Impact on gas consumption
Gas consumption is affected by the boiler power and the quality of the mixture.
Gas consumption depends on various factors. In large houses, boilers are installed that consume more fuel mixture than units in small buildings or apartments.
Fuel consumption is affected by:
- boiler power;
- outside temperature;
- quality of the gas mixture.
Some gas distribution companies supply undrained gas mixtures into the pipeline, which contain moisture and impurities. Calorie content decreases and volume consumed increases.
Calculation of gas consumption
The power of a boiler or convector depends on the heat loss in the building. The average calculation is carried out taking into account the total area of the house.
When calculating gas consumption, heating rates per square meter are taken into account for ceiling heights of up to 3 m:
- in the southern regions 80 W/m² is taken;
- in the northern regions - up to 200 W/m².
The formulas take into account the total cubic capacity of individual rooms and premises in the building. For heating every 1 m³ of the total volume, 30 - 40 W are allocated, depending on the area.
By boiler power
Bottled and natural gas are calculated in different units.
The calculation is based on the power and heating area. The average consumption rate is 1 kW per 10 m². It should be clarified that it is not the electrical power of the boiler that is taken, but the thermal power of the equipment. Often such concepts are replaced, and the result is an incorrect calculation of gas consumption in a private home.
The volume of natural gas is measured in m³/h, and liquefied gas in kg/h. Practice shows that to obtain 1 kW of thermal power, 0.112 m³/h of the main fuel mixture is consumed.
By quadrature
Specific heat consumption is calculated using the presented formula if the difference between the outside and inside temperatures is approximately 40°C.
The ratio used is V = Q / (g K / 100), where:
- V—volume of natural gas fuel, m³;
- Q is the thermal power of the equipment, kW;
- g is the lowest calorific value of gas, usually equal to 9.2 kW/m³;
- K is the efficiency of the installation.
Depending on pressure
The amount of gas is recorded by the meter.
The volume of gas passing through the pipeline is measured by the meter, and the flow rate is calculated as the difference between the readings at the beginning and end of the journey. The measurement depends on the pressure threshold in the converging nozzle.
Rotary meters are used to measure pressures greater than 0.1 MPa, and the difference between outdoor and indoor temperatures is 50°C. The gas fuel consumption indicator is read under normal environmental conditions. In industry, proportional conditions are considered to be a pressure of 10 - 320 Pa, a temperature difference of 20 ° C and a relative air humidity of 0. Fuel consumption is expressed in m³/h.
Calculation by diameter
Calculation of the diameter of the gas pipeline is carried out before the start of construction.
The gas speed in a high-pressure gas pipeline depends on the cross-sectional area of the collector and averages 2 - 25 m/s.
The throughput is found by the formula: Q = 0.67 D² p, where:
- Q—gas consumption;
- D is the nominal flow diameter of the gas pipeline;
- p is the working pressure in the gas pipe or the absolute pressure of the mixture.
The value of the indicator is affected by outside temperature, heating of the mixture, excess pressure, atmospheric characteristics and humidity. Calculation of the diameter of the gas pipeline is done when drawing up the system design.
Taking into account heat loss
To calculate the consumption of the gas mixture, it is necessary to know the heat losses of the structure.
The formula used is Q = F (T1 – T2) (1 + Σb) n / R, where:
- Q—heat loss;
- F is the area of the insulating layer;
- T1 - outside temperature;
- T2 - internal temperature;
- Σb—sum of additional heat losses;
- n is the coefficient of arrangement of the protective layer (in special tables);
- R - resistance to heat transfer (calculated in a specific case).
Determining heat loss is a complex calculation and is carried out by specialists at the project stage. You can order the discovery of losses at any stage of operation of the building.
With and without meter
Gas consumption depends on the insulation of the walls and the climatic conditions of the region.
The device determines the gas consumption per month. Standard mixture consumption rates apply if a meter is not installed. For each region of the country, standards are set separately, but on average they are taken at the rate of 9 - 13 m³ per month per person.
The indicator is set by local governments and depends on climatic conditions. The calculation is carried out taking into account the number of owners of the premises and people actually living in the specified living space.
We calculate how much gas a gas boiler consumes per hour, day and month
When designing individual heating systems for private houses, 2 main indicators are used: the total area of the house and the power of the heating equipment. With simple average calculations, it is generally accepted that for heating every 10 m2 of area, 1 kW of thermal power + 15-20% of the power reserve is sufficient.
How to calculate the required boiler powerIndividual calculation, formula and correction factors
It is known that the calorific value of natural gas is 9.3-10 kW per m3, which means that for 1 kW of thermal power of a gas boiler, about 0.1-0.108 m3 of natural gas is needed. At the time of writing, the cost of 1 m3 of main gas in the Moscow region is 5.6 rubles/m3 or 0.52-0.56 rubles for each kW of boiler thermal power.
But this method can be used if the boiler’s passport data is unknown, because the characteristics of almost any boiler indicate the gas consumption during its continuous operation at maximum power.
For example, the well-known floor-standing single-circuit gas boiler Protherm Volk 16 KSO (power 16 kW), operating on natural gas, consumes 1.9 m3/hour.
- Per day – 24 (hours) * 1.9 (m3/hour) = 45.6 m3. In value terms – 45.5 (m3) * 5.6 (tariff for Moscow region, rub.) = 254.8 rub/day.
- Per month – 30 (days) * 45.6 (daily consumption, m3) = 1,368 m3. In value terms – 1,368 (cubic meters) * 5.6 (tariff, rub.) = 7,660.8 rubles/month.
- For the heating season (suppose from October 15 to March 31) - 136 (days) * 45.6 (m3) = 6,201.6 cubic meters. In value terms – 6,201.6 * 5.6 = 34,728.9 rubles/season.
That is, in practice, depending on the conditions and heating mode, the same Protherm Wolf 16 KSO consumes 700-950 cubic meters of gas per month, which is about 3,920-5,320 rubles/month. It is impossible to accurately determine gas consumption by calculation!
To obtain accurate values, metering devices (gas meters) are used, because gas consumption in gas heating boilers depends on the correctly selected power of the heating equipment and model technology, the owner’s preferred temperature, the arrangement of the heating system, the average temperature in the region during the heating season and many other factors , individual for each private home.
Consumption table for well-known boiler models, according to their passport data
| Model | power, kWt | Max natural gas consumption, cubic meters m/hour |
| Lemax Premium-10 | 10 | 0,6 |
| ATON Atmo 10ЕВМ | 10 | 1,2 |
| Baxi SLIM 1.150i 3E | 15 | 1,74 |
| Protherm Bear 20 PLO | 17 | 2 |
| De Dietrich DTG X 23 N | 23 | 3,15 |
| Bosch Gaz 2500 F 30 | 26 | 2,85 |
| Viessmann Vitogas 100-F 29 | 29 | 3,39 |
| Navien GST 35KN | 35 | 4 |
| Vaillant ecoVIT VKK INT 366/4 | 34 | 3,7 |
| Buderus Logano G234-60 | 60 | 6,57 |
Calculator for quick calculations
Let us remind you that the calculator uses the same principles as in the example above; real flow data depend on the model and operating conditions of the heating equipment and can only be 50-80% of the data calculated under the condition that the boiler operates continuously and at full capacity .
Calculation of liquefied gas consumption
Calculating gas using propane or butane has its own characteristics, but is not particularly difficult. What matters is the density of the flammable substance, which changes with increasing or decreasing temperature and depends on the composition of the gas mixture. Only the weight of the liquefied fuel remains constant.
The volume of gas used differs in winter and summer, so it makes no sense to use m³ units to determine the consumption of liquefied gas per 1 kW of heat; kilograms are taken for designation, which do not change with the change of seasons.
Calculation for 1 kW of heat
The amount is calculated for heating the house and heating the water in the system. If you cook food using gas, this needs to be taken into account additionally.
The formula used is Q = (169.95 / 12.88) F, where:
- Q—fuel mass;
- 169.95 - annual amount of kW for heating 1 m² of a house;
- 12.88 - calorific value of propane;
- F is the quadrature of the structure.
The resulting value is multiplied by the cost of 1 kg of liquefied mixture to calculate the cost of purchasing the required quantity. The price is usually given per 1 kg and not per 1 m³, which should be taken into account.
How to take into account standards in waybills
If an enterprise uses a car only for production needs, and at the same time is not a transport organization, it can independently develop forms of waybills, keeping the required details in them.
In the case of using cars with LPG, this will be very important, since in any case gasoline is used to start the engine in such cars. In addition, the second type of fuel can be used in other cases:
- entry into the repair area;
- warming up the engine in winter;
- other emergency situations, for example, the car needs to get to a gas station, when the main fuel has run out, etc.
The waybill must display separately gasoline consumption and gas use. You can supplement the approved waybill form so that it reflects both types of fuel. To do this, the document provides additional information:
- Technical characteristics of gas equipment;
- Volume of the gas tank (along with gasoline), etc.
A self-developed waybill form must be approved by an internal local document.
Reducing gas consumption
Saving gas is directly related to reducing heat loss. Enclosing structures such as walls, ceilings, and floors in the house must be protected from the influence of cold air or soil. Automatic adjustment of the operation of heating equipment is used for the effective interaction of the external climate and the operating intensity of the gas boiler.
Insulation of walls, roofs, ceilings
You can reduce gas consumption by insulating the walls.
The outer heat-protective layer creates a barrier to cooling surfaces in order to consume the least amount of fuel.
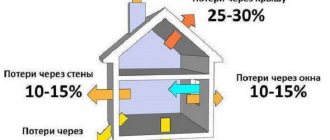
Statistics show that part of the heated air escapes through structures:
- roof - 35 - 45%;
- non-insulated window openings - 10 - 30%;
- thin walls - 25 - 45%;
- entrance doors - 5 - 15%.
Floors are protected with a material that has acceptable moisture permeability according to the norm, since when wet, the thermal insulation characteristics are lost. It is better to insulate the walls from the outside; the ceiling is insulated from the attic side.
Window replacement
Plastic windows let in less heat in winter.
Modern metal-plastic frames with double- and triple-glazed windows do not let air flow through and prevent drafts. This leads to a reduction in losses through the gaps that existed in old wooden frames. For ventilation, tilt-and-turn mechanisms are provided for the doors, which contribute to the economical consumption of internal heat.
The glass in the structures is covered with a special energy-saving film, which allows ultraviolet and infrared rays to pass through, but prevents their reverse penetration. The glass is equipped with a network of elements that heat the area to thaw snow and ice. Existing frame structures are additionally insulated with plastic film on the outside or thick curtains are used.
other methods
It is beneficial to use modern gas-fuelled condensing boilers and install an automated coordination system. Thermal heads are installed on all radiators, and a hydraulic arrow is mounted on the unit’s piping, which saves 15–20% of heat.
Detectors and temperature regulators are installed in the heating system, which regulate the boiler power depending on the state of the external climate. If the weather is warm outside, it is more efficient and economical to switch to heating with air conditioners.