An example of the successful use of polystyrene foam. Super lightweight and easy to process, foam plastic is often used by modern sculptors to create bas-reliefs or mobile statues.
There is no universal insulation; each one is selected for the task. It's the same story with polystyrene foam. If you use it in certain cases and according to technology, it will show all its advantages and the result will be excellent.
What is polystyrene foam and important characteristics of the material
Expanded polystyrene is understood as a gas-filled material based on polystyrene, its derivatives and styrene copolymers. The product is produced by foaming a molten polymer mass consisting of styrene granules with a low-boiling hydrocarbon liquid - pentane, isopentane or dichloromethane. At the end, the material is molded to produce slabs, in which the finished product is produced.
What colors is polystyrene foam available in?
The main form of production is sheets with dimensions of 1000x1000, 1000x1200, 2000x1000, 2000x1200 mm. Thickness varies between 20-100 mm. Expanded polystyrene has a cellular structure. Solid matter in it occupies only 2%, while 98% is allocated to voids. They are miniature polystyrene chambers (cells) with air inside. They are the ones who ensure the waterproofness of the material. Among other characteristics of expanded polystyrene it is worth noting:
- Vapor permeability is 0.05 mg/m·year·Pa (virtually vapor-tight). Steam does not penetrate into extruded polystyrene foam at all, since the material is not cut - it is released from the extruder in the form of finished slabs.
- Density – 10-50 kg/m3. It is used to determine the grades of material - according to GOST-15588-86, polystyrene foam is classified as 15, 25, 35 and 50.
- Static bending strength – 0.02-0.2 kg/cm2.
- Thermal conductivity – λ = 0.028-0.038 W/m·K. The higher the density of the foam , the higher the degree of thermal insulation.
- Daily water absorption by volume is up to 2%. Dense polystyrene foam, made by extrusion, practically does not absorb water at all - it absorbs 10 times less than ordinary polystyrene foam.
Please note: for heated floors, it is optimal to use foil polystyrene foam. It significantly increases the insulating properties of the material.
The properties of expanded polystyrene are determined by its structure
Elasticity
Plasticity is an additional advantage of the material. Elastic insulation can be mounted on uneven walls and on complex-shaped facades.
Mineral wool is characterized by high plasticity. Loose flexible material takes the shape of any surface. If we compare basalt wool and quartz-based thermal insulation, the second is more flexible. Mineral wool is especially elastic in rolls, not in slabs - they are denser and stiffer.
Polystyrene foam is not elastic; it is rarely used for insulating facades of complex shapes. It is suitable for thermal insulation of a flat, even surface (if there are uneven surfaces on the wall, the insulation will not fit tightly to it).
Conclusion: mineral wool is elastic, foam plastic is not.
Types of expanded polystyrene and their designation
In the product designation you can find different letters, by which it is easy to determine the type of polystyrene foam. It is standardly labeled as “PS”. Depending on the product brand, other letters and numbers are added to them. There are different types of polystyrene foam:
- Pressless (PSB, PSB-S - self-extinguishing type). It is not subjected to pressure during manufacturing. Polystyrene granules are simply dried at 80 °C and then foamed. This is repeated several times, and then the product is left to cool. It turns out to be more compact, and due to the reduction in the volume of pentane used, it is cheaper.
Pressless expanded polystyrene
- Extruded (XPS, Extruded Polystyrene). Produced by extrusion - passing through a molding hole. Its main advantage is absolute waterproofness. It is known on the market under such brands as Technoplex, Penoplex, TechnoNIKOL, URSA XPS. Due to low vapor permeability and flammability, it is used to insulate underground structures and facades.
Extruded polystyrene foam
- Press (PS). By pressing it is possible to obtain a more dense and durable material, although in terms of the degree of thermal insulation it is no different from non-pressed material. The material is not widely used because its production is more difficult and expensive.
Pressed polystyrene foam
- Autoclave. Produced by the American company Dow Chemical Company, marketed under the generic name Styrofoam.
We advise you to study in more detail: “Everything about XPS extruded polystyrene foam: composition, characteristics, pros and cons, review of manufacturers.”
Brands of pressless polystyrene foam - how to choose the right one
Today, the most common type is non-pressed polystyrene foam. When choosing which foam plastic to use for thermal insulation, you need to take into account its types, which are distinguished by density:
- PSB-15. Foam with the lowest density. It is used where special mechanical strength is not required from the insulation, for example, for thermal insulation of cars, attics or pitched roofs. Not suitable for the internal layer of external walls and facades of permanent residential buildings.
- PSB-25. It is considered the most popular and even universal brand. Relevant for insulating facades, loggias, walls, floors. Additionally, it can be used as sound insulation.
- PSB-35. A material with an already increased density, which allows it to be used for insulating underground structures and foundations. Another area of application is the production of sandwich panels, as well as the creation of permanent formwork from polystyrene foam .
- PSB-50. The brand with the highest density, used where there are strict requirements for the mechanical strength of the insulation. This is the construction of interfloor ceilings, the construction of roads in swampy areas, the installation of floors in a garage or industrial facilities, including refrigeration facilities.
The difference in characteristics of the listed types of polystyrene foam boards is presented in the table:
| Brand of slabs | ||||
| An indicator for comparing different brands of slabs | PSB-15 | PSB-25 | PSB-35 | PSB-50 |
| Material density, kg/m3 | up to 15 | 15-25 | 25-35 | 35-50 |
| Compressive strength at 10% of linear deformation, MPa | 0,07-0,15 | 0,15-0,18 | 0,18-0,26 | 0,26-0,38 |
| Bending strength, MPa | 0,15-0,23 | 0,32 | 0,30-0,38 | 0,38-0,42 |
| Thermal conductivity at a temperature of 25±5 °C and normal relative humidity, W/(m K) | 0,032-0,036 | 0,029-0,033 | ||
| Humidity of slabs, % | 2 | |||
Intended use
Large manufacturers of EPS and EPS, such as URSA, KNAUF and TechnoNIKOL, in addition to certificates, accompany their materials with detailed instructions on how and where to use them correctly.
Extruded polystyrene foam URSA XPS
TechnoNIKOL XPS carbon
What are the advantages of expanded polystyrene
One of the main advantages of polystyrene foam is its low cost compared to other types of insulation. Other advantages include:
- Biostability. Back in 2004, American scientists conducted a series of experiments that proved that mold cannot live on polystyrene foam.
- Long service life. It is at least 30 years old, but only if the installation technology is followed.
- A light weight. Provides ease of transportation and installation, reduces the duration of foam insulation .
- Resistance to cement, mineral fertilizers, gypsum, bitumen.
Thermal insulation of pipelines
Until recently, the thermal insulation of engineering communications was not given much importance, and because of them, the share of heat loss is about 30%. For pipelines of ventilation ducts, cold water supply, buried cables and telephone lines, foam plastic is now increasingly being used as insulation. This material is also used to protect sewer and water pipes from freezing. The undoubted advantage of using polystyrene foam for these purposes is the ability to give this material various shapes.
What are the disadvantages of expanded polystyrene
Even with all its advantages, polystyrene foam has several disadvantages. They are very important to consider when choosing this material as thermal insulation. The main disadvantages include:
- Limited mechanical density. Expanded polystyrene after installation must be protected from external influences.
- Almost complete vapor tightness. This imposes some restrictions on the use of the material as insulation.
- Exposure to sunlight, atmospheric conditions (snow, rain, wind) and various nitro paints, paints, turpentine, drying oil, acetone. They can not only damage, but also completely dissolve the foam.
- Harmful secretions. Newly laid polystyrene foam insulation will still release styrene for some time, since complete polymerization cannot be achieved at the production stage. Until it completes itself, styrene will be released. Also, when heated to above 80 °C, harmful vapors are released: benzene, carbon monoxide, toluene, styrene.
- Relative fire resistance. Expanded polystyrene belongs to classes G3-G4, i.e. the most dangerous. It burns in the area of contact with fire. The situation is somewhat corrected by fire retardants, which are added to the polymer mass during production. This type of polystyrene foam is marked with the letter “C”, which means “self-extinguishing”.
Let's sum it up
So, which insulation is better: polystyrene foam or mineral wool?
We compared both materials. We learned that the heat and sound insulation properties of mineral wool and foam insulation are similar.
Mineral wool is an environmentally friendly, harmless breathable insulation material. It will protect your home from cold and noise, and will become a barrier to fire in case of fire. It is easy to install and is resistant to physical and chemical influences. It has a wide range of applications - mineral wool is used to insulate facades made of any materials (wood, brick, etc.), roofs, and fireproof ceilings are made from it.
So which is better: thermal insulation made of mineral wool or expanded polystyrene? We recommend mineral wool. In the Metal Profile online store you will find insulation based on basalt and quartz from reliable manufacturers.
Let your home be warm and cozy!
Expanded polystyrene or mineral wool – what to choose
When choosing between two materials, it is worth taking into account 2 main characteristics: thermal conductivity and vapor permeability. They determine the required thickness of the insulation, as well as the fact whether moisture will form on it.
The vapor permeability of polystyrene foam is 0.05 mg/m·year·Pa, i.e. the material passes steam through itself very poorly. This determines some features of the use of this insulation.
- With heavy dense materials (concrete, brick).
For example, a sheet of foam plastic 10 cm thick will have a vapor permeability resistance of 2 m2 h Pa/mg, while for a concrete wall 30 cm thick (standard wall thickness of a panel house) this parameter will be 10 m2 h Pa/mg, and for brickwork with an average thickness of 38 cm - 3.5 m2 h Pa/mg. Thus, most of the moisture will condense not in the foam, but in concrete or brick, but due to their high heat capacity and density, dew will not condense in them.
Comparison of the thickness of layers with the same thermal insulation, but from different materials
- With light porous materials, in particular with aerated concrete blocks.
Aerated concrete with a standard width of 30 cm and foam plastic with a thickness of 10 cm have almost the same vapor resistance, but aerated concrete has a vapor permeability coefficient of 0.2 mg/m year Pa, which is greater than that of expanded polystyrene (0.05 mg/m year Pa).
In addition, aerated concrete blocks are lighter than concrete or brick. Because of this, it is in the aerated concrete that steam will be retained, or rather, the foam will retain it there. All this can lead to serious problems, especially if the dew point is inside the wall.
Rules for choosing polystyrene foam for facade insulation
PSB-S-25 foam is best suited for façade insulation. There are several reasons for this:
- this material has sufficient density and strength for installation on any supporting base;
- has a degree of thermal conductivity low enough to prevent heat loss from the interior;
- is light in weight;
- easy to transport;
- is characterized by low cost;
- self-extinguishing;
- durable.
Foam plastic for facade insulation
The most important indicator of the quality of PPP is density. It depends on the production method and the characteristics of the foam granules. During sintering, polystyrene foam granules swell; when pressed, they stick together. The stronger the pressing, the tighter the granules adhere to each other. The degree of thermal conductivity and vapor permeability of the product at the outlet directly depends on this.
What's bad about low-density foam?
With a low density of EPS, its structure is relatively loose, since the distance between the granules is significant. These gaps are the reason for the good vapor permeability of the material. But the polystyrene foam granules themselves, due to their higher density than the air between them, allow steam to pass through much worse.
This leads to the accumulation of moisture inside the insulation, which is removed more slowly than required. As a result, the plaster applied to the foam will attract moisture and gradually deteriorate. The same can be said about other materials adjacent to the insulation, or located next to it. Therefore, it is so important to make sure that the foam purchased in the store is of sufficiently high density.
What is sold under the brand name PSB-25
The high demand for polystyrene foam has led to the emergence of a large number of large and small manufacturers and distributors of polystyrene foam on the market. They all understand that this material is chosen as insulation primarily due to its low price. This fact, coupled with high competition, forces manufacturers to win back their market segment by reducing prices, which cannot but affect the quality of their products.
For this reason, the situation on the market is such that under the PSB-25 brand they sell products whose quality does not stand up to criticism. This also applies to foam plastics of other popular brands.
Video - Polystyrene foam PSB-S 25 TU and foam plastic PSB-S 35 TU
It is important to know: for many years, the production of polystyrene foam has not been standardized by GOST to the extent necessary. Each enterprise that manufactures PPP develops its own technical specifications (TS) regulating the technological process. This gives the owner of the enterprise freedom of action, and he has every right not to comply with previously adopted standards.
Foam production diagram
The need to reduce the price of the finished product forces the manufacturer to reduce the cost of the material. GOST according to PSB-25 allows the production of a product with a density of 15 to 25 kg/m3 under this brand.
This has led to the fact that building materials stores under the PSB-25 brand offer foam plastic, the density of which is significantly lower than 25 kg/m3. But, as mentioned above, this is not consumer deception. This is permitted by the standards body.
How to find out the density of foam plastic
How to determine the density of foam plastic
The density of PPS is calculated as follows: 1 m3 of this material is weighed. The resulting value is an indicator of density. That is, 1 m3 of PSB-25 should weigh 25 kg. In practice this is extremely rare.
The most common situation is that foam plastic with a density of 16.1-16.5 kg/m3 is sold under this brand. You can check the density of the sample directly at the retail outlet where it is purchased.
As a rule, all building materials stores or market pavilions are equipped with equipment for weighing goods. It is necessary to take a sheet of foam plastic of the required thickness and calculate its volume. To do this, multiply the length of the canvas by its width and height (thickness). Then you need to find out the weight of this sheet and divide the resulting value by the volume indicator.
Example calculation for a sheet 2 m long, 1 m wide, 2.5 cm thick:
- calculate the volume of the sheet: 2 m x 1 m x 0.025 m = 0.05 m3;
- weigh the sheet;
- divide the weight by the volume.
Calculations can be done using a calculator, which is available on any mobile phone. This approach will help you buy the insulation that will serve flawlessly for many years.
Video - How to determine the density of foam plastic
So what is the difference between polystyrene foam and mineral wool?
The described properties of expanded polystyrene impose restrictions on its use as insulation. It cannot be combined with wood and other “breathable” materials, as it will cause them to argue.
Mineral wool does not have this drawback - due to its high vapor permeability (0.3 - 0.6 mg/m·year·Pa), it can be combined with any materials. Mineral wool easily absorbs steam and releases it just as easily. But when working with it, it is very important to observe one condition - the insulation must be ventilated. This is necessary to prevent the mineral wool from getting wet, since in this case its thermal conductivity coefficient (0.045 - 0.055 W/m K) is significantly reduced. With good ventilation, the cotton wool will dry out and the water will come out.
Mineral wool is available in the form of slabs and rolls
Study in more detail one of the popular types of mineral wool: “What you need to know about basalt insulation: composition, characteristics, pros and cons, types and review of popular manufacturers.”
What other differences should be taken into account when choosing between mineral wool and expanded polystyrene:
| Parameter | Mineral wool | Styrofoam |
| Specific gravity | Depending on the density, it is 2-10 times heavier than polystyrene foam. | Very light material, practically does not bear additional load on the structure. |
| Soundproofing | Excellent level of sound insulation. | Mediocre sound protection. It might just tone them down a little. |
| Water absorption | In this respect, mineral wool is similar to a large washcloth - upon contact with water, it immediately absorbs it. | Very low, and for extruded ones – zero. |
| Features of application | Not recommended for use for insulation:
Used for pipelines, shaped structures, roofs with a wooden rafter system. | Not recommended for insulation:
In the case of wood, it can be used, but only if there is no contact between the wood and the side of the foam. Polystyrene foam can be used to insulate walls made of heavy materials:
The foam is covered with a layer of plaster on top. The thickness of the non-insulated fire-resistant plaster layer must be at least 5 mm for external insulation and at least 2 cm for internal insulation. |
Flammability class and combustion toxicity
Opponents of foam plastics in construction, first of all, talk about their flammability and toxicity. Let's figure out how dangerous this is.
If the mineral wool does not burn at all (class NG), then the foam plastic and the extruder do burn. EPS and EPS can be of 4 flammability classes:
- G1 - low
- G2 - moderate
- G3 - average
- G4 - increased
The first and second classes die out within a few seconds as soon as the direct source of fire disappears. Additionally, special additives are used to prevent the formation of flammable droplets - fire retardants; they reduce the access of oxygen during combustion. EPS flares up, but does not support combustion, but EPS burns, so its class is third and fourth.
It turns out that foam plastic marked G1 and G2 can be used to insulate residential buildings and apartments, but what about the extruder with its G3 and G4?
An extruder is perfect for:
- for insulation of damp and cold rooms,
- floors and pipes,
- basement and basement,
- foundation and blind area,
- garden paths,
- flat inversion roofing,
- stylobate and parking,
- balconies and loggias,
- highways,
- and even the runway.
EPS can be used in contact with the ground; it can withstand large temperature changes and prevent concrete from freezing.
How to choose the right polystyrene foam
When choosing such insulation, it is important to correctly calculate its thickness. The rule “the thicker the better” does not apply here. With a large thickness, due to temperature changes inside, the material will go into waves and cracks. In Europe there is even a restriction - to insulate the facade of a house, do not use polystyrene foam with a thickness of more than 3.5 cm.
But to obtain a more accurate value, it is necessary to carry out a thermal engineering calculation of the enclosing structure. SP 23-101-2004 “Design of Thermal Protection of Buildings” will help with this. In general, the following recommendations will help when choosing expanded polystyrene:
- Be sure to take into account the density of the material (from 25 to 50), since the strength of the thermal insulation depends on it.
- Check the standards to which the product is manufactured. If this is TU and not GOST, then the technology may be different.
- If possible, before purchasing, break off a piece of material and look at its edge. Along the fault line you should get regular polyhedra.
- Give preference to the well-known ones, BASF, Styrochem, Nova Chemicals, Polimeri Europa, etc.
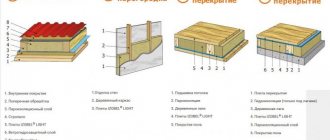
Roof insulation
Here you need to understand where and what width of material to use. The “non-ventilated roof” is covered with 70 mm thick foam plastic, then a bitumen waterproof layer is laid on its surface. “Ventilated roof” involves installing slabs on the back side of the roof, while the ventilated cavity remains, preventing condensation.
Attic spaces can be excellent living rooms. At the same time, the thermal insulation of a gable roof brings great benefits at low costs. To do this, you need to install foam plastic in the cracks between the rafters.