To ensure comfortable living in the cold season, even at the stage of designing a private house, you need to take care of the calculation and installation of heating. Correctly performed thermal calculations will allow you to determine the optimal and cost-effective heating system. Any error can lead to you freezing or the building becoming hot and stuffy.
Independent calculations will not be a problem for people with technical education. However, not everyone has physical and mathematical skills, so an online calculator will be a good guide to calculations. It will help identify heat losses at home and calculate the power that the boiler should have. It will also determine the number of radiators needed and how many sections it should have. It will calculate heating costs for you, which will be useful for choosing a suitable heat source. Collect the necessary data for the calculation.
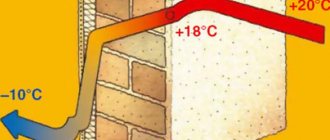
Determine heat losses. To do this, you need to know what material the external walls and floor coverings are made of, how they are insulated and their thickness. Measure the area of the house, windows and exterior doors. High intensity of heat loss from ventilation and sewerage. They also need to be taken into account in the calculations.
The climatic conditions of the location of the house play an important role in the choice of heating system. Find out the average annual and minimum temperatures in your area, as well as the average wind speed.
Calculation of heating radiators per square meter
Despite the diversity of the heating systems market, radiators always remain in trend. However, owners of heating equipment often make mistakes in its operation. The most common is the discrepancy between the heat transfer of the battery and the area of the room. The simplest way to calculate a battery is 100 W per 1 m2. Knowing the area of the room, multiply it by 100.
If the radiator is multi-sectional, then use the formula: N = Q/ Qс, where N is the number of sections, and Qс is the power of each section separately. If the ceiling height exceeds 2.7 m, use the volume calculation. For more accurate information on heat transfer, you can use the following coefficients:
- Number of external walls (Cf. 1.1, 1.2);
- Orientation of the room to the cardinal directions (Cf. 1.1, if to the north and east);
- Wall insulation coefficient (0.85, 1, 1.27);
- Climatic conditions (-35° - Kf. 1.5, -25° - Kf. 1.3, -15° - Kf. 1.1, -10° - Kf. 0.7);
- Ceiling height (Cf. From 1 to 1.2);
- Apartment floor (Cf. From 1 to 0.8);
Type of window frame (wooden -1.27, single-layer glass - 1, double glass - 0.85);
Q = S × 100 ×… (coefficient value)
Infrared heater
The most advanced and economical heating devices are infrared heaters. A quartz emitter is more suitable for temporary heating if you do not need to heat the entire room
| Principle of operation | An infrared heater, unlike traditional heaters, heats nearby objects rather than the air. It emits thermal energy (like the sun), which is absorbed by surrounding surfaces (floors, walls, furniture, etc.) and people. Infrared heaters allow you to create zones with local heating and save energy. They heat objects and do not heat the air. Infrared heaters are designed for suspended ceilings, heating residential and non-residential premises, as well as people in open areas. They are used for heating bathrooms and shower rooms, terraces, balconies, cafes and restaurants. |
| Advantages | Energy saving, silent, local heating - when installed above a workplace, an infrared heater provides comfortable conditions for a working person without heating the entire room |
Recommendations for using heating devices:
| |
| Flaws | It only heats the area where the infrared beam is directed. If used, for example, for heating outside in the cold season, the right side of the body will warm, and the left will freeze |
| conclusions | Infrared quartz heaters are used to heat certain areas of the room. They can warm up the workplace |
Calculation of heating costs
A good heating system requires quite a large financial investment. The main costs are related to:
- Heating system equipment. It includes a boiler, pump, radiators and wiring material.
- Installation of a heating system.
- Fuel costs. The amount of money you spend depends on the fuel you choose.
- Maintaining equipment in working order.
When calculating costs, the specific heat of combustion must be taken into account. Calculate by dividing the heat loss per season by the calorific value of the raw material to obtain the amount of fuel used. Multiply by cost per unit.
Another calculation method is kW consumption per hour. A house with an area of 120 m2 consumes 12 kW of heat energy. 8640 kW comes out per month. The method is suitable for gas and electricity users
Calculation of heat transfer from one aluminum radiator video
In the video you will learn how to calculate the heat transfer of one section of an aluminum battery for different parameters of the incoming and outgoing coolant.
One section of the aluminum radiator has a power of 199 Watts, but this is provided that the declared temperature difference of 70 0C is observed. This means that the coolant temperature at the inlet is 110 0C, and at the outlet 70 degrees. With such a difference, the room should warm up to 20 degrees. This temperature difference is designated DT.
Some radiator manufacturers provide a heat transfer conversion table and coefficient along with their product. Its value is floating: the higher the temperature of the coolant, the greater the heat transfer rate.
As an example, this parameter can be calculated with the following data:
- The coolant temperature at the radiator inlet is 85 0C;
- The cooling of water when leaving the radiator is 63 0C;
- Heating of the room - 23 0C.
You need to add the first two values together, divide them by 2 and subtract the room temperature, this is clearly done like this:
The resulting number is equal to DT; from the proposed table it can be established that its coefficient is 0.68. Taking this into account, we can determine the heat transfer of one section:
Then, knowing the heat loss in each room, you can calculate how many radiator sections are needed for installation in a certain room. Even if, according to calculations, the result is one section, you need to install at least 3, otherwise the entire heating system will look ridiculous and will not warm the area sufficiently.
In the following article you will learn how to properly connect heating radiators: https://ksportal.ru/828-podklyuchit-radiator-otopleniya.html.
Calculation of the number of radiators is always relevant
This is especially important for those who are building a private house. Apartment owners who want to change radiators should also know how to easily calculate the number of sections on new radiator models
Fan heater
The simplest and most affordable heating device. Used to quickly warm up small rooms. Fan heaters have a power of 2.0-2.5 kW. Compared to an oil radiator and convector they have small dimensions. Fan heaters can be located on the floor, on a table, or there are models with wall mounting
| Principle of operation | In the fan heater, the air is heated by a hot electric coil and is supplied by a fan to the heating zone. The temperature of the open electric coil is about 80°C, and the air at the outlet of the fan heater is always up to 20°C. To improve the uniformity of heating of the room, the fan rotates in the housing. The material of the fan heater body is usually plastic |
| Advantages | The air is heated very quickly and distributed throughout the room. Turns off if dropped. Protected from overheating. Thanks to the thermostat, the set temperature is regulated and does not require shutdown. Compact and aesthetic |
| Flaws | Noise produced when operating at high speeds. Air pollution due to the combustion of oxygen and dust particles. Collected dust, burning on a hot spiral, can be a source of unpleasant odor in the room |
| conclusions | Fan heaters provide the highest rate of room heating, but create increased noise at high speeds, and models with an open spiral have another drawback: they burn oxygen and pollute the air with combustion products |
How much kWh of energy is spent heating water?
This calculator will calculate how much money, electricity and time is spent heating water. You don't need any formulas or coefficients: just enter your data and get the answer.
To calculate the consumed electricity, you must indicate the temperature of cold and hot water, as well as its volume (mass). You can indicate the efficiency of the heating device if you know it. If you set the efficiency to 100%, the calculation will show only the useful power spent on heating water. When indicating the real efficiency, the calculation will give the total power consumed from the network.
To estimate how long it takes to heat up, indicate the power of the electrical appliance you use to heat water, in kilowatts (kW). The power is often indicated on the body of the device, as well as in its instruction manual or passport.
Boiling water in an electric kettle
I usually fill the kettle with water at room temperature 20°C to the 1 liter mark and always bring it to a boil (up to 100 degrees). Kettle power 2 kW. The simplest calculation shows that boiling will cost approximately 0.1 kWh (kilowatt hours) of electricity, 3 minutes of time, and, according to Moscow tariffs, fifty kopecks of money.
This means that each tea drink adds half a ruble to your electricity bill, but this is significantly less than the price of a serving of tea or coffee.
Heating water in a storage water heater
Every time I take a shower, I completely empty all the hot water from the storage heater, because at the end the water turns cold. In winter, the heater heats cold tap water from 5 to 45 degrees. Tank volume 80 liters. With a heating element power of 2 kW, fresh water in the tank will heat up for 2 hours, while approximately 4 kW of electricity and 20 rubles of money will be spent to pay for it. In summer, the water heats up from 18 to 45.
This means that in winter, each shower costs the family treasury 20 rubles, and in summer - 15 rubles, not counting the cost of cold water.
Convectors
These are modern and quite effective devices that can warm up a large room in a short time. The basis of the heating element is a spiral made of a special metal alloy. The air in the room passes through the convector and comes out of the grille already warm.
Such a device is located on the floor, due to which the cold air is immediately warmed up and neutralized by warm air - a natural movement of the air mass occurs - convection, which is why the name of the heater comes from. The advantage of a convector is the rapid heating of large volumes of the room and completely silent operation. Plus, it doesn't take up much space. There are practically no disadvantages.
Models and prices for them are presented in the table.
| model | specifications | price, rub |
| Ballu BEP/EXT-1500 | 4600 | |
| Electrolux ECH/AG-1000MFR4 | 2700 | |
| RESANTA OK-500S | 900 | |
| Ballu BEC/EVM-1500 | 2200 | |
| Ballu BEC/EM-1000 | 1700 |
Accounting for thermal insulation
Thermal insulation plays a significant role in calculating the required power. For example, a 2 m layer of mineral wool will significantly reduce heat loss, λ = 0.06 (for the above parameters):
Q= 0.06*30*40/0.2 = 360 (W) = 0.36 (kW).
When calculating floor heat loss, it is taken into account that the soil has an initial temperature of about 5 degrees Celsius.
If the room is insulated, then an average of 3 to 5 kW will be needed to compensate for heat loss. You can make your own calculation using the example given; data on specific materials can be easily found in reference books.
Specifics and other features
It is also possible that the premises for which the calculation is being made may have other specific features; not all of them are similar or exactly the same. These could be indicators such as:
- the coolant temperature is less than 70 degrees – the number of parts must be increased accordingly;
- absence of a door in the opening between two rooms. Then you need to calculate the total area of both rooms in order to calculate the number of radiators for optimal heating;
- Double-glazed windows installed on windows prevent heat loss, therefore, fewer battery sections can be installed.
When replacing old cast iron batteries. which ensured normal temperature in the room, for new aluminum or bimetallic ones, the calculation is very simple. Multiply the heat output of one cast iron section (average 150 W). Divide the result by the amount of heat of one new part.
Storage water heaters (boilers)
Without physical and mathematical formulas, a household calculation is described as follows: in 1 hour, 1 kW heats 860 liters per 1 K. To more accurately determine the heating time, power characteristics, and volume, a universal formula is used, from which the remaining results are then derived:
This formula consists of several and reflects a number of parameters, taking into account the heat loss factor. (With low power characteristics and large volume, this factor becomes more significant, however, in household heaters this accounting value is often neglected):
N full – power characteristics of the heating element,
Q c – heat loss of the water heating tank.
- c= Q/m*(tк-tн)
- C – specific heat capacity,
- Q – amount of heat,
- m – mass in kilograms (or volume in liters),
- tк and tн (in °С) – final and initial temperatures.
- N=Q/t
- N – heating power characteristics.
- t—heating time in seconds.
- N = N full — (1000/24)*Q c
Simplified formulas with a constant coefficient:
- Calculation of the power of the heating element for heating water at the desired temperature: W= 0.00117*V*(tk-tn)/T
- Determination of the time required to heat water in a water heater: T= 0.00117*V*(tк-tн)/W
Formula components:
- W (in kW) – power characteristic of heating elements (heating element),
- T (in hours) – water heating time,
- V (in liters) – tank volume,
- tк and tн (in °С) – final and initial temperatures (final – usually 60°C).
Volume is often equated to mass (m). Then the power of the heating element will be determined using the formula: W= 0.00117*m*(tk-tn)/T. The formulas are considered simplified, also because they do not take into account:
- actual power of the electrical network,
- ambient temperature,
- design features and potential heat loss of the tank,
- recommendations of some manufacturers regarding temperature (about 5-8 °C in summer and 15-18 °C in winter).
When purchasing a device, you must take into account that the relatively low power characteristics of storage water heaters compared to instantaneous water heaters do not yet guarantee financial savings. Savings ones “take away” less, but due to the fact that they work longer, they spend more. For financial savings, a more reliable strategy would be a general reduction in water consumption through the installation of various types of savers (https://water-save.com/) and strict accounting of water consumption.
How to wind a spiral from nichrome
A resistive or heating coil can be made at home. To do this, you need nichrome wire of a suitable grade and the correct calculation of the required length.
The calculation of a nichrome spiral is based on the resistivity of the wire and the required power or resistance, depending on the purpose of the spiral. When calculating power, you need to take into account the maximum permissible current at which the coil heats up to a certain temperature.
Temperature accounting
For example, a wire with a diameter of 0.3 mm at a current of 2.7 A will heat up to 700 ° C, and a current of 3.4 A will heat it to 900 C. There are reference tables for calculating temperature and current. But you still need to take into account the operating conditions of the heater. When immersed in water, heat transfer increases, then the maximum current can be increased by up to 50% of the calculated one. A closed tubular heater, on the contrary, impairs heat dissipation. In this case, the permissible current must be reduced by 10-50%.
The intensity of heat removal, and therefore the temperature of the heater, is affected by the pitch of the spiral winding. Densely spaced coils generate more heat, while a larger pitch increases cooling. It should be taken into account that all tabular calculations are given for a heater located horizontally. When the angle to the horizon changes, the heat removal conditions worsen.
Calculation of the resistance of a nichrome spiral and its length
Having decided on the power, we proceed to calculate the required resistance. If the determining parameter is power, then first we find the required current using the formula I=P/U. Having the current strength, we determine the required resistance. To do this, we use Ohm's law: R=U/I.
The notations here are generally accepted:
- P – allocated power;
- U is the voltage at the ends of the spiral;
- R – spiral resistance;
- I – current strength.
The calculation of the resistance of nichrome wire is ready. Now let's determine the length we need. It depends on the resistivity and wire diameter. You can make a calculation based on the resistivity of nichrome: L=(Rπd2)/4ρ. Here:
- L – required length;
- R – wire resistance;
- d – wire diameter;
- ρ – resistivity of nichrome;
- π – constant 3.14.
But it’s easier to take ready-made linear resistance from the tables of GOST 12766.1-90. You can also take temperature corrections there if you need to take into account changes in resistance when heated. In this case, the calculation will look like this: L=R/ρld, where ρld is the resistance of one meter of wire having a diameter d.
Review of manufacturers
The modern Russian market offers a large selection of economical electric heaters of both domestic and foreign (mainly European) production.
- Almac (Almak) is a Russian brand under which domestically produced heat regulators, heat guns, fans and heaters are sold. The models have affordable prices and are well suited for infrequent use - this way they will last as long as possible.
- BALLU is an international company specializing in heating equipment for home and professional use. Mainly produces infrared heaters (wall and ceiling). They can be used in a city apartment as additional heating sources.
- TIMBERK is a Swedish brand whose products are distinguished by their special quality. Assembly is carried out in Russia, Poland and other countries, but at each stage there are quite a lot of quality requirements for the process, so you can count on the durability of the device.
- FRIRO is a Swiss manufacturer, its heating equipment is distinguished by its special quality and durability, which is why it still remains a leader in the European product market.
- ECOLINE is a brand of the Russian company TST. The products largely comply with European quality standards, but they are also more expensive in price than other Russian products.
Thus, first of all, one should proceed from the frequency of use of the heater. If you plan to use it every day or more than 4 times a week, preference should be given to European models, which are durable. For normal urban use (i.e. only during periods of maximum cold), domestic models are suitable.
How to calculate boiler power two methods
To ensure a comfortable temperature throughout the winter, the heating boiler must produce the amount of thermal energy that is necessary to replenish all heat losses of the building/room. Plus, it is also necessary to have a small power reserve in case of abnormal cold weather or expansion of the area. We’ll talk about how to calculate the required power in this article.
To determine the performance of heating equipment, you must first determine the heat loss of the building/room. This calculation is called thermotechnical. This is one of the most complex calculations in the industry as there are many components to consider.
To determine the boiler power, it is necessary to take into account all heat losses
Of course, the amount of heat loss is influenced by the materials used in the construction of the house. Therefore, the building materials from which the foundation, walls, floor, ceiling, ceilings, attic, roofing, window and door openings are made are taken into account
The type of system wiring and the presence of heated floors are taken into account. In some cases, they even consider the presence of household appliances that generate heat during operation.
But such precision is not always required. There are methods that allow you to quickly estimate the required performance of a heating boiler without plunging into the jungle of heating engineering.
Heat guns
In fact, these are large fan heaters, since the principles of their operation are the same. Accordingly, the shortcomings are the same. Guns create a lot of noise, although their incomparable advantage is the fastest heating of large rooms. They are used to warm up warehouses, as well as when installing suspended ceilings to warm up the fabric, which stretches naturally after cooling.
An overview of models and prices is in the table.
| model | specifications | price, rub |
| MASTER V 3.3 | 6200 | |
| Ballu BHP-PE-5 | 3200 | |
| RESANTA TEP-2000 | 1900 | |
| RESANTA TEP-9000 | 4500 |
Online calculator
Note! Today, the Internet allows you to use a computer to calculate the power of heating radiators, taking into account all innovative construction technologies
Calculation of heating radiators
The online calculation formula is similar to the standard one, but is slightly modified to take into account adjustment factors. They are installed:
- On plastic windows that reduce heat loss.
- For external walls - the more there are, the higher the coefficient.
- To the height of the room. If it is more than 2.5 meters, then the coefficient increases.
The basic online calculation takes as a basis the average values for each type of heating battery, the center distance of which is 500 mm. For heat transfer, the following data are accepted into the standard calculation:
- For cast iron radiators - 145 W.
- For bimetallic - 185 W.
- For aluminum - 190 W.
To carry out the calculation, you need to enter all the requested data into the computer database:
- Area and height of the room.
- Number of windows and external walls.
- Type of room and selected radiator.
- Condition and material of the walls.
- Minimum temperature outside.
After filling out the fields of the online form, you only need to click the “Run calculation” option, and after a few seconds the computer will display the result. It's very simple and convenient. An online calculator can be found on the radiator manufacturer's website.
Scheme 2: according to housing characteristics
An electric boiler does not always exactly match the heating energy needs of a home. Often its power is selected with a reserve. Here are some examples of such scenarios:
A dual-circuit device provides the house with hot water;
The power of a double-circuit boiler is excessive, since it must provide the house with hot water. Including during the heating season.
- It is planned to add additional rooms to the house with the connection of heating devices in them to the existing circuit;
- The region is characterized by rare but severe frosts, and the heating system is designed specifically for them.
The photo shows winter Sevastopol. Even in warm regions there are severe frosts. The heating system has to be designed with a safety margin.
If the boiler power is obviously excessive, you will have to focus not on it, but on the actual heat consumption of the house. Most accurately, it can be calculated using the formula Q=V*Dt*k/860.
We invite you to read why batteries do not heat up in a private house
The variables in this formula from left to right are:
- Energy consumption (kW);
- The volume of the room that needs to be heated. It is indicated in SI units - cubic meters;
- Difference between indoor and outdoor temperatures;
- Insulation coefficient.
Where do I get the last two parameters?
The temperature delta is taken equal to the difference between the sanitary norm for the room and the coldest five days of winter.
| Description | Temperature norm, C |
| A room in the center of the house, the lowest winter temperature is above -31C | 18 |
| A room in the center of the house, the lowest winter temperature is below -31C | 20 |
| Corner or end room, lower winter temperature above -31C | 20 |
| Corner or end room, lower winter temperature below -31C | 22 |
| City | Value, C |
| Khabarovsk | -29 |
| Surgut | -43 |
| Smolensk | -25 |
| Saint Petersburg | -24 |
| Saratov | -25 |
| Petrozavodsk | -28 |
| Permian | -25 |
| Eagle | -25 |
| Omsk | -37 |
| Novosibirsk | -37 |
| Murmansk | -30 |
| Moscow | -25 |
| Magadan | -29 |
| Kemerovo | -39 |
| Kazan | -31 |
| Irkutsk | -33 |
| Ekaterinburg | -32 |
| Volgograd | -22 |
| Vladivostok | -23 |
| Vladimir | -28 |
| Verkhoyansk | -58 |
| Bryansk | -24 |
| Barnaul | -36 |
| Astrakhan | -21 |
| Arkhangelsk | -33 |
Distribution of winter temperatures across Russia.
The insulation coefficient can be selected from the following range of values:
- A house with an insulated facade and triple glazing - 0.6-0.9;
- Two-brick walls without insulation and double-glazed windows - 1-1.9;
- Brick walls and single-strand glazed windows - 2 - 2.9.
Example
House size: 6x8x3 meters.
Climatic zone: Sevastopol, Crimea peninsula (the temperature of the coldest five-day period is -11C).
Insulation: single glass with high thermal conductivity, walls made of rubble stone half a meter thick.
A rubble house with single glazing requires intense heating in winter.
We also went through the technique of further calculations:
- The boiler will consume an average of 5.5*24=132 kWh per day;
- It will consume 132*30=3960 kilowatt-hours of electricity per month.
If the average power of the boiler is known, it is not a problem to calculate how much the device consumes per month and over the entire winter.
Example
Let's find out, as an example, how much energy is needed for a boiler with a rated power of 12 kilowatts:
- Its average power is 12/2=6 kW;
- Consumption per day - 6*24=96 kilowatt-hours;
- Heating will consume 96*30=2880 kWh per month;
- Electricity consumption during the winter with a heating season of 180 days (from October 15 to April 15) will be 180*96=17280 kWh.
The length of the heating season in your region can be found on this map. The heating turns on when the air temperature drops below 8 and turns off when the temperature rises above 8.
Now let's do one more calculation - find out how much heating will cost. I use data for a single-rate tariff in Sevastopol as of January 2022:
- When consuming up to 150 kWh per month, a social tariff of 2.42 rubles applies;
- In the range of 150 - 600 kilowatt-hours per month, the price increases to 2.96 rubles;
- Electricity above 600 kWh per month costs pennies.
Current electricity tariffs. Sevastopol, first half of 2022.
Total 12312 1332 363 = 14007 rubles.
When using a single-tariff meter, electric heating will cost a pretty penny.
Switching to mains gas will greatly reduce your home heating costs.
Automatic thermoregulation
Previously, home owners simply had no choice but to calculate all the numbers and monitor heat loss in the house, the power of heaters, etc. However, these days, you can greatly simplify your task thanks to a modern device - a thermostat that operates on the basis of heat sensors.
Automatic thermoregulation is carried out using a special device
Of course, all innovations concern only autonomous heating, which has a serious advantage over central heating. For example, if you want the room temperature to be 22 degrees, then you need to be truly a genius to calculate all the heat loss using the formula and guess which radiators to put in the rooms. However, if you have temperature sensors, everything is simple - you set the desired temperature, and the boiler itself heats the batteries as much as necessary. The sensor will show when the boiler should stop, and vice versa will inform the device when the temperature has dropped below again and the room needs to be heated. If you want to accurately and conveniently control the level of heat in your home, then we advise you to use autonomous heating and not complicate your life with complex calculations.
Examples of calculations. The easiest ways
An efficiency close to 100 percent can only be achieved by an electric heating boiler. Throughout the entire life of the device, this indicator will remain stable, the numbers confirm this. The level may change, but the difference will remain small, it all depends on the specific conditions.
About 30-35 kW is the waste of electricity to heat one cubic meter. Thermal insulation of the structure may influence this parameter, but not to a significant extent. The power of the heating boiler should be 15 kW if a house of 150 sq.m.2 and with rooms of three meters in height is heated. Using this formula, it is easy to calculate the power of an electric heating boiler. When you first purchase a device, it is best to calculate in advance so that there is a small reserve left. The calculation is easy to do.
If insufficient power is generated, the temperature in the room will decrease. Compensating for such a deficiency is much more difficult than simply setting the device to a weak operating mode. And calculating the boiler will not help. You will have to either install additional heating equipment or insulate the building itself.
A number of important rules apply here:
- The power of an electric heating boiler must be known in order to calculate the annual electricity demand.
- The use of a resource for a boiler can be found out for the entire season if the total price for its use is known.
- The calculation will be like this. The resulting value is divided by two. An electric boiler simply cannot operate at maximum load all the time. The operation of the boiler is not so necessary during the thaw period.
- To get the same figure, but for a month, we simply multiply the final figure by 30. This process is not very complicated.
It is generally accepted that we need heating with a boiler for seven months. Depending on climatic conditions, adjustments can be made to this information. The monthly electricity consumption must be multiplied by the duration of the heating period to get the result for the whole year. But you should not consider it as accurate as possible; the difference in reality can be up to 15-20 percent; even the most accurate approach will not save you from errors.
Often calculations are made based on the fact that each consumer needs about 3 kW. But in practice, such boiler power cannot cope with the loads. This is especially true in regions with cold climates, where the energy consumption of the boiler may increase.
Rice. 3 Convenient parameter adjustment