Sep 6
At first glance, it seems logical that the heat meter is selected according to the diameter of the pipeline, but in fact, the value of the diameter is secondary, and the main criterion is the maximum coolant flow.
Sometimes it is possible to install a heat meter of a smaller diameter, thereby saving money, but only if the characteristics of the heating system allow this to be done without compromising the quality of the heat supply.
Examples of technical conditions for the installation of heat meters
The technical specifications indicate:
- thermal load of the building,
- thermal regime,
- pressure in forward and return pipelines,
- description of thermal input,
- if possible, coolant flow.
If the coolant flow is not indicated in the technical specifications, it is calculated based on the heat load and mode data using the formula:
If technical conditions require the ability to remotely read meter archives, then it will need to be equipped with a GSM modem.
Law
For the first time, the issue of installing communal electricity meters was raised in 2009, in which Federal Law No. 261-FZ “On Energy Saving and Increasing Energy Efficiency” was issued. According to the original version, the legislation prescribed the mandatory installation of communal heat meters in apartment buildings before January 1, 2012.
Subsequent legislative regulations extended this period several times. The last change in the deadline is until January 1, 2019 and until January 1, 2021 (Sevastopol and Crimea). It was enshrined in Federal Law of the Russian Federation N196-ФЗ dated July 26, 2017.
Based on this, it can be argued that the law on communal heat meters indicates the need to install this electrical equipment in apartment buildings.
There are several exceptions - it is not necessary to install building-wide heat meters in emergency, dilapidated and demolished multi-storey buildings. At some sites, installation of a thermal electric meter is technically impossible due to the inconsistency of the characteristics of the utility network with the conditions for installing the equipment.
How can you roughly decide which heat meter you need?
Those. what features of your building should be taken into account when selecting it.
The heat meter consists of a flow meter, a calculator and a pair of matched thermal converters. Flow meters differ in operating principles - vortex, electromagnetic, etc., and heat meters are also called vortex, electromagnetic, etc., based on the flow meter used in them.
Which flow meter is best to choose for your metering unit?
Who should install
The installation of the heat meter is carried out by qualified specialists hired by the housing and communal services service of a multi-storey building. Residents of an apartment building pay for the installation of electrical equipment. Since a common building heat meter records the amount of heat entering a high-rise building, it is worth considering the benefits of such a device.
ATTENTION! Residents do not have the right to install a communal heat meter on their own; to do this, they must use the services of a special service.
The need to install a heat meter is determined at a general meeting of residents of an apartment building. Installation of electrical equipment of this type is carried out after a written application submitted by representatives of the management company to the relevant organization. In order to calculate the heat energy consumed, the electricity meter data is divided by the total area of the room. Of course, there are certain benefits from installing heat meters.
Without it, payment for heat consumption will be carried out at inflated coefficients. Unfortunately, the equipment does not allow you to regulate the heat supply to the house, which is a significant disadvantage of the device.
Comparative characteristics of different types of flow meters
| Flow meter type | Stamps | Advantages | Flaws |
| Mechanical: at pi at pi>50 - turbine | VSG(n), VST(n) |
|
|
| Ultrasonic | Ultraheat, Karat |
|
|
| Electromagnetic | PREM Masterflow Peterflow |
|
|
| Vortex | Sayany KST 22 (VPR) VPS |
|
|
Ultrasonic, electromagnetic, and vortex flowmeters suffer greatly from the passage of eddy currents through the pipes, which arise when electricity is stolen.
Purpose, pros and cons
According to the Housing Code, the common property of an apartment building is considered the property of the residents, which increases their responsibility. The owners of living space are responsible for the maintenance and maintenance of common property. Since it is impossible to refuse regular payments for general house needs, the best option is to reduce the cost of heating non-residential and residential premises by paying for the heat actually received.
To measure the actual volume of heat energy consumed in apartment buildings, a common building heat meter is installed.
Property owners not only have the opportunity to pay for heating in an apartment building by meter, they can control energy consumption and keep track of utility costs. This is an important advantage of installing ODPU.
When installing heating devices in apartment buildings, the management company pursues several goals. One of them is to encourage owners to save heat outside their apartments and treat common property responsibly. If the entrance doors to the front door and the windows in the entrance are tightly closed in winter, the heat will remain in the building, and residents will receive utilities in full.
ATTENTION! It is worth considering that a common house heat meter does not save heat. This is an energy metering device that allows you to obtain accurate data for calculating heating bills.
The main advantages of using a common house heat meter in an apartment building:
- You can save on installation costs, since self-installation is expensive. The cost of installing communal equipment is shared among residents.
- All residents will try to keep warm. Therefore, they will begin to take a more responsible approach to the problem of an open door or window structure in a common entrance.
An important disadvantage is the high cost of the electrical appliance. Moreover, if the devices fail, the residents of the multi-story building will have to pay for the repair work. The main disadvantage of a common house heat meter is the inability to save on heating living space due to lower consumption of thermal energy.
Types of heat meters
The function of the meter is to record the incoming heat and send the results to the energy supplier.
The operating principle of the registration units is almost the same for all types.
Device functions:
- a flow meter built into the supply circuit and a temperature meter provide information to the computing electronic device;
- the processor calculates the amount of supplied thermal energy and displays the result on the monitor.
The functions of a common house heat meter include transmitting information via GSM mobile communications or via the Internet to the energy supplier on duty.
Tachometer counter
Used in residential buildings and small public buildings. The device operates on small-diameter heating mains and is designed to account for energy resources in a small volume. The device does not connect to the mains, operates reliably and is inexpensive.
Depending on the type of moving element, tachometer counters are divided into types:
- single-jet, where the entire flow of liquid passes through the impeller;
- multi-jet, in which the water jet is divided into 2-3 streams in front of the blade compartment.
The device of the second structure is popular because it reduces the formation of nonlinear waves and increases the clarity of readings.
Tachometer coolant meter
Depending on the interaction with the liquid, there are counting mechanisms:
- land vehicles;
- wet.
The first type works longer due to the absence of unfavorable factors and is used for measuring hot water. The passing flow rotates the blades, and the counter receives information about the number of rotations of the impeller. The indicator in the form of a roller scales the readings using a mechanical gearbox and displays the result on the display.
In dry-propelled devices, the blades and the counting module interact using a magnetic field.
Vortex counter
Vortex flow meter for the heating system of an apartment building
The second most popular measuring device is installed on a straight section of the main line. It operates on the principle of the appearance of vortices behind an obstacle in the path of water flow. A vortex common house heat meter is installed on a horizontal or vertical pipe, the length of which is not significant.
The device must be installed on a line with a diameter of 20 – 300 mm. The flow compartment contains a triangle-shaped prism, a magnet and an electrode. Energy consumption is taken into account due to its movement along a vortex path, the liquid pressure affects the value of the readings.
In front of the common house heat meter, you need to install a filter to purify the water from accidentally ingressed impurities - this way the device will show the exact value and will last longer.
The vortex counter does not respond to the presence of rust elements in the liquid, but is sensitive to impurities, additives and dirt.
Electromagnetic counter
An electromagnetic meter that records the amount of coolant.
The flow meter operates on the principle of the emergence of an electric current in the coolant when it moves in a magnetic field - the feature of electromagnetic induction is used. The volume of consumption of the electrically conductive carrier, the average speed and voltage of the medium are interconnected, different potentials arise at the cathode and anode.
Electromagnetic devices calculate:
- the amount of thermal power and energy based on information about the volume of energy carrier and its consumption;
- temperature on the return and forward sections of the line with registration of changes in the heat capacity of the liquid as the indicator at the outlet and inlet decreases.
Electromagnetic meters are sensitive to operating conditions and installation method, since small currents appear. Poor-quality joining of wires causes resistance in the contacts and increases the error in the indicators. Despite their sensitivity, electrical appliances are stable; they are installed in single-circuit and double-circuit heating systems.
Regular maintenance and repairs are required; over time, the inside of the meter becomes coated, which distorts the amount of heat consumed. A filter is placed in front of the recorder so that rust and impurities do not force you to pay for excess energy.
Ultrasonic counter
Ultrasonic coolant metering device
The principle lies in the speed of passage of the ultrasonic wave from the emitter to the special signal receiver. The value depends on the flow rate of the coolant. On the pipeline, the source and receiver of the wave are installed opposite each other. The travel time between elements is directly proportional to the speed of the water. ODPU of thermal energy measures the flow of energy in the pipe based on the signal flow time.
A metering device based on an ultrasonic water flow meter has low resistance to the coolant. It operates in conditions of purified liquid, therefore it requires filters in front of the insertion area. If there are impurities in the water or bubbles appear, the readings are read with a large error. Ultrasonic meters are damaged by a layer of scale inside the device.
The devices are installed in their own houses, apartments or rebuilt high-rise buildings, where new communications have been laid or old ones have been replaced. In other cases, heat meters will fail or show inaccurate information.
Ultrasonic meters more often than other types fail due to poor water quality in urban heating mains.
Replacing and installing a meter
For installation, a technical design is drawn up, taking into account the characteristics of the house. The document is approved by the service, then the device is purchased according to the recommendation in the calculation output. For installation, contact a specialized organization. You cannot install the meter yourself.
The meter is replaced in the following cases:
- the end of the operating time prescribed by the manufacturer;
- detection of mechanical or electrical damage that affects the accuracy of the data;
- violation of the control seal;
- if the check shows an excess of the possible error, the information does not correspond to reality;
- missing technical inspection time.
The fee will be calculated not according to actual consumption, but according to the average tariff, if the faulty device is not replaced in time.
Principle of operation
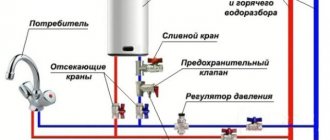
A common house heat meter performs several functions simultaneously. It allows you to see the operating time of electrical appliances indicated on a specific metering unit. The heat meter shows the temperature of the coolant and records the exact amount of thermal energy consumed. The circuit of a general heat energy meter includes the elements:
- Thermal converters are sensors that measure temperature.
- A computer that calculates the amount of heat spent.
- A flow meter that measures the mass and volume flow of a substance.
- Power unit.
The heat meter is designed to record the received heat supplied by the coolant. The equipment determines the amount of energy used by the device per hour, taking into account the temperature of the fluid entering/leaving the system. In this way, the temperature difference over a certain period of time is determined. For this purpose, a special computer is built into the electric meter.
IMPORTANT! Calculation of thermal energy is carried out with an error of 3-6%.
Data is supplied using built-in temperature and flow sensors. The first temperature sensor is installed in the supply pipe of the engineering system, and the second - in the outgoing pipe. The computer analyzes all the data received, after which the exact figure for thermal energy consumption is displayed on the device screen.