Here you will learn:
- Operating principle of gas heaters
- Types of gas heaters
- Tips for choosing gas heaters
A variety of heating devices have been developed for heating residential buildings, administrative, industrial, utility and many other premises. These include water heating batteries, various convectors, heat guns, infrared heaters and much more. A gas heater is another modern heating device that is optimally suited for heating any type of room and even open areas.
In this review we will look at:
- main types of gas heaters;
- principles of device operation;
- advice on choosing and purchasing such devices.
We will also tell you where and how to make the most profitable purchase.
Principle of operation
So, first you should understand what gas heaters are and how they work.
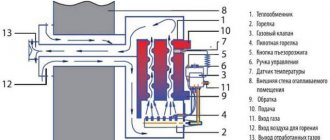
All models have common constituent parts, namely:
- frame;
- heat exchanger;
- heater;
- burner.
These elements are found in all gas heaters - from budget to the most modern.
More expensive models add convenience features such as a thermostat or automatic shutoff.
There is one more common point for all models - they run on gas, natural or liquefied. Using the device, fuel is converted into heat. Such a heater can be connected to both main gas and bottled gas.
Which one is better to choose?
There are many models of home heaters on the market today, equipped with a wide variety of additional functions. When choosing a device, you must first rely on the following parameters:
- - how much area it should warm (at the rate of ten kilowatts per square meter with a ceiling height of three meters);
- — the purpose of the room where it will be located (for a child’s room, for example, there are increased safety requirements);
- - economical.
Optional checklist
After the power of the device has been calculated, it is important to decide on the type of heater. The market offers oil radiators, fan heaters, quartz and ceramic panels, convectors and those based on infrared radiation. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The next thing to consider is size. You need to think in advance where the heater will be located, and, if necessary, provide a mount for it. According to the type of control, all models are divided into mechanical and electronic. The second option usually has more flexible settings. Additional functions may include, for example, an on-off timer, moisture and dust protection, the ability to integrate into the Smart Home system, and others.
Varieties
All gas heaters are divided into portable and stationary.
The first ones are usually used temporarily, that is, from time to time. They are small in size and weight and are most often placed on the floor. Their productivity is, of course, less.
Such gas heaters are usually chosen for utility rooms or for summer cottages, as well as in the absence of a main gas supply. Such a unit will not withstand full and constant heating of a residential building.
The second (stationary) gas heaters are devices powered by main or bottled gas. These devices are installed only in a permanent place and will cope with winter heating of the house. Such heaters are large, powerful and require additional equipment such as a chimney.
Gas heaters are also divided according to their operating principle. There are three main categories:
- infrared;
- convection;
- catalytic.
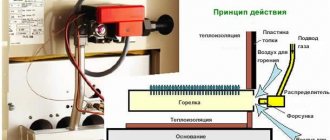
- The operating principle of infrared heaters. Inside the housing there are burners with emitters made of metal or ceramics. When heated, they begin to emit heat - infrared waves. Those, in turn, heat not the air, but objects located at a certain distance from the heat source. Depending on the power, such devices are capable of heating large rooms and even open spaces.
- The operating principle of convection heaters. This is the simplest device. Roughly speaking, these are ordinary burners that burn gas. The resulting heat passes into special finned radiators. Thanks to convection and according to the laws of physics, heated air rises, and cold air takes its place, gradually warming up. If the correct power is selected for the room, the heat can be felt after just a couple of hours.
- Operating principle of catalytic models. These are perhaps the most fireproof gas stoves. There is no combustion process involved here. Heat is released as a result of a chemical reaction - gas oxidation. The fuel enters the catalytic panel, where it is oxidized, generating heat. The heating itself occurs by infrared, convection or mixed type.
Manufacturers
Gas heating convectors are becoming more and more popular. And all because they heat up really quickly, are quickly installed, and even the heating is not too expensive. Therefore, new and new manufacturers are constantly appearing on the market. But buying equipment from unknown companies is a big risk. There are many proven ones. If we talk about those that belong to the category of “infrared gas fireplace” (on wheels), BARTOLINI has the best reviews. They are beyond competition. Even despite the fact that the price of its closest competitors - REMINGTON - is two times lower. But no one complained about Bartolini. The equipment always turns out to be up to par and no one has ever regretted the purchase. All other brands are slightly worse in quality.
Also have good reviews:
- MASTER (China, but not bad)
- REMINGTON
- Ballu
- Timberk
- Alpine Air
- Prorab
- Aesto
- Neoclima.
All of the listed companies produce good equipment, but there is also a very long list of unknown ones that may be much lower, but the characteristics are the same. What is typical is that they can produce the same parameters. But alas, miracles do not happen. Usually, after a couple of seasons, a ceramic stove burns out. It begins to crumble and crumble. Accordingly, in this place the burner does not ignite, but gas flows! If no one notices this, the gas will fill the room... And the undamaged part of the burner is burning. What's next is clear. That’s why it’s better not to experiment and buy proven equipment. The most reliable one is made in Europe. If "what happens", known. So there is no doubt about the safety of their products.
There are devices that do not require either a stationary heating system or coolant to operate. Their use is convenient in any conditions, even in the absence of any communications. Gas infrared heaters from a cylinder operate using a supply of propane. And although this method of heating a room cannot be called the safest, it is quite popular among a wide range of users. Let's try to figure out why.
Gas infrared heater does not require connection to communication systems
Pros and cons of different types of gas heaters
The large selection of different models often simply leads to a stupor. Which heater will be better? Unfortunately, there is no definite answer; each type is bad in some ways and good in some ways. To choose the unit that is suitable for your needs, you need to familiarize yourself with their pros and cons.
We will not study the convection heater, since there are more modern and safer models. Instead, let's consider a new generation ceramic gas heater. Below are tables with the positive and negative characteristics of each type.
Catalytic
| pros | Minuses |
| Very compact. The operating principle allows you to keep the size of the device to a minimum. | Cannot be used in confined spaces. Be sure to have good ventilation. |
| No additional pipes or dirt, since there are no combustion products. | |
| The device does not require electricity to operate - it is completely autonomous. | |
| Economical fuel consumption. | |
| Safety. There are no burners or open flames. |
These devices are very effective. As stated above, heating can occur in three ways. Some models are additionally equipped with fans for uniform heat distribution.
Infrared
| pros | Minuses |
| Possibility of heating open and closed spaces. Such models are great for cafes, playgrounds or pool areas. | Burns oxygen. That is, ventilation is necessary in any case. |
| Large coverage area - outdoor models can heat objects at a distance of up to 6 meters. | Low fire protection. Even with the maximum protective measures taken by manufacturers, the device can cause a fire. |
| Mobility. Lightweight and compact models. | |
| High efficiency. | |
| In most cases, the device operates completely autonomously. |
Ceramic
| pros | Minuses |
| Easy to use. | Requires regular maintenance, which is not an easy task. The list includes: calibration, filling the cylinder, cleaning the main parts and checking for wear. |
| Mobile and compact. | |
| Reliable. | |
| Economical in comparison with liquid fuel analogues. | |
| Heats up the room very quickly. | |
| Safe. |
Differences from gasoline and multi-fuel models
Gas appliances are the most common, but not the only type of catalytic equipment. Heating units can also operate on other types of fuel.
Depending on this criterion, three more types of devices are distinguished:
- Gasoline. Devices with a built-in fuel tank connected to a catalytic cartridge. Gasoline vapors in them enter the cartridge and undergo oxidation when interacting with the catalyst. Mobility and modest size contribute to the particular popularity of gasoline heaters among outdoor enthusiasts, hunters, and fishermen.
- On technical alcohol. Designs with a special internal compartment into which a container with alcohol or dry fuel is placed. They are presented in small-sized models weighing no more than 1.5-2 kg. They are used exclusively in field conditions: they heat tents, dry clothes, and heat food and drink.
- Multi-fuel. Universal heaters that work with any available type of fuel, both gaseous and liquid. They are characterized by rather limited power - 500-1200 W.
Apart from external characteristics, there are no significant differences between gas, gasoline and multi-fuel catalytic heaters. They all work on the principle of catalytic combustion and have a similar internal structure.
The main advantages of gasoline and multi-fuel models are mobility, compact dimensions, and relatively affordable price. As for technical and operational parameters, gas installations are an order of magnitude superior
Gas appliances are easier to maintain, have high performance, and are designed for a wide range of applications.
Gasoline devices are a little more difficult to operate. To ensure efficient and uninterrupted operation, you need to fill them with gasoline of the highest purity.
What you need to know when choosing
And yet, how to choose a gas heater? First you need to know exactly the purpose of the heater.
So, for open areas (sites, etc.), a unit in the form of a high lantern is recommended. It will heat a circular area, such as a terrace, playground or pool area.
When choosing a gas heater for your dacha, you should pay attention to floor-standing models.
For residential premises, a device with a catalytic operating principle is more suitable. This is the safest option for others.
If possible, you should pay attention to stationary gas heaters. These are ideal for a year-round home.
What power should the heater have?
The best gas heaters
To help you at least a little with your choice, we present an overview of the best gas heaters in different categories.
The first place in the ranking of mobile heaters for summer cottages is occupied by the Timberk TGN 4200 SM1 .
Main characteristics:
- floor;
- heats up to 60 cubic meters. m;
- power 4.2 kW;
- closed;
- weight 7.4 kg;
- electric ignition;
- gas control;
- three burner operating modes.
Powered by a gas cylinder, which is installed in a metal case. The delivery set includes a hose, reducer and clamps.
The device also has a CO2 sensor and tip-over protection. Convenient to move thanks to wheels.
The only negative is that you need to periodically ventilate the room.
The average price of the model is 4,800 rubles.
Hosseven HP-3 model received gold .
Main characteristics:
- wall;
- heats up to 30 sq. m;
- power 3 kW;
- weight 28.5 kg;
- thermostat;
- temperature adjustment;
- mechanical control.
The first thing that catches your eye is the unique design of the device: the body is black, the front panel is made of heat-resistant, impact-resistant glass. Very reminiscent of a fireplace.
This stationary heater can operate on both main and bottled gas.
Heats up the room quickly and looks great.
The price of the model is on average 25,000 rubles.
The rating of street models was topped by Enders Elegance .
Main characteristics:
- street;
- heating diameter - 9 m;
- power 8 kW;
- weight 12.5 kg;
- height 2.2 m;
- wheels for moving;
- shutdown when tilted more than 45 degrees;
- mechanical ignition.
This model is perfect for gazebos, verandas and other outdoor recreation areas or cafes. Thanks to its stylish appearance, it will not only fit in, but also decorate any place.
The device uses the new Enders-Eco-Plus technology. It is this that provides heating at 12 kW with a real power of 8 kW.
The average cost of such a model is about 24,000 rubles.
Calculation of power by volume
This type of calculation is more accurate because it takes into account the height of the ceilings. The ratio that is taken when calculating the heat load is that to heat 1 m3 of the total volume of the room, 40 W of heat will be required.
Algorithm for determining power by room volume:
- Use a tape measure to measure the height, length and width of the room and determine the volume.
- Multiply the resulting value by 0.04 and get the recommended thermal power.
- Correction factors for insulation, glazing, and type of room are taken into account.
By performing the calculation, you can make sure that the efficiency and economy of heating largely depends on the level of insulation and glazing of the house, so the owner should be interested in carrying out insulation work and replacing double-glazed windows with energy-efficient ones.
Calculation of gas consumption
After determining the thermal power, they begin to calculate gas fuel for heating needs, on natural gas, they perform it according to the formula: L = Q / (qH x 0.90), where: L is the volumetric indicator of hourly gas consumption per 1 m3/hour; Q – design power of the convector, kW; Q ng – lower calorific value of natural gas, for main gas it is equal to 10.2 kW/m3; 0.95 – convector efficiency. For the above example, heating a house with an area of 150 m2 and a maximum thermal load of 15 kW, the calculation is:
15 / 10.2 x 0.95 = 1.54 m3 / h of natural gas.
Gas consumption per day is 1.54 x 24 = 36.96 m3, and
Monthly consumption – 36.96 x 30 = 1081 m3.