
The general layout of the chimney looks like this:
If the temperature of the exhaust gases is low, as in modern low-temperature boilers, then so-called electric smoke exhausters are installed in the upper part of the chimney.
They are a small fan with blades. Such a device forcibly removes combustion products from the pipe, thereby increasing the traction force. And then the traction force no longer directly affects the height of the chimney, because it is achieved in a different way, and not by “catching the wind.”
If there is no additional device, then you will still have to catch the wind. And in this case, you need to build on the available power of the boiler, stove or fireplace, which can be found in the technical documentation. It is expressed in the amount of fuel that is burned in one hour of work.
If the amount of fuel volume is known, then the volume of gases is calculated using the following formula:
Vg = B∙V∙(1+t/273)/3600
The result will be in m3/s. This is the speed of gas movement in the pipe. We calculate the cross-section of the pipe using the following formula:
F = π∙d²/4
And the resulting value is determined in m2. This is the cross-sectional area of the chimney, and the diameter is calculated using the formula:
dt = √4∙B∙V∙(1+t/273)/π∙ω∙3600
The remaining characteristics are almost the same for most heating devices. Thus, the exit speed of gases in the chimney is usually no less than 2 meters per second, and the temperature of the gases at the entrance to the pipes is from 150 to 200 degrees.
Also, the standard gas pressure per 1 meter is no less than 0.4 mm H2O, or 4 Pa:
Therefore, according to SNiP, the height of the chimney from the grate must be at least 5 meters.
What to do if the chimney cross-section is square?
Cylindrical chimneys, especially after the advent of sandwich pipes, are the most common types of devices. But when building a brick kiln, you have to lay out a square or rectangular shape.
In such chimneys, turbulence is formed, which prevents the normal passage of exhaust gases and reduces draft. But for wood stoves or fireplaces, rectangular pipes remain the most popular shape. Such devices do not require an increased level of exhaust gas extraction.
The calculation of a chimney for a wood-burning stove with a square or rectangular cross-section is made taking into account the ratio of the dimensions of the pipe to the size of the blower hole on the stove. This proportion is 1/1.5, where 1 is the internal cross-section of the pipeline, and 1.5 is the dimensions of the blower or ash pan.
Alternative to stainless steel: asbestos cement
Asbestos pipes are an alternative to steel structures. But they cannot be used for all types of gas ducts. Products made from the materials in question can be used in operating conditions up to three hundred degrees.
The key advantage of asbestos-cement pipelines is their low price. The cost of these products is significantly cheaper than stainless steel pipes. However, in terms of its performance qualities it is inferior to the products discussed in this article. If you want to create a truly reliable pipeline, use stainless steel pipes.
Watch the video:
What should be the height of the chimney pipe for a stove?
Calculation of this parameter allows you to avoid the occurrence of backdraft and other possible troubles. This issue is regulated by the rules of SNiP and other documents.
Why is this parameter needed?
In order to understand the importance of this factor, let's take a closer look at several physical laws and the consequences of incorrectly made chimneys. As heated gases pass through, the temperature drops, but warm air or gases always rise.
At the outlet of the pipe, the temperature drops even more. Exhaust gases located in a pipeline with a reliable layer of thermal insulation have a high temperature and a column of heated smoke, rising upward, increases the draft in the firebox.
Let's analyze the situation - we reduce the internal cross-section of the pipe and increase the height of the pipe above the roof ridge. If you think that the volume of heated gas increases, the cooling time of the smoke increases and the draft increases, this statement is only half true. The traction will be excellent, even with a large surplus. Firewood will burn quickly and the cost of purchasing fuel will increase.
An excessive increase in the height of the chimney can cause an increase in aerodynamic turbulence and a decrease in the draft level. This is fraught with the occurrence of reverse draft and smoke escaping into living spaces.
SNiP requirements
The length of exhaust gas exhaust pipelines is regulated by the requirements of SNiP 2.04.05. the rules require compliance with several basic installation rules:
- The minimum distance from the grate in the firebox to the protective canopy on the roof is 5000 mm. Height above the level of the flat roof covering 500 mm;
- the height of the pipe above the roof slope or ridge must correspond to the recommended one. We will talk about this in a separate chapter;
- if there are buildings on a flat roof, the pipe should be higher. In this case, with a large pipe height, it is secured with braces made of wire or cable;
- if the building is equipped with a ventilation system, their height should not exceed the exhaust gas outlet hood.
Self-calculation method
How to independently calculate the height of the smoke channel, for this you will need to perform a calculation using the formula:
, Where:
- “A” – climatic and weather conditions in a given region. For the north, this coefficient is 160. You can find the value in other areas on the Internet;
- “Mi” is the mass of gases passing through the chimney in a certain time. This value can be found in the documentation of your heating device;
- “F” is the time for ash and other waste to settle on the walls of the chimney. For wood stoves the coefficient is 25, for electric units - 1;
- “Spdki”, “Sfi” – level of concentration of substances in the exhaust gas;
- “V” – exhaust gas volume level;
- “T” is the temperature difference between the air coming from the atmosphere and the exhaust gases.
Important! Independent calculation will require finding a large number of quantities and performing complex calculations. Therefore, we recommend turning to professionals.
There is no point in giving a trial calculation - the coefficients and other values will not be suitable for your unit, and extracting square roots will require downloading an engineering calculator.
Table “Height of the chimney above the ridge”
The table of the height of the chimney above the roof structure will help you determine the size of the pipes without making complex calculations. First, we will analyze the selection of pipe length for flat roofs.
| Selection of pipe length for flat roofs. | Min. pipe height in mm |
| There are no parapets or other structures or devices on the roof. | 1200. |
| A protective curb or other structures are built on the roof and the distance to them is up to 300 mm. | 1300. |
| Excess over other ventilation ducts | 500. The minimum distance to the ventilation shaft is 5000. |
| For pitched types of roof structures. | Min. pipe height in mm |
| The chimney exits to the roof at a distance of 1500 mm from the ridge. | 500. |
| The pipe is located at a distance of 1500-3000 mm from the ridge. | The pipe is brought out to the level of the roof ridge. |
| The distance from the ridge to the passage of the exhaust pipeline is over 3000 mm. | We set aside 100 from the ridge cavity. The top of the pipe should be at the level of this line. |
Checking the planned pipe for the amount of natural draft
In fact, we have already determined the main parameters of the chimney - the sufficient cross-section of its channel and height. But for devices with natural draft, it is never a bad idea to check the strength of this very draft. So that it does not happen that the constructed chimney suddenly refuses to perform its main functions.
Draft is essentially the difference in pressure between hot gases in the pipe and the outside air. It is this difference that stimulates the movement of gas flow through the chimney channel.
It is believed that for normal operation of a chimney with natural draft, this difference must be at least 4 pascals for each meter of pipe height (0.408 mm of water column or 0.03 mm of mercury). That is, for a five-meter pipe (our minimum), the thrust should be at least 20 Pa. This ensures both normal gas removal and the necessary air flow for continuous combustion of the fuel.
How to calculate this thrust. Naturally, it largely depends on the densities of gases, which, in turn, are closely related to temperature. You can verify this by looking at the formula with which we will work:
ΔP = Htr × g × Patm × (1 / TV – 1 / Tds) / 287.1
ΔP is the natural draft in the pipe, Pa.
Htr—chimney height, m.
g—gravitational acceleration (9.8 m/s²);
Patm - atmospheric pressure. A value of 750 mmHg is considered normal. However, the area for which the calculation is carried out may have its own specifics. We must understand correctly that sea level is considered the norm. And with increasing altitude, this rate begins to decrease. And quite significantly. So when making calculations you will need to be guided by the norm for your region of residence.
Atmospheric pressure is usually measured in millimeters of mercury. However, to calculate in the SI system it is necessary to convert it to pascals. This is not difficult if you know that 1 mm Hg. Art. = 133.3 Pa.
TV - outside air temperature. Moreover, reduced to the Kelvin scale, that is, C° + 273.
Tds is the average temperature of gases in the chimney. Defined as the arithmetic average of the input and output indicators, followed by conversion to the Kelvin scale.
287.1 is the gas constant of air. It would be more correct to select this value for the specific chemical composition of the exhaust gases. But in our case, the error will not be significant, greatly affecting the final result.
A few important notes on inlet and outlet temperatures
You should always strive for its optimal values. Statistics show that most fires occur with sauna stoves, into which there is practically no heat removal; the heat in the steam room builds up in a short time, and the chimney usually heats up to dangerous temperatures. Therefore, you need to be able to control the temperatures in the pipe using available means - gate valves, valves, additional heat recovery devices (for example, water heating tanks).
In household and heating stoves this is easier, but control is still necessary. In boilers, where the very essence of the work is the constant transfer of heat to the circulating coolant, these issues are not so pressing.
The 900 ÷ 600 ℃ (input and output) mode, found on some sauna stoves, is extremely dangerous in all respects, and should not even be considered! Reasonable limits (and even then their upper limit) are 600 ÷ 400 degrees for household brick and metal stoves. Usually they try to maintain it in the range of 400 ÷ 200 ℃. For gas equipment, the lower limit can fall below 100 degrees.
If all the initial values for substitution into the formula are known, you can proceed to the calculation. To do this, we again suggest using the capabilities of a special online calculator.
Requirements for the installation of a chimney for a gas boiler
- there must be good traction;
- reliability and durability;
- corrosion resistance;
- resistance of the chimney for a gas boiler to aggressive chemical environments;
- ability to withstand high temperatures.
The height of the pipe depends on the cross-section and power of the equipment
In modern construction, only round or oval fireplaces are used as outlets for combustion products in heating systems. Soot practically does not settle on their walls. It is also important that the surface of the internal diameter of the chimney for a gas boiler is smooth. Square-section structures are more problematic to operate. The soot gets stuck in the corners, so you have to get it out somehow, it’s a hassle. Ideally, with constant use of the heating system, inspection of the chimney for the heating boiler should be carried out twice a year. Performed by an experienced person, a master. If the cross-section is round, you can get by by calling a specialist only once a year.
Be sure to carry out preventive maintenance every year if we are talking about a house in which you live permanently. Before the start of the heating season, call a specialist. Otherwise, the soot, accumulating, will reduce the diameter of the chimney for the gas boiler.
Organization of a node through the walls of a house or bathhouse
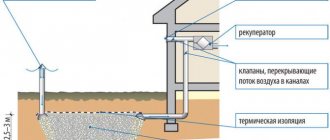
Today, installing a sandwich chimney is practiced mainly in two ways: inside the house or outside. After all, you can increasingly see that chimneys are installed directly through the wall to the street and from the first floor - and from there they are already directed vertically upward. And this makes sense: this way the chimney cools much faster and does not pass through fireproof ceilings and roofs. On the other hand, a chimney that rises through the attic usually serves as an additional heating element. But the risk of fire here, of course, will be higher.
Surprisingly, the outer shell of the stainless steel sandwich is not far from the temperature of a single-circuit fireplace. Indeed, such a chimney was originally designed to improve draft, and therefore the gases leaving the stove usually have a temperature of 800 degrees Celsius, and the outer casing can heat up to 300 degrees! And this is far from a fireproof surface.
A modern sandwich chimney is exhausted both through the roof and directly through the walls of a residential building:
The node can be seen in more detail in this illustration:
So, the following step-by-step instructions will help you position your sandwich fireplace at the right angle so that it fits through the walls:
- Step 1. Before starting work, be sure to calculate the length of the horizontal multilayer pipe that will need to be passed through the wall. And also think about the shirt you install. Calculate the slope of the roof so that the chimney does not come too close to the eaves.
- Step 2. Fill the box that you insert into the wall with non-flammable basalt material.
- Step 3: Cover the inlet assembly with the lid so that the basalt cardboard spacer remains visible.
- Step 4. Cover the edges of such a knotted cover with a film made from the components of the exterior of the house, for example, siding.
- Step 5: Seal the edges of the box with clear roofing sealant.
- Step 6. Install a major repair to the chimney outlet from the wall.
- Step 7. Secure the chimney with special wall brackets, one for every 1.5-2 meters.
- Step 8: Then, after installing the pipe, check that it is vertical using a spirit level.
- Step 9: Make sure the seam is facing the house.
After all, the most important rule is the following: the passage of the fireplace through the wall of the house or bathroom should be protected as much as possible from fire. Here is a good example of such a node:
In order for the horizontal element of the sandwich chimney to be securely installed, it must be correctly supported with a metal corner:
Special drawings will also help you secure such a fireplace to the wall in a strictly vertical position:
Believe me, at this stage the work is not finished yet, especially if your fireplace has a complex design (which we strongly do not recommend):
Why are solid fuel devices considered?
It's simple - there are always more problems with them in these matters compared to gas ones.
Let us explain why: First of all, gas heating appliances are almost always factory-made products. That is, they must have a pipe of a certain cross-section for connection to the chimney. The cross-sectional area of the channel is also specified in the technical documentation of the model. That is, everything is quite simple - it is not allowed to narrow the channel in any of the sections of the upward chimney.
Factory-assembled boilers or stoves always have a pipe for connecting the chimney. That is, there is no longer a problem with the cross-section of the chimney - it should be no less than that specified in the technical documentation.
- The temperature of the gas combustion products leaving the chimney is disproportionately lower than that generated during the combustion of wood or other solid fuel.
- It is also difficult to compare the volumes of gas mixtures formed during the combustion of “blue” and solid fuels. The difference here is quite significant!
But solid fuel heating devices, stoves or boilers, are very often created independently. Or they are “inherited” from the former owners of the house. And here it is never superfluous to check the parameters of the chimney connected to such a device.
However, what concerns the height of the pipe and checking draft can probably be fully attributed to gas heating equipment. The cross section is known, but it wouldn’t hurt to check the rest.
But let's start with the section.
Building regulations
The installation of chimneys is determined by the provisions of SNiP 41-01-2003.
The chimney design must meet the following regulatory requirements:
- the minimum height must be at least 5 meters from the combustion point or grate;
- the pipe must rise above the flat roof to a height of at least 1 meter;
- when located on the roof slope at a distance of less than 1.5 m to the ridge, the pipe should be 0.5 m higher than the ridge;
- when located on the roof slope at a distance of 1.5-3 m to the ridge, the pipe may not be lower than the ridge;
- when located on the roof slope at a distance of more than 3 m to the ridge, the angle between the horizontal and the line passing through the ridge and the top of the pipe should be no more than 10°;
the maximum length of each horizontal and inclined section should not be more than 1 m, the total length of their projections onto the horizontal should not exceed 2 m. If there are oblique and horizontal sections, it is necessary to extend the pipe by the length of the horizontal projections. For ceramics, horizontal sections are not allowed.
Fire safety requirements for chimneys
The distance from the surface of ceramic, insulated steel and asbestos-cement chimneys to combustible house structures must be at least 0.25 m; for brick chimneys and sandwich pipe structures - at least 130 mm.
If the roof is covered with flammable materials (roofing felt, bitumen tiles, ondulin), or leaves or fluff can accumulate on it, a spark arrestor made of mesh should be installed on the head of the pipe.
Traction force
Factors influencing traction force:
- height of the structure;
- condition of the internal channel - smoothness of the walls, regularity of soot removal;
the presence of inclined or horizontal sections. For pipes of long-burning units, the presence of horizontal and inclined sections is not allowed, since the exhaust gases have a low temperature and lengthening the chimney is undesirable - the gases will cool, the draft will decrease until they tip over;
- installing a deflector;
- quality and thickness of insulation;
- air supply to the firebox.
Your safety depends on the presence and strength of traction, so you need to check the presence of traction and take measures to clear the channel of soot and icing of the pipe head.
Types of chimney systems
Brick chimneys and shafts for subsequent lining are square and rectangular, they are laid in 4, 5 and 6 bricks, calculating their area is not difficult - just multiply one side by the other. A standard stove brick has a size of 12.5 × 25 cm. The calculation is carried out on the inner surface. For ease of perception, it is presented below in centimeters.
Standard sections of brick chimneys
A square pipe laid in four bricks has internal dimensions of 12.5 × 12.5 cm, which corresponds to an area of 156.25 cm 2.
Rectangular with five bricks - 12.5 × 25 = 312.5 cm 2.
Square with six bricks - 625cm 2.
To calculate the area of a round chimney, you should remember the school mathematics course and the formula S = π×R 2. Knowing the radius, it is not difficult to make the calculation.
Connecting a collective smoke duct
With a collective chimney, heating devices must be of the same type
The need to have one smoker for several households arises if there is a need to save money, space, or if it is not possible to organize the exhaust gas removal system differently. From a technical point of view, this is a completely acceptable option and such structures are effectively operated. In this case, it is necessary to consider two options:
- Connecting heating devices of the same type to the device.
- Connecting fundamentally different heating units to the line, for example, a gas boiler and a brick fireplace.
In the first case, there is no difficulty in including equipment in a common channel, since for such devices it is possible to calculate a smoke channel for one draft value at which all units will operate correctly.
In the second option, it will not be possible to coordinate the devices, since the chimney for the fireplace should occupy 1/10 of the firebox area, and this is too much for the boiler. The result is either excessive or insufficient thrust for one of the devices, which is fraught with negative consequences.
The most correct solution would be to use a two-channel system. Its essence is that the internal space of the pipe is divided into two channels, each of which is designed for its own heating equipment.
Sad consequences
The scale of the impact of air pollution on human health and the entire ecosystem as a whole is simply enormous, and many people underestimate it. It's worth starting with the environment.
- Firstly, due to polluted air, a greenhouse effect has developed, which is gradually but globally changing the climate, leading to warming and melting of glaciers, and provoking natural disasters. It can be said that it leads to irreversible consequences in the state of the environment.
- Secondly, acid rain is becoming more and more frequent, which has a negative impact on all life on Earth. Through their fault, entire populations of fish die, unable to live in such an acidic environment. A negative impact is observed when examining historical monuments and architectural monuments.
- Thirdly, fauna and flora suffer, since dangerous fumes are inhaled by animals, they also enter plants and gradually destroy them.
A polluted atmosphere has an extremely negative impact on human health. The emissions enter the lungs and cause disruptions in the respiratory system and severe allergic reactions. Together with the blood, dangerous compounds are carried throughout the body and greatly wear it out. And some elements can provoke mutation and degeneration of cells.
Materials
The properties of fireplace chimneys largely depend on the materials purchased. To do this, you need to know which material you need to give your preference.
The materials used have the following properties:
Ceramics.
Ceramic chimneys
- High heat capacity.
- Resistant to temperature changes.
- Long service life.
Stainless steel.
- Easy installation and light weight of the finished product.
- Not affected by acids.
Brick.
- Long service life.
- High heat capacity.
Asbestos cement pipes.
Main characteristics of an asbestos-cement chimney
Limitation on the temperature of the exhaust flue gases. The optimal temperature for such pipes is 300 degrees.
Tools
You just need cutting tools - an angle grinder, a jigsaw, a knife. All work is done manually and does not require special equipment.
Installation diagram
There are several types of fireplaces; the most suitable type of design is selected individually.
Installation methods
It is important to take into account the collection of condensate in the system, therefore it is necessary to have a plug, a condensate drain and a container for collecting condensate.
If a pot-bellied stove is installed through a wall made of a pipe located on the street, it would be advisable to lead the chimney through a window so that you do not have to prepare a hole for the pipe in the ceiling.
The outer part of the chimney is insulated with thermal insulation coated with a protective material. A mushroom is installed at the end of the pipe, which will protect the chimney from debris, rain, various small animals and foreign objects.
Floor preparation
The chimney for a stove is often installed in such a way that it passes through the ceiling, therefore, before installing and fixing the pipe structure, it is necessary to drill a hole in the ceiling: with a jigsaw or other suitable cutting tool, the diameter is up to the passage of the glass for the elbows of the internal chimney.
Example of a hole for a chimney
Through the glass
Before installing the chimney for the stove, through glass is installed in the hole. The diameter of the glass should be chosen based on the diameter of the inner pipe, although sometimes the joint is made before the chimney passes through the ceiling. It should be understood that it is important to securely fasten the glass - it serves as a latch. But in addition to this, the pipeline must be fixed to the wall surface.
If installed incorrectly, the following consequences may occur:
If there are flammable materials, insulation or wood in the ceiling, they must be removed so they do not come into contact with passing glass.
Once the pipe is inserted, the whole thing must be sealed with a fire-resistant material, such as heat-resistant sealant or special fire-resistant wool.
The photo shows the following stages of work:
Seal
Bring the pipe to the roof
We work on the roof
At the last stage, you need to put a deflector on the pipe
Tips for working
- The pipes used in the design are located exclusively in a vertical position; To secure them, it is advisable to use special brackets with dimensions corresponding to the system elbows. To save money, you can make the brackets yourself using a metal corner.
- All connections should be treated with sealant so that there are no holes through which smoke could escape into the room air. There is a wide selection of suitable sealants on the market for sealing pipe joints from the chimney:
- Sealants for high temperatures;
- Heat-resistant sealants;
- Heat-resistant sealants;
- Heat-resistant sealants;
High temperature and heat resistant sealants are used to seal areas that reach temperatures of up to 350 degrees Celsius. Because the furnace flue reaches higher temperatures, these types of sealants are only suitable for parts outside the piping system.
Heat-resistant and heat-resistant polymers can withstand enormous temperatures, up to 1500 degrees Celsius - they are better suited for a fireplace than a stove.