The general principle of operation of all water heating systems is the same: the coolant is heated in the boiler and moves through the pipes to the radiators, transfers heat to the room, and then returns to the boiler. In this case, circulation can be natural or forced. It all depends on what sets the coolant in motion. In the first case it is gravity, in the second it is a pump.
Water heating and what is it?
Water heating is a circuit of pipes within which a coolant liquid (water or antifreeze) circulates. Boiler equipment is used to heat the coolant. The liquid is transported through pipelines. Convectors, collectors, and radiators act as heating devices.
Compared to steam heating, water heating is safer due to the low temperature of the coolant and the stable state of the liquid. In this case, the circulation of the liquid medium can be forced or natural. The second option is simpler and more reliable, but the heating efficiency in this case is reduced.
Pros and cons of a water system
Among the advantages of water heating of residential buildings are the following:
- The air heated from the radiators is evenly distributed throughout all rooms.
- System parameters can be managed and monitored in one place.
- If necessary, you can use hidden piping, leaving only the radiators visible. When installing a heated floor, all devices that emit heat into the room are completely hidden.
- Since the temperature of the circulating coolant does not exceed 95 degrees, and the surface of the batteries does not heat above 65°C, the circuit elements are completely safe. If you touch them for a short period of time, you cannot get burned.
- The room temperature can be adjusted. Heating occurs gradually.
- The significant thermal capacity of the liquid carrier and radiators allows the room to be heated for some time after the boiler equipment has stopped operating.
The disadvantages of water heating include the likelihood of leaks. Although if the circuit is mounted from high-quality polypropylene pipes, then this probability is reduced to zero. If water and not antifreeze circulates in the circuit, then when heating equipment stops operating for a long period in winter, there is a risk of the coolant freezing.
Classification of water heating
There is the following classification of heating systems:
- depending on the temperature of the coolant in the supply line, the systems are low-temperature (70 degrees), medium-temperature (70-100°C) and high-temperature (water temperature in central heating is above 100 degrees);
- According to the location of the supply and return pipelines, water heating is divided into circuits with lower and upper wiring (in the first case, the supply pipe is located below the radiator, in the second case – above);
- the layout of pipelines connecting radiators can be vertical or horizontal;
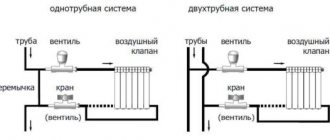
- also, the wiring can be one-pipe and two-pipe (with one-pipe wiring, the batteries are connected in series, with two-pipe wiring - in parallel);
- depending on the coolant current in the supply and return pipelines, the systems can be either passing or dead-end (in the first case, the fluid flow in both lines coincides, in the second, water flows in the opposite direction);
- according to the principle of coolant movement, systems come with natural and forced circulation (in the first case, the liquid flows due to the slope of the pipes and gravity, and in the second, a circulation pump is responsible for the flow of water).
There are also bifilar heating systems that provide uniform heating of all radiators, as with a two-pipe distribution, but in practice they are single-pipe. They also come with vertical and horizontal pipe layout.
Heating with forced circulation
So, we see that systems with natural circulation of liquid have a number of rather significant disadvantages. An alternative to them are systems with forced circulation, which use additional equipment that increases the flow of coolant in the system. Namely the circulation pump.
Yes, this type of water heating at home will be more expensive and complex, but you get many advantages:
- Possibility to heat a large room. We have already said that natural circulation is not suitable for large houses. If you are the owner of just such a thing, then your only option is a forced circulation system.
- Complication of the system. By installing a pump, you do not depend on such an indicator as pressure. Therefore, what was an obstacle in a gravity system is not a problem in a forced one. For example, you can now increase the number of pipe bends if the layout of your home requires it.
- Use of smaller pipes. Agree, the neat appearance of the heating system is not the last indicator that is worth paying attention to.
- Less dependence of heating quality on the presence of air in the system. With self-circulation, the entry of air into the system would significantly complicate the transportation of coolant through the pipes. A forced system solves this problem, but in the case of installing metal pipes, special expansion tanks with air vents and fuses should be used in order to avoid corrosion of the system.
- Possibility of using more wear-resistant and lightweight plastic pipes.
- Concealed installation of pipes is possible. You can hide pipes in screeds and walls without any problems
System characteristics
Water heating of a country house and apartment buildings differs in its characteristics. In this case, the connection diagram can be independent or dependent. With an independent or closed connection, the coolant coming from the main line enters the heat exchanger, which is installed in the consumer’s heating station. Here the secondary coolant is heated, which enters the house heating system.
Dependent or open connection is used in apartment buildings. With this scheme, the heated coolant enters the pipelines and radiators of the house directly from the central line.
Water heating device in a private house
Depending on the number of floors and dimensions of the country house, single-pipe or two-pipe wiring is used. In the first case, heating devices are connected to the main line in series. Single-pipe wiring is easier to install and does not require a large number of elements. But its disadvantage is that in each subsequent radiator the temperature of the coolant decreases, which contributes to uneven heating of the residential building. To solve the problem, it is necessary to install more sections.
Baseboard heating, installation of water and electric radiators
To install a two-pipe system, you need to carry out complex calculations and use a larger number of constituent elements. The installation itself is also more difficult. The main advantage of two-pipe wiring is that all devices are connected to the main in parallel, which ensures equal coolant temperature in each radiator and uniform heating of the entire house.
Important! Single-pipe wiring is suitable for heating a small one-story house. And two-pipe systems are used in two-story private houses.
Scheme of water heating of an apartment building
In apartment buildings, single-pipe wiring is used, but a heating riser is used. The heating devices of each apartment are connected to it in parallel. One house may have many risers that connect to the central supply main. Since the pressure in the central heating system is quite high, equal hydraulic conditions are ensured in all risers.
In apartment buildings, all radiators are installed on bypasses, so that in order to turn off one device in order to repair or replace it, there is no need to stop the operation of the entire heating system of the house. To regulate the temperature in a separate room, a balancing valve is installed on each battery.
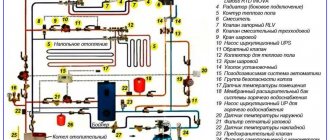
Components
To install water heating, you will need the following components:
- pipelines;
- heating equipment (boiler or furnace);
- heating devices (radiators);
- expansion tank (open or closed type);
- circulation pump (only in systems with forced coolant flow);
- safety group, which includes a pressure gauge, automatic air vent and safety valve (used only in closed systems).
With natural coolant flow, a circulation pump is not needed. Since gravity systems are usually made of an open type, there is no need to install a safety group. However, it is important to slope the return pipeline towards the heating equipment, for which the boiler is installed below the level of the radiators (in the basement or ground floor). In addition, in open-type systems, the expansion tank is mounted at the highest point of the system (in an insulated attic).
Radiator connection diagrams
For ordinary people who do not think about how radiators are connected in their own home, it does not matter what circuit is used. The main thing for them is warmth in the house. But, as practice shows, it is the connection diagram of radiator batteries that affects the quality of heat transfer. And there are two schemes: one- and two-pipe.
How to make a one-pipe heating system for a private house with your own hands
First of all, you need to understand why it is called that. In essence, a single-pipe is a ring with a boiler in the center. The pipes are laid close to the floor in a circle, with batteries connected to them. Each of them takes the coolant from one side from the lower pipe and squeezes out already cooled water into the same pipe from the other opposite pipe (lower).
Let's face it, it's not the best option, because it has one significant drawback. The radiators far from the boiler receive coolant with a significantly reduced temperature. That is, the batteries closest to the boiler will be hot, the ones farther away will be warm. This means that some rooms will be cool.
Single-pipe with connection of radiators to one circuit
But if a private house is small with 3–6 rooms, then a single-pipe heating system in it is justified due to the ease of installation with your own hands, plus a small number of pipes, shut-off valves and fittings. That is, this is the most economical option in terms of construction. Although the scheme and procedure for installing single-pipe heating are considered simple, the responsibility of the operations carried out is still high. This is especially true for systems with natural coolant circulation. Here it is important to accurately observe the slope of the pipework.
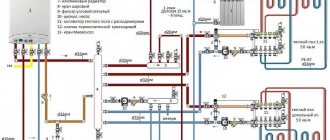
Two-pipe scheme
This water system is more complex for installation work, plus it uses more materials. But it works much better than a single-pipe one. Purely structurally, the layout of the pipes in it consists of two circuits: supply and return. It should be noted that both pipelines are blind and are connected to each other only through radiators and a heating boiler. From the names themselves, it becomes clear that heated coolant is supplied to the radiators through the supply circuit, and cooled coolant is discharged to the boiler through the return circuit.
In this case, radiators can be connected to the supply circuit in different ways. Option one is a circuit with lower wiring. This is when the coolant supply pipe runs along the floor with a connection to the upper radiator pipes. The return is carried out right there, but with a connection to the lower pipes of the heating batteries.
Two-pipe with bottom wiring
The second option is a top-wiring scheme. This is when a pipe riser is drawn upward from the boiler, which goes into a circuit that distributes the coolant to the radiators. The latter is mounted under the ceiling or in the attic. The return line is installed, as usual, at floor level or in the basement.
Attention! All pipes in unheated rooms (attic) are thermally insulated.
It is necessary to indicate that the upper distribution is two options for distributing pipes from the riser.
- When one horizontal pipe is laid, and risers of small diameter pipes are lowered from it to the radiators from above.
- When a collector is installed on the riser, from which each battery has its own circuit. Such a system is called a collector system. Although people often hear other names - spider or ray circuit. By the way, experts believe that this is the best option for a private home if the task is to install heating yourself. It is the most effective, but also the most expensive in terms of pipe consumption.
Two-pipe with top wiring
Pay attention to the photo above. It clearly shows sections of the heating system, where “1” is the general circuit, “2” is the main riser from the boiler, “3” is a horizontal section with a slope, usually located in the attic. “4” are risers that supply coolant to the radiators. “5” are risers that remove coolant from the batteries and “6” is the return line.
And there are two more types of two-pipe systems - with horizontal wiring and vertical. The first is used for one- or two-story buildings, the second for multi-story ones. A distinctive feature of the second before the first is the presence of a high riser, from which supply circuits are distributed among the floors.
Water temperature and pressure in heating networks
The normalized temperature in water heating systems depends on the air temperature outside the building:
- If outside the window it is not below zero degrees, then the temperature of the coolant in the supply pipeline is maintained within 40-45 degrees. In this case, the return water will be at a temperature of 35°C.
- If the temperature outside is 20 degrees below zero, then water with a temperature of 67-77°C circulates in the supply line. Then the coolant in the return will be no colder than 53 degrees.
- When the outside temperature drops to -40°C, the hottest coolant (+95°C) is supplied to the heating devices. In this case, the return temperature can reach 70 degrees.
In networks with natural circulation, the pressure inside the circuit is slightly higher than the static pressure. In one-story buildings with forced coolant flow, the pressure in the heating pipeline is maintained in the region of 1.5-2.5 bar. As the number of floors increases, the pressure in the network increases. So, in five-story buildings it reaches 4 bar, in nine-story buildings - 7 bar, and in high-rise buildings it reaches 10 bar.
Boiler power calculation
Regardless of the type of fuel used (solid or liquid, gas or electricity), the principle of connecting all heating systems is the same. The only difference is at the boiler installation stage. In this case, its power is calculated using a single formula:
where W is the specific power required for heating 10 square meters. m of room; S – total area of the house.
For Russian regions, the following power values are taken into account: • for houses located in central Russia up to 1.5 kW; • for Siberia and the North: for every 10 sq. m up to 2 kW; • for southern regions: up to 0.9 kW.
Since 10 sq.m. is sufficient for heating. m of a residential building located in central Russia requires up to 1.5 kW of power, then, for example, for heating 100 sq. m you will need a 15 kW boiler:
(100 x 1.5)/10 = 15 kW
This figure is increased by 15-20% (power reserve for possible heat loss, which is inevitably lost even with ideal insulation of the building). Thus, to heat a house of 100 sq. m will need (15 + 2.3) = 17.3 kW.
Recommended boiler power
How is the heating system filled?
Before filling the heating system with coolant, its required volume is calculated. To do this, sum up the volume of the boiler equipment, all radiators, pipelines and expansion tank.
The sequence of actions is as follows:
Preparing water for the heating system and how to soften it correctly
- Fill the system through the tap at the lowest point. In this case, the air outlet valves at the top of the network must be open.
- Water is pumped in by connecting an electric pump. It is recommended to open the taps halfway to avoid water hammer.
- After filling the system, bleed the air. In apartment buildings, Mayevsky taps are used for this, and in private houses, special valves installed on boiler equipment.
Requirements for the operation of the heating system
With all the variety of water heating systems, there are a number of general requirements for their operation.
They have to:
- uniformly warm up all the air in the rooms;
- be repairable;
- do not create difficulties during operation;
- be linked to ventilation systems;
- be regulated.
The operating principle of the heating system itself is also common: water is heated, after which it circulates through the pipeline and releases the resulting heat, warming the rooms.
The coolant in winter can be a non-freezing liquid - antifreeze. So that the ethylene glycol contained in its composition does not cause corrosion of pipelines
Antifreeze in a water heating system
In seasonal homes and regions with particularly harsh winters, antifreeze is used in heating circuits instead of water. For this purpose, solutions of inorganic salts, aqueous solutions based on propylene glycol or ethylene glycol are used. The safest mixtures are solutions based on food-grade propylene glycol.
Attention! It is prohibited to use automotive antifreeze, which contains many harmful additives, in heating systems.
The disadvantages of filling the heating system with antifreeze are its increased viscosity and low fluidity, as well as reduced heat capacity. Because of this, the number of sections in radiators must be increased, and the use of galvanized pipes is also prohibited.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparison of two-pipe and one-pipe heating systems:
The house you plan to live in all year round needs heating during the cold season. To make your living conditions comfortable, you need to choose a water heating system that is most suitable for your individual conditions.
We hope that the information contained in this article will help you make the right choice. After all, high-quality heating is not only comfort and coziness. This is also a prerequisite for maintaining your health.
Do you have anything to add or have questions about water heating systems? You can leave comments on the publication and participate in discussions. The contact form is located in the lower block.
Water heating methods
There are different options for water heating of apartment and private buildings. In addition to radiator heating, warm baseboards and heated floors can be used.
Warm floor
To install heated floors, pipelines with high strength and flexibility are used. They can be used indoors with any level of humidity and even in places without heating. The pipes are laid in a layer of screed or tile adhesive.
Advantages of heated floors:
- compatible with different flooring options;
- home heating costs are halved;
- the design is quite simple and can be done by hand;
- can be used in combined heating at home.
Baseboard heating
Such devices resemble smaller radiators that are located in the baseboard. The operating principle is similar to a traditional radiator. Warm air rises up along the walls, protecting the premises from heat loss through the enclosing structures.
Advantages of baseboard heating:
- The room warms up more gently and evenly, because there is no active circulation of heated air and dust.
- With this heating, the walls are reliably protected from the formation of mold and the accumulation of dampness in the corners.
- Baseboard heating does not spoil the interior of the room, because there are no pipes or bulky heating devices.
- Relatively simple system assembly.
The disadvantage is that it is impossible to lay the circuit behind the built-in cabinets. Also, the length of one circuit cannot exceed 15 m. Otherwise, several circuits will have to be made, which affects the cost of the system.