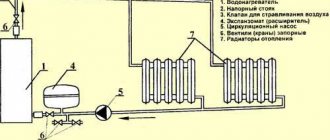
The basis of any heating is a boiler. Whether the house will be warm depends on how correctly its parameters are selected. In order for the parameters to be correct, it is necessary to calculate the boiler power. These are not the most complex calculations - at the third grade level, you will only need a calculator and some data on your possessions. You can handle everything yourself, with your own hands.
There are several ways to calculate the power of a heating boiler
General points
In order for the house to be warm, the heating system must replenish all existing heat losses in full. Heat escapes through walls, windows, floors, and roofs. That is, when calculating the boiler power, it is necessary to take into account the degree of insulation of all these parts of the apartment or house. With a serious approach, they order a calculation of the building’s heat loss from specialists, and based on the results, they select the boiler and all other parameters of the heating system. This task is not to say that it is very difficult, but it is necessary to take into account what the walls, floor, ceiling are made of, their thickness and the degree of insulation. They also take into account the cost of windows and doors, whether there is a supply ventilation system and what its performance is. In general, a long process.
There is a second way to determine heat loss. You can actually determine the amount of heat that a house/room loses using a thermal imager. This is a small device that displays the actual picture of heat loss on the screen. At the same time, you can see where the outflow of heat is greater and take measures to eliminate leaks.
Determining actual heat loss - an easier way
Now let’s talk about whether it’s worth taking a boiler with a power reserve. In general, constant operation of equipment at the limit of its capabilities negatively affects its service life. Therefore, it is advisable to have a performance reserve. Small, about 15-20% of the calculated value. It is quite enough to ensure that the equipment does not work at the limit of its capabilities.
Too much stock is not economically profitable: the more powerful the equipment, the more expensive it is. Moreover, the price difference is significant. So, if you are not considering the possibility of increasing the heated area, you should not take a boiler with a large power reserve.
Solid propellant
How to heat a house if there is no gas in your village?
The holder of an honorable second place in terms of cheapness of heating is a solid fuel boiler. Traditional boilers of this type have a fairly high rated thermal power and allow it to be regulated in a way as ancient as the world - by limiting the access of oxygen (in other words, by a covered ash pan, which at the same time serves as an ash pit door).
Construction of a solid fuel boiler
Technological progress has made very minor changes to the design of a traditional heating device: the only difference is that in modern boiler models, the ash door is controlled via a chain by a mechanical thermostat.
Traditional solid fuel stove with mechanical thermostat
Restricting the access of oxygen to the firebox has one negative consequence - incomplete combustion of fuel. Gaseous products of combustion of wood or coal contain many volatile hydrocarbons. When the boiler vent is closed, your money literally flies down the drain.
So-called pyrolysis (or gas generator) boilers and furnaces do not have this drawback.
Gas generator from Viessmann
The combustion process of solid fuel is divided into two stages:
- Initially, it smolders in the firebox with limited access to oxygen. The products of incomplete combustion are carbon monoxide and those same volatile hydrocarbons;
- Then, in a separate chamber, atmospheric air is mixed with the products of incomplete combustion. They burn, giving up their heat to the heat exchanger and at the same time supporting the smoldering process of firewood or pellets in the primary firebox.
Calculation of boiler power by area
This is the easiest way to select a heating boiler by power. When analyzing many ready-made calculations, an average figure was derived: heating 10 square meters of area requires 1 kW of heat. This pattern is valid for rooms with a ceiling height of 2.5-2.7 m and average insulation. If your house or apartment fits these parameters, knowing the area of your house, you can easily determine the approximate performance of the boiler.
Heat flows out of the house in different directions
To make it clearer, we give an example of calculating the power of a heating boiler by area. There is a one-story house 12*14 m. Find its area. To do this, multiply its length and width: 12 m * 14 m = 168 sq.m. According to the method, we divide the area by 10 and get the required number of kilowatts: 168 / 10 = 16.8 kW. For ease of use, the figure can be rounded: the required heating boiler power is 17 kW.
Taking ceiling heights into account
But in private homes, ceilings may be higher. If the difference is only 10-15 cm, it can be ignored, but if the ceiling height is more than 2.9 m, you will have to recalculate. To do this, find a correction factor (dividing the actual height by the standard 2.6 m) and multiply the found figure by it.
Example of correction for ceiling heights . The building's ceiling height is 3.2 meters. It is necessary to recalculate the power of the heating boiler for these conditions (the parameters of the house are the same as in the first example):
- We calculate the coefficient. 3.2 m / 2.6 m = 1.23.
- Let's correct the result: 17 kW * 1.23 = 20.91 kW.
- Rounding up, we get 21 kW required for heating.
When choosing a boiler based on power, do not forget that with increasing power, the size of the unit also increases
As you can see, the difference is quite significant. If you do not take it into account, there is no guarantee that the house will be warm even at average winter temperatures, let alone severe frosts.
Accounting for region of residence
Something else worth considering is the location. After all, it is clear that in the south much less heat is required than in the Middle Zone, and for those who live in the north, the “Moscow region” power will clearly be insufficient. There are also coefficients to take into account the region of residence. They are given with a certain range, since within one zone the climate still varies greatly. If the house is located closer to the southern border, a smaller coefficient is used, closer to the northern - a larger one. It is also worth considering the presence/absence of strong winds and choosing a coefficient taking them into account.
- Central Russia is taken as a standard. Here the coefficient is 1-1.1 (closer to the northern border of the region it is still worth increasing the boiler power).
- For Moscow and the Moscow region, the result obtained must be multiplied by 1.2 - 1.5.
- For northern regions, when calculating the boiler power by area, the found figure is multiplied by 1.5-2.0.
- For the southern part of the region, the reduction coefficients are: 0.7-0.9.
It is also necessary to take into account your region of residence
Example of adjustment by zones. Let the house for which we calculate the boiler power be located in the north of the Moscow region. Then the found figure of 21 kW is multiplied by 1.5. Total we get: 21 kW * 1.5 = 31.5 kW.
As you can see, when compared with the original figure obtained when calculating by area (17 kW), obtained as a result of using only two coefficients, it is significantly different. Almost twice. So these parameters need to be taken into account.
Double-circuit boiler power
Above we discussed calculating the power of a boiler that only works for heating. If you also plan to heat water, you need to increase the productivity even more. When calculating the power of a boiler with the ability to heat water for domestic needs, 20-25% of the reserve is included (must be multiplied by 1.2-1.25).
To avoid having to buy a very powerful boiler, you need to insulate the house as much as possible
Example: we adjust for the possibility of DHW. We multiply the found figure of 31.5 kW by 1.2 and get 37.8 kW. The difference is significant. Please note that the reserve for water heating is taken after the location is taken into account in the calculations - the water temperature also depends on the location.
How to choose economical fuel
The most economical energy carrier is the one that is most accessible. This also applies to what is commonly believed to be cheap gas. If this blue fuel is supplied from the main line, it is inexpensive. But only if the pipeline runs close. Otherwise, the connection will cost a hefty sum, which will affect the final cost of heating. Liquefied gas will cost even more. Perhaps the price per cubic meter is not too different from the main one, but the cost of arranging a storage capacity is always very high.
Therefore, it is cheaper to use the energy carrier that is most accessible. So, if there is a coal mine nearby, coal will do; if there are a lot of forests nearby, firewood or pellets will do. At the same time, you need to think through the nuances of its use. Sometimes the difficulties in installing or operating heating equipment, the high cost of storing or delivering energy outweigh the benefits of using the cheapest fuel. Then they choose a more expensive, but also more convenient option.
In general, if you consider the total cost of obtaining a unit of heat, the cheapest option is main gas. Further, in ascending order, you can put pellets, coal, firewood, liquefied gas, diesel fuel and the most expensive - electricity.
Features of calculating boiler performance for apartments
Calculation of boiler power for heating apartments is calculated according to the same norm: 1 kW of heat per 10 square meters. But the correction is taking place according to other parameters. The first thing that needs to be taken into account is the presence or absence of an unheated room above and below.
- if there is another heated apartment below/above, a coefficient of 0.7 is applied;
- if the room below/at the top is unheated, we do not make any changes;
- heated basement/attic - coefficient 0.9.
When making calculations, it is also worth taking into account the number of walls facing the street. Corner apartments require more heat:
- if there is one external wall - 1.1;
- two walls face the street - 1.2;
- three external ones - 1.3.
You need to take into account the number of external walls
. These are the main areas through which heat escapes. It is imperative to take them into account. You can also take into account the quality of the windows. If these are double-glazed windows, adjustments need not be made. If there are old wooden windows, the found figure must be multiplied by 1.2.
You can also take into account factors such as the location of the apartment. In the same way, you need to increase the power if you want to buy a double-circuit boiler (for heating hot water).
Calculation by volume
In the case of determining the power of a heating boiler for an apartment, you can use another method, which is based on SNiP standards. They stipulate standards for heating buildings:
- heating one cubic meter in a panel house requires 41 W of heat;
- to compensate for heat loss in a brick building - 34 W.
To use this method, you need to know the total volume of the premises. In principle, this approach is more correct, since it immediately takes into account the height of the ceilings. A slight difficulty may arise here: usually we know the area of our apartment. The volume will have to be calculated. To do this, we multiply the total heated area by the height of the ceilings. We get the required volume.
Heating boiler calculations for apartments can be done according to standards
An example of calculating the power of a boiler for heating an apartment. Let the apartment be on the third floor of a five-story brick building. Its total area is 87 sq. m, ceiling height 2.8 m.
- Finding the volume. 87 * 2.7 = 234.9 cu. m.
- Round up - 235 cubic meters. m.
- We calculate the required power: 235 cubic meters. m * 34 W = 7990 W or 7.99 kW.
- Round up, we get 8 kW.
- Since there are heated apartments at the top and bottom, we apply a coefficient of 0.7. 8 kW * 0.7 = 5.6 kW.
- Round up: 6 kW.
- The boiler will also heat water for domestic needs. We will give a reserve of 25% for this. 6 kW * 1.25 = 7.5 kW.
- The windows in the apartment have not been replaced; they are old, wooden. Therefore, we use a multiplying factor of 1.2: 7.5 kW * 1.2 = 9 kW.
- Two walls in the apartment are external, so once again we multiply the found figure by 1.2: 9 kW * 1.2 = 10.8 kW.
- Round up: 11 kW.
In general, here is this technique for you. In principle, it can also be used to calculate the power of a boiler for a brick house. For other types of building materials, standards are not prescribed, and a panel private house is a rarity.
Solar collectors
In regions with a lot of sunny days, solar energy can be utilized for heating needs. A collector with an area of 2 square meters can produce up to 8 kilowatt-hours of absolutely free heat per day.
One or more collectors are connected as an additional heat source and significantly reduce the load on the main boiler.
Homemade flat-plate collectors
Connecting collectors to heating and hot water systems
Step number nine: If your area experiences clear winter weather, use solar heat to heat your home.
What is energy and how is it different from heat?
Heat, or the amount of heat, is part of the internal energy of a body that spontaneously, without external influence, moves from bodies that are more heated to bodies that are less heated through thermal conductivity or radiation (due to electromagnetic radiation).
Thermal conduction can occur through a solid body and due to convection currents. Thus, we have three ways of heat transfer:
- radiant;
- on a solid body;
- convection.
The most effective method of heat transfer is radiant, since it is possible to achieve a maximum temperature gradient between cooled and heated bodies, up to several thousand degrees and, accordingly, high heat transfer rates.
In what units is energy measured?
It is measured in joules, calories and watts.
Historically, physicists count work, energy, and the amount of heat in joules. Heating engineers calculate heat for heating a home in calories, while electricians and power engineers calculate energy in watts. Calories are heat flow because this energy is counted over a certain time.
It is very important to understand that energy can be spent in different ways: it can be quickly, or it can be slowly.
The heat meter counts the gigacalories of thermal energy spent per month, and the electric meter counts the watts of electrical energy spent per month. But not just watts, but kilowatts (kW) spent in one hour (kW/hour).
Heating costs with a diesel boiler room
Next, let's look at a diesel boiler room. Similarly, we calculate the thermal capacity of 1 liter of diesel fuel using the following indicators:
- The calorific value of 1 kg of diesel fuel is 11,860 kW/h;
- Density of diesel fuel – 0.86 kg/l;
- The calorific value of 1 liter of diesel fuel is 10.20 kW/h;
- The efficiency of a diesel boiler is 0.9.
- The efficiency of a diesel boiler is slightly lower, it is about 90%.
- The average cost of 1 liter of diesel fuel in Moscow is 36.8 rubles.
We substitute all the initial data into the formula:
Cost of 1 liter of diesel fuel / (calorific value of 1 liter of diesel fuel x efficiency)
and we find that the cost of 1 kW/h of heat from diesel fuel is 4.01 rubles.