For many homeowners, creating an autonomous heating circuit is the only way to heat their home if it is impossible to connect the building to a centralized heating main. To ensure efficient heating using the created network, a pump is installed in the heating system of a private house. Tell us about the advantages of having such a device in the thermal circuit of a building. Let's also consider the types of pumps, important parameters for selecting an electrical appliance, and the features of its installation.
Installed pump in a private residential building Source 1-teplodom.ru
Where is it better to install a circulation pump?
In principle, there is no big difference, the main thing is that the pump does not become airborne during operation and is installed correctly. However, this is with one small exception, if the pump is installed for a gas or electric boiler.
When installing a circulation pump to operate a solid fuel boiler, it must be installed on the return line. Why is that? Everything is very simple, and if for some reason the solid fuel boiler boils, the pump installed on the return line will continue to operate after the electricity is restored.
A wood-burning boiler can boil for one simple reason when the electricity goes out. Moreover, if the pump is installed on the supply side, then most likely steam will get into it, and the pump itself will fail. Therefore, when installing a solid fuel heating boiler, the pump should always be installed on the return side, and not on the supply side.
Connection methods
The pump can have a variety of connection options and wiring diagrams.
The first method involves installing an electrical outlet close to the place where the circulation pump is being installed. Sometimes they come complete with a plug and cable. In this case, you can simply connect the device to electricity using an outlet. You just need to make sure that there is a third (grounding) contact in the outlet. The wires must be stranded copper, which will provide resistance to bending. For a permanent connection, a non-flexible copper or aluminum cable can be used. Its immobility must be ensured by installation. To do this, the cable is secured with clamps along the entire route. A differential circuit breaker (residual current device) is used in this embodiment. You can use a regular single-pole circuit breaker instead and pass only the phase wire through the device. The cable from the machine to the pump must be three-core if the device is installed in a panel with a PE bus. If there is no such bus, then the PE terminal should be connected to a grounding device. This connection can be made with a separate wire.
To install the circulation pump you need to have the usual tools
What materials are needed for installation:
- Detachable connections;
- Shut-off ball valves;
- To arrange a bypass - pipes;
- Reliable additional filter, which is necessary for rough cleaning;
- Connection couplings and various limit switches.
The location of the device and the characteristics of the heated object determine the choice of a specific option.
Expansion tanks
One of the most important features of heating systems with an intermediate coolant, especially for water systems, is that when heated, the coolant expands, increases in volume, excess pressure is formed, it needs to go somewhere.
The expansion tank is able to equalize the pressure, which prevents deformation of the system as a whole. Therefore, without it, installation of the system is impossible.
Expansion tanks are produced in two types:
- open, actively used for open systems with natural or less often with forced (which is not recommended) circulation of coolant, advantages - simplicity of design, low cost, disadvantages - tendency to corrosion, the need for constant replenishment of coolant, installation at the highest point;
- closed, installation is carried out only in systems with forced circulation of the coolant, the tank is a sealed vessel with a very elastic membrane located inside a metal body, it can be diaphragm or bolted, the principle of operation is quite simple - in one part there is air or an inert gas is pumped under a given pressure, to another place for the resulting additional volume of coolant, advantages - no need to add liquid, corrosion resistance, disadvantages - higher cost.
Closed expansion tanks are available in two types - with a replaceable membrane (so-called flanged) or a membrane that cannot be replaced. The pressure can be monitored using a pressure gauge and adjusted by installing a safety valve.
From theory to practice
So. Let's start by defining what home heating is. Without going into terminology, this is heating the air in rooms to a given temperature and maintaining the set temperature for a certain time.
Air can be heated in three ways:
- by convection (the convection method is classic and ancient, that is, air flows in the rooms constantly circulate, cold air heats up below and rises up), convection systems can be floor- and wall-mounted;
- by radiant heating (this is an innovative method, the essence is that the energy from the heating device falls directly on the surface of objects and enclosing surfaces, one part is absorbed, the second is reflected, radiant heat exchange is formed, which makes it possible to ensure the desired temperature in the room), radiant systems are floor-mounted , wall and ceiling;
- combined.
The second point is the type of heating:
- the direct, classic principle by which fireplaces, stoves, and convectors operate is that the heating device directly heats the air in the room;
- using intermediate coolants, in this case it is not the air itself that is heated, but the coolant circulating in the system, transferring thermal energy and allowing the air to be heated in a certain room for residential or domestic purposes.
Heating systems for a private home involve the use of two types of intermediate coolants:
- classic option - water, pros - cost, cons - likelihood of the system defrosting;
- antifreeze (solutions of propylene glycol and ethylene glycol with various modifying additives), plus – resistance to low temperatures (does not freeze), ensuring the safety of thermal registers, minus – higher cost;
- steam, pros - high heat transfer, efficiency, cons - deformation of heating system elements, inability to accurately regulate the temperature, likelihood of burns (registers heat up to a very high temperature);
- air, there are also systems where the air is heated, transfers thermal energy to a heating device, which heats either the air in the room, or objects and fences, and in some cases the heating device is a wall with channels for air circulation and a chimney.
The next point, all heating systems are:
- local, necessary to maintain a given temperature in one or more rooms;
- centralized common ones, designed to maintain temperature conditions in several rooms.
Local systems, as a rule, are direct, that is, they heat the air directly, while general systems use an intermediate coolant. By form factor, like
- noted above, system elements can be installed on:
- walls, a classic option for complex engineering systems;
- ceiling, this is more related to radiant, local heating, although there are convection options, for example, thermal curtains;
- floor (including island) and under the floor (in particular, “warm floor”), can be both local and general.
Everything is described and presented in more detail in the article “Types of heating”.
System components
What does the heating system of a private house consist of?
If we talk about local systems, then this is a source of heat that allows you to heat the air in a single room, the classic version is a stove and fireplace, modern ones are convectors, heat generators, thermal curtains, guns, infrared radiant heating panels, oil radiators, fan heaters and a number of others.
That is, a heater is installed in a separate room, which heats the air in this and adjacent rooms.
The general, centralized system, based on the use of an intermediate coolant, is more complex, it consists of:
- heat source, the classic and most widespread option - a boiler, designed to convert various types of energy into heat with subsequent heating of the coolant;
- pipelines, necessary for transferring coolant to heating devices, this includes pipes and a number of other elements;
- heating appliances, six groups in total - convectors, radiators, smooth-tube appliances, panels, finned tubes and air heaters.
Functionality of the circulation pump in the heating system
The purpose is to accelerate and regulate the flow of coolant in the circuit:
- in systems with forced circulation (especially if the supply goes to two or more floors);
- in systems designed for natural circulation , it significantly increases heating efficiency.
Photo 1. Circulation pump model UPS 32-100 with a wet rotor, Denmark.
In private homes, a device with a wet rotor is usually installed:
- silent;
- maintenance- free ;
- with economical energy consumption.
For long circuits and systems serving multi-storey buildings, they buy devices with a dry rotor, powerful, with high efficiency.
Such devices require regular inspection and maintenance. They have to be installed in special rooms or where their noise will not interfere.
Bottom line
As you can see, the main difficulty of installation for a circulation pump is the need for welding, cutting pipes, and threading. The assembly itself is elementary: you need to carefully measure all the distances and screw in the elements. The connections are sealed with tow and sealant.
What to pay attention to during operation:
- it is necessary to periodically clean the filter and check the pressure gauge readings;
- The noise emitted by the device does not always indicate a breakdown; often the cause is air accumulating in the circuit. The problem can be solved simply - by bleeding with special valves;
- Dry pumps may require periodic lubrication.
With warm floor
When filling the system with coolant, it is not always possible to get rid of the air present here. Accumulated gases often block the movement of fluid, and not every manifold can be used as a relief valve. To solve this problem, the circulation pump has a special outlet valve made in the form of a disk.
To release accumulated gases, you need to turn this part with a screwdriver counterclockwise. After supplying water from the slot, the disk is tightened and the pump is started again. A similar procedure is repeated several times in a row.
Correct choice of circulation pump
It makes no sense to buy overly powerful pumping equipment. In addition to the fact that it will not have to work at full capacity, a powerful pump will create negative noise interference. To equip a heating system with complex architecture, accurate calculations must be made by heating engineers. For the owner of a country house to select a pump, a primitive formula is sufficient, since the technical parameters of the installed unit must still exceed the calculated values by 10%.
The ability of the pump to meet the needs of the heating circuit depends on the diameter of the pipeline, the maximum parameters of the pressure and volume of the coolant, the density and temperature of the water.
- The coolant flow rate Q (expressed in l/min) passing through an arbitrary section of a closed circuit is calculated by analogy with the liquid flow rate for a boiler. That is, they simply equate the flow rates and boiler power parameters (P=Q). Simplified: if the boiler power is 20 kW, then 20 liters of coolant per minute can pass through it.
- Batteries with a power of 10 kW will consume 10 l/min of water. Taking into account the power of the radiators, you need to calculate the water flow in each of the rings of the heating network.
- The coolant flow in the pipes depends on the diameter of the pipeline. The narrower they are, the more resistance appears in the path of water movement. With a standard speed of movement through pipes of 1.5 m/sec, the attached table will help in the calculations.
Table for calculating water flow in the pipeline
The pump power is directly proportional to the length of the pipeline. That is, 10 meters of each section of the heating system will require 0.6 m of pressure from the pumping equipment. Simpler: to ensure productive operation of a 100-meter ring, a pump head of 6.0 m is needed.
To stimulate the movement of coolant in heating systems, two types of pumping devices are used:
- “dry” pumps, the rotor of which is not in contact with the coolant;
- “wet” pumps, the working part of which is immersed in the water they pump.
Equipment with a “dry”, hermetically insulated rotor is used mainly for the arrangement of multi-storey buildings, large industrial, shopping and entertainment centers. Due to the noticeable noise effects associated with the air turbulence created during the work process, dry pumps are not in demand in the field of arrangement of private buildings.
Circulation pumps with wet rotor
To modernize the heating of country houses, they mainly use “wet” pumps in brass or bronze cases, inside of which there are parts made of stainless steel and ceramics. The coolant they pump also acts as a lubricant, extending the “life” of the equipment.
Carrying out installation work
The water pump is installed in the heating system through a bypass. Take a look at its drawing and familiarize yourself with the main elements:
The connection diagram with a bypass is good because it allows you to switch from natural circulation to forced circulation at any time. It will also help you replace the water pump without stopping and draining the entire heating system.
- The circulation pump (1) is the main “person” in the system;
- Shut-off valves (3) – disconnect the pump from the heating;
- Bypass valve (4) – ensures that the coolant moves only through the pump or along both channels;
- Dirt filter (2) – provides coarse filtration from large mechanical contaminants.
Let's see how to connect a pump to a heating boiler and what is needed for this. First, we inspect the installation site to find free space to place the bypass. At the next stage, we assemble the bypass elements, prepare the taps, nuts, drains and dirt filter. We will also need a set of keys to connect individual units, and seals.
Let's start assembling the bypass - we form a section with a water pump, screwing a dirt filter and taps to it. Next, we proceed to inspect the section of the pipe where the insertion will take place. We cut out a piece for the bypass tap, take the area with the pump, and cut holes for it. Next, we weld all the elements and only then tighten all the threaded connections with wrenches - this cannot be done before welding.
Having connected the water pump to a floor-standing or wall-mounted boiler, we proceed to electrical work - we connect electrical wires with power to the terminals. Here it is recommended to install a separate RCD, choosing a 1 or 2 kW sample.
The next step is to start the water pump. To do this, you need to fill it with water, removing air from it. The air plug is removed through a built-in bleeder or through a plug screw. We open all the taps, open the drain or unscrew the screw plug, wait until the air comes out and water flows. After this, we seal the system and try to start the water pump. If the device is noisy, it means that not all of the air plug has come out - partially unscrew the plug screw and keep the system open until the air bubbles disappear.
Next, all that remains is to adjust the shaft rotation speed so that the productivity is slightly less than normal. There is nothing wrong with installing a water pump in a heating system with your own hands - you just need to know how to work with tools. If problems arise, consult with specialists.
What to consider when choosing the right location
When installing the device in the circuit, the following is taken into account:
- correct orientation (indicated in the instructions, horizontal or vertical);
- correct harness (correctly selected set of additional devices);
- if there are two or more branches, then the best option is to install a separate pump for each (in this case, it is possible to immediately achieve equal temperatures in the rooms for each branch and use fuel more economically).
Where is it better to install: supply or return
Professionals recommend installing the pump before the first branch of the circuit. The device is designed for temperatures of the pumped liquid up to 115°C, so the choice of supply or return pipe is not important.
This is significant when installed in a system with a steam boiler, since the coolant at the outlet has a temperature above 100°C, which is unacceptable. On the return pipe, the temperature is set within normal limits.
Return is the only option for solid fuel , with the exception of systems with automated control.
Important! Boilers without automation often overheat the coolant to boiling , so steam enters the pump installed in the supply. This leads to an almost complete stop of fluid movement along the circuit and an emergency situation, even an explosion .
The return pump may also be filled with steam , but in this case the response time of the safety valve increases, which allows you to solve the problem and avoid disaster.
Operating rules
Nowadays, good pumps are produced that have a long service life. However, of course, like any other device, the circular pump can break down. A number of reasons may help this:
- excessively strong/weak water supply;
- the device works in the case when there is no heat carrier in the system;
- for a long time the usual;
- when water heating greatly exceeds the norm (more than 65°C).
Summarizing everything described above, it should be noted that the circular pump
- an obligatory part of the heating system of the house. With this device you will be protected from a variety of errors, which then lead to very small and large troubles. You can install the circulation pump either with the help of professionals or on your own. The main thing is to strictly follow the rules of the instructions.
Option one - classic boilers
The first option is traditional, classic, which has been used for thousands of years in conventional stoves, put in firewood or coal, and adjusted the air supply with a damper. The main disadvantages are the need for constant supervision and low efficiency, the inability to accurately regulate the combustion process. Advantages - the simplest boiler in technical terms and maintenance, operating on almost any type of solid fuel.
Examples of classic boilers:
- ZOTA Carbon
with a steel heat exchanger, operating on coal with a fraction of
10.00 - 50.00 mm
, power
from 15.00 to 60.00 kW
, with top fuel loading, a movable grate and a design that ensures maximum afterburning of fuel and precise oxygen supply to firebox; - Buderus Logano
with a steel heat exchanger, can work either separately or in combination with a gas or liquid fuel boiler with a capacity of
12, 16, 20, 24, 27, 32, 45 kW
, in systems with natural and forced circulation of coolant, is small in size and heat exchanger protection, large volume of ash pan and loading chamber, works on wood (logs up to 33.00 and 53.00 cm long), coal, coke.
The burning time of such boilers is 3-7 hours.
Where to install the circulation pump in the heating system: heated floor
Heating a home by heating floors is gaining increasing popularity. To operate the system, it is equipped with a mixing unit and a circulation pump, which ensures the movement of the coolant along the contours (loops) of the heating pipeline. This is due to the fact that the water temperature should not exceed the set value normalized for the floor covering used.
The “circulator” is installed between the three-way valve and the underfloor heating manifold. Only this arrangement will ensure the functionality of the system. If you mount the pump unit between the connection to the radiator network and the three-way valve, the mixing unit will be non-functional, and the heated floor will not heat up. The supercharger is secured to the flanges with threaded nuts. If the wiring is done correctly, there will be no problems with installing the pump unit.
Types of circulation pumps
A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor
To understand how this device works, you need to know the differences between the two types of circulation pumping equipment. Although the fundamental design of a heating system based on a heat pump does not change, the two types of such units differ in their operating features:
- A pump with a “wet” rotor is made of stainless steel, cast iron, bronze or aluminum. Inside there is a ceramic or steel motor. The technopolymer impeller is mounted on the rotor shaft. When the impeller blades rotate, the water in the system is set in motion. This water simultaneously functions as an engine cooler and a lubricant for the working elements of the device. Since the “wet” device circuit does not provide for the use of a fan, the operation of the unit is almost silent. Such equipment only works in a horizontal position, otherwise the device will simply overheat and fail. The main advantages of a wet pump are that it does not require maintenance and also has excellent maintainability. However, the efficiency of the device is only 45%, which is a minor drawback. But for domestic use this unit is perfect.
- A pump with a “dry” rotor differs from its counterpart in that its motor does not come into contact with the liquid. As a result, the unit has less durability. If the device operates “dry,” then the risk of overheating and failure is low, but there is a risk of leakage due to abrasion of the seal. Since the efficiency of a dry circulation pump is 70%, it is advisable to use it to solve utility and industrial problems. To cool the engine, the device circuit provides for the use of a fan, which causes an increase in the noise level during operation, which is a disadvantage of this type of pump. Since in this unit water does not serve as a lubricant for working elements, during operation of the unit it is necessary to periodically carry out technical inspection and lubricate parts.
In turn, “dry” circulation units are divided into several types according to the type of installation and connection to the engine:
- Console. In these devices, the engine and housing have their own place. They are separated and firmly fixed on it. The drive and working shafts of such a pump are connected by a coupling. To install this type of device, you will need to build a foundation, and maintaining this unit is quite expensive.
- Monoblock pumps can be used for three years. The body and engine are located separately, but are combined by a monoblock. The wheel in such a device is installed on the rotor shaft.
- Vertical. The service life of these devices reaches up to five years. These are sealed advanced units with a seal on the end side made of two polished rings. For the manufacture of seals, graphite, ceramics, stainless steel, and aluminum are used. When the device is running, these rings rotate relative to each other.
There are also more powerful devices on sale that have two rotors. This dual circuit allows you to increase the performance of the device at maximum load. If one of the rotors fails, the second can take over its functions. This allows not only to enhance the operation of the unit, but also to save energy, because with a decrease in heat requirements, only one rotor works.
About the choice of equipment and the rules for its independent calculation
The key indicator that determines the efficiency of the circulation pump is its power. For a household heating system, there is no need to try to purchase the highest-power installation. It will only make a loud noise and waste electricity.
Mounted circulation pump
You need to correctly calculate the power of the unit based on the following data:
- hot water pressure indicator;
- pipe section;
- productivity and throughput of the heating boiler;
- coolant temperature.
Hot water consumption is determined simply. It is equal to the power indicator of the heating unit. If, for example, you have a 20 kW gas boiler, no more than 20 liters of water will be consumed per hour. The pressure of the circulation unit for the heating system for every 10 m of pipes is about 50 cm. The longer the pipeline, the more powerful the pump you need to purchase. Here you should immediately pay attention to the thickness of the pipe products. The resistance to water movement in the system will be stronger if you install pipes with a small cross-section.
In pipelines with a diameter of half an inch, the coolant flow rate is 5.7 liters per minute at the generally accepted (1.5 m/s) speed of water movement, with a diameter of 1 inch - 30 liters. But for pipes with a cross-section of 2 inches, the flow rate will already be at the level of 170 liters. Always select the diameter of the pipes in such a way that you do not have to overpay extra money for energy resources.
The flow rate of the pump itself is determined by the following ratio: N/t2-t1. In this formula, t1 refers to the temperature of the water in the return pipes (usually it is 65–70 °C), and t2 is the temperature provided by the heating unit (at least 90 °C). And the letter N denotes the boiler power (this value is in the equipment passport). The pump pressure is set according to the standards accepted in our country and Europe. It is believed that 1 kW of power of a circulation unit is quite enough for high-quality heating of 1 square meter of a private home.
Pump device
Since the engine stator is energized, it is separated from the rotor using a glass made of stainless steel or carbon material
The main elements that make up the circulation pump are:
- housing made of stainless steel, bronze, cast iron or aluminum;
- rotor shaft and rotor;
- wheel with blades or impeller;
- engine.
Typically, an impeller is a structure of two parallel disks that are connected to each other by means of radially curved blades. One of the disks has a hole for liquid to flow through. The second disk secures the impeller to the motor shaft. The coolant passing through the engine acts as a lubricant and coolant for the rotor shaft where the impeller is fixed.
Since the engine stator is energized, it is separated from the rotor using a glass made of stainless steel or carbon material. The walls of the glass are 0.3 mm thick. The rotor is fixed on ceramic or graphite bearings for sliding.
Installation diagrams in various types of systems
To begin with, let’s clarify the place where to install the flow pump, which circulates water through the boiler and forcibly directs it to the radiators of the heating system. According to our expert Vladimir Sukhorukov, whose experience is trustworthy, the installation location must be chosen in such a way that the unit is convenient to maintain. On the supply side it should be located after the safety group and shut-off valves, as shown in the installation diagram:
In order for the unit to be removed and serviced, shut-off valves must be installed on the sides
On the return line, the pump must be placed directly in front of the heat generator, and in tandem with a filter - a mud trap, so that you do not have to buy and install extra taps. The wiring diagram for the pumping unit looks like this:
When installing on the return line, it is better to place the mud collector in front of the pump unit
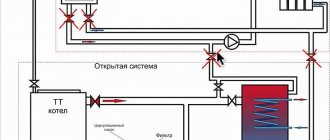
Recommendation. A circulation pump can be installed in this way in both a closed and an open heating system, there is not much difference. The statement also applies to the collector system, where the coolant moves to the radiators through separate connections connected to the distribution comb.
A separate issue is an open heating system with a circulation pump, capable of operating in 2 modes - forced and gravity. The latter is useful for homes where power outages often occur, and the owners’ income does not allow them to buy an uninterruptible power supply unit or a generator. Then the device with shut-off valves must be installed on the bypass, and a tap must be inserted into a straight line, as shown in the diagram:
This scheme can operate in forced and gravity mode
Important point. On sale there are ready-made bypass units with a pump, where instead of a tap on the flow there is a check valve. Such a solution cannot be called correct, since a spring-type check valve creates a resistance of the order of 0.08-0.1 Bar, which is too much for a gravity heating system. Instead, you can use a petal valve, but it must be installed only in a horizontal position.
Finally, we will explain how to install and connect a circulation pump to a boiler that burns solid fuel. As mentioned above, it is better to place the unit on the line coming from the heating system to the heat generator, as shown in the diagram:
As you can see, the piping uses a pump connection to the boiler circulation circuit with a bypass and a three-way mixing valve. The important role of these piping elements is described in detail in the manual on connecting solid fuel boilers.
Installation rules
The design of a household circulation pump from any manufacturer provides for its fastening to pipelines or shut-off valves using union nuts (American). This allows it to be quickly dismantled if necessary, for example, for replacement or repair. When installing the pump unit, follow these recommendations:
- Place the device on any sections of pipelines - horizontal, vertical or inclined, but with one condition: the rotor axis must be in a horizontal position. That is, installation “head down” or up is unacceptable.
- Please note that the plastic box with electrical contacts is located on top of the case, otherwise it will be flooded with water in the event of an accident. Yes, and servicing the product will not be easy. This is easy to achieve: unscrew the screws securing the casing and turn it to the desired angle.
- Remember to follow the flow direction indicated by the arrow on the housing.
- So that the product can be removed without emptying the system, install shut-off valves before and after it, as shown in the diagrams in the previous section.
A visual aid showing what position the pump unit should be in
Advice. It so happened that the load from the weight of the circulation unit will fall on 1 or 2 ball valves (depending on the orientation of the area in space). Hence the recommendation: do not save money and buy high-quality shut-off valves, whose body will not crack over time from mechanical stress.
Diagram of a pump in the forward pipeline and diagram of a pump in the return pipeline
The main problem with independent heating networks is the uneven distribution of heat - one room is hot, another is cold. There are two options - either change the entire heating main and rebuild it again, or install circulation equipment. A circulation pump solves the problem by evenly distributing the liquid, thereby heating all rooms equally. If you have equipment with a wet shaft, it is permissible to build it into the supply and return, if with a dry shaft - only into the return.
The video will help you figure out where it is most profitable to install equipment
At what speed should the pump in the heating system operate?
The purpose of forced circulation is to effectively heat the house through the reliable delivery of heat to all consumers of the system, right up to the furthest radiator. To do this, the pumping unit must develop the required pressure (otherwise known as pressure), which is ideally calculated by design engineers based on the hydraulic resistance of the pipeline network.
Most household pumps have from 3 to 7 rotor speeds, due to which the performance and pressure generated can be increased or decreased. In order not to torment you with hydraulic calculations, we offer the following method for selecting the optimal speed:
- Find a laser surface thermometer (pyrometer). Put the heating system into operating mode.
- Measure the surface temperature of the pipe at the inlet and outlet of the boiler.
- If the temperature difference is more than 20 °C, increase the rotor speed. After 30 minutes, repeat the measurement.
- When the temperature difference is less than 10 °C, the water flow rate must be reduced. The goal is to achieve a delta between supply and return of about 15 °C.
The minimum number of rotor rotation speeds is 3, but there are 7 or more
. Advice. Do not switch the pump to a different circulation speed “on the fly”. Disconnect it from the network, move the regulator to a different position, and then put it back into operation.
You can do without a pyrometer when thermometers are installed on the supply and return lines. If the adjustment limits do not allow you to enter the range of 10-20 °C temperature difference, your system is not working efficiently due to an incorrectly selected circulation pump. Too cold return water increases the load on the boiler and increases fuel consumption. Water that is too hot means that it flows too quickly and does not have time to transfer heat to the heating devices.
The leading European brand Grundfos offers the latest generation Alpfa3 circulation pumps, which can independently select performance depending on the load and thus adapt the work to changing conditions. With their help, you can even balance the heating system, which our expert will tell you about in the next video:
Basic rules for heating a private home
Heating in a private home is a very complex and capacious concept. Therefore, the first rule is that the development of the system and its installation should be carried out only by professionals. You need to remember this and not engage in amateur performances.
Only a heating engineer with the necessary knowledge and practical experience is able to correctly and competently create a heating project, taking into account the architectural features of the building, the functional purpose of the premises, the requirements and wishes of the customer, and his financial capabilities.
Therefore, it is necessary to perform a thermal engineering calculation, calculate heat losses, select the equipment correctly, know the specifics and features of its use, select the installation location, and carry out the installation.
Only in this case will the heating system in a private house be as efficient and economical as possible, and the costs of its installation and maintenance will be minimal. The purpose of this article is to outline the basic parameters based on which a contractor can develop the optimal heating plan for a home. Rule two is “cheaper in bulk.” To save on heating installation, you need to contact companies that provide comprehensive services.
That is:
- draw up design documentation based on the requirements and wishes of the customer, architectural features of the building, functionality of individual rooms, operating mode, climatic and many other factors, performing thermal, hydraulic, thermal calculations, calculation of heat losses, establish the thermal load and determine many other parameters;
- select the optimal equipment configuration, install it, start up the heating system, check its performance with further warranty and post-warranty service;
- are engaged in the sale of everything necessary, and even better, they are dealers of manufacturers, this allows you to avoid additional trade markups, and the installation technicians thoroughly know the features of all models, even those that are not listed in the manufacturer’s technical documentation and identified during installation and operation.
Only with this approach will a heating system in a private house be installed quickly, at the lowest possible cost, without headaches for the person and work as efficiently as possible.
Where to put the pump: detailed diagrams
When installing the unit, not only the manufacturers’ recommendations are taken into account, but also the possibility of its periodic maintenance. More recently, wet rotor designs were installed exclusively on the return line. This ensured a longer service life. Modern blowers are designed for prolonged contact with hot liquid, so they can also be used on the supply side.
Which installation scheme is best to choose depends on the configuration of the heating equipment. Each layout has its pros and cons, which are taken into account when designing heating systems. Common connection schemes:
- On the serve. The pump is installed at the boiler outlet after the safety group.
- On the way back. Install the supercharger in front of the boiler, but after the expansion tank. It must be equipped with a filter and shut-off valves.
- In an open heating system. The pump group can be installed anywhere, but preferably as close to the boiler as possible. It must be equipped with a bypass line, which allows the system to be operated in 2 modes: with forced and natural circulation.
If a solid fuel boiler is installed in an open system, the pump group is installed on the return line. In this case, there should be a tap on the bypass, and not a check valve, which creates additional resistance to the movement of the coolant.
Shut-off valves and other elements
It should be remembered that the main enemy of any heating system is air. Therefore, it is necessary to fight it. For this purpose, valves are installed to remove air from the system (automatic vents, air vents, they also allow you to partially compensate for water hammer if necessary) and radiator needle air valves, popularly called “Mayevsky taps”. Installation locations are radiators, collectors, and in some cases other places, it all depends on the system configuration.
The main shut-off valves in the heating system are taps and balancers, which are placed on heating devices and boiler room piping and other elements of the heating system.
It is better to use proven high-quality shut-off valves. Installing cheap fittings can lead to a sudden accident - a leak, a breakthrough of the heating system, which can lead to the heating system stopping, which can lead to defrosting of the heating system in the winter season. High-quality shut-off valves: Giacomini
,
Grundfoss
,
Dunfos
,
Bugatti
.
Shut-off valves
Second point
. As noted above, the coolant tends to expand and an expansion tank is clearly not enough. Therefore, it is mandatory to install a safety group; it consists of an automatic air vent, a safety valve and a pressure gauge located on a common console.
Third point.
Whatever you do, there will always be foreign impurities in the coolant, and this can lead to failure of the circulation pump, automation and boiler. Therefore, a filter with a coarse mesh is installed on the return line in front of the pump. Don't forget to clean it periodically.
Fourth point.
When using an intermediate coolant, you cannot do without shut-off, shut-off and control, mixing and control valves. It allows you to regulate the intensity of the coolant flow and, as a result, the temperature in a certain room.
The classic option is a tap (shut-off valve). They are installed in various places. One, as a rule, is after the circulation pump in front of the boiler and serves to drain the coolant from the system, the others are at the radiators or on the collector, if such a system is used, in some cases, in front of the pump, which is very convenient. To replace the pump, you can simply shut off the return line and that’s it. Conventionally, reinforcement is divided into two groups:
- mechanical (valves, ball valves, different types of valves, valves of various types (including shut-off and check valves, balancing and safety), sensors for determining coolant flow and pressure, air vents, pressure reducers, butterfly valves, pressure gauges), advantages - structural simplicity, low cost, disadvantages – manual adjustment;
- thermostatic (allows automatic temperature changes in accordance with specified parameters), it includes thermostatic heads and valves with mechanical or electronic control, advantages - high accuracy of maintaining the temperature in the room without human intervention, disadvantages - higher cost and structural complexity.
Heat pipe elements
After you have decided on the heat source, expansion tank, circulation pump, shut-off and control valves, you need to select a heat pipe or, in simple terms, heating pipes. There are several options to choose from, the main one being the material. Main pipe options:
- steel, a classic of the genre, advantages - durability, high resistance to troubles (water hammer, high pressure and pressure surges), reduced temperature coefficient of the resulting linear expansion, affordable cost, disadvantages - corrosion, stray currents, the occurrence of deposits inside, high cost of installation;
- polypropylene, advantages - durability, resistance to corrosion, chemical resistance, low noise level, tightness and reliability of connections, oxygen impermeability, low cost, mechanical strength, resistance to high temperatures and possible defrosting, environmental safety, disadvantages - low temperature stability;
- metal-plastic, advantages - small linear elongation when heated, possibility of use in rooms with complex configurations, long coil length (from 50 to 500 meters), corrosion resistance, durability, oxygen impermeability, resistance to deposits, disadvantages - low resistance to ultraviolet radiation, mechanical loads;
- stainless steel, including corrugated, pluses - durability, flexibility, resistance to water hammer, linear expansion, defrosting, high heat transfer, biological stability, minus - high cost;
- copper, annealed and unannealed, pros - high corrosion resistance, high heat transfer, excellent appearance, minus - prohibitive cost and difficulty in installation;
- PEX (cross-linked polyethylene), pros - high strength and resistance to high temperatures, cons - difficult to install, high cost.
Second parameter
- connection type. They can be detachable or permanent, depending on the material from which the pipes are made. Main options:
- one-piece, welding (with a welding machine for metal or a “soldering iron” for polymers) and soldering, socket and coupling;
- detachable threaded and collet connections, using couplings, tees, angles, flanges;
- conditionally detachable compression fittings;
- one-piece press fittings (pressure testing);
- split flaring.
Third important parameter
– pipe diameter, external (external), nominal and internal. It is better to leave his calculations to the masters. This is a complex engineering calculation associated with the need to take into account such factors as the thermal power of the system, the speed of movement of the coolant in the system, the temperature difference between the supply and return, and a number of others, taking into account the specified standard values.
An incorrectly selected diameter is bad: less than the specified diameter means noise in the system and increased load on the elements; more than the specified diameter means loss of system efficiency.
And, one more important point. If there are financial possibilities, then you can use a radial, collector circuit, and for this you need a collector, it is designed for a uniform or specified distribution of the coolant. That is, you can regulate the temperature in rooms, even to the point of turning off the heat supply to a certain place.
The manifold consists of a comb, with leads for connecting pipes and devices, the number of leads is different. Valves for draining coolant and air, a heat meter, and taps (inlet, shut-off and adjustment) are installed on the terminals. There are at least a pair of combs – feed and return. The collectors are hidden in cabinets, and the pipe routing is hidden.