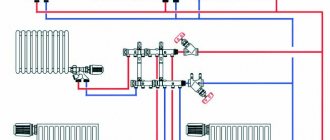
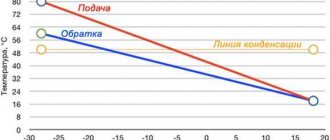
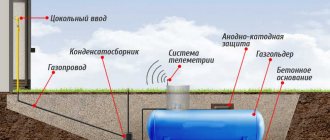
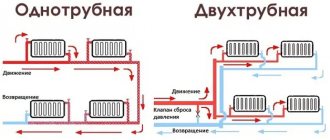
The means by which thermal energy is transferred from the boiler to the radiator is called a thermal agent or coolant. Let's consider what the coolant should be for the heating system of a private house, what it is, what properties it has and what requirements are imposed on it, as well as what features exist for water, antifreeze, antifreeze and other substances used in its role. We will also analyze the selection rules, the TOP 10 best antifreeze liquids on the market today, and the features of pouring antifreeze into the heating system.
Coolant for an open heating system Source expertology.ru
What is a coolant, requirements, properties
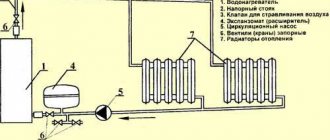
A coolant is a liquid substance that meets a number of operational requirements and is capable of effectively transferring thermal energy from the heating boiler circuit to the radiators in the room. In a simplified form, the principle of its operation is the following algorithm:
- The flow of substance washes the heating circuit of the heating boiler.
- Having acquired a given temperature, it then passes through pipes to receivers - radiators.
- In contact with the internal structures of the batteries, the thermal agent cools and transfers heat to the walls of the device, which in turn release it to the surrounding space.
- The cooled coolant, leaving the radiator, returns in the return line to the heating circuit and the cycle repeats.
Moreover, not every liquid can be used as a heat agent.
Scheme of autonomous heating at home Source survival.com.ua
Requirements
For successful and safe use, the liquid substance must meet the following series of requirements:
- The ability to quickly and fully absorb, transfer and release heat - which corresponds to a high value of heat capacity.
- Neutrality or the minimum possible chemical activity with contacting material - equipment, pipes, radiators and sealing elements.
- Wide range of operating temperatures – both in the heating and cooling zones. Ideally, the heating liquid should not boil quickly and turn into a vapor state at standard boiler operating rates. It should also not thicken or completely crystallize when cooled well below 0 °C and lead to destruction of system equipment in winter.
- The absence of dissolved components in the composition that can crystallize with constant heating of the liquid. Since they can be deposited in the form of insoluble growths on the walls of pipes, radiators and boiler circuits. This will lead to a narrowing of the working clearance and a deterioration in the heat transfer of the equipment, as well as a load on the pumping station.
Clogging of pipes with insoluble sediment Source ds-m.ru
- Absence or minimal corrosion activity on the metal surfaces of system elements.
- Chemical stability - the absence of processes of decomposition or transformation of coolant components into other compounds under the influence of heat, time of use and other factors.
- Constancy of performance characteristics - fluidity indicators, thermal capacity, chemical inertness, etc. - throughout the entire period of operation and under given conditions.
- Absolute safety for the residents of the house. Absence of toxic, flammable, explosive, radioactive and other components hazardous to life and health.
Important! Whatever the requirements, an ideal coolant does not exist in nature. Therefore, in each individual case, it is necessary to select a fluid that matches the nature of the application, equipment configuration, type of building, climate and other operating factors. Some boiler manufacturers directly recommend specific brands of products for filling the system.
Antifreeze supply system Source remont-book.com
Which coolant should I buy?
There are a large number of coolants of different brands on the market. All of them are approximately the same in their properties and technical characteristics. In most cases, the different costs are due to marketing and advertising costs. Those. The more popular the brand, the more expensive the products. There are, of course, certain nuances and patented compositions, but as a rule they do not justify the high cost of the product and are exclusively marketing “tricks”, i.e. They don’t make any kind of revolution in the coolant market and absolutely certainly aren’t worth overpaying for.
In turn, we can recommend you the ThermoStream coolant from a domestic manufacturer - the optimal price-quality ratio. Nothing extra and a reasonable price.
Water as a coolant - pros and cons
Ordinary water is the most commonly used liquid for heating a private home. The main reason for this is accessibility. There are also a number of other advantages of its use:
- Natural prevalence . This makes water a free, accessible and easily replenished resource for any heating system. This not only reduces, but completely eliminates coolant costs for maintenance and repairs.
- Maximum heat capacity – high efficiency of heat transfer from the boiler to the radiator.
- Optimal technical indicators - fluidity, operating temperature, stability.
- Operational safety for people, animals, the environment and the equipment itself - does not burn, does not explode, does not poison.
However, the use of water in the heating system also has its disadvantages:
- High freezing point . When the ambient temperature drops below 0 °C, crystallization will occur with all the ensuing negative consequences - rupture of pipes, batteries, damage to equipment.
- Corrosivity . Water is easily and quickly saturated with oxygen, which, when in contact with metal surfaces of equipment, leads to rusting and destruction of its structure.
Pipes destroyed by corrosion Source gidpokraske.ru
- Formation of scale, growths, siltation. Due to the presence of dissolved impurities of various substances in ordinary water from natural sources, deposits of salts, silt and other components often form on the inner surface of pipes, circuits and batteries. As a result, the clearance narrows, heat transfer properties deteriorate and the service life of the equipment decreases.
Recommendation! Despite the obvious disadvantages, water is the most popular coolant for the heating system of a country house. However, in order to avoid the disadvantages associated with its use, some manipulations are carried out on it. For example, to get rid of impurities, it is boiled, distilled, passed through filters, or special additives are added to it.
How is antifreeze different from water?
If you live in a private house permanently, it is recommended to fill the heating system with distilled water. If there is a possibility that such a coolant will freeze, use antifreeze. One of the advantages of the product is that pipes and radiators do not need to be emptied, even if no one lives in the house in winter. When filling pipes with water, this will have to be done, since due to expansion due to crystallization, the pipeline may burst .
The disastrous consequences of a frozen pipe in a radiator
The main advantage of antifreeze compared to water is their low freezing point. As a rule, solutions used in private homes are designed to work at a lower temperature threshold of -65...-30 °C . For some products this threshold reaches -70 °C . But even if the temperatures are lower, the substance does not harden, but goes into a jelly-like state and is characterized by a lower expansion rate than water. After defrosting, the “anti-freeze” does not lose its performance properties. This deprives the home owner of worries that during severe frosts the pipes and boiler will be damaged, and with a subsequent increase in temperature the house will flood.
Another disadvantage of water is that it reacts with metals and causes their gradual destruction, or corrosion . During the heating process, scale , which settles on the inner walls of pipes, radiators, and other components.
Antifreezes usually contain special substances - additives that prevent the formation of lime deposits and help extend the life of metal surfaces. At the same time, the active substances used in the production of antifreeze are mostly quite aggressive substances. They are also capable of destroying heating system elements. To prevent this from happening, additives are included in the composition.
Scale in heating radiators when using hard water
Prices for popular models of heating radiators
Heating radiators
But antifreeze also has disadvantages compared to water:
- high viscosity , which requires the installation of more powerful pumping equipment;
- heat capacity is 15% lower , which affects heat transfer;
- the need for more thorough sealing of connections;
- excessive toxicity of some products;
- the need for disposal of substances , which can pose certain problems;
- formation of solid sediment , due to which the system becomes clogged, destroyed, and carbon deposits form in the boiler;
- high cost - 20-30 USD. e. for 20 l.
Table 1. Comparison of the properties of antifreeze and water.
| Options | Water, % | Antifreeze,% |
| Specific thermal conductivity indicators | 100 | Up to 90 |
| Density | From 110 | |
| Viscosity (t° 80°С) | From 130 | |
| Volume expansion | From 130 | |
| Fluidity | Up to 150 |
Therefore, experts advise using antifreeze only if people rarely live in a house with steam heating in winter.
Antifreeze is used when there is a risk of heating system freezing
Antifreeze, types, features
Water purified from harmful impurities and inhibited by special additives still does not become an ideal coolant. Since it is impossible to get rid of the main drawback - freezing at 0 degrees. Therefore, today special antifreeze liquid is widely used everywhere.
Antifreeze antifreeze down to -30 degrees Source antifreez.ru
Properties and features of antifreeze
The main feature of using such a liquid is the operating temperature range suitable for winter operating conditions. Antifreeze for heating freezes at a much lower temperature than ordinary water. Besides this, it has other obvious advantages:
- The structure of antifreeze does not allow it to completely crystallize when the temperature drops, but only to transition from a liquid to a gel state. This essential property preserves the integrity and performance of pipes, circuits and batteries. Therefore, even if the temperature drops below critical due to an unexpected shutdown of the system in cold weather, the equipment will not defrost.
- Economical use due to the possibility of diluting the concentrate with distilled water. Most formulations are sold in concentrated form. The lower limit of their operating temperature is -60-70 °C. However, in most regions the ambient temperature rarely drops below -40-30 degrees. Therefore, the liquid can be diluted without loss of properties according to the factory instructions.
Antifreeze and distilled water for dilution Source koffkindom.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in engineering systems (heating, water supply, sewerage and others) and related work
- Chemical stability and inertness. Antifreeze contains components that do not decompose when heated within the performance parameters and are inert with respect to the equipment material. In this case, the liquid lasts for at least 5 years.
With all the obvious advantages and superiority over ordinary water, however, antifreezes also have a number of specific disadvantages:
- High viscosity values. For normal circulation through the antifreeze fluid system, it is necessary to provide greater pressure, which means using a more powerful pump. At the same time, it is unacceptable to use antifreeze in variations with natural circulation.
- Up to 15% lower heat capacity than water. For this reason, the overall efficiency of the system will be reduced. Consequently, greater energy consumption, the use of radiators with an increased area and an increase in their number will be required in order to achieve a normal heating effect.
- The high degree of fluidity of the substance forces a more careful approach to the selection of sealing elements and more frequent procedures for their maintenance, repair and replacement in all connecting units.
Replacing seals in the radiator Source stroy-podskazka.ru
- Toxic components in many coolants pose a direct threat to all living things in the surrounding space.
- The need to install a larger expansion tank is due to the increased expansion coefficient.
Important! It is unacceptable to use inexpensive options for an open-type expansion tank with antifreeze for two reasons - loss of the substance through evaporation and contamination of indoor air with toxic fumes.
Varieties
Non-freezing heating fluid can have a different chemical basis. On this basis, antifreezes are divided into the following categories:
- Ethylene glycol.
- Propylene glycol.
- Glycerol.
- Bishofite.
There are also compositions specifically used in electrode-type heating boilers. In addition, many users recommend using regular antifreeze as an alternative to modern antifreeze. Let's look at the features of each option in detail.
Ethylene glycol coolant Source dialrus.com
Ethylene glycol
This is the most common, accessible and cheap antifreeze for the heating system of a country house. Available in two forms - concentrated and diluted. The second option is applicable at temperatures down to -30 °C, concentrate - up to -65 degrees. Among the main features of its operation are the following:
- Foaming under strong heating and, as a result, the formation of gas plugs. Eliminated by adding additives and temperature control.
- Oxidation of zinc-coated surfaces despite the use of inhibitors.
- Chemical decomposition when heated above 110 °C. The problem is eliminated by automatic control of the boiler temperature.
- Possibility of insoluble precipitate formation due to overheating. As a result, the entire pipeline system becomes clogged.
Ethylene glycol is poisonous. Therefore, it can only be poured into closed-loop systems.
Closed heating Source ytimg.com
Propylene glycol
A non-freezing liquid for the heating system based on propylene glycol is at least twice as expensive as the analogue considered. However, despite this, he is in great demand. The reason is complete harmlessness to humans. In purified form, the compound is often added even to confectionery products as a flavoring additive. When used in heating systems, antifreeze exhibits the following series of properties:
- Increased fluidity, which implies strict control over the tightness of the system and places high demands on the sealing elements.
- Oxidation of zinc surfaces.
- Easy flammability - at 421 degrees.
- Service life – up to 10 years.
- Operating temperature – up to -50 °C.
Propylene glycol antifreeze can be used in open systems, as well as double-circuit junctions, when there is a risk of coolant getting into household water.
Glycerol
Glycerin coolant for heating is actually an analogue of the antifreeze discussed above. At the same time, it is 25% cheaper and is characterized by the following number of advantages:
- Non-toxic.
- Wide range of operating temperatures – from -30 to +110 degrees.
- Does not destroy pipes when frozen.
Glycerin-based coolant Source fabrikatepla.ru
Instructions for use
If your system previously ran on water, switching to antifreeze will not be easy. Theoretically, radiators with a boiler can be emptied and filled with cold-resistant coolant, but in practice the following will happen:
- due to lower heat capacity, the output of batteries and the efficiency of heating rooms will decrease;
- due to viscosity, the load on the pump will increase, coolant flow will drop, and less heat will reach the radiators;
- antifreeze expands more than water, so the capacity of the old tank will not be enough, the pressure in the network will rise;
- To improve the situation, you will have to increase the temperature on the boiler, which will lead to excessive fuel consumption and increased pressure.
Addition. After filling the liquid, the old connections sealed with flax and paint are guaranteed to flow.
Leaking joints must be repacked, sealing the threads with dry flax or thread with sealant
. In order for heating to function normally using a chemical coolant, you need to calculate in advance or remake the existing system according to the new requirements:
- Select the capacity of the expansion tank at the rate of 15% of the total volume of liquid (water was 10%);
- The pump performance is assumed to be 10% more, and the generated pressure is assumed to be 50% more. Let us explain with an example: if previously there was a unit with a working pressure of 0.4 Bar (4 meters of water column), then use a 0.6 Bar pump for antifreeze.
- In order to operate the boiler in optimal mode and not raise the temperature of the coolant, it is advisable to add 1-3 (depending on power) sections to each battery.
- Pack all joints with dry flax or use high-quality pastes - sealants such as LOCTITE, ABRO or Hermesil.
- When purchasing shut-off and control valves, consult with the seller about the resistance of rubber seals to glycol mixtures.
- Pressure test the system again by filling the pipes and heating equipment with water.
- When starting the boiler unit at negative temperatures, set the minimum power. Cold antifreeze needs to be warmed up slowly.
Advice. The total amount of coolant is easy to calculate - the cross-sectional area of the pipe is multiplied by its length, the capacity of the boiler and radiators is indicated in the product data sheets. Find out how to properly place and connect the expansion tank in our separate publication.
Before pumping in frost-resistant liquid, fill in water and test the pipelines with a pressure exceeding the operating pressure by 25%. The
concentrated coolant must be diluted with water, ideally with distillate. Do not rely on an excessive reserve of frost resistance - the more water you add, the better the heating will work. Recommendations for preparing coolant:
- For heating elements, electric and gas double-circuit heat generators, prepare the mixture at minus 20 degrees. A more concentrated solution may foam upon contact with the heater, and carbon deposits will form on the surface of the heating element.
- In other cases, mix the components at freezing point according to the table below. Proportions are indicated per 100 liters of coolant.
- If there is no distillate, first conduct an experiment - dilute the concentrate in a jar with plain water. If you see a precipitate of white flakes - a product of the decomposition of inhibitors and additives, this water should not be used.
- A similar check is done before mixing antifreeze from two different manufacturers. It is unacceptable to dilute ethylene glycol with propylene composition.
- Prepare the coolant immediately before pouring.
The ratio of concentrate and water is given per 100 liters.
To find out the amount of ingredients for a volume of 150 liters, multiply the given figures by a factor of 1.5. The maximum service life of any non-freezing substance in pipes and heating radiators is 5 years. At the end of the specified period, the liquid is drained, the system is flushed twice and filled with fresh antifreeze.
Rules for choosing antifreeze
An objective concept of which coolant is best to use in the heating system of a private house under specific conditions arises when taking into account the following series of criteria:
- Type of base and its applicability to equipment and operating conditions.
- Freezing and boiling points, optimal operating heating range - taking into account the dilution of the concentrate.
- Possibility of reducing concentration by adding water.
- Life time.
Note! Antifreeze is not recommended for use in open systems and with natural circulation. In addition, the antifreeze liquid should not come into contact with an unprotected galvanized surface and rubber, silicone seals, as well as oiled tow. In addition, only reliable automation can provide accurate control over compliance with its heating parameters.
Pouring antifreeze into the heating system Source hstream.ru
What is used for electrode boilers
In houses where this type of heating equipment is installed, a special type of antifreeze is used. This is due to the fact that alternating current passes through the coolant and ionization of the solution occurs. This puts forward certain requirements for the chemical composition of the product. Appropriate ionization, electrical thermal conductivity, and electrical resistance must be ensured. Usually the boiler manufacturer himself makes recommendations about which product is best to use. And often, depending on the implementation of the recommendation, the warranty on the equipment is maintained.
We recommend an informative article on the topic - Wood-burning boiler for heating a home, where we discussed in detail how to choose a simple and effective boiler.
Antifreeze is an excellent tool for extending the life of a heating system, especially if it is preserved for some time. However, this product must be used correctly. Before use, you should read all operating instructions from the heating equipment manufacturer, as well as the instructions for use of the products. Only in this case will success be guaranteed; radiators and pipes will last for many decades.
Tips for use
Before you start pouring antifreeze into the heating system of a private home, you must consider the following set of recommendations:
- It is almost impossible to make a fairly accurate calculation of what concentration and corresponding physicochemical parameters an antifreeze liquid will require. Therefore, after filling, it may be necessary to increase the pump power, increase the volume of the expansion tank, increase the number of battery sections and even the cross-section of the heating circuit.
- Automatic valves for bleeding gas plugs may not work properly. Therefore, it is better to immediately install manual analogues, such as the Mayevsky crane.
- Before filling in new artificial coolant, the system must be washed with a special agent.
- To dilute the concentrate to the desired concentration, only distilled water can be used.
- After filling in compliance with all recommended standards, the system can only be started gradually. This is necessary to check the compatibility of all components with the new type of coolant.
Propylene glycol
But propylene glycol is safer in terms of toxicity, that is, it is completely non-toxic, so it is allowed to be used in all countries. Moreover, it can even often be found in food (look for it under code E 1520). So, the advantages of the substance include complete safety in terms of environmental protection, as well as excellent physical characteristics (such as a very low crystallization temperature - minus 40 degrees). But all the advantages pale in comparison to the main disadvantage - the very high cost (from 150 rubles per kilogram) . This is why propylene glycol is so rare.
TOP 10 best antifreezes
In order to choose the best antifreeze for your heating system today, you need to consider the TOP 10 products from modern manufacturers:
- DIXIS-65.
Universal for gas and electric boilers. Works down to -65 degrees. Service life 5 years.
- Warm House Eco.
Based on propylene glycol - harmless. Compatible with sealants and tow. Does not destroy pipes when frozen.
- THERMAGENT-65.
Retains properties for up to 20 seasons. Suitable for low temperature climate areas. Contains ethylene glycol.
Purchasing coolants: modern manufacturers
The market offers goods from domestic producers and imported products. The latter option will cost 2-3 times more. EU manufacturers provide guaranteed safe products for human health. Also, when purchasing imported products, there is a risk of running into counterfeit products. Domestic products will cost less.
Among oil antifreezes, it is worth highlighting the products of Total and RODA. Certified quality from European manufacturers. Dyes are added to the oil to help identify leaks.
Domestic manufacturers of coolants that deserve trust:
- Khimprom is one of the first enterprises in Western Siberia. Market leader. It produces products based on propylene glycol specifically for our climate, with a low freezing point.
- Spetsavia is a modern manufacturer of propylene glycol coolants that are distinguished by high performance. Modern equipment allows us to produce products that are not inferior to European analogues. Has its own accredited laboratory
- Himavto is the manufacturer of the first household antifreeze on the domestic market, which was released in 2001. Since then, the company has been among the leading manufacturers. Has representatives in the CIS countries. Domestic companies can compete with European products. But you need to purchase their goods only in specialized stores, and not in the market.
Video description
Video about what you need to consider when pouring antifreeze into the heating system:
- RODA.
Glycerin coolant, works down to -30 degrees. Does not require rinsing before filling. Completely safe.
- AMT-300.
Designed for closed systems, applicable down to -15 degrees. Does not cause corrosion. Requires powerful pumping equipment.
- Hot Stream.
Based on ethylene glycol with additives. Serves for 10 years, works at temperatures down to -30 degrees. Available in diluted form.
- Teplokom.
Based on food grade glycerin. Completely safe. Suitable for use in systems with steel and aluminum radiators. Valid down to -50 degrees.
- WARME BASIC-65.
Contains ethylene glycol. Applicable down to -65 °C. Suitable for northern regions. Service life 2 years.
- Thermagent Eco 30.
Based on propylene glycol. Maintains performance characteristics at temperatures down to -30 degrees. Safe, lasts up to 10 years.
- FTX-30.
Coolant with additives based on propylene glycol. Freezes below -30 degrees. Does not corrode seals.
When choosing a coolant, price is not the last thing. However, more important characteristics are equipment efficiency and safety.
Heat transfer fluids based on ethylene glycol
For some heating units to operate, it is necessary to use a coolant that freezes only at very low temperatures. Low-freezing coolant (or antifreeze) based on ethylene glycol is one of them.
The low temperature at which crystallization of these types of coolants begins depends on the ratio of the base component - ethylene glycol and distilled water in solution. To improve the performance characteristics of these coolants, a package of functional additives is added to their composition, which protect the metal surfaces of equipment from the corrosive effects of ethylene glycol.
Antifreeze is suitable for use in automotive cooling systems of internal combustion engines and in systems that are used for heating buildings, structures and as a coolant in various industries. It belongs to the category of mid-price coolants.
The temperature at which this type of coolant begins to crystallize can reach minus 70 °C and does not form deposits on the heat pipes.
Among the key characteristics of such a coolant are the following:
- low-freezing properties (freezing depends on the concentration of ethylene glycol in the solution);
- practicality and safety of use (during cooling and crystallization it acquires an amorphous structure - it does not expand significantly, and therefore is not capable of damaging the heating system equipment);
- contains a package of additives (protecting against corrosion, scale, foaming and stabilizing, antioxidant);
- does not change its original basic special properties throughout the entire service life;
- has a high initial boiling point in a closed system;
- does not have an aggressive effect on various materials (metal, plastic, rubber, textiles) during the warranty period, since the composition contains the necessary additives in sufficient quantities.
The main disadvantage of such a coolant is its toxicity. They are moderately toxic in terms of their effects on the human body (hazard class 3) and dangerous in terms of environmental parameters. For this reason, it is not used in open heating systems. When using it, it is important to prevent it from coming into contact with any objects. Otherwise, it would be advisable to replace them.
Features of pouring coolant into the heating system
For successful and trouble-free operation of autonomous heating of a private home, it is important not only to know which coolant is best to use in the heating system, but also how to fill it correctly. There are two main ways to do this:
- By gravity.
- By pump.
In the first case, the liquid is poured through an open socket at the highest point of the heating piping system. The method is quite simple, but requires a lot of effort and time. More suitable for small-volume open systems operating in a one-story house.
The second is more preferable when large volumes of coolant need to be filled. In this case, the use of both submersible and pressure testing pumping equipment is allowed. The main nuance of pumping coolant in this way is to eliminate or minimize the entry of air into the system.
The procedure for pumping coolant into the heating system must be carried out by experienced specialists strictly in accordance with the technology and control of technical parameters of pressure and volume, as well as the removal of air pockets.
How to pump coolant
Problems usually arise only with closed systems, since open ones are filled through an expansion tank. The coolant for the heating system is simply poured into it. It spreads throughout the system under the influence of gravity. It is important that all air vents are open when filling the system.
An open heating system is filled through an expansion tank
There are several ways to charge a closed heating system with coolant. There is a method of filling without the use of equipment - by gravity, there is a submersible pump of the “Kid” type or a special one, with the help of which pressure testing of the system is done.
Fill by gravity
Although this method of pumping coolant for a heating system does not require equipment, it takes a lot of time. You have to squeeze out the air for a long time and also gain the required pressure for a long time. By the way, we pump it up with a car pump. So you will still need equipment.
Finding the highest point. Usually this is one of the gas vents (we remove it). When filling, open the valve to drain the coolant (lowest point). When water runs through it, the system is full.
With this method, you can connect a hose from the water supply, you can pour prepared water into a barrel, raise it above the entry point and then pour it into the system. Antifreeze is also added, but when working with ethylene glycol you will need a respirator, protective rubber gloves and clothing. If the substance gets on fabric or other material, it also becomes toxic and must be destroyed.
You need to monitor the pressure using a pressure gauge
When the system is full (water runs out of the drain tap), take a rubber hose about 1.5 meters long and attach it to the entrance to the system. We select the entrance so that the pressure gauge is visible. At this point we install a check valve and a ball valve. To the free end of the hose we attach an easily removable adapter for connecting a car pump. Having removed the adapter, pour coolant into the hose (keep it raised up). After filling the hose, use an adapter to connect the pump, open the ball valve and pump liquid into the system. You need to make sure that air is not pumped in. When almost all the water contained in the hose has been pumped in, the tap is closed and the operation is repeated. On small systems, to get 1.5 Bar, you will have to repeat it 5-7 times, with larger ones you will have to tinker longer.
Fill using a submersible pump
To create working pressure, the coolant for the heating system can be pumped with a low-power submersible pump like Malysh. We connect it to the lowest point (not the system drain point). We connect the pump through a ball valve and a check valve, and install a ball valve at the drain point of the system.
We pour the coolant into the container, lower the pump, and turn it on. During operation, we constantly add coolant - the pump should not drive air.
We monitor the pressure gauge during this process. As soon as its needle moves from the zero mark, the system is full. Until this point, manual air vents on radiators can be opened and air will escape through them. As soon as the system is full, they must be closed.
Next, we begin to increase the pressure - we continue to pump the coolant for the heating system with the pump. When it reaches the required level, we stop the pump and close the ball valve. We open all the air vents (on the radiators too). The air comes out, the pressure drops. We turn on the pump again, pump up a little coolant until the pressure reaches the design value. We release the air again. We repeat this until air stops coming out of their air vents.
Next, you can start the circulation pump and bleed the air again. If the pressure remains within normal limits, the coolant for the heating system is pumped. You can put it to work.
We use a pump for crimping
The system is filled in the same way as in the case described above. In this case, a special pump is used. It is usually manual, with a container into which the coolant for the heating system is poured. From this container, liquid is pumped through a hose into the system. You can rent it from companies that sell water pipes. In principle, it makes sense to buy it - if you use antifreeze, you will have to change it periodically, that is, you will need to fill the system again.
This is a manual pump for pressure testing, with which you can pump coolant for the heating system
When the system is filled, the lever moves more or less easily, but when the pressure rises, it becomes more difficult to work. There is a pressure gauge both on the pump and in the system. You can follow where it is more convenient. Next, the sequence is the same as described above: pump up to the required pressure, deflate the air, repeat again. Do this until there is no air left in the system. After that, we also start the circulation system for about five minutes (or the entire system, if the pump is in the boiler), and bleed the air. We also repeat several times.
Briefly about the main thing
The coolant for heating a private house allows you to efficiently and safely transfer thermal energy from the heating circuit of the boiler to the radiators, which in turn release heat to the surrounding space. The coolant must meet the following series of requirements:
- Complete heat transfer.
- Chemical inertness.
- Optimal operating temperature range.
- Absence of harmful components.
- Stability and constancy of operating parameters.
- Safety for people and the environment.
Water can be used as a coolant. It tolerates heat best, is free and accessible. However, it freezes already at zero degrees, causes corrosion and can form insoluble salts. Non-freezing liquids do not have such disadvantages.
Antifreezes are divided according to their chemical composition into ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and glycerin. There are also special ones for electrode boilers and mineral ones. Antifreeze cannot be used as a cheap alternative. You can add antifreeze manually or with a pump. At the same time, monitoring performance characteristics and strict adherence to technology are extremely important.
The main characteristics that you need to focus on when choosing a coolant
There are a number of requirements for work environments. Each of them is a specific characteristic of coolants for heat exchange systems, including heating processes.
- Good heat storage capacity, allowing to reduce energy costs for movement.
- Transportability. It is important to have a stable state of aggregation and the ability to transfer heat (cold) over the required distances.
- Low level of toxicity or its minimal impact on the health of personnel.
- Environmental Safety. It is necessary that possible unintended leaks and emissions do not have a negative impact on the environment.
- Chemical inertness in relation to materials of heat exchange systems and technological equipment of various industries (metals, alloys, sealing products, rubber, etc.).
- Optimal operating temperature range, which ensures stability of heat transfer and stable control of the modes of various production processes and reduces operating costs.
- Explosion and fire safety. It is important that the heated coolant does not ignite when in contact with air.
Some physical characteristics are no less important: a high thermal conductivity coefficient, the value of the coefficient characterizing surface tension and the optimal viscosity value over a wide temperature range.
specializes in the production and sale of industrial coolants of a wide range of different brands.
Prices: summary comparison table
To compare characteristics and prices, the important properties of the antifreezes considered are collected in a table.
| Brand | Working, OS | pH | The basis | Color | Minimum price per kg, rub. |
| Thermagent ECO-30 | -30–106 | 8 | propylene glycol | green | 270 |
| Warm house ECO-30 | -30–106 | 7,5-9 | propylene glycol | green | 150 |
| DIXIS TOP-30 | -30–104 | 8 | propylene glycol | yellow | 120 |
| DIXIS-65 | -65–110 | 7,5-9 | ethylene glycol | Yellow green | 125 |
| Hot Stream EcoPro 30 | -30–105 | 8 | propylene glycol | green | 170 |
| Warme ECO PRO 30 | -30–110 | 7-9 | propylene glycol | blue, green tint | 250 |
| Coziness Technology -65 | -65–115 | 8,5 | ethylene glycol | red | 170 |
The correspondence of the color indicated in the table is checked upon purchase - this partially guarantees against the purchase of counterfeit products.
For all samples examined, manufacturers indicate a service life of 10 years.