When choosing boiler equipment for a heating system, a very disturbing thought persistently drills into your head - how voracious will the unit be? Surely the answer will appear when the heating starts working and the meter begins to count the gas consumption of the floor-standing boiler, regularly accelerating. However, it will be too late to lament if the amounts payable for gas are not satisfactory...
Competent sales consultants, of course, answer most of the questions that arise; you can always turn to a competent engineer for help, but it’s a good idea to have at least basic knowledge yourself.
Learn from this article as much as possible about the methods for calculating energy consumption and the factors that must be taken into account in the calculations. Below you will find not only boring formulas, but also examples. Finally, we talk about what can be done to reduce gas consumption.
What affects gas consumption?
Fuel consumption is determined, firstly, by power - the more powerful the boiler, the more intensively gas is consumed. At the same time, it is difficult to influence this dependence from the outside.
Even if you turn down a 20-kilowatt device to minimum, it will still consume more fuel than its less powerful 10-kilowatt counterpart turned on at maximum.
This table shows the relationship between the heated area and the power of the gas boiler. The more powerful the boiler, the more expensive it is. But the larger the area of the heated premises, the faster the boiler pays for itself
Secondly, we take into account the type of boiler and the principle of its operation:
- open or closed combustion chamber;
- convection or condensation;
- regular chimney or coaxial;
- one circuit or two circuits;
- the presence of automatic sensors.
In a closed chamber, fuel is burned more economically than in an open chamber. The efficiency of the condensing unit, thanks to the built-in additional heat exchanger for condensing the vapors present in the combustion product, increases to 98-100% compared to 90-92% efficiency of the convection unit.
With a coaxial chimney, the efficiency value also increases - cold air from the street is heated by a heated exhaust pipe. Due to the second circuit, of course, there is an increase in gas consumption, but in this case the gas boiler also serves not one, but two systems - heating and hot water supply.
Automatic sensors are a useful thing; they detect the external temperature and adjust the boiler to the optimal mode.
Thirdly, we look at the technical condition of the equipment and the quality of the gas itself. Scale and scale on the walls of the heat exchanger significantly reduce heat transfer; its deficiency must be compensated by increasing power.
Alas, gas can also contain water and other impurities, but instead of making claims to suppliers, we switch the power regulator a few notches towards the maximum level.
One of the modern highly economical models is a floor-standing gas condensing boiler of the Baxi Power brand with a power of 160 kW. Such a boiler heats 1600 sq. m of area, i.e. a large house with several floors. At the same time, according to the passport data, it consumes 16.35 cubic meters of natural gas. m per hour and has an efficiency of 108%
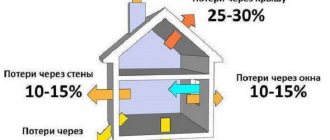
And, fourthly, the area of heated premises, natural heat loss, duration of the heating season, weather conditions. The more spacious the area, the higher the ceilings, the more floors, the more fuel will be required to heat such a room.
We take into account some heat leakage through windows, doors, walls, and roof. It doesn’t change from year to year, there are warm winters and bitter frosts - you can’t predict the weather, but the cubic meters of gas spent on heating directly depend on it.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The videos below talk about gas consumption for floor-standing boilers.
Heating using liquefied gas (propane). Fuel consumption, personal experience:
Gas consumption of a floor-standing gas boiler HOT SPOT 12 kW (user review):
Gas is a popular energy resource, and the problem of saving both the resource itself and the money to pay for it remains relevant.
Reasonable gas consumption means a good, economical boiler, professional installation of the heating system, and the fight against heat loss. The high efficiency of the unit is a guarantee of long-term savings on gas costs.
If you doubt the accuracy of your own calculations, ask for help from a qualified specialist who knows the smallest nuances of the formulas. His authoritative opinion will save you from mistakes both at the design stage of the heating system and during its operation.
Quick estimate
It is quite simple to estimate by eye how much gas will be consumed by your gas boiler.
We will start from either the volume of the heated room or its area:
- in the first case, we use the standard 30-40 W/cubic meter. m;
- in the second case - 100 W/sq. m.
The standards are taken taking into account the ceiling height in the room up to 3 meters. If you live in the southern regions, the numbers can be reduced by 20-25%, and for the north, on the contrary, they can be increased by one and a half times or doubled. Those. take in the second case, for example, 75-80 W/sq.m or 200 W/sq.m.
By multiplying the corresponding standard by the volume or area, we get how many watts of boiler power are needed to heat the room. Next, we proceed from the standard statement that modern gas equipment consumes 0.112 cubic meters of gas to generate 1 kW of thermal power.
We multiply again - this time the gas consumption standard (number 0.112) by the boiler power obtained in the previous multiplication (do not forget to convert watts to kW). We get the approximate gas consumption per hour.
The boiler usually works 15-16 hours a day. We calculate the daily gas consumption. Well, when the daily consumption is already known, we can easily determine the gas consumption for the month and for the entire heating season. The calculations are approximate, but quite sufficient to understand both the principle of calculation and the expected gas consumption.
A regular calculating machine is sufficient to calculate gas consumption. If you don’t want to delve into calculation formulas, use online calculator programs online. Enter the initial data and immediately get the result
Example.
Let's say the area of the room is 100 m².
Let's calculate the boiler power: 100 W/sq. m * 100 m² = 10000 W (or 10 kW).
Let's calculate the gas consumption per hour: 0.112 cubic meters. m * 10 kW = 1.12 cubic meters. m/hour.
Let's calculate gas consumption per day (16 hours of operation), per month (30 days), for the entire heating season (7 months):
1.12 cu. m * 16 = 17.92 cubic meters m 17.92 cu.m. m * 30 = 537.6 cubic meters. m 537.6 cubic meters m * 7 = 3763.2 cubic meters. m
Note: you can immediately determine the monthly and seasonal power consumption of the boiler in kW/hour, and then convert it into gas consumption.
10 kW * 24/3*2 * 30 = 4800 kW/hour - per month 0.112 cubic meters * 4800 kW/hour = 537.6 cubic meters. m 4800 kW/hour * 7 = 33600 kW/hour - per season 0.112 cubic meters * 33600 kW/hour = 3763.2 cubic meters. m
All that remains is to take the current gas tariff and convert the total into money. And if the project involves installing a double-circuit system that will not only heat the house, but also heat water for domestic needs, add another 25% to the power of the equipment and, accordingly, to the gas consumption of floor-standing gas heating boilers.
The simplest thermal imagers cost at least $300, and the price of professional ones starts from several thousand, but these devices show all the places through which cold air enters the house and heat escapes out
How many cubic meters of gas are in a liter of liquefied propane?
With a density of propane in the liquid state of about 508 g/l and a molecular weight of 44.g/mol , all this, when divided, turns out to be 11.5192 mol in one kilogram of liquid propane gas. It follows that one liter of liquid propane contains 11.51 mol of gas, which upon evaporation under normal conditions, it will occupy a volume of 22.4 liters. From this we get 11.51 mol x 22.4 l/mol = 257.88 l. Knowing that in one cubic meter of gas 1000 liters by 257.88 liters and get 3.877 liters in one cubic meter of gas from a cylinder. Knowing how many kilograms were filled into the cylinder we can approximately calculate how many cubic meters of gas we need for heating
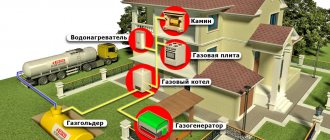
The boiler is connected to the main gas pipeline
Let us analyze the calculation algorithm that allows us to accurately determine the consumption of blue fuel for a unit installed in a house or apartment connected to centralized gas supply networks.
Calculation of gas consumption in formulas
For a more accurate calculation, the power of gas heating units is calculated using the formula:
Boiler power = Qt * K,
where Qt is the planned heat loss, kW; K - correction factor (from 1.15 to 1.2).
The planned heat loss (in W) in turn is calculated as follows:
Qt = S * ∆t * k / R,
Where
S—total area of enclosing surfaces, sq. m; ∆t—internal/outdoor temperature difference, °C; k—dispersion coefficient; R is the value of the thermal resistance of the material, m2•°C/W.
Dispersion coefficient value:
- wooden structure, metal structure (3.0 - 4.0);
- single brick masonry, old windows and roof (2.0 - 2.9);
- double brickwork, standard roof, doors, windows (1.1 - 1.9);
- walls, roof, floor with insulation, double glazed windows (0.6 - 1.0).
Formula for calculating the maximum hourly gas consumption based on the received power:
Gas volume = Qmax / (Qр * ŋ),
where Qmax is equipment power, kcal/hour; Qр is the calorific value of natural gas (8000 kcal/m3); ŋ — boiler efficiency.
In order to determine the consumption of gaseous fuel, you simply need to multiply the data, some of which must be taken from the technical data sheet of your boiler, some from construction reference books published on the Internet.
Using formulas by example
Let's assume that we have a building with a total area of 100 sq. m. Building height - 5 m, width - 10 m, length - 10 m, twelve windows measuring 1.5 x 1.4 m. Internal / external temperature: 20 ° C / - 15 °C.
We calculate the area of the enclosing surfaces:
- Floor 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Roof: 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Windows: 1.5 * 1.4 * 12 pcs. = 25.2 sq. m
- Walls: (10 + 10 + 10 + 10) * 5 = 200 sq. m Minus windows: 200 – 25.2 = 174.8 sq. m
Thermal resistance value of materials (formula):
R = d / λ, where d is the thickness of the material, m λ is the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material, W/[m•°С].
Calculate R:
- For the floor (concrete screed 8 cm + mineral wool 150 kg/m3 x 10 cm) R (floor) = 0.08 / 1.75 + 0.1 / 0.037 = 0.14 + 2.7 = 2.84 (m2• °C/W)
- For the roof (mineral wool sandwich panels 12 cm) R (roof) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2•°C/W)
- For windows (double-glazed unit) R (windows) = 0.49 (m2•°C/W)
- For walls (mineral wool sandwich panels 12 cm) R (walls) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2•°C/W)
The values of thermal conductivity coefficients for different materials were copied from a reference book.
Get into the habit of regularly taking meter readings, recording them and doing a comparative analysis taking into account the intensity of the boiler operation, weather conditions, etc. Operate the boiler in different modes, look for the optimal load option
Now let's calculate the heat losses.
Q (floor) = 100 m2 * 20 °C * 1/ 2.84 (m2*K)/W = 704.2 W = 0.8 kW Q (roof) = 100 m2 * 35 °C * 1 / 3, 24 (m2*K)/W = 1080.25 W = 8.0 kW Q (windows) = 25.2 m2 * 35 °C * 1/ 0.49 (m2*K)/W = 1800 W = 6, 3 kW Q (walls) = 174.8 m2 * 35 °C * 1/ 3.24 (m2*K)/W = 1888.3 W = 5.5 kW
Heat loss from enclosing structures:
Q (total) = 704.2 + 1080.25 + 1800 + 1888.3 = 5472.75 W/h
You can also add heat loss through ventilation. To heat 1 m3 of air from –15 °C to +20 °C, 15.5 W of thermal energy is required. A person consumes approximately 9 liters of air per minute (0.54 cubic meters per hour).
Let's assume that there are 6 people in our house. They need 0.54 * 6 = 3.24 cu. m of air per hour. We calculate the heat loss for ventilation: 15.5 * 3.24 = 50.22 W.
And the total heat loss: 5472.75 W/h + 50.22 W = 5522.97 W = 5.53 kW.
Having carried out a thermal engineering calculation, we first calculate the boiler power, and then the gas consumption per hour in a gas boiler in cubic meters:
Boiler power = 5.53 * 1.2 = 6.64 kW (rounded to 7 kW).
To use the formula for calculating gas consumption, we convert the resulting power indicator from kilowatts to kilocalories: 7 kW = 6018.9 kcal. And let’s take the boiler efficiency = 92% (manufacturers of modern gas floor-standing boilers state this figure within 92 – 98%).
Maximum hourly gas consumption = 6018.9 / (8000 * 0.92) = 0.82 m3/h.
Energy sources and price of 1 kW.
How much is it contained in 1.0 kg of coal, gasoline, gas, diesel fuel, firewood and the cost of fuel per 1 kW of heat generated. Knowing these figures, you can compare the premium at which heat management companies sell it. In Novosibirsk it is sold at the official tariff for 1300.07 rubles/gcal (
To simplify the calculations, we can assume that 1.0 liters of diesel fuel, 1.0 liters of gasoline, 1.0 liters of propane and also 1.0 cubic meter of natural gas provide about 10 kW of energy.
A. Hard coal.
1.0 kg of coal contains 7-8 kW of energy, 0.375 rubles/kW.
Price of 1 kg of coal = 3 rubles. (Novosibirsk, 2022). The cost of 1.0 kW of energy obtained by burning coal will be:
1.0 kg = 3.0 rub./8 kW = 0.375 rub./kW.
B. Firewood.
1 kg of firewood contains approximately 2.5 kW of energy, at 0.716 rubles/kW.
The average cost of firewood in Novosibirsk is 1,200 rubles. for 1.0 m³. The mass of 1.0 m³ of birch firewood is approximately 670 kg. That is, 1.0 kg of firewood costs about 1.79 rubles on average.
To obtain 1 kW/hour of thermal energy, approximately 0.4 kg of firewood is consumed:
The cost of 1.0 kW/hour of thermal energy when burning wood is approximately:
1 m³ contains approximately 10 kW of energy, at 0.584 rubles/kW.
The cost of natural gas in Novosibirsk is 5.835 rubles/m³.
For production of 1.0 kW/hour. Approximately 0.1 m³ of gas is consumed in thermal energy. Accordingly, the cost of producing 1.0 kW of thermal energy using natural gas is approximately:
5.835 rub./m³ *0.1 m³ = 0.5835 rub.
The cost of 1.0 Gcal of heat obtained from gas combustion will be:
583.5/0.8598 = 501.7 rub.
G. Liquefied gas.
D. Liquid fuel (diesel).
The cost of 1.0 liter of diesel fuel in Novosibirsk is 45 rubles.
The boiler is powered from a gas tank or cylinder
The formula Gas volume = Qmax / (Qр * ŋ) is suitable for determining the need for various fuels, incl. and liquefied gas. Let’s take from the previous example the resulting boiler power indicator - 7 kW. If such a boiler requires 0.82 m3/h of natural gas, how much propane-butane will be required?
About once a week you will have to go to a gas station with gas cylinders, which means transportation costs and loss of personal time. A drop in temperature below zero can also bring an unpleasant surprise if gas cylinders are placed outside. In a frozen cylinder, the gas does not freeze, but it does not evaporate, turning into liquid. And the boiler stops working
To calculate, you need to know what its calorific value is. Ud. the calorific value (this is the calorific value) of liquefied hydrocarbons in megajoules is 46.8 MJ/kg or 25.3 MJ/l. In kilowatt hours - 13.0 kW*h/kg and 7.0 kW*h/l, respectively.
Let's leave the efficiency of the gas heating boiler equal to 92% and calculate the hourly gas demand:
Gas volume = 7 / (13 * 0.92) = 0.59 kg/h
One liter of liquefied gas weighs 0.54 kg; in an hour the boiler will burn 0.59 / 0.54 = 1.1 liters of propane-butane. Now we calculate how much liquefied gas a gas boiler consumes per day and per month.
If the boiler operates for 16 hours, then per day - 17.6 liters, per month (30 days) - 528 liters. A typical 50-liter cylinder contains about 42 liters of gas. It turns out that our house with an area of 100 m2 will require 528 / 42 = 13 cylinders per month.
A gas holder with a reserve volume allows you to save on gas. The cost of refueling rises in the fall, while spring is a period of falling prices. Try to fill the tank as much as possible in the spring
Installing a gas tank is much more convenient than replacing empty cylinders with full ones. It is enough to refill the gas tank 2-3 times during the entire heating season.
Calculation example
It is necessary to determine how many cubic meters of gas one cylinder with a 50-liter propane-butane mixture contains if you pass its contents through a gas meter:
- the mass of the gas mixture pumped into it is about 21 kilograms;
- volume in m³ is equal to 50/5 = 10;
- after adjusting for the filling of the cylinder, we get 10 × 0.85 = 8.5 m³.
This indicator may vary depending on the ambient temperature, since when it decreases, the pressure inside the container decreases, with a corresponding decrease in the volume of fuel.
How to minimize gas consumption
To pay less money for the gas consumed by a floor-standing boiler and not widen your eyes in amazement at the sight of the next payment, follow these recommendations.
First, pay attention to the condensing boiler - the most economical one today. Its efficiency reaches 98-100% and higher. The price is high, but it will justify itself and will soon pay off. Read customer reviews for each model.
If you do not need water heating, take a single-circuit boiler. In a dual-circuit system, the gas demand includes an additional 20–25% that you don’t need.
Secondly, conscientiously insulate not only the walls, but also the roof, floor, foundation and basement. Install energy-saving double-glazed windows on your windows. Use a thermal imager. All cold spots must be found and eliminated. At the entrance to the house (corridor, hall, hallway) build a heated floor.
Third, use timers and sensors. The temperature you set for heating the air in the room will be adjusted automatically - for example, the batteries will heat up at night and cool slightly during the day.
If you decide to leave the house for a week, you can set the heating system to minimum during your absence and return to normal operation by the time you arrive. Once a year, a technical inspection is required to clear blockages and scale from the heat exchanger, traces of soot from the burner, and soot from the chimney.
Do not operate the boiler to its maximum. Its design data includes a 10-20% power reserve for emergencies and record-breaking cold winters. Don’t rush to turn the temperature dial another notch. A trifle, but it will affect the average monthly gas consumption
Fourthly, install a buffer storage tank in the heating system, which will contain a certain supply of coolant (hot water). Thanks to this “thermos”, which feeds the batteries for some time when the boiler is turned off, it is possible to save up to 20% of fuel.
Fifth, do not ignore proper ventilation. A window sash that is constantly ajar will transfer more heat to the street than a window that is wide open for five minutes.
Calculator and conversion factors for energy and energy carriers
Table of conversion factors for various types of energy and energy carriers in Joules. Energy unit conversion calculator (at the bottom of the table).
If you need to convert from one unit to another, you need to select the source units (column “FROM”) and the final units (column “B”) and click the “CONVERT” button.
The table contains different-sized, widely used duplicates! For example, kilocalories (often used in the energy value of products) and gagacalories (usually used in energy).
For some energy carriers, such as natural gas , which can be measured in both weight and volume units, values are given for both volume and weight .
Some physical constants and technical quantities that may be needed for calculations.
| SI prefix | Factor | ||
| Designation | |||
| Name | Russian This value is not one kilogram, but one cubic meter! Here, for example, is this indicator from the natural gas passport issued by Gazprom: Source | ||
Calorific value of solid materials
This category includes wood, peat, coke, oil shale, briquette and pulverized fuel. The main component of solid fuel is carbon.
Features of different types of wood
Maximum efficiency from the use of firewood is achieved provided that two conditions are met - dry wood and a slow combustion process.
Pieces of wood are sawn or chopped into pieces up to 25-30 cm long so that firewood can be conveniently loaded into the firebox
Oak, birch, and ash bars are considered ideal for wood-burning stove heating. Hawthorn and hazel are characterized by good indicators. But coniferous trees have a low calorific value, but a high burning rate.
How different rocks burn:
- Beech, birch, ash, and hazel are difficult to melt, but they can burn wet due to their low moisture content.
- Alder and aspen do not form soot and “know how” to remove it from the chimney.
- Birch requires a sufficient amount of air in the firebox, otherwise it will smoke and deposit resin on the walls of the pipe.
- Pine contains more resin than spruce, so it sparks and burns hotter.
- Pear and apple trees split easier than others and burn well.
- The cedar gradually turns into smoldering coal.
- Cherry and elm smoke, and sycamore is difficult to split.
- Linden and poplar burn out quickly.
TST indicators of different breeds strongly depend on the density of specific breeds. 1 cubic meter of firewood is equivalent to approximately 200 liters of liquid fuel and 200 m3 of natural gas. Wood and firewood fall into the low energy efficiency category.
Effect of age on coal properties
Coal is a natural material of plant origin. It is mined from sedimentary rocks. This fuel contains carbon and other chemical elements.
In addition to the type, the heat of combustion of coal is also influenced by the age of the material. Brown belongs to the young category, followed by stone, and anthracite is considered the oldest.
The moisture content is also determined by the age of the fuel: the younger the coal, the higher its moisture content. Which also affects the properties of this type of fuel
The process of coal combustion is accompanied by the release of substances that pollute the environment, and the boiler grates are covered with slag. Another unfavorable factor for the atmosphere is the presence of sulfur in the fuel. This element, upon contact with air, transforms into sulfuric acid.
Manufacturers manage to reduce the sulfur content in coal as much as possible. As a result, TST differs even within the same species. The production geography also influences the performance. Not only pure coal, but also briquetted slag can be used as solid fuel.
The highest fuel capacity is observed in coking coal. Stone, charcoal, brown coal, and anthracite also have good characteristics.
Characteristics of pellets and briquettes
This solid fuel is produced industrially from various wood and plant waste.
Shredded shavings, bark, cardboard, and straw are dried and turned into granules using special equipment. In order for the mass to acquire a certain degree of viscosity, a polymer, lignin, is added to it.
Pellets have an acceptable cost, which is influenced by high demand and features of the manufacturing process. This material can only be used in boilers designed for this type of fuel.
Briquettes differ only in shape; they can be loaded into furnaces and boilers. Both types of fuel are divided into types based on raw materials: round timber, peat, sunflower, straw.
Pellets and briquettes have significant advantages over other types of fuel:
- complete environmental friendliness;
- possibility of storage in almost any conditions;
- resistance to mechanical stress and fungus;
- uniform and long burning;
- optimal granule size for loading into a heating device.
Eco-friendly fuel is a good alternative to traditional heat sources, which are not renewable and have an adverse effect on the environment. But pellets and briquettes are characterized by an increased fire hazard, which should be taken into account when organizing a storage location.
Is it possible to get high-quality text without technical specifications?
Only a specialist with extensive experience who understands the subject matter of the order and understands what points need to be emphasized and what can be omitted can write an article on a given topic without knowing the requirements. It is difficult to find such an author on the market.
Only a specialist with extensive experience can work without technical specifications.
To understand how well the author understands the required field, you need to study his portfolio, which will allow you to evaluate the quality of the copywriter’s work and determine whether he is suitable for the task or not.
Reviews can also tell about the author indirectly, but you should understand that authors often gain positive characteristics from other people on easy, cheap orders. Therefore, you should not completely rely on a good copywriter rating.