I welcome my dear reader and offer him an article on how to connect metal-plastic pipes when installing engineering systems in an apartment or cottage.
The direction of development of modern technologies is to complete any work faster, cheaper, easier. The most obvious example of this is the transition from the use of heavy and corrosion-resistant steel pipes to light, stainless and technologically advanced plastic and metal-plastic ones.
The installation of engineering systems in the house has become an activity accessible to everyone. First, plastic pipes appeared, then they came up with the idea of creating composite products - more durable, reinforced with aluminum foil. Installation of modern metal-plastic no longer requires heavy equipment, such as a welding machine, or special skills from the installer.
Advantages and disadvantages of these pipes
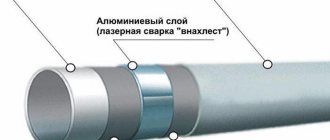
Metal-plastic pipes consist of a polymer (thermoplastic) and a frame made of aluminum foil or a mesh steel base. Products with a durable mesh frame are not used for engineering systems of buildings. For household engineering systems, polyethylene, polypropylene, cross-linked polyethylene (PEX), and heat-stable polyethylene (PE RT) are mainly used.
Reinforcement allows you to combine the plasticity of polymers with the strength of metal, in this case aluminum. Aluminum foil has a thickness of tenths of a millimeter. The foil is welded together using ultrasonic welding. The frame is filled with polymer. An adhesive is used to enhance the adhesion between the plastic and the foil.
Metal-plastic pipes allow you to combine the advantages of traditional steel pipes and stainless, but less durable plastic ones.
Advantages of metal-plastic
The biggest advantage of reinforced pipes over steel is their resistance to corrosion. They cost less compared to steel and especially copper systems, installation is cheaper and easier. Metal-plastic systems are resistant to aggressive environments, and the water in them does not acquire an unpleasant odor or taste.
The service life under standard operating conditions is tens of years; in cold water communications it can reach half a century (perhaps even more). The potential service life of cross-linked polyethylene systems for cold water can reach 100 years (but not yet tested, we'll see).
The durability of metal-plastic communications depends on the operating pressure and temperature - in hot water supply and heating systems, metal-plastic serves less.
Reinforcement reduces the permeability of pipelines to gases, in particular oxygen, which extends the service life of metal parts. Metal-plastic products are durable, harmless to humans, environmentally friendly, and do not rot.
The smooth inner surface causes low hydraulic resistance of metal-plastic communications. Salt deposits do not settle on the walls of pipelines.
Thermal expansion is 3-5 times less than that of plastic without reinforcement, its frost resistance is up to -55 ° C. Thermal resistance is sufficient for use in hot water supply and heating systems (withstands long-term heating up to +95 °C, short-term heating up to +110 °C).
Aesthetics make it possible not to hide communications behind screens and casings; color modifications of materials are available. There is no need for anti-corrosion treatment, cleaning or painting. Pipelines are easy to clean, cut and bend; the connection is made using fittings or diffusion welding (PP).
Metal-plastic has flexibility and ductility, the ability to maintain a curved shape. Low weight facilitates transportation, storage, and installation.
Flaws:
Metal-plastic pipes also have disadvantages:
- The strength of metal-plastic structures is lower than that of copper and steel structures. For utilities in a private house, this parameter is not so important, unless we are talking about laying external pipelines in difficult conditions.
- Polypropylene and polyethylene are not resistant to ultraviolet radiation.
- Less fire resistance compared to metal communications.
- The flexibility of metal-plastic pipes reinforced with foil is less compared to products without reinforcement.
Example of water supply system layout
First, we draw a water supply layout plan. This can be done on a piece of paper, marking the necessary fittings. Please note that installation of taps requires installation of a fitting with a thread at the end. Taps are needed on taps to household appliances and plumbing fixtures, to heating radiators. This makes it possible to turn off devices without shutting down the entire system. The type of thread and its size are selected depending on the type of tap used.
An example of a water supply system using metal-plastic pipes
Also, transition fittings are needed before and after the meter (water or heating depends on the type of system). Having drawn a detailed plan, put down dimensions on all areas. Using this drawing, you calculate how much and what you need. Fittings can be purchased strictly according to the list, and it is advisable to take pipes with some reserve. Firstly, you could make a mistake when measuring, and secondly, in the absence of experience, you can spoil some piece - cut off less than required or crimp incorrectly, etc.
Agree on the possibility of an exchange
When purchasing everything you need, agree with the seller that you can exchange/return some fittings if necessary. Even professionals often make mistakes with them, and even more so those who decide to do the wiring of a plumbing or heating system from metal-plastic with their own hands. No one will take the rest of the pipe back from you, but fittings will easily be taken back. But to be sure, keep the receipt.
There are manifolds for plumbing and heating
When and how to start work
When you get home, lay out the fittings and proceed: installation of metal-plastic pipes in the summer can be done immediately, in the winter you need to wait some time (12 hours) until all the elements warm up to room temperature. It is advisable to cut one piece of pipe of the required length at a time. It's a little longer, but you definitely won't get confused. Further actions depending on the selected type of fittings.
Heating installation with metal-plastic pipes is done only with press fittings
After completing the installation of metal-plastic pipes, the pipeline is checked. If it is a water supply, just open the tap at the inlet. This must be done gradually and smoothly. The system will immediately begin to fill with water. If nothing leaks anywhere, you did everything right. If any connections are leaking, they must either be redone if press fittings were used, or tightened if the assembly was based on crimp connectors.
If a heating system was assembled from metal-plastic pipes, before starting it must be pressurized - tested with high pressure by pumping cold water into the system. If the test was successful, you can do a test run of the heating.
Methods for connecting metal-plastic pipes
The fitting connection (without welding) is made in two ways:
- Detachable - using compression or collet connectors.
- One-piece - using press or push fittings.
Compression fittings
The simplest are compression or crimp fittings. They consist of a threaded body (collet), an outer crimp nut, a thrust ring, and rubber seals. Sometimes an American union nut is installed on the body instead of a thread.
By design there are straight, angular, tees. Functionally, there are connecting or transitional valves between plastic and metal shut-off valves.
The compression fitting forms a reliable connection, but it must be inspected and tightened at least once a year - the connection is considered serviceable. If necessary, the connection can be disassembled and reassembled - this is very convenient for repairs. Compression joints are not used for underfloor heating systems and for covering with plasterboard.
Push fittings
A modern fitting that can be tightened without tools. It forms a non-separable, but not the most reliable connection - the pipe rotates in the connection. The push fitting is quite expensive, and before using it, you should think about whether it is worth the expense.
Press fittings
Press connectors consist of a body with an internal liner, a thrust ring, an outer press sleeve, and sealing collars. When crimping, the press sleeve tightly compresses the pipe blank and creates a permanent and very reliable connection. Press connection can be used even for underfloor heating systems.
For polyethylene, they produce push-on fittings in which the upper crimp sleeve is not screwed on, but pushed on, and the inner liner-fitting is equipped with a “ruff”, due to which a very reliable sealed connection is formed.
Push-in fittings
Push-in fittings are made of low-density polyethylene and are used to connect HDPE products. Structurally, they are the same as compression connectors, but are much larger in size and look quite bulky. The connection is quite reliable.
The shapes are divided into straight, angular and tees. Functionally - connecting, reducing (for connecting pipes of different diameters), transition (for connecting plastic with metal fittings).
Which way is better
The choice of connection method depends on the polymer from which the metal-plastic pipe is made and operating conditions.
Polypropylene communications are often installed using soldering - this is a completely sealed, reliable and very cheap method (couplings and angles for welded joints are inexpensive).
For very common water pipes made of all types of polyethylene, compression, press and push fittings are used. For HDPE, collet products are most often used, although compression and press connections are also occasionally used.
After soldering, the most reliable connection method is using press fittings; they can be used even for underfloor heating systems. Then come compression fittings, then push fittings. The latter are positioned as a means for quickly assembling engineering systems without the use of tools, but the tube in the push connection rotates - this raises doubts about the reliability and durability of the connection.
The easiest installation method is using collet or push fittings.
In terms of cost, the most expensive are push fittings. The cheapest are polypropylene couplings and tees for welding.
In terms of aesthetics, steel connectors are more compact and beautiful than bulky collet products made of polyethylene.
How to connect a metal pipe with a metal-plastic one
It is possible to connect a metal pipe to a metal-plastic one only using a threaded connection and transition elements that have a threaded pipe on one side or an American union nut for connection with the metal part of the system. This could be an input point, a water point - a mixer or tap.
On the other hand, such adapters have either a plastic part for connection with a metal-plastic pipe (with a collet clamp), or a metal part in the form of a press or compression connector.
Collet parts
Push-in fittings for metal-plastic pipes are used very often when drawing pipelines. If the joint with collet parts is made correctly, and in accordance with all requirements, then you will not have to worry about strength and tightness.
It is also important to note that installation work in this case is carried out quickly and simply. Everything you need to install collet elements: devices for chamfering; scissors; spanners; calibrator
The main advantage of the joint formed by a collet connecting element is the possibility of subsequent disassembly if necessary. But they will require constant maintenance. It involves constantly tightening the union nut.
Many manufacturers produce collet fittings, and they are available in huge quantities on the market. For example, there are more than a dozen Italian companies producing products of this line, and there are many more Chinese manufacturers.
How to attach metal-plastic pipes to walls
Good fastening of metal-plastic communications extends their service life. When heated, pipes elongate and may “lead”; in addition, poorly and sparsely secured communications are more susceptible to vibration, which has a bad effect on the reliability of the connection. Therefore, metal-plastic pipes must be securely fastened. The clamps must be close to the fitting.
Fastenings are placed in increments of 0.7-1 m, for heating and hot water supply - 0.5-0.7 m. The stores are full of all kinds of clips and clamps of all diameters. You can also use homemade brackets. Fasteners are attached to concrete walls with 6x40 mm dowels, to plastered, gas or foam concrete walls - 6x60 mm or even longer.
How to bend a metal-plastic pipe correctly
Metal-plastic pipes are very flexible, so they are quite easy to bend. Various devices and small machines are used to bend metal-plastic materials. Below I will talk about the most common methods of bending polymer pipes.
To obtain a high-quality bend, the minimum bending radius must be at least 5 diameters. This rule applies to all sizes.
Which method is better
Despite the flexibility of metal-plastic pipes, it is better to bend them not by hand, but with the help of devices. When bent, the tubes do not form kinks or cracks and retain their round shape. The best method is using a pipe bender. Among manual methods, the best results are obtained when using a spring.
Bending pipes by hand
It is difficult to bend polypropylene, HDPE and PVC pipes by hand - they are too rigid for this. Tubes with a diameter of up to 20 mm made of cross-linked polyethylene bend well. Bending is carried out in several stages, otherwise a crease will form on it at the bending point.
Spring
Spring conductors of different diameters are made from thick wire. For small diameters, you can use an external jig; for workpieces with a larger diameter, it is inserted inside the pipe. The center of the spring and the bend must coincide exactly. Using a spring, it is easy to bend cross-linked polyethylene blanks. It is advisable to preheat HDPE and PVC using a hair dryer.
Pipe bender
The best bending quality is obtained when using a pipe bender. The tool either shapes the workpiece between rollers or bends (pulls) the workpiece on a mandrel. The bending of the workpiece is smooth and without defects - crumpling, creases, cracks.
They also use a homemade pipe bender called a Volnova machine.
Using a hair dryer
Metal-plastic pipes based on polyvinyl chloride or polypropylene are quite rigid; the blanks must be heated before bending. Bending is performed using fillers - sand, salt, small metal objects (finely cut wire). The workpiece is filled with filler, the holes at the ends are tightly closed, clamped in a vice, the bend area is heated with a hairdryer and bent.
Types of tools for installing metal-plastic pipes
The following tools are used to connect metal-plastic pipes:
- Pipe cutter or scissors for cutting metal-plastic.
- Angle grinder (grinder).
- Pipe bender
- Construction hairdryer.
- Hand press or press tongs.
The grinder and hair dryer are driven by an electric motor. Household pipe benders for metal-plastic pipes are usually manually driven. The manual crimping press has several varieties with different types of drives.
Mechanical
Manual or mechanical mini pliers are used for crimping water pipes with a diameter of up to 20 mm. These are used for internal distribution of hot and cold water. These tools do not have an electric drive or hydraulic boosters; human muscle power is used to operate them.
Manual drive
Manual pipe benders and homemade Volnov machines have a more complex design than simple tools. The force required for bending is quite significant, and levers are used to operate such structures.
To crimp metal-plastic heating pipes (25 mm, sometimes 32 mm), use a standard manual press for crimping press fittings. To enhance a person’s muscular strength, a gear drive is used, and it also helps to correctly adjust the crimping force.
Hydraulic
For crimping larger diameter pipelines (up to 32 mm), hydraulic models of pliers are produced. A reinforcing hydraulic cylinder is built into one of the pliers handles. When the handles are compressed, the pressure in the hydraulic cylinder increases and the force is transferred to the crimping head of the pliers. Such pliers are quite expensive (from 10,000 rubles), they require qualified maintenance.
Electrohydraulic option
All previous models are used for the installation of metal-plastic engineering systems in small volumes. In industrial construction or if you constantly install plumbing systems, it makes sense to purchase a powerful electro-hydraulic pressing tool. Such equipment is used for installation of pipelines with a diameter of up to 108 mm.
Electro-hydraulic pressing tools have high productivity and the highest quality and tightest compression. The devices are equipped with nozzles for crimping pipes of different diameters. Electric pliers for household running diameters up to 50 mm can be powered by batteries.
Tees
Fitting - tee for metal-plastic pipes is an important part for bends and branches on highways. These device options make it possible to connect three pipelines.
Video - review of press fittings and proper crimping
PRESS FITTING for METAL-PLASTIC PIPE | REVIEW
Tees can be equal or transitional. A transition tee is placed at the junction of pipelines with different volumes, and equal-bore type devices are installed on pipelines with the same volume.
One important feature of these shaped products is that they help reduce the area of the constructed highway to minimum dimensions.
The cost of tees depends on the material they are made of. To ensure that the operation of this mechanism does not turn out to be dangerous, it is worth purchasing the product from trusted manufacturers. Otherwise, the quality of the tee may be low, and for this option this is not acceptable.
Installation rules
Any installation begins with a project or at least a diagram. Then the places for laying pipelines on the walls and ceilings are marked and the exact dimensions of the workpieces are determined.
Before laying and connecting metal-plastic communications, it is necessary to punch holes in the walls in the right places. Sleeves made of steel, plastic, metal-plastic pipes with a larger diameter than the outer diameter of future communications are placed in the holes.
The sleeves are cut flush with the wall. Pipeline wiring through walls must be done only using sleeves. The pipes in them must move freely - this is necessary to compensate for thermal expansion when heated. After installation, the sleeves are decorated with special plugs.
For any type of connection, it is necessary to carefully process the ends of the workpieces - cut them off carefully and perpendicularly, clean the end of the workpiece from debris, file off the burrs, and, if necessary, calibrate them. The workpiece should be round, not oval.
When installing using press fittings, it is advisable to remove the chamfer. Connection with press connector:
- Place the sleeve on the end of the pipe blank.
- Insert the inner liner into the workpiece until it stops.
- Insert the fitting with the inserted workpiece into a hand press (press jaws).
- Press the handles of the pliers together with force. Clear annular marks will appear on the sleeve from the press clamps.
When connecting metal-plastic communications using press fittings, you should keep in mind that this fitting cannot be re-crimped - if the crimping is unsuccessful, you will have to cut and extend the pipe and use a new fitting.
How to connect metal-plastic pipes using compression and collet fittings:
- Unscrew the crimp nut.
- Insert the piece of pipe into the fitting with a little force.
- Tighten the nut.
- Tighten the nut. When tightening, hold the body (collet) with one wrench and turn the nut with the second.
- When tightening, tighten the nut one turn or a quarter turn.
The video shows how to connect metal-plastic communications in detail.
Compression fittings
The crimp-type press fitting is equipped with a stainless steel sleeve and an elastic ring-clip, which allows you to attach the sleeve to the fitting and prevents the spread of galvanic currents.
Installation of the compression fitting is extremely quick:
- A chamfer is removed inside and outside the pipe (using a chamfer remover or a regular knife), after which a sleeve is put on it.
- The fitting is inserted into the pipe.
- The sleeve is crimped with a special tool called “press pliers”. At the same time, it is deformed, so that the annular projections present on the fitting appear on it.
Sometimes the fitting and sleeve are a one-piece structure. With this design, there is a hole in the sleeve in which, if seated correctly, the pipe should be visible.
Press tongs are available manual and electric. When using the latter, you should only grasp the plastic-insulated handles. For greater safety, work should be carried out with rubber gloves.
Please note that low quality press fittings may be sold in markets and small shops. You can recognize them by the following signs:
- the fitting itself is almost weightless - a sign that short-lived and fragile silumin was used instead of high-quality brass for its manufacture;
- “clumsily” embossed markings – the signs have different depths, some may be absent altogether;
- the sleeve is clearly flimsy - made of aluminum or very thin steel.
Crimped connections
Crimped type press fittings are attached to the metal-plastic pipe extremely securely, so monitoring their condition is not required. This allows them to be used for hidden installations. But it must be taken into account that such connections are permanent: when replacing an old or damaged pipe, the fitting will have to be thrown out along with it.