Everyone is well aware that already at zero degrees Celsius, water turns from a liquid state of aggregation into a solid state. And this brings with it a lot of problems both for motorists and for heating systems of private or country houses. To prevent freezing and, as a consequence, failure of important functional components, a special liquid is required, which is popularly called “anti-freeze”. Making it yourself is quite simple. Moreover, the cost of the finished product will be low.
An old and proven method is to use vodka, well-known and used almost everywhere in our country. The quality of alcohol does not play any role, so you can use the cheapest option. To prepare such a liquid, in addition to an alcohol-containing product, you will need ordinary water and any kitchen dishwashing detergent. The latter is necessary to give the final product good cleaning properties.
An alcoholic drink should be poured into a pre-prepared five-liter bottle. Next, add two or three drops of detergent. No more is necessary, as this can lead to increased foaming, which will be inconvenient when cleaning the glass. Next, you need to fill the bottle with water, close the lid and shake thoroughly. This is how you make an antifreeze with your own hands. The proportions may be slightly changed based on environmental conditions. A liquid made according to this recipe will be effective at temperatures down to -25 degrees. If more severe frosts are expected, you can increase the share of vodka to two bottles.
An alcohol solution is not suitable in this case. This is due to the fact that when heated, the alcohol will simply evaporate. That is, as a result, there will be simple water in the heating circuit, which at zero degrees will turn into ice. And this can lead to other, sadder consequences. Some people recommend using antifreeze and antifreeze, but in this case the manufacturer may remove the equipment from warranty service. It will also require additional monitoring of all connections in the circuit that may be damaged under the influence of special fluids.
The heating networks of country houses are not always filled with clean water. In special operating conditions, it is practiced to pump in non-freezing liquids - antifreeze, plus the addition of additives with a certain set of properties (inhibitors and salts). We propose to consider 2 questions - which coolant for the heating system is better and how to properly use various chemical compositions.
Making your own antifreeze
Freezing of water is the main reason for using antifreeze
It should be immediately noted that ordinary water is the best type of coolant. It has sufficient heat capacity, has optimal density, and is affordable. Therefore, if the likelihood of exposure to negative temperatures affecting the heat supply is minimal, it is best to use distilled water.
But if this condition cannot be met, a special non-freezing liquid for heating boilers will be required. It is a solution in which water occupies up to 70% of the total volume. The rest is additives that reduce the crystallization threshold to -60°C. They include:
- The main component is ethylene glycol, propylene glycol or glycerin. This non-freezing liquid for the home heating system has a high viscosity coefficient, which leads to the desired effect;
- Additives . It is thanks to them that the non-freezing liquid for water heating does not foam and does not form a crystalline precipitate when the temperature rises.
Device for filling antifreeze liquid
The problem with making such a composition yourself is the correct selection of the last component. All manufacturers do not disclose the full list of components. But even knowing how to make the correct composition, it is impossible to do this at home - this will require special equipment and adherence to manufacturing technology.
How to make your own non-freezing liquid for heating, and what consequences can its use lead to?
- An increase in the level of foam during heating of the coolant will lead to the rapid formation of sediment on the walls of pipes and radiators;
- Reducing the heat transfer of homemade antifreeze liquid. This will cause a significant decrease in heating efficiency;
- Do-it-yourself non-freezing heating fluid can have a negative effect on the steel elements of the system due to the high oxygen content. Corrosion processes will accelerate.
Any non-freezing liquid for stove heating or solid fuel boiler should not cause these undesirable effects. Therefore, to maintain the safety of the system, it is recommended to use only high-quality antifreeze liquid for water heating from a reliable manufacturer.
Before using antifreeze, you should familiarize yourself not only with its composition and recommendations for use, but also carefully study the instructions for the heating boiler. It should indicate the types of coolant that can be filled.
How to make anti-freeze: main points
Whatever composition you prepare, it should:
- clean the windshield from dirt and ice;
- remain liquid at subzero temperatures;
- be safe for both humans and machine parts.
That's all, perhaps, nothing more is required from the washer.
As a rule, the base of non-freezing liquid includes ordinary distilled water, alcohol and some additives for fragrance, coloring and improving cleaning properties. Among the alcohols used in production are methyl, ethyl and isopropyl.
Methyl alcohol is harmful to health, so anti-freeze products based on it are prohibited in Russia. And even if you have a canister of this substance lying around somewhere in your garage, you should not pour it into your car.
Isopropyl alcohol is extremely rare among people; this technical liquid has a pungent odor. You can ask someone who repairs and cleans office equipment at home. True, such a master usually doesn’t have more than half a liter in stock. And by the way, it costs much more than ethanol.
Ethyl alcohol is the most affordable option. Many people have a bottle of medical, technical or even food grade ethanol at home. However, no one has canceled our favorite vodka either, because in essence it is an aqueous solution of ethyl alcohol.
To make anti-freeze in the washer at home, many also use salt, acids, and detergents. But first things first.
Types of non-freezing liquid for heating
Factory antifreeze for heating
Having decided that non-freezing coolants for the heating system should only be of factory quality, you can begin to select a specific composition. It must be adapted to a specific heat supply scheme, and its performance indicators cannot worsen the parameters of the system.
Before pouring non-freezing liquid into the heating system, you need to find out whether it will negatively affect the heating components. To do this, you should read the instructions for use, which must be included. It is also important to pay attention to the main component of the antifreeze fluid for heating boilers. Not only the condition of the heat supply components, but also the operating conditions depend on this:
- Ethylene glycol . Characterized by high toxicity. Therefore, it can only be used in closed circuits. Difficulties may arise when pouring this type of freezing liquid into the heating system. In a vapor state, it is hazardous to human health;
- Propylene glycol . In fact, it is a food additive, so it can be used in both open and closed heating systems. In contrast to ethylene glycol, the crystallization temperature is +80°C, which makes it possible to use it to operate high-temperature solid fuel boilers. The only drawback is the high cost;
- Glycerin . The most popular type of non-freezing liquid for stove heating. Its performance qualities are slightly lower than those of propylene glycol. However, at the same time, the cost of glycerin antifreeze is an order of magnitude less. Disadvantages include high turnover. This may affect the tightness of the pipelines. The solution is to replace the rubber gaskets with paronite gaskets.
Currently, the use of non-freezing liquid for a home heating system based on glycerin is the best option.
| Name | Compound | Price, rub/l |
| Warm house -30°С | Propylene glycol | 65 |
| Dixis -65 | Glycerol | 75 |
| Coziness Technology -65 | Ethylene glycol | 120 |
Manufacturers offer 2 types of non-freezing coolants for heating systems - ready-to-use and concentrate. For large heat supply schemes, it is more profitable to purchase concentrate. However, this complicates the process of filling the system.
When purchasing ready-to-use liquid, you need to pay attention to the lower critical level of freezing temperature. It can be from -25°C to -65°C.
Choosing an “anti-freeze” for heating
Tip number one: buy and fill in antifreeze only in extreme cases - for periodic heating of remote country houses, garages or buildings under construction. Try to use water - regular and distilled, this is the least troublesome option.
When choosing a frost-resistant coolant, follow the following recommendations:
- If your budget is limited, take ethylene glycol from any well-known brand - “Teply Dom”, Dixis, Spektrogen Teplo Coolant, Bautherm, Termo Tactic or “Thermagent”. The cost of the concentrate -65 °C from Dixis is only 1.3 USD. e. (90 rubles) per 1 kg.
- If there is a danger of antifreeze getting into household water (for example, through an indirect heating boiler, double-circuit boiler), or you are very concerned about the environment and safety, buy harmless propylene glycol. But keep in mind: the price of the chemical is higher; a ready-made Dixis solution (minus 30 degrees) will cost 100 rubles (1.45 USD) per kilogram.
- For large heating systems, we recommend using premium class HNT coolant. The liquid is made on the basis of propylene glycol, but it has an increased service life of 15 years.
- Do not buy glycerin solutions at all. Reasons: sedimentation in the system, too high viscosity, tendency to foam, a large number of low-quality products made from technical glycerin.
In the light of the flashlight, tiny white flakes are visible - a sediment of technical glycerin
- Electrode boilers require a special liquid, for example, HNT-35. Before use, be sure to consult with a representative of the manufacturer.
- Do not confuse automobile antifreezes with chemicals used in heating systems. Yes, both formulations are glycol-based, but the additive packages are completely different. Engine coolant is not compatible with residential water heating.
- For open and gravity-flow heating systems, it is better to use water, or, in extreme cases, propylene glycol diluted at minus 20 °C.
- If the heating distribution is made with galvanized pipes, there is no point in purchasing glycol mixtures. The substance will deal with zinc, lose the package of additives and quickly degrade.
Clarification. It is not profitable to use frost-resistant liquid for an open heating system. Hot antifreeze will evaporate into the atmosphere through the expansion tank, the antifreeze will have to be constantly topped up, and money will be spent. It is unacceptable to pump in ethylene glycol, since its vapors are toxic.
There is a lot of debate about the harmfulness of ethylene glycol compounds, including on the pages of construction forums. Without denying the harmful effects of the chemical on human health, let us draw attention to a convincing fact.
Features of pouring antifreeze into the heating system
manual pump for testing and filling heating with antifreeze
In order not to make an antifreeze heating fluid yourself and at the same time risk the performance of the entire system, you need to purchase a ready-made composition. However, in addition to this, you should familiarize yourself with the filling technology.
If there is old coolant in the system, it should be drained. It is recommended to check its condition. The degree of contamination will indicate the relevance of comprehensive cleaning. This is done before adding antifreeze to the heating system. The subsequent stages of work consist of completing the following points:
- If antifreeze was used before , the system must be completely flushed. Otherwise, mixing two different antifreeze fluids for furnace heating may lead to undesirable chemical reactions;
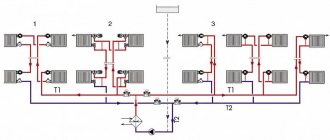
- Closed system . In it, the filling point should be lower than all other heating devices. Using pumping equipment, the heating system of a private home is filled with non-freezing liquid. It is important that the pressure in the pipes does not exceed 3 atm;
- Open system . For it, the use of antifreeze liquid for water heating is not recommended. Constant exposure to air can lead to a significant increase in foaming. Filling is done through the upper expansion tank;
- Heating testing . The temperature in the system increases gradually. At the same time, the tightness of all components is checked, as well as the absence of extraneous noise during coolant circulation.
During operation, you will need to add antifreeze heating fluid yourself. Therefore, it is recommended to purchase it with a reserve - 15-20% more than the calculated volume of the system.
You cannot make your own non-freezing liquid for heating. The use of automotive antifreeze is also not recommended, since in most cases they are based on unsafe propylene glycol.
Instructions for use
If your system previously ran on water, switching to antifreeze will not be easy. Theoretically, radiators with a boiler can be emptied and filled with cold-resistant coolant, but in practice the following will happen:
Addition. After filling the liquid, the old connections sealed with flax and paint are guaranteed to flow.
In order for heating to function normally using a chemical coolant, you need to calculate in advance or remake the existing system according to the new requirements:
- Select the capacity of the expansion tank at the rate of 15% of the total volume of liquid (water was 10%);
- The pump performance is assumed to be 10% more, and the generated pressure is assumed to be 50% more. Let us explain with an example: if previously there was a unit with a working pressure of 0.4 Bar (4 meters of water column), then use a 0.6 Bar pump for antifreeze.
- In order to operate the boiler in optimal mode and not raise the temperature of the coolant, it is advisable to add 1-3 (depending on power) sections to each battery.
- Pack all joints with dry flax or use high-quality pastes - sealants such as LOCTITE, ABRO or Hermesil.
- When purchasing shut-off and control valves, consult with the seller about the resistance of rubber seals to glycol mixtures.
- Pressure test the system again by filling the pipes and heating equipment with water.
- When starting the boiler unit at negative temperatures, set the minimum power. Cold antifreeze needs to be warmed up slowly.
Advice. The total amount of coolant is easy to calculate - the cross-sectional area of the pipe is multiplied by its length, the capacity of the boiler and radiators is indicated in the product data sheets. Find out how to properly place and connect the expansion tank in our separate publication.
The concentrated coolant must be diluted with water, ideally with distillate. Do not rely on an excessive reserve of frost resistance - the more water you add, the better the heating will work. Recommendations for preparing coolant:
- For heating elements, electric and gas double-circuit heat generators, prepare the mixture at minus 20 degrees. A more concentrated solution may foam upon contact with the heater, and carbon deposits will form on the surface of the heating element.
- In other cases, mix the components at freezing point according to the table below. Proportions are indicated per 100 liters of coolant.
- If there is no distillate, first conduct an experiment - dilute the concentrate in a jar with plain water. If you see a precipitate of white flakes - a product of the decomposition of inhibitors and additives, this water should not be used.
- A similar check is done before mixing antifreeze from two different manufacturers. It is unacceptable to dilute ethylene glycol with propylene composition.
- Prepare the coolant immediately before pouring.
The ratio of concentrate and water is given per 100 liters. To find out the amount of ingredients for a volume of 150 liters, multiply the given figures by a factor of 1.5
The maximum service life of any antifreeze substance in pipes and heating radiators is 5 years. At the end of the specified period, the liquid is drained, the system is flushed twice and filled with fresh antifreeze.
Restrictions on the use of antifreeze in heating supply
Damage to heating elements of electric boilers due to incorrectly selected antifreeze liquid
Despite all its positive aspects, not every non-freezing liquid is suitable for heating boilers. Improper use can lead to gradual destruction of the heat exchanger and rapid failure of expensive equipment.
In addition, there are a number of other restrictions that must be taken into account when using non-freezing coolant in heating systems:
- Many models of double-circuit boilers are not designed for antifreeze. It can get into the hot water supply system, which is an undesirable factor;
- Antifreeze liquid has a negative effect on galvanized surfaces. The protective layer quickly deteriorates and, as a consequence, the heating element fails;
- Since the viscosity of antifreeze is much higher than that of water, it is necessary to supplement the heating with powerful circulation pumps. The lower the critical level of freezing temperature, the greater the productivity of the pumps;
- Antifreeze replacement should be carried out strictly according to the manufacturer's recommendations. It loses its properties over time, which directly affects the performance of the heating system.
The antifreeze concentrate is diluted only with distilled water. An ordinary flow-through system is not suitable for this - a large number of third-party elements can cause an undesirable chemical reaction.
The video details the parameters for choosing antifreeze for heating systems:
About the pros and cons of glycol antifreeze
The main advantage of artificial coolants based on glycols is the preservation of the liquid phase at subzero temperatures. We list other positive aspects of using antifreeze in closed water heating systems:
- coolants do not contain calcium and magnesium salts, which form scale inside the heat exchangers;
- due to the penetrating ability of glycols, the effect of lubrication of moving parts occurs, ball valves and thermostatic valves do not sour, the fittings last longer;
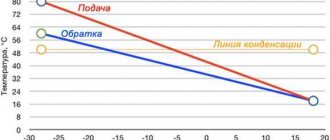
- the boiling point of antifreeze 103-106 °C delays the moment of vaporization and airing in case of overheating of a solid fuel boiler;
- When the temperature drops below the freezing threshold, glycol solutions turn into a gel mass.
Note. The paragraph about scale implies that the “anti-freeze” is diluted with demineralized distilled water.
Let's clarify the last 2 points. Ordinary water, often poured into the heating system of country houses, begins to boil at 96-98 ° C, actively releasing steam. If the circulation pump is on the TT boiler supply, the steam phase penetrates the chamber with the impeller, water pumping stops, and the boiler completely overheats. A higher boiling point of antifreeze will delay the moment of the accident.
In what cases should antifreeze not be used?
Why is the question posed this way? Everything is very simple - you can easily familiarize yourself with the specific positive qualities of any brand of antifreeze. Such information is actively distributed by manufacturers. For our part, we want to present those features of this technical fluid that they are trying to keep silent about:
- Antifreeze cannot be used in double-circuit boilers - it is possible to mix coolant from the heating circuit into the water supply circuit. As is known, non-freezing liquid is poisonous due to its physical and chemical properties.
- It also cannot be used in open systems - evaporation of the coolant is possible.
- It is unacceptable to use antifreeze in a system with a galvanized pipeline - it is fraught with chemical changes and loss of its original properties.
- The heat capacity of non-freezing liquid is lower than that of water, which means that radiator batteries of higher power will be required.
- The viscosity of antifreeze is also higher - more powerful circulation pumps are needed.
The container for antifreeze must be of sufficient volume and correctly calculated according to the project
Selection of coolant by heating type
Some will decide to use ethylene glycol as a coolant. This liquid is dangerous when exchanged between several coolants. Why? Ethylene glycol is not recommended for use in boilers with two circuits, since any damage to the exchanger wall will immediately lead to negative consequences. It also cannot be used in systems that use an opening type with an expansion tank.
Today, a large number of antifreezes are based on ethylene glycol. At the same time, its price is quite low. It is also distinguished by its ability to have good thermophysical properties. Its freezing point ranges from -35°C to -65°C depending on the concentration.
Antifreeze based on propylene glycol has great advantages because it is non-toxic. Therefore, it is allowed for use as a coolant for heating systems. Propylene glycol has a low crystallization temperature - -40°C. For example, Gulfstream antifreeze is produced on the basis of propylene glycol, as well as glycerin.
Its positive properties are as follows:
- Eco-friendly.
- High physical characteristics.
- Low freezing point.
But, despite all these advantages, not everyone can afford to buy it due to the high price. That is why some refuse to use it and look for alternative sources of coolant.
An alternative circulating fluid may be water containing ethyl alcohol (40-55% alcohol). This solution crystallizes at -30°C. The use of this antifreeze is limited only to a closed system, which is equipped with forced circulation. If you use it with an open system, the alcohol will evaporate very quickly. Moreover, a clear disadvantage is the low boiling point, which ranges from 85°-90°. Most heating heaters heat the liquid to 95° and under such circumstances, water with ethyl alcohol is not suitable. Moreover, if automation is used, which regulates the air temperature, but not the temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
Propylene glycol antifreeze
Propylene glycol in the heating system is not as toxic as the previous type. Such antifreeze may contain food additives that are not even dangerous to human health.
True, such a coolant may contain various additives that can affect the materials from which various elements of the heating system are made. How additives work depends on the material from which the heating system components are made. Some additives are needed to prevent various oxidation or foam formations from occurring inside the heating system.
Is it possible to mix antifreezes and what does the color affect?
The question of antifreeze compatibility usually arises among car owners who have purchased a used car and are not able to determine the brand of liquid poured into the cooling system. Moreover, when solving this problem, car enthusiasts who do not understand the technical intricacies first of all take into account the color of the compound splashing in the expansion tank. And, indeed, manufacturers use dyes with a wide variety of shades to color coolants. The most popular colors: red, green, blue, yellow, purple, orange.
Some standards even regulate the use of certain shades. However, in fact, color is perhaps the last criterion that should be taken into account when mixing different brands of antifreeze. Dyes added to antifreeze are used only to make it clear that the liquid is technical, and, therefore, can threaten human health. In addition, thanks to the acquired tint, the visibility of antifreeze (initially colorless liquid) in the same reservoir of the cooling system improves. There is no direct connection between the color and properties of the coolant.
What considerations should be followed when mixing antifreeze? Here you can give at least a couple of tips:
- Without problems, you can combine antifreezes that have the same base and meet generally recognized quality standards. True, the composition of the liquid is often not published by the manufacturer, so all that remains is to follow the recommendations indicated on the label.
- Different types of antifreeze (with inorganic and organic additives) are allowed to be mixed only if the manufacturer clearly indicates this possibility.
The incompatibility of antifreezes lies in the likelihood of a reaction between the additives included in their composition. This may cause sediment to form or deteriorate performance, which may affect engine performance.
Features when starting the heating system
Different compositions of solutions affect the operation of the heating system. Thus, the presence of ethylene glycol affects the initial stage of system startup. The heating process must be started at low power, then gradually increased to the required level. This method will reduce the toxic effects of this substance.
A product based on propylene glycol does not require such adjustments when starting heating equipment.
When all the requirements are met, then there is no need to be afraid of using “anti-freeze” as a coolant. It will solve a lot of problems if used skillfully.
Prices for non-freezing liquid vary, and so does the quality. The policy here should be this: when it is not possible to buy a good product, it is better to stick with water. In this case, you must ensure that the coolant is drained from the system before the onset of frost, or turn on the heating devices on time.
Should I dilute with water or not?
The origin of this issue is due to the fact that equipment manufacturers set the same requirements, worrying about the safest and most efficient operation possible. Buyers stick to their line, driven by the need to save money. And coolant manufacturers maneuver between the requirements of manufacturers, buyers and sales practices. As always, the truth is somewhere in the middle.
Manufacturers of antifreeze liquids mainly offer “-65C” or “-30C” coolants to the market. Firstly, this is due to established demand, and secondly, such a coolant is guaranteed not to be frozen at the time of sale.
Equipment manufacturers have their own truth. Thus, the density of non-freezing liquid marked “-25C”, mainly recommended by equipment manufacturers for reasons of optimal fluidity, is 1.03 g/cm3, and that of liquid “-30C” is 1.04 g/cm3.
The fact that the content of the main substance in the coolant will be several percent higher is not an “exorbitant” deviation, but taking into account the fact that water can be “added” to the coolant either when recharging the circuit, or if water is not completely drained from the system after flushing , a “reserve” of concentration is simply necessary.
On the other hand, diluting the coolant from “-30C” to “-25C” - and this value is 3-4% - will not bring tangible savings to the buyer, but will increase the risk of losing other necessary properties. But in the case when the buyer plans to use concentrated coolant “-65C” and dilute it, the savings can already be up to 20%.
Other components
Recipes for factory-made antifreeze liquids necessarily contain surfactants. They are designed to remove dirt, soot, grime, oil and anything else that may limit visibility from the glass surface.
For a liquid to be effective in cleaning glass, very few surfactants are required. Flavorings are also used in the production process. They serve to give the product a pleasant smell. Manufacturers often use the scent of apples, citrus fruits or any other product with a persistent and “tasty” aroma. Dyes color liquids in different colors. This makes it easier for the buyer to identify the desired product. Separately, it is necessary to say about water. For the manufacture of the highest class products, distilled is best suited. In some cases, it is possible to use artesian water with a minimum of salts. But the most ordinary one (from the tap) is not suitable for making anti-freeze.
If you take anti-freeze, what brand?
Liquids for heating systems
Today's market offers varied offerings of these specific products.
However, there are also leaders here. Heating fluid called “Warm Home” is in great demand among consumers. This product is produced in Russia.
“Warm House” has been successfully used for many years, so we can confidently say that the liquid has stood the test of time. And this antifreeze is best characterized by reviews from homeowners who have considerable experience in operating heating systems using antifreeze liquid.
According to them, this brand does not lose its characteristics over ten heating seasons.
This fully corresponds to the service life declared by the manufacturer. As you know, reviews from satisfied consumers are the best proof of quality.
Also popular are brands such as Energos Universal, Energos Lux, Thermagent, Dixis, etc.
Russian manufacturers produce antifreezes based on ethylene glycol in two versions: with a freezing temperature of up to -30°C, and also with a freezing temperature of up to -65°C.
The above-mentioned manufacturers are actively expanding their range of non-freezing coolants made from food-grade propylene glycol, an environmentally friendly raw material. And this is not in vain, because the demand for heating antifreeze is growing, which means there must be supply.
Cases in which the use of antifreeze is strictly prohibited
When not to use antifreeze
It is not difficult to familiarize yourself with all the advantages of antifreeze from any manufacturer.
This information is actively advertised by brands. On the other hand, we should talk about the features of this liquid, which manufacturers try not to emphasize:
- It is prohibited to use antifreeze in double-circuit boilers. After all, the design features of this heating system are such that coolant can leak from the heating duct into the water supply circuit. And due to its chemical properties, the non-freezing liquid is poisonous.
- It is strictly forbidden to use antifreeze in open systems; in this case, it may evaporate.
- Also, antifreeze should not be used in heating systems with galvanized pipelines. When interacting with them, loss of original properties and chemical changes are possible. It is not recommended to pour antifreeze into cast iron boilers. At the very least, you need to make sure that your unit contains paronite gaskets that can prevent the harmful effects of antifreeze. The technical data sheet of the product will help you with this.
- The heat capacity of antifreeze is lower than water, as a result, radiator batteries of higher power are needed.
- Since the viscosity of the non-freezing liquid is higher, more powerful circulation pumps will be required.
In any case, the final decision is always yours. It is impossible to say for sure which is better, water or non-freezing liquid.
It all depends on individual heating parameters. Before making a final decision on the choice of a particular coolant, you should seek advice from specialists.
Recommendations from experts
- Antifreeze is best used in house systems that are rarely visited in winter and the system does not work for most of the time.
- It is necessary to use equipment that is designed to work with antifreeze.
- The power of radiators should be 30-40% greater than that of conventional ones.
- Due to the high level of antifreeze viscosity, pumps must be used with enhanced hydraulics.
- In the case when it is necessary to make a solution from a concentrate, only distilled water should be used.
- You cannot mix different types of antifreeze; it is best to use one. But in the case when this is the only way out, it is recommended to mix them in a container and observe the precipitation.
- The use of automobile antifreeze for heating systems is not allowed, due to the fact that it contains elements whose use in residential buildings is unacceptable.
- A concentrate whose freezing threshold is -65°C cannot be used in its pure form, as this may cause overheating of the heat exchanger and decomposition of additives.
- And if you use a solution whose freezing point is not higher than -25 ° C, and the temperature has dropped below (which is quite unlikely), then there is no need to worry. The heating installation will not be damaged at all. The antifreeze will thicken, and as soon as the temperature rises to a certain value it will return to its original state without any loss of its properties.
- In order to prevent leaks at the sealing joints, you can use automotive sealant.
To summarize, I would like to note that there are different types of coolants. Before purchasing antifreeze for a heating system, you should consider a number of points: the material from which the pipes and radiators are made, the conditions of use and the possibility of periodic maintenance. The choice is also influenced by the financial side of the issue.
Thus, everyone can afford imported antifreeze for heating systems, the cost of which is much higher than ordinary distilled water. In this case, a high-quality domestically produced product is recommended. It must be remembered that the system requires timely flushing. This directly affects its efficiency and long-term operation.
Antifreeze classification
There are many types of these products on the market. Antifreeze liquid for heating boilers can be made based on an aqueous solution of glycerin, ethylene glycol, propylene glycol, and so on. Since all substances are highly aggressive, the liquids contain special additives.
Each type has certain specific characteristics:
- Ethylene glycol-based liquid is common among buyers because it has the most affordable price. But it is the most toxic and cannot be used for double-circuit boilers. May pose a health hazard if released into water supplies. If the boiling point rises above 110 degrees, the substance may produce a precipitate that can stop the operation of a number of system elements;
- from propylene glycol - the properties of the composition are almost similar to the previous one, but it is less harmful and safer;
- based on glycerin - environmentally friendly antifreeze, non-toxic, protects the system from corrosion. When it turns into a solid state, it does not increase its volume, and in order for the system to start, it just needs to be warmed up;
- from a natural bischofite solution - has a high level of heat transfer and heat capacity, the freezing point is low and the boiling point is high;
- salt carriers - are produced on the basis of solutions of sodium, calcium and other mineral salts. They have high corrosiveness to pipes.
New mineral coolants
We decided to highlight the description of these liquids, since they are made based on the natural mineral - bischofite. The substance is a magnesium salt of hydrochloric acid, the full name is magnesium chloride hexahydrate. The manufacturer declares the following characteristics of the finished antifreeze, designed for a minimum temperature of minus 30 degrees:
- the color of the aqueous solution is light yellow, the density is 1117...1250 kg/m³;
- boiling threshold - 116 °C, freezing point - minus 30 °C;
- specific heat capacity - 0.77 kcal/kg •°С (3.23 kJ/kg•°С);
- thanks to the additives, there is no foaming and no aggressive effect on various seals - silicone, paronite, EPDM and BMS rubber;
- the substance is not toxic;
- In terms of viscosity and fluidity, the drug is very close to glycol chemicals.
Reference. The product appeared on the market after 2010. The price of liquid as of 2022 is about 1 USD. e. per liter of finished coolant (-30 ° C).
Compared to traditional glycol analogues, mineral antifreeze benefits due to its high boiling point, cost and health safety. The negative point is the increased density and low heat capacity, 23% worse than that of water.
The practical use of the coolant has revealed a number of shortcomings, as evidenced by reviews from homeowners:
- The fluidity of the solution is extremely high. There have been cases where antifreeze penetrated through the soldered joint of polypropylene pipes.
- Upon contact with air, the liquid fraction quickly evaporates, leaving a noticeable salt build-up. Similar phenomena are observed in heat exchangers and pipelines where air bubbles have penetrated.
- The substance reacts with bare metal on welds. Stalactites of iron and salt form inside the system, reducing the flow area and clogging the mud traps.
- In case of overheating, antifreeze turns into a liquid of unknown color, as shown in the photo.
User responses about this type of “anti-freeze” can be read on the well-known construction forum: https://www.stroimdom.com.ua/forum/showthread.php?t=157650
Taking into account the experience of users, we do not dare to recommend mineral antifreezes for use in heating systems of private houses. Perhaps over time, manufacturers will eliminate the above problems and the magnesium chloride solution will be able to compete on equal terms with glycols.
Can antifreeze be used?
heat supply diagram with antifreeze instead of water
Antifreeze or antifreeze liquids are known to almost everyone. They are widely used in car cooling systems in winter. In a car engine, antifreeze transfers excess heat away from the engine, cooling it. Moreover, even in the most severe frosts it does not freeze. It is these properties - the ability to transfer heat even at the lowest temperatures - that led to the use of antifreeze for the construction of heating systems. It is especially important to use such a coolant in a system where part of the pipeline runs through open areas.
A good feature of “anti-freeze” is that it provokes less corrosion on the inner surface of pipeline systems than ordinary water. Another undoubted advantage is the absence of suspended limestone solutions in non-freezing liquids - so you don’t have to worry about possible scale formation.
There are several modifications of antifreeze liquids that can be used in heating systems. The choice of a specific type is made taking into account the climatic conditions and configuration of the heating system of your home.
What is flushing fluid for the heating system and does it need to be flushed?
In addition to the coolant itself, when operating the heating system, you will also have to purchase a liquid intended for flushing the pipeline and heating radiators.
Of course, as a last resort, you can wash the inner surface of the pipes with ordinary tap water, but it is better to do this with the help of special liquids that contain special chemical additives.
An alternative washing option may be to use water with a caustic soda solution added to it. This mixture is poured into the heating system and remains inside it for about an hour. The soda solution comes into contact with the scale on the inner surface of the system and dissolves it. In addition, the baking soda solution will dissolve areas with corrosion.
How to choose a liquid for a heating system?
First of all, it is necessary to determine the operating parameters of the system. Here two extreme values will be important to you - the maximum coolant temperature when heating in the boiler and the minimum ambient temperature. Next, you need to carefully study the technical characteristics of your heating system
Actually, the main attention should be paid to the characteristics of the heat exchanger in the boiler. Some manufacturers may not allow the use of antifreeze fluids. And finally, after determining the admissibility of using non-freezing liquid and its possible temperature parameters, proceed directly to choosing the brand of liquid, focusing on its lowest toxicity
Still, the heating system will be located in a living room, and possible liquid leaks should not lead to poisoning.
Using alcohol as a coolant
No matter how blasphemous it may sound to the male ear, it is allowed to use alcohol as a coolant. Alcohol does not freeze and can be used in a wide range of temperatures. Naturally, industrial alcohol is used in this capacity, which is a deadly poison for humans. However, many manufacturers of boilers and heat exchangers are critical of the use of liquids such as bischofite or ethylene glycol as a coolant.
The disadvantage of using pure alcohol as a coolant is its high volatility - about five liters per year will evaporate through microscopic pores in the system.
Water or antifreeze: what to choose?
Traditionally, ordinary water is poured into the heating system. There is an opinion that it is not advisable to fill in other coolants. However, situations may arise when you simply cannot do without an anti-freeze agent.
For example, in a country house where there are no permanent residents, but for some reason it is not possible to “mothball” the heating system. To understand what liquids to pour into the heating, and what will bring greater benefits, you need to find out the positive and negative sides.
A comfortable stay in a heated room depends on how correctly the coolant is selected. It should be taken into account that the composition of liquids for steam heating is different for each manufacturer.
Here are the main components that are currently actively used:
- glycerol;
- salt solutions;
- propylene glycol;
- ethylene glycol;
- bischofite
These funds were not chosen by chance. They perform certain functions that water cannot replace.
The main disadvantage of water as a coolant
Water is an environmentally friendly product. If a leak is detected in the radiators, it will not cause harm to a person. But while water is affordable and suitable for most heating systems, it has several disadvantages.
In case of unexpected temperature changes, if the mercury level in the thermometer drops below zero, the water will freeze when the boiler is turned off. Once the radiators and pipes rupture, it will be almost impossible to repair it; the entire system will need to be replaced. More often than not, the boiler will be the first to suffer. Thus, you will have to spend a lot of money to restore heating.
Metal pipes from water gradually rust. If electricity is used as an energy source, its consumption will increase due to the formation of scale and rust.
Types of low-freezing liquids
Non-freezing liquid for heating a house is the same as antifreeze or antifreeze. doesn't matter. More precisely, there is a difference, but it concerns more the composition of antifreezes than the basic properties. And their main property is not to turn into ice when the temperature drops, down to -60 degrees. At the same time, the cooled composition thickens.
Propylene glycol is part of an environmentally friendly antifreeze
Any heating liquid is non-freezing, a warm house in particular is made according to the same principle. Their composition:
- glycol (alcohol) base;
- main active ingredient;
- substances that prevent corrosion (inhibitors);
- substances responsible for the characteristics of the composition (additives).
So, it is already clear that non-freezing liquid for water heating is an alcoholic substance. Glycol itself is not dangerous, but some additives can be very harmful to health. The active component in anti-freeze products can be:
Ethylene glycol liquid, in which ethylene glycol acts as the active substance, is strictly not recommended for use in permanent homes. It is very toxic; if it gets on the skin, it causes burns. If the composition enters a person in the form of a liquid or gas, it leads to serious consequences, including death.
Low-quality antifreeze and the well-known engine antifreeze, which is also sometimes poured into heating systems, are made on an ethylene basis. If there is even the slightest possibility of human contact with ethylene glycol, then it is better to refuse its use:
- evaporation from an open type expansion tank;
- a leak;
- mixing into the DHW circuit in double-circuit boilers.
You cannot use ethylene glycol antifreeze liquids for heating, where a double-circuit boiler acts as a heater.
Propylene glycol non-freezing liquid for heating boilers is completely non-toxic. This does not mean that it can be drunk, but accidental contact in minimal doses on the skin or even internally will not lead to health complications. This antifreeze can be used safely.
Glycerin antifreeze liquid has been poured into the heating system since the mid-twentieth century and is still successfully used to this day. Glycerin is, in general, a universal remedy. What is characteristic is that, unlike the two types of anti-freeze listed above, glycerin does not dry out the rubber, but, on the contrary, restores it and gives it a second life. That is, it acts on it like a silicone lubricant, so you don’t have to worry about the condition of the rubber seals.
The problem of heating a winter greenhouse has been solved, everything is quite simple.
Methods for filling the system with coolant
The issue of filling usually arises only in the case of a closed-type system, since open circuits can be filled without problems through an expansion tank. Coolant is simply poured into it, which, under the influence of gravity, spreads along all contours
It is important that all air vents are open
There are several methods for filling a closed heating system with coolant: by gravity, with a submersible pump or using special pressure testing equipment. Let's look at each method in more detail.
By gravity. Although this method of pumping coolant for a heating system does not require equipment, it takes a lot of time. You have to squeeze out the air for a long time and also gain the required pressure for a long time. By the way, it is pumped up with a car pump. So you will still need equipment.
You need to find the highest point. Usually, this is one of the gas vents (it needs to be removed). When filling, open the tap to drain the coolant (lowest point). When water runs through it, the system is full:
- When the system is full (water runs out of the drain tap), take a rubber hose about 1.5 meters long and attach it to the entrance to the system.
- Select the inlet so that the pressure gauge is visible. Install a check valve and ball valve at this point.
- Attach an easily removable adapter for connecting a car pump to the free end of the hose.
- After removing the adapter, pour coolant into the hose (keep it up).
- After filling the hose, use an adapter to connect the pump, open the ball valve and pump liquid into the system. You need to make sure that air is not pumped in.
- When almost all the water contained in the hose has been pumped in, the tap is closed and the operation is repeated.
- On small systems, to get 1.5 Bar, you will have to repeat it 5-7 times, with larger ones you will have to tinker longer.
With this method, you can connect a hose from the water supply, you can pour prepared water into a barrel, raise it above the entry point and then pour it into the system. Antifreeze is also added, but when working with ethylene glycol you will need a respirator, protective rubber gloves and clothing. If the substance gets on fabric or other material, it also becomes toxic and must be destroyed.
Using a submersible pump. To create working pressure, the coolant for the heating system can be pumped with a low-power submersible pump:
- The pump must be connected to the lowest point (not the system drain point) through a ball valve and a check valve; a ball valve must be installed at the system drain point.
- Pour coolant into the container, lower the pump, and turn it on. During operation, constantly add coolant - the pump should not drive air.
- Keep an eye on the pressure gauge during the process. As soon as its needle moves from the zero mark, the system is full. Until this point, manual air vents on radiators can be opened and air will escape through them. As soon as the system is full, they must be closed.
- Next, you need to increase the pressure while continuing to pump the coolant for the heating system with the pump. When it reaches the required level, stop the pump and close the ball valve
- Open all air vents (on radiators too). The air comes out, the pressure drops.
- Turn on the pump again, pump up a little coolant until the pressure reaches the design value. Bleed the air again.
- Repeat this until air stops coming out of their air vents.
Next, you can start the circulation pump and bleed the air again. If the pressure remains within normal limits, the coolant for the heating system is pumped. You can put it to work.
Pressure testing pump. The system is filled in the same way as in the case described above. In this case, a special pump is used. It is usually manual, with a container into which the coolant for the heating system is poured. From this container, liquid is pumped through a hose into the system.
When the system is filled, the lever moves more or less easily, but when the pressure rises, it becomes more difficult to work. There is a pressure gauge both on the pump and in the system. You can follow where it is more convenient.
Next, the sequence is the same as described above: pump up to the required pressure, deflate the air, repeat again. Do this until there is no air left in the system. After that, you also need to start the circulation pump for about five minutes and bleed off the air. Repeat this several times.
How to choose the right heating fluid
It is difficult to imagine comfortable living in an apartment or private house in winter without high-quality heating.
Residents of urban high-rise buildings with centralized heating are lucky. After all, there is no need to think or worry about the safety of pipes during the cold period. Maintenance falls on the shoulders of housing maintenance offices. But you have to monitor the proper operation of the autonomous heating system in the private sector yourself. A coolant is used as a heating element in the heating network. It is a heating fluid that circulates through the circuit. May be of different types. The operation and maintenance of the system depends on what kind of liquid is used. Therefore, this article will focus on the coolant, its types and rules of use.
How to protect pipes from freezing
In some cases, defrosting of the heating system may not be noticed. When defrosting, pipes may burst, and as a result, the basement may flood. Of course, after such a situation you will have to carry out repairs, which will require large expenses. To prevent this situation, it is recommended to use modern systems that can prevent the coolant from freezing.
A good system is to de-ice pipes. In such a system, a resistive cable is laid along the pipe. The cable should be located next to the pipe. To protect short sections of pipe, you can use a resistive cable that is equipped with an additional thermostat. The cable can be used for long sections of pipe. It is more profitable to use a self-regulating cable.
The pipe anti-icing system is also used in drinking water pipes. The only difference is the cable routing. In this case, it is placed inside the pipe.
Characteristics of non-freezing liquids for heating
How low-freezing liquid for heating systems behaves in the circuit is primarily influenced by the quality of the additive package and, of course, operating conditions. Regardless of what main active element is added to the glycol base, all compositions have anti-corrosion and anti-foaming properties.
Without these additives, heating fluid is very aggressive. All antifreezes foam, but glycerin antifreeze liquids for home heating systems especially. Foam is an air-containing substance, and air leads to disruption of circulation, the formation of air pockets, as well as water hammer in the heating system.
The additive package has its own temporary resource. After a certain time, additives break down at the molecular level.
In this case, a precipitate forms and acid is released. It turns out that nothing can smooth out the aggressiveness of the coolant for heating the house, and moreover, everything is aggravated by the release of acid. Service life of antifreeze liquid:
- based on ethylene glycol – five years;
- based on propylene glycol – five years;
- glycerin-based - up to ten years.
This is the service life of the composition under favorable operating conditions. The main requirement is, of course, temperature. When the coolant temperature rises to 90 degrees, the non-freezing liquid begins to disintegrate and loses its properties. This only happens if the boiler is not started correctly after a long period of inactivity, or if there are errors during installation.
Direct contact of the heat exchanger with the flame is undesirable if antifreeze is poured into the circuit
For example, when a heat exchanger is built into a conventional oven. Some install it so that it comes into contact with an open flame. If you plan to use antifreeze for stove heating, then you cannot do this. It is necessary that there is a layer of brick between the heat exchanger and the flame. It will protect the coolant from too hot flames and distribute the heat evenly. In this case, the non-freezing liquid for stove heating will not overheat.
Characteristics that are affected by the quality of the additive package:
- thermal conductivity;
- density;
- viscosity;
- fluidity;
- thermal expansion.
The better the additives, the higher the performance will be. That is, as close as possible to the characteristics of water. In the case of the coefficient of thermal expansion, it should be as small as possible.
Considering the fact that the volumetric expansion of the antifreeze is greater than that of water, it is necessary to provide an expansion chamber with a 40% larger volume.
The thermal conductivity of antifreeze is lower than that of water. Glycerin antifreeze liquids have the lowest thermal conductivity. In relation to water, it is only 85%; for other anti-freeze products the figure can reach 90%. As you can see, the difference is not that big.
Antifreeze liquids are half as dense and viscous as water. These qualities make circulation difficult. To pump the coolant through the circuit, you will need a pump of greater power, and it would also be a good idea to assemble a heating circuit from pipes with a cross-section that is one step larger. For example, if we are talking about polypropylene pipes. then instead of 25 diameter, it is better to take 32.
Despite the fact that antifreeze liquid is denser and more viscous, it has a lower surface tension coefficient, that is, it is more fluid. Do you know that you can fill a glass with heaps of water? The slide, of course, will be small, but even visually it can be seen that the liquid rises above the edge of the vessel. This won't work with anti-freeze. Due to such high fluidity, it flows out where water does not penetrate due to surface tension. In other words, if there are microcracks and even very small holes, then the non-freezing liquid will find its way out there.
Therefore, often, after there was water in the circuit and they decided to pour anti-freeze into it, leaks appear. Main leak points:
- pipe joints;
- connections between radiator sections;
- connection points for additional elements;
- in the boiler itself.
Water has another useful property, thanks to which a minor leak can disappear by itself. Metal particles settle on the edges of cracks and seal them. Of course, this is just scale, which, if the system is flushed and further pressure tested, will be removed and the flow will resume.
Finally, about coolants for electrode boilers
Electric water heaters of this type operate on the principle of a “soldier’s boiler” consisting of two blades connected to a 220 volt network. Water simultaneously serves as a coolant and electrolyte; heating occurs due to its conductivity, which depends on the content of magnesium and calcium salts.
This is why electrode boilers do not work with distillate and significantly lose power with under-salted water. According to the passport of the Galan heater, the resistance of the working fluid should be no more than 3200 Ohms per 1 cm.
If you pour regular ethylene glycol into an electrolysis heat generator, the substance will enter into a chemical reaction, foam and lose additives against corrosion and scale formation. The problem can be solved in 2 ways:
- A special antifreeze designed for electrode-type units is purchased. Special additives that resist foaming are dissolved in the working environment.
- A saline solution of the required concentration is prepared, as shown in the video below. Such water will begin to crystallize at a lower temperature, although it cannot be compared with antifreeze in terms of frost resistance.
You should pay attention to the preparation of tap water - pass it through a filter and let it sit for 1-3 days. A good solution is to buy a corrosion inhibitor separately and add it to the coolant for the heating system in advance.
During operation of the heating system, the coolant may freeze. This leads to the creation of emergency situations. They can only be avoided by replacing the water in the mains with a special composition whose freezing point is significantly below 0°C. Is it possible to make a similar non-freezing liquid for home heating systems with your own hands?
How to choose the right liquid
Today, there are hundreds of product options on the market for heating devices and consumables for them.
It is quite difficult to choose a high-quality and safe antifreeze among them, because each brand uses all sorts of marketing tricks to attract buyer attention to its product. In order not to fall for the bait set by advertisers, the homeowner needs to understand what requirements the heating boiler fluid poured into the circuit must meet
Before you buy heating fluid. the owner needs to find out some technical characteristics of the boilers, as well as familiarize himself with the list of antifreezes compatible with radiators and pipelines connected to the circuit. In addition, it is necessary to clarify the operating parameters of the heating system and operating features. Next, you should study the specific requirements that specialists place on antifreezes that can make the heating system productive, stable and safe.
You should pay attention to the following parameters:
- Operating temperature range;
- heat capacity;
- inertness of the chemical composition;
- presence of anti-corrosion properties;
- no sediment in the liquid when heated;
- stability of chemical properties - density, viscosity, heat capacity;
- no toxic emissions during use.
Functional liquid fuel, gas and solid fuel heating boilers will last much longer if they are filled with antifreeze with a maximum operating temperature range, a stable chemical composition and acceptable performance characteristics that guarantee protection of heating devices from corrosion, scale and solid sediment.
You can buy such liquid only from a trusted manufacturer. But using the wrong antifreeze can lead to a number of undesirable effects. Negative effects that may appear:
- foam formation inside the circuit when heating the coolant;
- precipitation, which provokes overgrowing of pipes and clogging of the boiler heat exchanger;
- corrosion formation;
- the appearance of leaks;
- violation of the boiler tightness;
- release of toxic substances.
How to calculate the required quantity?
To purchase the required amount of antifreeze liquid, you need to know the exact capacity of the system. This information may be available to the specialists who created the project or carried out the installation. If the data is lost, you can still find out the parameters, although you need to spend some time.
First you need to measure the total length of the lines and distribute them according to the diameter. After this, the flow area is calculated. All this is multiplied by the total length. The volume of water in the radiators is added (data can be found in the relevant technical documentation). This will give you the required total volume of coolant.
The required amount of anti-freeze can be found out at the time of purchase. The ratio with which antifreeze should be diluted with water is indicated on the packaging.
Using your home allows you to forget about the danger of coolant freezing and future repairs. The use of antifreeze has its advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account when choosing and during operation.