New developments aimed at saving home heating costs are increasingly attracting attention. New products also include vacuum heating radiators. These are ordinary batteries in appearance, but completely different in operating principle.
They are suitable for both centralized heating systems and autonomous ones. In this material we will talk in detail about the operating principles of vacuum radiators, their varieties, and also dwell on the nuances that you need to keep in mind when choosing heating radiators for your home.
Operating principle of a vacuum heating device
Hot water flowing from the heating system to the bottom of the radiator (connected to the heating system using standard couplings) transfers heat to the lithium bromide fluid. It quickly begins to evaporate, heating all sections of the radiator. The condensate flows down, then again turns into steam and rises up. Thus, the outer wall of the pipe, adjacent to the coolant, is constantly cooled. And the temperature difference between its inner and outer surfaces increases the heat flow.
Radiator sections, heated by hot steam in a couple of minutes, release heat to the surrounding air. Moreover, according to manufacturers, this happens instantly. The heat transfer they claim for one section of this device is 300 watts, and a very small amount of water is used. These are serious numbers - next we will try to find out if this is so. And at the same time we’ll check how wonderful the new heating devices are.
Design features
In appearance, these radiators are no different from ordinary ones. But inside there are big differences. Firstly, there is a pipeline that is laid at the bottom of the radiator. Hot water moves through it, which is heated in a conventional boiler. Secondly, the entire remaining volume is filled with a special boron-lithium mixture, which is there under vacuum. Hence the name.
Why such difficulties?
The boron-lithium mixture (refrigerant) begins to boil at a temperature of +35C. That is, hot water passing through the lower pipe heats this mixture, which boils and heats the metal body of the radiator. Hot vapors of the mixture rise upward, where they cool and condense, falling down. In this case, the temperature of the coolant may not be as high as in the case of conventional heating batteries. In them it is usually +75C. Accordingly, lowering the coolant temperature makes it possible to reduce fuel consumption costs. This is where the savings lie.
Experts note that the heat transfer of such models is lower than, say, aluminum batteries. Everything is true, but, firstly, the difference is not so significant as to make a choice between the first and second. Secondly, decent savings outweigh all other indicators. To achieve increased heat transfer, you can simply purchase a device with more sections or install another one. For private houses with a large number of rooms and a large area, these radiators are the optimal solution when it comes to the funds allocated to cover heating costs.
Vacuum battery
Types of vacuum radiators
The line of vacuum devices includes products designed for electric heating, vacuum registers, panel radiators . You can also find exclusive designer products on sale.
The vacuum electric radiator model deserves special attention, although they are more expensive. This is a good solution for owners of rarely visited suburban real estate.
Designer vacuum radiator in the form of a firewood stand. You can not only stack logs on it, but also dry them
Instead of a horizontal channel with a coolant, this device has a cartridge-type tubular heating element with a power of more than 50 W per section.
This heater transfers heat to the filler - oil or water, thereby heating the lithium bromide liquid. When installing such models, grounding is required.
Electrical
They are distinguished by their high cost; they are usually installed in suburban facilities that are used from time to time. Here, instead of a horizontal pipe through which the coolant circulates, a cartridge tubular heating element is installed. The power of each section in this case is from 50 W. The heater transfers thermal energy to the oil or water filler, resulting in an increase in the temperature of the lithium bromide fluid. Grounding must be provided during installation.
Panel
Optimal for heating large areas, economical and comfortable to use. The main advantage of the solution is high efficiency. The devices are easy to install and require little maintenance.
Vacuum registers
They can be implemented in centralized and autonomous heating systems; single-section models are the most common. Vacuum registers are optimal for use in production, warehouse, livestock, greenhouse, and public facilities. In production, profile pipes of various sections are used. The length of the sections can be up to 4 m; in the standard version they are painted with enamel and equipped with wall and floor brackets.
What does a vacuum register look like?
Recommendations for use
The equipment in question has proven to be an economical and very effective way to heat summer cottages used seasonally and large private houses intended for year-round use. The heating system is activated within a few minutes and does not require pre-bleeding.
Experts advise, even at the installation stage, to take care of creating certain conditions that will facilitate the rationalization of the use of vacuum equipment:
- a building or an apartment must be insulated as much as possible in order to reduce the level of heat loss. A reasonable solution would be to install modern types of double-glazed windows on the windows, seal the cracks, and provide the roof and floor with high-quality thermal insulation. In this case, the devices will function more efficiently;
- the number of sections, respectively, and their overall performance must match the parameters of the sections being serviced. Even at the stage of selecting devices, you need to take into account the height of the ceilings and the size of the rooms;
- The heat transfer of equipment is always determined by the temperature of the working environment; optimal conditions are when the water is heated to at least 60°C.
In the core market, there is a systematic increase in demand for batteries using a lithium-bromide mixture, due to which manufacturers have significantly expanded the possibilities of their use. In addition to heating cottages and private houses, vacuum systems are in demand at production and warehouse facilities, when arranging garages and public buildings, greenhouses and farms.
Technology and rules for installing vacuum radiators with your own hands
The first step is to choose a convenient connection method in accordance with your own capabilities and environmental conditions. After preparing the tools and materials, you can begin sequential installation of the equipment.
Options for implementation in the heating system
Installation of equipment corresponds to the type of communications used in the house:
- to connect a radiator to an autonomous system, a standard method is suitable - the battery is installed using couplings to the inlets and outlets of the hot coolant;
- if the fuel is electricity, a stationary or portable heater can be installed to heat the lithium bromide medium (the first option is more reliable);
- if you plan to connect the radiator to a solar source or central heating, you can use the first method.
Both bottom and vertical wiring are equally functional.
Radiator installation rules
First of all, you need to choose the optimal area for fixing the battery. When fixing the device, it is advisable to maintain a distance of at least 5 cm from the nearest wall; the height of the fixation relative to the floor should be at least 2-5 cm from the bottom edge. It is also important that the top edge of the radiator does not reach the window sill by about 10 cm.
Immediately before installation, you need to drain the battery, that is, create such conditions so that the easily evaporating working composition stacks down
It is advisable to insulate the section of the wall that will be located directly behind the vacuum radiator using reflective material. Construction foil and isolon can be useful here. Immediately before installation, you need to drain the battery, that is, create conditions so that the easily evaporating working composition flows down. During installation, you can use plugs usually used for aluminum heating devices. If the walls were previously thermally insulated, you will need to select extended brackets for mounting the equipment.
Device installation sequence
To make the work easier, in addition to the radiator and brackets, it is advisable to prepare materials and tools:
- Ball Valves;
- impact drill;
- open-end wrenches;
- roulette;
- pencil and hydraulic level;
- sealant, tow;
- pobedit drills;
- screwdriver
Vacuum radiator installation steps:
- If it is necessary to reconstruct the old heating system, the radiators are dismantled and the walls are leveled.
- Create markings in accordance with the above recommendations regarding the placement of equipment.
- The brackets are fixed at specified points.
- Sections of vacuum radiators are mounted on brackets.
- Ball valves are introduced, strengthening the joints with sealant and tow.
- Main pipelines are connected to the taps and the connections are sealed.
Vacuum radiators: selection and independent production
It is difficult to come up with something new in the design of conventional radiators, unless you use different types of metals and optimize the shape in order to increase the surface area. Vacuum devices can be considered an interesting experiment that has not yet become widespread. Nevertheless, such devices are innovative, because, according to the manufacturers, they are more efficient than conventional ones, and electric vacuum radiators are even capable of reducing electricity consumption significantly.
Vacuum battery
Design Features
When using a conventional heating radiator, a coolant (most often hot water) is supposed to circulate through it, it warms up, and accordingly the temperature in the room increases.
This may cause problems such as:
- uneven heating - can be caused either by air pockets in the battery itself, or by contamination due to poor quality coolant;
Note! If you can deal with an air lock yourself using a Mayevsky tap, then battery contamination cannot be easily eliminated.
- corrosion of metal . This does not always occur, but when such a phenomenon occurs, the risk of leakage increases; this usually happens at the most inopportune moment.
On the left is a thermogram of a vacuum radiator, on the right is a regular one with air pockets
Vacuum radiators involve a slightly different principle of heat transfer from the coolant to the room. If in a conventional battery the coolant flows through the entire heating device, then in a vacuum battery it flows only through a pipe passing through the bottom of the device.
The radiator space is partially filled with lithium bromide liquid, and during the manufacture of the device, air is pumped out of it, this is necessary in order to reduce the boiling point of the liquid.
As a result of these manipulations, manufacturers managed to ensure that the lithium-bromide liquid boils and begins to actively evaporate already at a temperature of about 35ᵒ C.
The work process looks something like this:
- the boiler quickly heats up the coolant;
- it flows through the pipe through the heating radiators;
- the lithium bromide liquid heats up to boiling point in a matter of seconds and evaporates, the vapors rise to the top of the device;
- here their temperature begins to decrease and vapor condensation occurs;
- drops of liquid flow down along the inner surface of the walls and the cycle repeats.
Operating principle of the heater
Absolutely all vacuum radiators, both flow and electric, work according to this scheme. The whole difference is that in the former, a pipe with a coolant is used for heating, and in electric ones, a heating element mounted in the lower part of the device.
Truth and fiction about vacuum radiators
As for the attitude towards the new product, people were divided into 3 groups:
- some people are absolutely indifferent to the innovation, the heating works, and that’s fine;
- others are sure that all this is the machinations of marketers, and the new product is absolutely useless;
- still others assure everyone that energy savings are almost 50-70% compared to conventional heating.
What do manufacturers promise?
The assurances of sellers should always be treated with caution, because the main task for them is to sell the product, the buyer’s interest comes in second place at best.
But it’s worth mentioning the stated advantages; judging by the advertising, a vacuum heating radiator will allow:
Characteristics of radiators from a popular manufacturer
Note! In total, in heating systems of this type, the volume of coolant can be in the range of 15-20 liters or even less.
- increase the heating rate of the radiator, if a regular cast iron one will heat up for several minutes, then a vacuum one will take less than a minute;
- lower the temperature of the coolant in the system; instead of 80ᵒС, it is enough to heat it to approximately 50-60ᵒС;
- it is simply impossible to make it impossible to pollute the insides of the radiator due to poor cleaning of the coolant, because water flows only through the lower tube;
The photo shows that the coolant flows through the bottom of the device
- the formation of air jams is also impossible;
As for the disadvantages, advertising usually only mentions a fairly high price, as well as the fact that if handled carelessly, the device may depressurize. Considering the high degree of danger of lithium bromide liquid, this is fraught with the most negative consequences.
Vacuum batteries in real life
The most important thing to understand is that the radiator is just an intermediary, its role is to transfer heat into the room as quickly as possible, it does not generate energy by itself. So the house’s need for energy for heating will remain the same, and it can be reduced through proper thermal insulation.
There are comments on a number of points:
- pollution and air pockets never really form, but in a conventional heating system it is enough to simply monitor the cleanliness of the water. And the installed Mayevsky valve will allow you to bleed excess air from the system in a matter of seconds;
- the volume of water will actually be needed less and the boiler will heat it up faster, but to maintain the required temperature it will have to turn on more often, that is, the system will have low inertia;
- Vacuum radiators have another drawback - the contact area of the pipe with the coolant and the lithium bromide liquid is small. So the efficiency of heat transfer is questionable;
The contact area is small
- You also need to remember that the temperature regime and the heating efficiency of the radiator have a nonlinear relationship. If in the case of a conventional one the surface temperature gradually increases with increasing temperature of the coolant, then in a vacuum one jumps can be observed when even a slight increase in the water temperature leads to an increase in heat transfer. This is due to the properties of lithium bromide liquid.
The relationship between heat transfer and coolant temperature is nonlinear
Note! Typically, the manufacturer himself sets the optimal temperature regime for his products. So, although the operating principle of vacuum heating radiators is the same, the optimal coolant temperature may be different for different models.
If the recommended coolant temperature is not observed, there is a high risk that the heat transfer from the battery will decrease significantly. This can happen if all the liquid suddenly evaporates, in which case you will need to lower the temperature of the water in the pipe and wait for the condensation process to begin.
At low temperatures, evaporation will be sluggish
Also, do not think that such batteries will be effective at low coolant temperatures. It’s just that very little lithium bromide liquid will evaporate, which will affect the heating of the metal of the case.
However, the listed features are rather theoretical, and there is a lack of experiment conducted by an independent organization.
For now, we can only rely on the experience of using similar systems:
- Tyumen - reduction by 1/3 of housing heating costs (200 m2), before this there were ordinary aluminum radiators;
- Ekaterinburg - in severe frost, 8 kW of energy was consumed per hour to heat a house (about 400 m2).
There are many similar examples, but there is also an unsuccessful experience of using vacuum radiators, when there was no significant difference with conventional batteries. So a lot also depends on the quality of the battery itself; high-quality ones are very expensive.
What to look for when choosing
Even a high price is not always a guarantee of equally high quality.
Climate
The issue of reducing home heating costs is equally relevant for owners of apartments and private houses.
This problem is especially acute in regions with a “harsh” climate, where the air cools to -40°C or more. One of the modern and effective developments in the field of energy saving are vacuum heating radiators, the use of which will reduce coolant consumption and maintain optimal temperature conditions in the room.
Content
Vacuum radiators - an innovation in the heating systems market
The main task of any heating system is the efficient transfer of heat from heating radiators to the room. There are two ways to increase the air temperature in a room:
- an increase in the power of the heating element, which will lead to an increase in the cost of energy;
- reduction of heat losses when the coolant passes through the pipeline.
Given the constant rise in energy prices, it is necessary to look for alternative options for optimizing the heating system. Vacuum heating radiators are considered one of the fairly effective examples of a combination of physical properties of materials and improved design.
Vacuum radiators appeared on the Russian market relatively recently, but have already gained popularity among buyers. Most users note a reduction in costs for the purchase of energy resources by about 30-40%. This saving is due to uniform and rapid heating of the radiator due to the use of a liquid with a low boiling point as a coolant.
Vacuum heating radiators: operating principle and technical characteristics
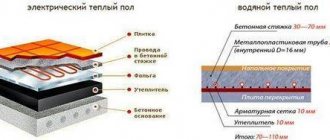
Externally, vacuum radiators look like ordinary sectional batteries, the main difference is the internal design.
At the bottom of the radiator there is a horizontal pipe through which the coolant (antifreeze or water) moves. This pipe is connected in series with vertical sections filled with lithium bromide liquid. All sections of the radiator are isolated from each other, and warm water does not mix with the “working” fluid.
The lower part of the collector is connected to the centralized heating system and after supplying warm water, the vacuum radiator begins to function.
The operating principle of a vacuum radiator is as follows:
- Warm water flows into the lower part of the collector.
- The steel walls of the horizontal pipe are heated to 35°C.
- Heat rises up the vertical sections.
- The metal body of the vertical pipes heats up, causing the lithium bromide liquid to boil and evaporate.
- Powerful evaporation heats the radiator body even more, releasing heat to the air in the room.
- The condensate goes down through the pipes, heats up and turns back into steam.
After turning off the heating system, the vacuum radiator cools down slowly, since in a vacuum environment the particles will gradually reduce their speed
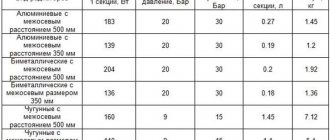
Let's look at the technical characteristics of vacuum-type heating radiators:
- the heat transfer of one radiator section fluctuates in the range of 150-300 W (depending on the case material);
- the weight of one radiator section is about 1.6 kg;
- section width – 80 mm, height – 540 mm;
- 1 section of the radiator is designed to heat approximately 2 sq.m.
During production, vacuum radiators undergo factory testing under a pressure of 15 atm. Most companies provide a 5-year warranty on equipment.
Advantages and disadvantages of vacuum radiators
Vacuum radiators have a number of advantages over other heating devices, namely:
- saving energy resources (30%) and coolant (80%);
- high rate of room heating;
- ability to work with different heat sources (diesel fuel, electricity, gas, wood, solar panels);
- lightness of design and ease of installation;
- no air pockets;
- high level of heat transfer;
- there is no need to use a powerful circulation pump;
- the internal surface of the radiator does not rust, so clogging of the section is excluded;
- the battery heats up evenly;
- do not require additional care and maintenance during operation;
- service life - about 30 years;
- safety of use - if the radiator fails, flooding does not occur (the volume of coolant and the pressure in the radiator are too low).
It is advisable to use vacuum radiators in an autonomous or centralized heating system, but subject to the installation of a heat meter
The main obstacle to purchasing such a device will be the cost of a vacuum heating radiator. You can buy a battery for 8 sections for an average of 7,000 rubles. It is enough to heat a room of 14-20 sq.m.
The disadvantages of a heating system with vacuum radiators also include the possibility of leakage of boiling lithium bromide liquid when the battery is depressurized.
Selecting a vacuum heating radiator
Before purchasing, a vacuum radiator must be checked to ensure that the device meets technical standards and is reliable. The good quality of a radiator can be judged by the following criteria:
- Availability of documents: certificate, test report and radiator passport indicating technical characteristics, transportation and operating conditions.
- There should not be a lot of lithium-bromide mixture. This can be checked by shaking the radiator: the sounds of water flowing indicate poor quality of the battery; optimally, a characteristic rustling sound should be made.
- Factory welding seams are smooth and easy to distinguish from “handmade” ones. The quality of the seams determines the tightness of the radiator.
- The battery must be painted using the powder method.
- Tightness of the filling valve.
Among the manufacturers we can highlight the company “EnergyEco”, whose products have good technical performance.
Vacuum radiator installation technology
Options for connecting a vacuum radiator to the heating system
Vacuum radiators can be connected to various types of heating systems:
- Connection to an autonomous system is similar to a standard connection - the radiator is connected to the hot water inlet/outlet using couplings.
- When electrically heating lithium bromide liquid, either a portable or stationary electric heating element can be used.
- Connecting radiators to a central or solar heating system occurs in the same way as to autonomous heating.
Advantages and disadvantages
Undoubtedly, a vacuum radiator is an interesting invention with good efficiency indicators.
However, by praising know-how as an invention that surpassed everything that existed before, managers greatly overdid it. Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of the device in the light of common sense.
- Small volume of coolant. Indeed, vacuum radiators require several times less coolant than similar aluminum or cast iron batteries. This makes the device lighter and more attractive for large heating systems where expensive antifreeze is used and every drop counts. For example, for a production workshop with an area of 240 m2 and 4-meter ceilings, 48 liters of anti-freeze were needed for the entire system. However, for city apartments and small houses with a water system, this is not such a significant factor. Again, you need to take into account that if the system quickly warms up a small amount of coolant, then it will cool down just as quickly. The inertia of such heating will be minimal, but whether this is good is a moot point.
- Warm-up speed. In fact, thermal imaging tests show that the radiator body heats up quickly. Literally in a few minutes. But you shouldn’t believe advertising claims that the house will warm up just as quickly. If radiators are used in a large mansion (as follows from the previous paragraph), then a considerable volume of air and objects in it will be heated in accordance with the laws of physics, and the time during which the radiator itself warms up is no longer so important.
- No air pockets. This positive quality relieves the owner of the need to install Mayevsky taps on each heating device and then regularly bleed off the accumulated air. It is clear that such valves still need to be installed in other parts of the water system.
- Impossibility of clogging and corrosion . Of course, most problems with aluminum radiators are associated precisely with instability to corrosion, and vacuum devices look very attractive against their background. This is especially important in urban systems, where the quality of the coolant leaves much to be desired, and in the summer the water is completely drained, leaving dry radiators to be eaten by rust.
- Low hydraulic resistance . In autonomous systems, where every turn and knee counts, this can actually be a good advantage. But in this case, you need to calculate the power of the heating boiler and the thickness of the heating pipes specifically for a set of vacuum batteries. In city apartments, this plus does not matter at all.
- Energy saving . Reading that compared to other radiators, this one is 2-4 times more economical, let’s remember the law of conservation of energy. The amount produced by the boiler is the same amount that goes into the living space. Here, first of all, it is important not to lose joules due to poor thermal insulation of walls and windows.
- Uniform heating of the entire surface . This is, of course, a plus, but not as significant as they might imagine. Any radiator, if connected correctly, warms up completely.
Some cons:
- Batteries do not combine well with a gravity heating system.
- Unsuitable for repair - if the vacuum state is lost due to a minor crack, the device fails.
- Lithium bromide liquid is poisonous and its leakage is worse than water leakage from a regular battery.
It is worth noting that while the production of vacuum radiators is in the early stages of development, the market cannot offer a rich model range.
Typically these are devices of classic sizes and shapes, painted white (glossy or matte).
The opinion of wise skeptics
Manufacturers do not talk about the disadvantages of vacuum heating batteries, so it is worth paying attention to the assessments of meticulous buyers. Many of them question the benefits stated by the manufacturers.
Let's look at the most controversial points.
Coolant savings
Indeed, if you use antifreeze concentrate, this fact matters (but you also need to compare the cost of antifreeze liquid with the price of these vacuum heating elements). In places of permanent residence, water is predominantly used as a coolant. In this case, it is pointless to talk about saving money by installing expensive sections (the average cost of one section is approximately 700 rubles).
Durability
Since they appeared on the market quite recently, no one has yet been able to check this parameter. The manufacturer could just as easily “extend” the service life to 50 years - time will confirm or refute this statement.
Operational safety
It completely depends on the integrity of the manufacturer: if he “sinned” somewhere - violated technological conditions or purchased cheap low-quality steel - microcracks may form in the section body. In this case, the internal pressure will become equal to atmospheric pressure, and the radiator will turn into useless scrap metal.
High heating rate of the radiator surface
This feature has little effect on the bed outcome. The heating system is started once a season, and since the battery warms up not in ten minutes, but in five, the total volume of the room will not warm up much faster.
Easy to install
This is the only statement made by vacuum model manufacturers that is not disputed by users.
High heat dissipation
This is a publicity stunt.
Advertising new items
The thermal conductivity of steel remains unchanged, and the quality of heating the room ultimately depends only on the temperature of the coolant. The higher it is, the hotter the surface of the radiator will be, and the more heat it will give off to the surrounding air.
And the secondary coolant in a vacuum environment is very sensitive to the temperature of the primary one. If the temperature of the first does not reach 35 degrees, this will not cause evaporation of the lithium bromide liquid, therefore the device will be inoperative.
And if the working solution leaks out, it can cause damage to the health of household members: lithium bromide water and its vapors are poisonous.
As you can see, even with a cursory study of the stated benefits, ordinary consumers have doubts. To study the miraculous radiator in more detail, some inquisitive users spared no expense and bought a prototype.
The test results did not arouse much enthusiasm: the pipe with the primary coolant turned out to be warmer than the sections. That is, the heat from the collector is not transferred in full (and not 1:1, as advertising convinces us).
The owner of a private house with an autonomous heating system should pay attention to the following aspect: the hydraulic pressure in the network depends on the height of the water column between the battery and the boiler. For vacuum devices this parameter is much less than for conventional ones, which creates problems in the functioning of the system
Critical analysis of positive qualities
The volume of an average cast iron radiator is about 4 liters (depending on the number of sections).
In steel and aluminum similar heating devices - even less. An autonomous medium-power heating system with a battery holds about 2000 liters of water. Therefore, it is doubtful that the volume of coolant in the system becomes 80% less. Apparently, the manufacturers had in mind the volume of coolant in one individual device. Then this is true, but there is no such thing as savings here. For centralized heating, such a “dignity” makes no sense at all. It is not at all clear how a vacuum in the radiator can affect the pressure in the system. The water in the system does not come into direct contact with the radiator coolant. The versatility of vacuum heating devices is beyond doubt. But it’s hard to call this an advantage - other radiators of any type also have a similar advantage.
The most important thing is saving heating costs. According to the law of conservation of energy, known to everyone since school physics, any heated body will give off exactly as much heat as it received
If 300 W of thermal energy is needed to heat a room, then no ingenious devices will help to obtain 300 W of heat, while spending the equivalent of less than 300 W of fuel or electricity.
No matter how the heat is transferred, its amount will not increase in the heating device itself. The radiator only transfers the thermal energy it receives, but does not generate it. Only those people who have poorly mastered the school physics course can talk about saving money when installing vacuum heating radiators.
Heating radiators Kazan.
In a conventional system, if the installation rules are followed and the design is correct, air locks do not occur. To prevent their formation, a modern analogue of the Mayevsky tap is installed - an automatic valve for releasing air.
Product selection rules
With the growing popularity of this high-tech equipment, there are more and more low-quality counterfeits on the market.
When purchasing, you should check whether the appropriate certificates and other technical documentation are included with the device. It should be remembered that the basic rule for effective operation of the unit is complete tightness.
Another important parameter for the radiator is the amount of coolant in the vertical sections - the lithium-bromide mixture. A large volume may result in liquid overflow.
To assess the compliance of the volume, you need to focus on the sound that occurs when the unit rocks. It should resemble a soft rustling sound. If the sound of flowing liquid is clearly distinguishable, the radiator, with a high degree of probability, may turn out to be a handicraft fake.
European manufacturers provide a guarantee of up to 5 years for most of their models. Their prices are directly proportional to the number of sections and they are higher than for water analogues
On products manufactured using factory technology, the welding seams do not have any flaws, unlike units of unknown origin.
Manufacturers with a good reputation cover product bodies with high-quality powder paint. Therefore, the integrity of the paint layer is difficult to damage even when in contact with a solvent. You should not miss such a moment as the tightness of the filling valve.
DIY installation subtleties
Installing a vacuum radiator is not difficult, but in order to avoid any alterations, you need to learn a few rules. It is necessary to follow the recommendations regarding the placement of the unit relative to the wall, floor, and window sill.
At the same time, the distance between the radiator and the wall is at least 50 mm, between the device and the floor - from 20 to 50 mm, the optimal distance to the back of the window sill is 50-100 mm.
The photo shows options for connecting radiators. You should be aware that the inclusion of other heating devices in the heating circuit, along with vacuum ones, reduces its efficiency
The installation itself is not much different from inserting other types of radiators into the system. The only difference is that the entrance and exit are at the bottom.
Installation of a vacuum unit involves a chain of actions following each other:
- Drain the coolant and dismantle the old heating device.
- Mark the installation sites.
- Attach the brackets. They are tested for stability and strength.
- Ball valves are installed. Through them the device is connected to the main line. The joints must be sealed using tow or sealant.
- Check the system for leaks.
To improve heat transfer, you can place a sheet of foil on the wall behind the radiator. If you have previously completed thermal insulation, you will have to increase the length of the brackets by an amount equal to the thickness of the thermal insulation layer. If the house is insulated, the efficiency of the heating system will increase.
Results
In what cases is it recommended to install a vacuum system for heating a home? With the exception of positive reviews about vacuum heating radiators, the installation of a solar system or expansion tank of the described type are auxiliary mechanisms for improving or optimizing the operation of the heating system.
A powerful vacuum pump for heating will improve water circulation, but will directly affect the thermal regime. The coolant simply does not have time to cool down sufficiently, which is unacceptable for a water heated floor - mixing flows will not lower the temperature to the required level.
When selecting and installing other elements of vacuum heating, their features should be taken into account.
Vacuum radiators
Installed electric vacuum radiator
In addition to the thermal power, the rules for installing vacuum heating radiators in a private home are observed.
The minimum distance from the heating surface to the window sill should be 8 cm. Moreover, the level from the floor to the bottom of the radiator also cannot be less than 4 cm. To improve heat transfer, it is recommended to install heat-reflecting materials on the wall behind the radiator.
Solar collectors
In some models, instead of a special liquid, you can use plain water. However, the efficiency of such installations is an order of magnitude lower than that of those described above. This point must be clarified with the seller.
Vacuum expansion tanks
Before making structures yourself, you need to choose the right material. It is best to use stainless or galvanized steel. But it should be taken into account that to weld it you need to use a special apparatus operating in a certain mode. The best way out of this situation is to purchase a suitable factory-made container and slightly modernize it by installing the necessary pipes for connection to the heating pipeline.
The video material clearly shows the operating principle of vacuum heating radiators:
The best manufacturers of vacuum radiators
Vacuum heating devices do not yet have a wide range of heating devices on the market. EnergyEco products enjoy special authority among consumers . This Russian manufacturer uses 1.5 mm steel to make batteries. Users note high-quality performance, good heat dissipation - about 170 kW per element.
The working pressure for the radiator is from 0.6 to 1.3 MPa. Even at 2 MPa the device can work, but 5 MPa is too much for it - it begins to collapse. The cost of a radiator from EnergyEko is considerable, but the demand for it does not fall.
The manufacturer Forvacuum produces wall-mounted and baseboard-type vacuum devices. The heat output of a register 1 m long at a coolant temperature of 50 °C is 239 W.
The thermosiphon register has a low metal consumption, since its thin-walled body is not designed for high internal pressure. At 50 °C and using ethanol it is only 0.027 MPa
You can also find Chinese-made radiators on the market. They will have a lower price, but sometimes of dubious quality. When purchasing, you should carefully inspect them and check the documentation.
Infrared heating of a private home: types of heaters and their application
There are several models of infrared heaters on sale with different technical characteristics. For example, short-wave devices are equipped with an open heating element, which heats up to 600 - 700 degrees, so they are unlikely to be suitable for small rooms; they are rather intended for large open spaces - balconies and terraces. The interior of the house is ideally heated by long-wave heaters with closed heating elements, the temperature of which reaches 200 - 250 degrees and their body almost does not heat up.
Infrared heaters must be equipped with thermostats that are designed to maintain a comfortable temperature in the room. Thermostats should be installed at a height of about one and a half meters from the floor and at some distance from the window.
Safety comes first!
Typically, consumers of all kinds of heating devices pay attention to the appearance of the devices. Another important criterion is heat transfer. Next comes the service life. After all, for some reason many people still believe that metal devices last a very long time.
A very important aspect of purchasing a heating device is its safety. Unfortunately, very few consumers are interested in this particular criterion when purchasing.
Very much in vain. Of course, such cases do not occur so often when, due to the rather low quality of heating radiators, all plugs, seals and fittings cannot withstand the pressure of the system or the aggressiveness of the coolant.
Operating principle of the heating device
And if this happens, then the financial costs of restoration will be measured in tens of thousands of rubles. Unfortunately, only those consumers who have already been taught by life think about security issues seriously.
A vacuum heating radiator is a safe device from this point of view. This is achieved through several aspects of the work:
Water heating radiators
- Minimum connections. The devices simply do not have nipples, plugs, gaskets, Mayevsky taps and other elements. The design of the device is a monolithic body that has two threaded connections to connect the heating system. It is very difficult to depressurize such a device.
- There is very little traditional coolant in a vacuum radiator. Even if there is mechanical damage, there will simply be no place for a flood in the room to come from.
- Hydraulic pressure in vacuum heating radiators is only at the bottom. This is where the through pipe passes for the coolant to flow. The pressure inside the battery in the area of the secondary coolant is very low. If it is 70 degrees on the convection surface, then it will only be no more than 0.78 atmospheres.
So, if the system suddenly depressurizes, the only trouble will be that the heating device itself will fail.