In the previous article we talked about waterproofing the basement and the importance of this event. Today we will talk about how to reduce heat loss at home through the ceiling. To do this, you need to insulate the attic hatch and ceiling. There are many thermal insulation materials suitable for work: bulk, liquid, in rolls and sheets. Each of the materials has its own characteristics, but the installation method for all of them is quite similar, not counting liquid thermal insulation, such as polyurethane foam and penoizol.
Polymer insulation for attic floors
The use of expanded polystyrene for attic insulation.
One of the most common options is insulating the attic floor with foam plastic or penoplex. The first option is much cheaper, and the characteristics of ordinary polystyrene foam are quite sufficient, since there is neither extreme dampness nor high mechanical loads in the attic. Therefore, a material with a minimum density of 15 kg/m can be used. cube It is laid between the joists, the joints are foamed with polyurethane foam. This material is very convenient if you need to insulate an attic hatch.
The polymer does not allow moisture and steam to pass through, which can become a problem. Moisture rises to the ceiling along with warm air. When insulating the attic floor with polystyrene foam, moisture has nowhere else to go but penetrate into the structure of the wood, because the polymer is vapor-proof. If there is too much water vapor, the tree cannot cope with its transit through itself and because of this, the wood is constantly wet. Where moisture stagnates, mold will not be long in coming, and the beams begin to turn black.
To avoid this, insulating the attic floor with your own hands should be accompanied by laying a vapor barrier. Installation diagram (bottom to top):
- ceiling;
- vapor barrier film;
- beams and insulation.
You can leave the insulation uncovered on top; the main goal is to prevent moisture from entering the wood structure from the room. When insulating the attic floor with your own hands, you don’t have to install a vapor barrier membrane if you plan to install a suspended ceiling. This is also a polymer film that does not allow moisture or steam to pass through. Moisture penetration around the perimeter will be minimal.
The first question from buyers about heating pipes is: which ones are better? It is impossible to answer in one phrase, because many factors need to be taken into account.
You can read everything about connecting heating pipes to a heating boiler in this article.
How to choose the optimal foam thickness?
The climatic indicators of the region are the starting point for calculating the thickness of the foam for roof insulation. There are special tables that display the thermal heat transfer parameters of each region.
In addition, the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient of the insulation is indicated on the packaging (sometimes in the certificate) of the foam.
The product of the values of the thermal conductivity coefficient and the thermal heat transfer of the region will be equal to the thickness of the insulation layer.
There are average material density indicators that experts focus on when choosing expanded polystyrene:
- for flat or attic roofs, use PSB-35 material (density - 35 kg/m3, thickness - from 50 to 100 mm );
- for pitched and attic - PSB-15 ( density - 15 kg/m3, thickness - from 50 to 100 mm) ;
- on the walls - PSB-25 ( density - 25 kg/m3, thickness - from 50 to 100 mm ).
Sometimes you have to lay the foam in two layers. In this case, the thermal insulation layer may be thicker than the width of the rafters, as a result of which it is necessary to build up frame boards.
With the technology of laying polystyrene foam between the rafters, additional work to increase the width of the wooden frame can be avoided, but then installation can become significantly more complicated.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool must be protected from moisture.
It is not entirely correct to use polystyrene foam, since you need to create all the conditions for the house to be environmentally friendly and fireproof. In this regard, it is better to use mineral wool. There are several types of mineral wool:
- glass wool;
- slag;
- basalt (stone) wool.
Most of them, except stone wool, are afraid of moisture. That is, they absorb it well, release it poorly and, when wet, lose their thermal insulation qualities. Therefore, it is necessary to prevent moisture from entering the insulation layer, and even if some of it does penetrate the thermal insulation, it must be allowed to escape. How to properly insulate an attic floor with mineral wool:
- From below, the thermal insulation is protected by a vapor barrier, which does not allow steam and water to pass through;
- the insulation layer must be at least 20 cm - in two rows of 10 cm with seams apart;
- waterproofing is laid over the wool, which does not allow water to pass through, but allows steam to escape;
- There must be ventilation gaps between the thermal insulation and the membranes.
If you choose how to insulate an attic floor among all types of mineral wool, then preference should be given to basalt wool. It practically does not absorb moisture, so it is allowed (although not advisable) to lay it without additional membranes. At the same time, rodents feel great in cotton wool, as well as in polystyrene foam, which becomes a serious problem.
To lay heating pipes in the floor, you need to protect them from mechanical damage and compensate for their thermal expansion. You can use plastic sleeves for this.
Here you can find information about noise in heating pipes: causes, elimination methods, possible consequences.
Instructions for installing polystyrene foam in the attic
The stages of working with polystyrene foam are not particularly difficult and you can insulate the attic from the inside with your own hands, without the involvement of hired workers. But there are certain points that are worth paying attention to.
As a rule, work begins with the installation of the lower part of the attic sandwich.
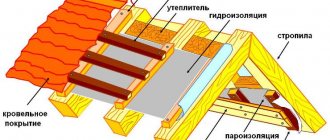
Let's consider the most common version of the load-bearing roof structure: wooden rafters with a section height of 200 mm, located with an axial pitch of 60 cm. All actions for arranging a roofing sandwich can be divided into those that are carried out from above, and those that are carried out from inside the room, from below. On the roof side, a waterproofing membrane is installed on the upper plane of the rafters, sheathing and roofing are installed. Before you start insulating the cells between the attic rafters with foam plastic, you should make sure that there is a membrane.
Attention! Vapor and waterproofing are sold in rolls, and during installation they must be overlapped. Typically, the overlap size is 10 cm. Therefore, when calculating the required amount of insulating membrane, you need to take into account the cost of overlapping layers.
Further work is carried out in the following order:
- The necessity of installing the bottom lathing is calculated. We compare the height of the rafter profile and the sum of the heights of the ventilation gap (between the foam and waterproofing) and the foam itself. Suppose, in accordance with the calculation, you have chosen a thickness of the insulating layer of 22 cm. Taking into account a ventilation gap of 3 cm and a margin of 1 cm, it is necessary to increase the rafters by a minimum of 6 cm. We install the sheathing with timber 6–7 cm high and a width equal to or slightly inferior to the thickness of the rafter beams. This installation can be performed after fixing the foam, but in this case, the operation of sealing the joints with foam will be divided into 2 parts and will take more time, and will also require more adhesive foam.
- Suppose you have chosen 10 cm and 12 cm thick PPS slabs to achieve the required insulation cross-section of 22 cm. We select a 10-centimeter material to perform the first (from the roof) layer. We create a stop to ensure a ventilation gap of 3 cm. This is easier to do with the help of clamps. We attach stops from below to the rafters with clamps, the distance from which to the waterproofing is 13 cm.
Thermal insulation design of the attic floor.
- We measure the width of the cell between the rafters and cut out a slab of the required size with a hacksaw. There is no need to adjust the size taking into account gaps or interference. The resulting piece should fit into place freely or with a slight tension that does not lead to destruction of the foam.
- We lay PPS slabs on the stops. To fix the insulation to the rafters, we use foam adhesive. We carefully foam all the gaps between the wood and the foam plastic, as well as between the PPS boards themselves. Before installing the insulation, you should allow 5 minutes for the glue to polymerize.
- After the first layer of insulation is installed, excess adhesive foam should be trimmed. Otherwise, it will be impossible to achieve a tight fit of the next layer.
- Before installing the second layer, apply a layer of adhesive foam along the rafters and over the joints of the first layer. After preliminary polymerization, we install 12 cm slabs so that the joints between them do not coincide with the joints of 10 cm slabs. Do not press hard when fixing the slabs. If there is a gap of about 5 mm between the layers, this is quite acceptable. We had another 1 cm of height for the sheathing strips in reserve, so we would not go beyond the indicated dimensions.
- After completing the work with the foam plastic, we install the vapor barrier membrane on the bottom sheathing using a stapler. Now the ceiling is ready for installation of decorative lining or slab covering made of plasterboard or OSB panels.
Video: insulation instructions from professionals
Liquid insulation for attic floors
Liquid insulation is sprayed over the beams and ceiling.
There are two types of liquid insulation that are used to insulate attic floors:
- polyurethane foam (PPU);
- penoizol.
Despite their similarity, these heat insulators differ in the materials used for their production and characteristics. In this case, the device for insulating the attic floor with both materials is identical. The liquid composition is sprayed over wooden floors. After polymerization, the thermal insulation can be covered with a finishing finish or left open. The advantage of these materials is that they allow steam to pass through, allowing the structure to breathe.
The density of polyurethane foam is much higher than that of penoizol, it is much more durable and, accordingly, more expensive.
Penoizol appeared as a cheaper alternative to polyurethane foam. Liquid thermal insulation has proven itself well, but not everyone could afford such luxury; today this type of insulation is more affordable. In addition to high performance characteristics, the material belongs to the G1 flammability group, that is, it does not burn and mice do not breed in it. Installation requires special equipment; the quality of work largely depends on the professionalism of the performer. Therefore, the option to do it yourself is eliminated.
Selection of materials
When choosing insulation to protect against cold air, you must be guided by its basic properties. It is important that the materials have the following characteristics:
- low thermal conductivity; fire safety; light weight; environmental friendliness; the ability to “breathe”.
There are various materials and products on the market for insulating attic walls, ceiling and floor cladding. One of the most popular and relatively inexpensive insulation materials is mineral wool. This fibrous material is characterized by frost resistance, it is not susceptible to biological influences, fungus and mold, and is resistant to fire.
Insulating the attic with polystyrene foam is an opportunity to protect the room from heat or cold for a long time with a technologically advanced and environmentally friendly material. It is not susceptible to insects, fungus, mold and other microorganisms that destroy the fiber texture. Working with extruded polystyrene foam is simple and not labor-intensive.
For insulation, you can also use cellulose material - ecowool.
This fiber is environmentally safe. It has similar characteristics to polystyrene: fire safety, low thermal conductivity, lightness. The material also has excellent sound insulation properties. But its use requires the use of special equipment.
Bulk insulation for attic floors
Vermiculite is the best option for insulating attic floors.
We wrote a separate article about bulk insulation materials, in which we talked about their types and characteristics. Today we will only briefly consider the main points that relate to the insulation of the attic floor. For this purpose the following can be used:
- expanded clay;
- perlite;
- vermiculite;
- sawdust;
- ecowool.
Perlite and vermiculite are rocks that, after swelling, can be used as thermal insulation. The material is quite expensive, but it lasts almost forever. It does not burn, does not enter into chemical reactions, and mice do not live in it. It has the property of distributing moisture evenly over its entire area and quickly removing it outside, when wet, it does not lose its characteristics. In principle, this is an ideal option for insulating horizontal floors.
The insulation of attic floors with expanded clay was already familiar to our grandfathers. The only advantage of expanded clay is its cost. The rest of the material is frankly weak.
Its thermal conductivity is high and it absorbs moisture (weakly, but still). Compared to other modern insulation materials, the characteristics are clearly inadequate, so it is used only when it is available for free. Although there are even worse options - insulating the attic floor with sawdust.
Expanded clay is a frankly weak thermal insulator.
To achieve at least some insulation effect, you need to pour sawdust in a layer of at least 30 cm. At the same time, they tend to absorb moisture and rot. In order to allow moisture to escape, sawdust is mixed with clay or expanded clay. Sawdust is not suitable as independent thermal insulation. By the way, vermiculite can be mixed with sawdust, resulting in quite decent insulation. Mixing should be 50/50.
We wrote about ecowool insulation in one of the previous articles. This is also a loose insulation material and can be applied dry or wet. Strongly absorbs moisture, while easily parting with it. The material contains a lot of chemistry, so it is indirectly related to environmental friendliness, and only due to the fact that it was developed as part of a program for recycling recyclable materials.
For all bulk heat insulators, insulation of the attic floor is carried out according to the following scheme:
- ceiling;
- film or membrane - prevents steam from entering and prevents thermal insulation from spilling into the house;
- layer of insulation.
If you plan to make a floor in the attic, then it can be laid directly on top of the thermal insulation without additional film barriers.
Roof insulation with foam plastic: technology and nuances
It seems possible even for a non-professional to insulate a roof with your own hands. Before you begin directly insulating the roof, you need to have a clear idea of where the attic, residential area or non-residential location for the attic will be located. The consumption of insulation material depends on this.
Next you should take the following steps:
- select the appropriate material , suitable in terms of characteristics and meeting the requirements of a particular building, designate the scheme and order of work;
- Be sure to check the rafters for strength, quality, and possible fungal damage. If defects or moisture are detected, unsuitable elements must be replaced;
- To increase service life, treat all elements of the roof frame with an antiseptic , including wires, water pipes, rafters. Both antipyretic and antiseptic agents can be used as impregnation for wooden structures.
When all the preparatory work is done, you can begin to insulate the roof.
Conclusions about insulating the attic floor
All methods of insulating the attic floor are aimed only at reducing heat loss in the room. As you know, the main amount of heat escapes through the ceiling, and then through windows/doors and walls. Warm air tends to rise upward, taking with it all the moisture. In fact, a lot of moisture is generated in the house, so the insulation in the attic needs to be protected with film barriers (waterproofing, vapor barrier).
To insulate the attic floor, you need to choose a material that meets the following requirements:
- low heat transfer coefficient;
- environmental friendliness;
- preferably should not be afraid of moisture;
- must allow steam to pass through;
- Mice should not live in it.
The material that will meet all these requirements will undoubtedly not be cheap. We are talking about vermiculite, but it is possible to slightly reduce the cost of insulation. It is necessary to mix vermiculite with sawdust, but this will lead to the fact that the material will be less able to protect the house from heat loss. In addition, a good budget option is penoizol (liquid thermal insulation). It is better to avoid polystyrene foam. The use of mineral wool has both pros and cons, although the material is very popular.
Is a vapor barrier necessary for thermal insulation?
In the process of life, a person produces a large amount of moisture. They are found in almost all residential areas in the form of vapors. In some there are more, and in others in less.
Therefore, warm air from all rooms tends to go outside. If the building is built of red brick or wood, which have good vapor permeability, everything escapes without lingering either in the walls themselves or on their surface. This means the microclimate throughout the house will be comfortable.
If the materials used for construction or finishing of housing have low vapor permeability, then unpleasant consequences arise. When moist air, passing through the thickness of the wall, collides with a colder surface, the moisture begins to condense. Depending on the location of the dew point, water droplets appear:
- On the outer surface.
- On the inner surface.
- In the thickness of the wall.
If condensation forms outside and the wall is well ventilated, then there will be no problems. But when formed inside a house or in the thickness of a structure, it will lead to the following consequences:
- the appearance of mold and mildew on the walls;
- accumulation of moisture in the insulation - which leads to a decrease in its technical characteristics;
- frozen water slowly destroys all materials.