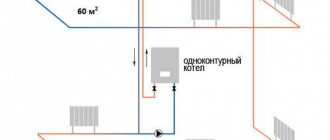
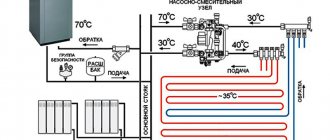
Modern man is a thermophilic creature. In the Russian climate it is cold in spring and autumn, and very cold in winter. All buildings need heating, and existing heating systems cannot be installed without pipes.
We welcome our regular reader and bring to your attention an article about what metal heating pipes are - a traditional material for installing plumbing systems.
Why choose metal for heating systems
For more than twenty years there was practically no alternative to pipes made of steel - carbon (in common parlance, ferrous metal), galvanized, stainless. The use of copper for heating was unheard of at that time; plastic pipes were not mentioned even in progressive scientific journals. Now the situation has changed radically: several types of inexpensive high-tech plastic have greatly displaced metal from heating systems.
However, metal pipes are still indispensable in many situations: when systems operate at very high operating pressures, in hot shops, when high strength is required from pipelines.
Use of metal-plastic
When the question is which pipes are best to use for heating, a metal-plastic option is possible.
Its design includes five layers, where aluminum and plastic alternate with an adhesive layer. It is for this reason that metal-plastic pipes tolerate temperature changes well and are resistant to rust and chemicals. They do not oxidize, water does not deposit salts on their walls. They are used not only for heating, but also for installing a water pipeline to provide hot and cold water.
The technical characteristics of metal-plastic pipes are as follows:
- the most permissible temperature is 95 degrees;
- withstands pressure at the highest temperatures up to 10 bar;
- tolerates short-term temperature changes of up to 130 degrees;
- withstands pressure of 25 bar at temperatures from 0 to +25 degrees.
If operating and installation conditions are observed, such pipes can last for at least half a century.
Therefore, many choose metal-plastic when deciding which pipes are best to use for heating.
They are connected to each other with brass fittings, the result is quite reliable and durable. The only negative side of the fitting method is that the cross-sectional size is reduced.
Conclusion. It makes sense to use metal-plastic pipes when the coolant is heated to 95 degrees.
Pros and cons of metal pipes
Advantages of metal products:
- Strength. Steel, copper and cast iron can withstand much greater pressure than plastic and are much more resistant to water hammer.
- Strength as a guarantee of non-destruction of pipes when working in workshops - often in production conditions there is a possibility of their damage during the operation of lifting mechanisms, equipment, and emergency situations in hot workshops. When laying heating openly between buildings, sufficient structural strength is also required - metal changes its geometry less when heated, metal is more resistant to vandalism.
- Fire resistance.
- Resistance to temperature fluctuations.
- Harmless to humans.
- UV resistance.
- A welded system is generally more airtight than prefabricated structures, and when installing gas systems this can be critical.
- Low thermal expansion - metal does not sag and does not change configuration when heated, like plastic.
- Long service life.
- Thermal conductivity. A metal heating system serves as an additional source of heat in the room; When laying pipes along the perimeter of the building, you can slightly warm up the corners of the rooms, increase air movement in them and protect them from the occurrence of dampness, mildew and mold.
Common disadvantages of metal pipes:
- For steel and cast iron – prone to corrosion/
- Heavy weight.
- For steel and cast iron – overgrowing of the inner surface with calcium and magnesium salts.
- Difficult installation using welding or threaded fittings.
Replacing old radiators
If you decide that old heating devices need to be replaced, then dismantling and updating them should be done in the summer. Since the heating system is turned off at this time of year and is not filled with coolant, removing and installing homemade or industrial radiators will not be difficult.
Replacing old equipment may be necessary in cases where they are too worn out and do not provide enough heat, or residents want to reduce or increase the number of sections in the radiators. If installation work is carried out, the surface of the walls behind the radiators can also be updated.
But remember that all work on the wall surface - plastering, painting or cladding - is carried out before installing the radiator.
Types and characteristics
Heating pipes are divided according to the material of manufacture. There are many standard sizes of any type, they are easily available in stores. Cast iron pipes are practically no longer found and are not used. According to the profile, only products with a round cross-section are used for heating. According to the manufacturing method, they can be welded or seamless. In terms of wall thickness - with a normal wall (for steel with running diameters 20-25 32 mm, the wall thickness is 3-3.5 mm).
Made of cast iron
The use of cast iron pipes for heating is very rare due to their low technology: difficulty or impossibility of welding, inability to cut threads in the right place, and high weight. In practice, it is very rare to find finned tubes that are used as radiators. They are mounted using flanges. Such radiator pipes are not used in housing.
From copper
Copper pipes are a relatively new material for heating systems on our market. Copper is very durable, does not overgrow, has very thin walls - the system is light and compact. Installation has a certain complexity - using welding and brass fittings. The widespread use of copper heating systems is hampered by price and the need to hire a welder.
Copper products can be annealed or unannealed. There is no difference for heating systems, but unannealed products are more often used - they are harder and less deformed during operation.
Made of black steel
They are quite durable, they become overgrown with salts from the inside, which reduces the lumen of the pipes and the efficiency of the system. The main installation method is by welding or on bends and threads. They are practically not used in houses and apartments - even partial repairs of the system are easier to perform with plastic.
Made from galvanized steel
Galvanized pipes do not become overgrown with salts from the inside for a long time (until the zinc layer is completely destroyed). The actual service life of old pipes for VGP is up to 50 years or more. Previously, they were used everywhere. They have a rather complicated installation - the workpieces need to be threaded and then coated with zinc. Mounted on threaded fittings. The installation method is not suitable for use in private construction. You cannot use welding - the connection will begin to rust at the same rate as ferrous metal, and the effect of zinc coating will disappear.
Stainless steel
The material has been used for heating pipes for a very long time. Stainless steel does not overgrow and does not rust. Previously they were mounted by welding, now they use both welding and threaded fittings. Distribution is limited by price and complex installation - both welding and thread cutting require certain skills from the master.
The material is plastic and resistant to water hammer - therefore, for heating, GOST provides for pipes with a small wall thickness (for example, 2 mm). There are corrugated stainless steel products, but their strength is lower than ordinary smooth ones.
Factory heating devices
It is worth noting that industrial enterprises also produce heating batteries from pipes. As a rule, this is equipment that includes two collectors - upper and lower. They are connected to each other by vertical tubes installed in two or three rows. At the same time, these devices do not have fins, which would increase the heat-releasing surface area, as in standard cast-iron radiators. Heat exchangers on such batteries are made of pipes with a cross-section of 2.5 cm, and collectors with a diameter of 5 cm.
The maximum pressure level that such batteries can withstand is 12 atmospheres. They are resistant to corrosion because the inner surface of the pipe is galvanized. The wall thickness of steel pipes is 1.5 mm.
The layout of the radiator in relation to the collectors can be:
- with parallel heat exchanger;
- with a perpendicular heat exchanger.
Considering the technical features of heating radiators made from pipes, they can be successfully used both in public institutions and residential urban buildings. The products have an attractive appearance and fit harmoniously into any environment. Moreover, the absence of sharp corners on tubular radiators makes it possible to install them in kindergartens and primary schools, as well as hospitals and clinics.
Another positive point is that cleaning such a radiator from dust will not be difficult, since there are no fins on it.
We hope that this material will be useful to you and will help you avoid mistakes when making and installing a homemade radiator from pipes.
Which pipes are better for heating?
Pipes made of ordinary steel are practically no longer used in houses and apartments - the tendency to corrosion outweighs their other advantages. If homeowners want to install a heating system that does not require worries and hassle for many years, then they should choose pipes made of copper or stainless steel. Their service life is more than 50 years, theoretically it can reach 100 years. Installation is moderately complicated, but the costs are more than offset by durability.
Galvanized steel pipes can be very durable only under one condition: if all parts of the pipes are coated with zinc. In reality, all parts of the pipeline must be galvanized after threading and installed using galvanized threaded fittings. When installing home heating systems, it is impossible to organize galvanizing of all workpieces.
Conclusion: it is better to install pipes made of stainless steel and copper. In terms of quality, these materials are quite equivalent, and the choice is only a matter of personal preference. Copper pipelines are more compact.
Briefly about the cost where to buy
The price of metal structures is indicated either per meter or per ton. Be sure to pay attention to this point. The cost of metal channels varies over a very wide range. The price depends on the quality of the material, production technology, wall thickness and other properties of the product.
Structures made of black steel are the cheapest. Next comes galvanization, which costs a little more. Stainless steel is the most expensive. However, as you have already learned, pipes made from it are the most reliable. Corrugated stainless steel channels are the most expensive.
The easiest way to order the products in question is from companies specializing in the sale of rolled metal products. It is advisable to deal with structural manufacturers or their official dealers. This will allow you to purchase the products you need at an affordable price.
In some cases, it makes sense to buy used pipes. The main thing is that they are in good condition. When purchasing, be sure to ask for a certificate of conformity. This will allow you to avoid purchasing inferior products.
How to calculate the diameter of heating pipes
When replacing the heating system in an apartment, the internal diameter must coincide with the diameter of the incoming supply and return - you can neither reduce nor increase it, otherwise you may run into trouble with the heating network.
Calculator
The diameter of the heating system pipelines has to be calculated for a private house. There are two options here: simplified and more realistic, but complex.
Option one: simple. Most private houses have no more than two floors and 200-250 m2 of area. When building such houses, purchased designs are used, which indicate the required power of the heating device = the power of heat loss through walls, windows, doors, roofing, floors and ventilation. For certain heat losses, the optimal ratios of the internal diameter of the pipeline and the power consumed have already been calculated:
- With a boiler power of 3-5 kW - 15 mm.
- 6-9 kW – 25 mm.
- 10-15 kW – 32 mm.
- 16-21 kW – 40 mm.
- 22-32 kW – 50 mm.
If your house is larger, you cannot do without the work of designers.
Option two: creative.
It is necessary to calculate all heat losses through walls, doors, windows, roofing, floors and using a table to determine the diameter of the pipeline. The flow rate in the pipes is taken from the pump data sheet of the heating device; the difference in supply and return temperatures is taken to be 20°C. We round the diameter found from the table to the nearest larger standard size.
Approximately, you can assume a heat loss of 0.1 kW per 1 m² with a room height of 2.5 m.
Below is a table for selecting the pipe diameter for heating at ΔT=20° C:
conclusions
- Polypropylene exists on the market and, in principle, you can work with it. It must be laid exclusively in an open way. Options for pouring concrete and placing them in wall cavities enclosing structures are not suitable.
- Copper pipes are suitable as a material for any boiler room and will delight the user for a long time.
- Due to the curvature, cross-linked polyethylene may not suit many users, since the boiler room and heating systems should look even.
- Metal-plastic can be used everywhere and in any system, especially in a hidden way.
Rules for installing heating pipes with your own hands
Installing a copper heating system using special press fittings can be done with your own hands. Detachable connections are formed that can be disassembled and reassembled if necessary.
Required tools and materials
To wire the heating system you will need:
- A hacksaw for metal, or even better, a pipe cutter.
- File, sandpaper.
- Calibrator.
- Two wrenches.
- Pipe bender
Drawings and diagrams
First of all, you need to draw a diagram or drawing. This will help you decide on the number of fittings and purchase the materials correctly.
Installation technology
Installation technology using compression fittings is simple. Fittings for copper pipelines are made of brass. They differ from fittings for plastic - the internal thrust ring is made without a cut (see photo). No special equipment required.
Work progress
- First, it is cut off and cleared of burrs. Then the cut is calibrated with a calibrator so that it has a round shape (copper is soft and the workpiece crumples when cutting).
- Then the crimp nut is twisted off the fitting, put on the workpiece, the pipe is inserted into the fitting, and the nut is tightened by hand with a little force.
- Then grab the fitting with a wrench, and use a second wrench to tighten the nut 1-1.5 turns.
- On the other hand, the work pieces are repeated. Then the entire workpiece is assembled into the system. Angle fittings are used for bends, but you can bend the pipe using a pipe bender.
- After about 80 centimeters, brackets are installed.
- After assembly, the system is filled with water and tested. If necessary, tighten the nuts using wrenches.
All the installation details can be seen in our video:
Installation features
Do not install piping on compression fittings for underfloor heating systems.
You should not increase or decrease the diameters of pipelines - this will not improve heating and will lead to imbalance of the system.
Tool
When working with any material, you need a professional tool. To work with polypropylene pipes, many installers do not strive to purchase expensive tools, but use cheap ones (about 800 rubles), which leads to all sorts of problems.
To start working with cross-linked polyethylene professionally and efficiently, you need to pay 150,000 - 200,000 rubles. This is significantly more than a cheap tool for working with polypropylene.
To work with metal-plastic pipes for heating, you also need to buy expensive equipment and parts for different diameters. For example, a mini press costs 1,700 euros; a set of pliers for it for different systems and diameters will each cost from 8,000 to 9,000 rubles. A set of 20 pliers will cost 150,000 - 180,000 rubles.
The enormous difference in the price of tools is another reason why some installers believe that metal-plastic is a bad material.