Quite often you hear from owners of private houses that they have a very capricious stove - it either lights up at the slightest spark, or requires increased attention and almost dances with a tambourine to get it to start working. This state of affairs is quite common among those owners who have only recently become property owners and have not yet fully understood all the intricacies of stove heating. At the same time, the most important issue for them becomes the problem of how to increase the draft in the furnace.
What is traction
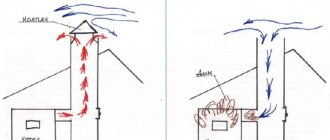
Draft is the movement of flue gases up the chimney of a house, from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure.
In a chimney (in a pipe) of a set diameter, with a height of at least 5 m, a vacuum is formed, this means that the required minimum pressure difference is formed between the lower part of the chimney and the upper, the air from the lower part, entering the pipe, goes up. This is called traction. The draft can be measured with special sensitive instruments, or you can take a piece of fluff and bring it to the pipe. Accordingly, if you take a pipe of sufficient diameter in which air has the opportunity to move, and stretch it high up, then air from the ground will begin to constantly flow upward. This happens because the pressure is lower at the top, and the vacuum is greater, and air tends there naturally. And in its place will come air from other sides. In the “firebox + chimney” system, the draft operates even if the stove in a private house is not working. When burning wood, increased pressure is formed in the internal combustion chamber and the flue gases generated during combustion require exit. All fireboxes and stoves are designed to exhaust flue gases into a chimney.
The height of each chimney is selected so that draft is created, an initial vacuum is created. When burning in the combustion chamber, heat and gases are released and excess pressure occurs. Gases move in the chimney under the influence of draft, tending to move from an area of high to an area of low pressure. The laws created by nature work.
Conclusion
The main thing in the design of a stove is the correct calculation of the parameters of the firebox and chimney. Seek help from specialists. Laying stoves is a very difficult task; it is no coincidence that the skill of a stove maker has been highly valued at all times. The second aspect of this problem is to use only high-quality materials that can withstand high temperatures and do not collapse.
Periodic maintenance of the chimney and firebox will not only eliminate draft problems, but also ensure fire safety. Monitor weather changes, use all stove settings correctly, and use high-quality fuel. If these simple conditions are met, your home will always be warm and cozy.
Why does backdraft occur in a stove or chimney?
Reverse draft is the movement of flue gases from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure, but not upward (as described earlier), but downward. Reverse draft occurs when pressure is inverted - when the pressure at the top is higher than at the bottom.
The reasons are the most ordinary things: if a private house or room is sealed, there are double-glazed windows, and an exhaust hood works together with the chimney, drawing air out of the room. This is where low pressure is created relative to the surrounding area. Therefore, during kindling, when the chimney is still cold, the air in the upper part of the chimney has greater pressure than in the room. The smoke will of course go where it is easier for it. This phenomenon is called a “cold column”. When the chimney cools, a low-temperature air mass forms inside, which presses down, causing reverse draft. If the pressure in a private house is not reduced, then warm air will go up into the chimney.
Thus, if the house does not have a kitchen hood and it is not airtight, there will be no stagnation of cold air in the firebox.
Check: if in winter, before lighting the fireplace, you first set fire to a newspaper and put it into the chimney (bypassing the combustion part), then the fire will not go into the room, no matter what the column of cold air is. The fire will burn and come out only into the chimney. This indicates that the pressure in the room is not low and warm air normally tends to rise.
When lighting a stove or fireplace in a private home, sometimes smoke comes into the room. This is due to the fact that the flue gases formed during the initial kindling have not yet had time to heat up, and, when rising upward, coming into contact with the cold walls, they immediately cool down. After that, they will naturally rush down. Again, reverse draft occurs in the chimney ventilation. To normalize the draft in the stove, it is important to melt correctly, understanding the processes occurring there.
The role of the damper in the operation of the heating system
Damper to reduce the intensity of combustion and draft
A damper, or damper, eliminates the possibility of developing reverse draft and increases the fire safety of the room. It is installed using 2 methods:
- into the chimney pipe;
- on the oven door.
The damper serves as a kind of regulator. When the gate is closed, the cross-sectional area of the pipe decreases along with the draft and vice versa.
Rollover traction
Another issue that arises is the tipping of the draft. In what cases does this happen?
If the chimney is long and cold (often brick), and the pressure is reduced. If the ratio of the dimensions of the firebox and the cross-section of the chimney correspond, if there is normal pressure in the house, a situation still arises when, when lighting the flame, there is not enough strength and the exhaust flue gases manage to cool in the chimney and collapse down. Why is there no draft in the chimney? This happens in cloudy weather and wind. It happens that the fire flares up normally, but then smoke pours into the house. Why is there no draft in the furnace? Why does back draft form in the chimney? Air is taken from the house and the pressure decreases, there is no air flow. As the flue gases rise, they cool and fall down. What do you need to know in such situations? Open the window slightly if the room has double-glazed windows and is sealed. The preparation of firewood and its quality are important.
Russian stove and its design
One of the reasons for insufficient traction may well be weather conditions. This applies to all wood stoves, regardless of their design.
This now seems implausible, but for many village families the stove was not only a “breadwinner”, but also a “meteorologist”. Based on the direction of the smoke column, the burning of coals, and the sounds that arise during the fire, experienced owners determined with a sufficient degree of reliability only the weather for several days.
Russian stove in the interior of a village house.
For example, if the atmospheric pressure is low, the stove takes a long time to light up, and the wood burns sluggishly, since the draft in the chimney becomes weaker. In this case, the smoke coming into the chimney from the fuel chamber often overflows onto the forehead of the stove.
If, due to poor draft caused by low pressure, damp firewood is also used, then acrid smoke can fill the entire room. All these manifestations together indicate that the next day the weather will be rainy and windy, and if it’s winter outside, then you should expect a snowstorm, which is very likely to bring a thaw.
But experienced owners, nevertheless, always knew how to distinguish external phenomena from malfunctions that arose in the design of the furnace itself. There are many other reasons that directly affect the level of draft and, accordingly, the efficiency of this heating structure.
And in order to deal with them, you need to know the internal structure of the furnace, at least schematically. Otherwise, it will be difficult to carry out repair work.
A Russian stove with an additional firebox allows you to use the structure for cooking food in the cooking chamber located in the front part of the hearth, without heating the entire structure.
The structure of a Russian stove is somewhat more complex than many other heating brick structures. And, by the way, there is no single, “dogmatic” scheme - even for one master stove maker, different stoves laid out can differ quite significantly. So, for example, a stove may have an additional firebox located under the main mouth or on the side, or do without it, have a different number of stoves, differ in size and location of the stove, etc.
In order not to get confused in the furnace sections, you need to know their location and names:
One of the most common design schemes for a Russian stove
So, the design of a Russian stove consists of the following elements and sections:
1 - A view or valve that blocks the chimney pipe.
2 - Bend - the second wall in front of the entrance to the chamber, located under the arch.
3 - Oven - the surface of the oven, turned towards the wall of the house.
4 - Damper - a removable steel or cast iron door that closes the mouth of the oven during heating, cooking or baking bread. She is pressed against the walls of the bracket.
5 - The mirror is the front surface of the stove, reflecting heat into the room.
6 - Bed - a sleeping place heated from the inside, from the roof of the cooking chamber.
7 - Ward - the lower part of the furnace located immediately on the foundation.
8 - Stoves - blind niche openings that allow you to retain and distribute heat throughout the room for a longer time. Cooking utensils are often placed in them to keep cooked foods warm.
9 - Under - the base of the cooking chamber. Usually done with a slight slope towards the mouth.
10 - Pre-stove - a wooden extension to the outside of the stove - a mirror. It is used as a ladder for climbing to a sun lounger, and also as a shelf for drying shoes.
11 - The vault is the ceiling of the cooking chamber laid out in the form of an arch.
12 - The lower part of the chimney pipe.
13 - The mouth is the area of the hearth located at the front of the hearth, which can serve as a cooking chamber.
14 - The head is the end of the hearth, that is, the lower part of the cooking chamber.
15 - Pole - part of the hearth protruding forward from the general surface of the wall.
Russian stove in the process of being laid. The bottom of the main hearth is lined. A special section at the bottom is clearly visible - the baking area.
In addition to the departments listed above, the “classic” of the Russian stove is usually the oven space, which is called the oven area. The necessary equipment is stored here, and firewood brought in from the street is also dried.
How to assemble a chimney correctly?
Sandwich chimneys (prefabricated), collected by smoke and condensate.
There is an opinion that it is more correct to collect by smoke. The explanation is that there are gaps at the pipe joints where the flue gases escaping into the pipe get clogged. In contrast, it is believed that if you collect the smoke, the smoke will stop coming out.
Such a dispute can be resolved if you drill a hole in the existing stove at home anywhere in the chimney and see what happens. It's most interesting to do this at the bottom. Drill any hole, at least a centimeter in diameter. What will you see? No smoke will come out of this hole (unless you close the chimney tightly from above).
Rules and regulations
If you do not clean the chimney for a long time, it becomes clogged with soot and creates an obstacle to the passage of smoke.
Most often, smoke occurs due to troubles with the chimney. It is either clogged or initially arranged incorrectly. The most important point is the height of the chimney. SNiPs indicate the exact dimensions for different structural dimensions of roofs or the location of the pipe structure itself on the roof. For houses with flat roofs, this parameter cannot be less than 60 cm, measured from the highest point of the parapet or superstructures, for example, a terrace canopy.
If there is a garden with tall trees around the house, or neighboring houses are located nearby and higher, it is better to make the pipe larger so that the smoke does not hit obstacles, but goes freely into space.
Ways to normalize cravings
The main thing is to take into account that condensation may occur in every chimney of a house, especially when it is still cold and warm flue gases are greatly cooled as they rise. Condensation may settle on the walls and flow down the pipe.
If the chimney is assembled according to smoke, then condensation easily penetrates into the cracks and moistens the insulation, completely depriving it of its heat-insulating properties. It's not far from the fire here. Therefore, the assembly of modular chimneys is carried out only using condensate. The chimneys are assembled at a clear joint, with sealant along the inner pipe. However, the chimneys themselves must be of high quality so that no extraneous cracks remain. If the gaps remain, air will enter through them, and it turns out that there will be no draft anyway.
But the chimney is big and tall! Not understanding the reason, they call the experts. Craftsmen use a simple method: they cover the top of the chimney and watch where the smoke comes from. Here all sorts of inconsistencies in the chimney are discovered, which lead to air being sucked into the chimney. Remember? The air tends upward, to where the pressure is lower. Therefore, the more cracks, the worse the traction below. The smoke assembly, unfortunately, does not take into account the very essence of draft. As a result, the fire burns and smoke rushes in all directions. Although the logic here is not complicated - smoke goes from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure, where it is easier for it.
Making a deflector with your own hands
The sizes of the deflectors are different chimney pipes.
The walls of the upper cylinder take the wind pressure and direct the air around; smoke suction is achieved by sliding along the inner surface of individual jets. The deflector cannot be classified as a fan, since the device has a simple shape and does not have working mechanisms.
The contours of the parts that were calculated and plotted on the drawing are drawn on the cardboard and cut out. Using patterns, parts are transferred to metal with the addition of 1.5 - 2 cm along the edges of the lines for ease of assembly. Structural elements are obtained in expanded form after cutting with metal scissors.
A hacksaw is used to cut strips of metal or corners to connect parts into a finished product. The prepared parts are bent and rolled in accordance with the drawing. During assembly, the elements are superimposed on each other and connected with rivets.
Required Tools
During production, materials and tools are used that do not require professional skills from the master:
- rubber or wooden mallet;
- scissors and hacksaw for metal;
- ruler, tape measure;
- chalk for drawing lines on the metal surface;
- electric drill, rivet gun;
- metal drills;
- pencil and regular scissors.
The material is thin galvanized steel, a metal strip or a small section corner. The size of the rivets is selected in accordance with the diameter of the drill. Nuts and bolts are used for installation on the pipe.
Size calculation
A drawing is made on paper, which indicates the key dimensions for creating a pattern for a weather vane-draft amplifier for the chimney.
Ratio when calculating sizes:
- the deflector height is 1.7 d;
- the width of the cap is assumed to be 2 d;
- The diffuser width is taken to be 1.3 d.
The symbol d indicates the diameter of the chimney (internal). A different size ratio will result in poor efficiency.
What else affects the amount of thrust?
First of all, the height of the chimney. The minimum required height is 5 meters. This is enough for a natural vacuum to occur and the upward movement to begin. The higher the chimney, the stronger the draft. However, in a brick chimney with an average cross-section of 140x140mm, at a height of over 10-12 meters, the draft no longer increases. This is because the wall roughness value increases with increasing height. Therefore, excess height does not affect traction. A similar question arises among those who want to use ducts for chimneys in their homes. They come in large heights and narrow cross-sections, so a serious fireplace is rarely connected to such a chimney.
Reasons affecting cravings:
- Flue gas temperature. The higher the temperature, the faster the flue gases rush upward, creating a greater draft.
- Chimney heating. The faster the chimney warms up, the faster the poor draft normalizes.
- The degree of roughness of the chimney and internal walls. Rough walls reduce traction, while smooth walls have better traction.
- The cross-sectional shape of the chimney. The circular section is a sample; oval, rectangular and so on. The more intricate the shape, the more strongly it affects traction, reducing it.
- It is important to note that the ratio of the size of the firebox, the diameter of the outlet pipe and the diameter of the chimney pipe also influences. If the height of the designed chimney is excessive, you should consider reducing the cross-section of the chimney by an average of 10%. Install an adapter on the firebox, on the smoke pipe (for example, from a 200-diameter to a 180-diameter) and take the 180-diameter pipe itself. This is allowed by the manufacturers. If we talk about “EdilKamin” as an example, you can see that in the instructions for the fireboxes he describes what diameter the chimney should be depending on the height.
For example:
- height up to 3 m – diameter 250,
- height from 3 m to 5 m – 200,
- height from 5 m and above – 180 or 160. Strict recommendations.
Other manufacturers (such as Supra) admit that changes are possible. Some don't allow it at all. Therefore, following the instructions, you should not forget about the processes occurring in the chimney.
Causes in the stove
The draft of the furnace depends on many factors, ranging from design solutions, the quality of the masonry, to meteorological factors and the need for periodic maintenance of the entire furnace system. Let's take a closer look at why there is poor draft in the furnace and what the possible reasons may be due to the design features:
- chimney design,
- pipe size,
- brick falling into the chimney,
- the chimney is clogged with soot.
Chimney design
The simplest chimney design is straight. Exit outside the premises occurs directly through the pipe. This can be observed in the example of simple “stove stoves” in temporary premises, tourist stoves and in the case of fireplaces.
The straight design provides the best draft, which is what is used for open fireplace fireplaces and temporary stoves. The draft in such a pipe near the stove is almost ideal and is less dependent on external factors.
But in stove heating systems of a home, the chimney is arranged through a heater. The purpose of such a stove is to heat the room and retain heat for as long as possible.
- There is a whole system of so-called “wells”; the smoke from the firebox passes through a winding path, heats the brickwork and only then exits through the chimney. Such systems require the greatest attention in terms of proper design, otherwise traction will constantly disappear under any unfavorable conditions. There is also a high probability of backdraft occurring when smoke begins to flow into the room instead of exiting through the pipe.
A complex gas movement system is one of the reasons for poor traction - The second design factor influencing draft is the correctly calculated cross-sectional diameter of the chimney in accordance with the volume of the stove. A chimney that is too narrow cannot remove combustion products from a large-volume stove, and they will inevitably partially enter the room.
- The shape of the section also matters; a round outlet is preferable, and in the corners of a square one, side turbulence occurs, which somewhat impedes the free movement of smoke.
- And lastly, the inner surface of the chimney itself should also not serve as an obstacle to the movement of gases and suspended particles.
Pipe size
How to increase draft in a stove if the chimney design is with a heater? All things being equal, the higher the pipe, the better the traction. But it's not that simple. A pipe that is too high will be affected more by winds, and if the pipe is too high, the draft may be unnecessary. Excessive draft leads to faster combustion of fuel and an increase in the combustion temperature in the furnace, which is unfavorable for masonry.
At the same time, rapid combustion does not have time to heat the entire heater array.
The optimal height of the chimney is about 5 meters or slightly above the ridge of the roof, in order to avoid exposure to air turbulence from it.
By the way, according to fire regulations, the length of the chimney above the ridge of the roof allows you to place the exit at any distance from it. Whereas, the lower pipe should be located from the edge of the roof and the ridge at a certain distance. These reasons must be provided for when laying the furnace; they cannot be corrected during operation.
Brick collapse
The causes of poor draft, which depend on the care of the stove and which can be eliminated as they occur, are temporary.
The draft of the correct chimney for your stove may also depend on temporary factors. One of these is the collapse of a brick inside a chimney. This happens most often due to poor quality material, but it may also be due to the reason mentioned above. Burnout of bricks at high temperatures of fuel combustion is one of the main causes of premature breakdowns. Pieces from cracked bricks clog the chimney where it turns and interfere with the free passage of gases. Clogging with foreign objects and soot is the main temporary problem when operating any furnace.
In this situation, you will have to redo the chimney.
The chimney is clogged with soot
There are several reasons for this problem. First of all, the possibility of clogging is affected by the design of the chimney. The more turns, the more opportunities for soot from combustion products to settle.
The more “wells” there are in a heater’s design, the more often it is necessary to clean the chimney and pipe due to a decrease in the speed of smoke passage and a decrease in draft. In this case, a vicious circle results - soot reduces thrust, and as thrust decreases, soot is deposited even more intensely.
Lots of soot
How to improve draft with such a problem in the oven without cleaning it in the standard way?
There are several methods - heat the stove for 24 hours with dry wood with a low resin content, briefly create a high combustion rate when burning flammable materials. Often, soot deposition also contributes to the formation of frost on the inner surface of the pipe.
To prevent this, if you leave the house for a long time, you need to close the pipe damper in time, which will prevent hot air from coming into contact with environmental humidity. If the chimney is neglected and clogged with foreign objects, cleaning is essential.
Elimination of these causes is carried out:
- Cleaning the chimney is done in the old proven way using a small weight with a brush on a strong cable. Clogging occurs most often in the outer wells at the bend of the chimney. A weight helps to knock stuck pieces of brick to the very bottom, a brush cleans soot from the walls of a pipe and well. At the very bottom of the well, which directly goes into the chimney, a technological hole is always made, closed with a brick and a special door. This brick is easy to remove and all debris and soot can be removed. With a large number of heating wells, such a hole is made in the first well, as in the most vulnerable place.
- Burning with wood or flammable materials. It is worth warning that cleaning a chimney using flammable liquids is fraught with unpredictable consequences. This could be a burn to the “specialist” himself, or the ignition of soot in the fire with the subsequent spread of combustion, or ordinary destruction of the furnace as a result of an uncontrolled explosion.
Rose of Wind
A situation when the prevailing winds blow directly into the chimney and reduce the draft or reverse it. The chimney is installed on the windward side, of course, if the wind directions are determined. If the chimney is located far from the ridge and below, the leeward side cannot be used. Multi-storey buildings and trees also affect traction. To compensate for gusts of wind and poor placement of the chimney, anti-wind deflectors are used. According to the standards, the chimney is installed half a meter above the ridge. If the distance from the ridge is 1.5 m - 3 m, then it is brought to the same level as the ridge. If the distance is more than 3 meters, then proceed according to the formula: from the horizontal drawn from the ridge, 10 degrees down. In practice, the chimney is made higher than the ridge, or at the same level as the ridge. It is important to use one chimney for one stove in the house.