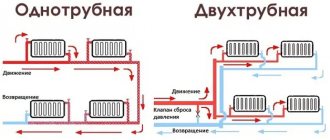
How to calculate heating by area?
Often, 100 W of thermal energy is taken as a norm per 1 m2 of area - this is considered the simplest method for those who calculate heating
according to the volume of the room with your own hands. For calculations, use the formula Q = S×100, where: Q is the required thermal power for the room; S – room area (m²);
Interesting materials:
How to create 2 accounts on Instagram? How to create a DM group on Instagram? How to create a group in Direct on Instagram? How to answer several questions at once on Instagram? How is the text in bold on Instagram? How to remove alt text on Instagram? How to remove black background on Instagram? How to remove from your feed on Instagram? How to remove from temporarily blocked on Instagram? How to remove online on Instagram on iPhone?
Apartment-by-apartment and general-house standards for utility consumption
Let's look at what the thermal energy consumption standard is and how it is calculated. The procedure for calculating and setting heating standards is regulated by Government Decree No. 306. General provisions and formulas for calculating heat supply, taking into account the presence or absence of metering devices, are established by Government Decree No. 354.
According to clause 10 of PP No. 306, standards are established in relation to individual consumption of utilities and maintenance of the common property of an apartment building. Owners who have not installed meters pay for heating according to standards that involve calculating the average rate of heat energy consumption.
The calculation formula takes into account the following features:
- the presence of a common house meter (read more about heat meters for heating here);
- number of installed individual metering devices;
- billing period: 12 calendar months or according to the heating season schedule.
The standards are established by regional regulations and, as of 2022, apply to apartment buildings that do not have individual or communal meters installed. If a house has a communal meter installed, but no individual meters are installed, then the calculation is made in accordance with its indicators. Owners with private ownership pay for heating according to individual requirements.
Important! Based on PP No. 603, increasing coefficients are not applied to consumers who have not installed IPU in residential premises when calculating heating fees.
There are also separate rules that regulate the commercial metering of thermal energy and coolant. This document describes in detail the requirements for individual investment management, accounting methods, and much more.
Who installs them?
Based on clause 9 of PP No. 306, average standards for thermal energy consumption per 1 sq. m has the right to establish:
- regional executive authorities;
- resource supply organizations;
- management companies;
- housing cooperatives;
- partnership.
The establishment of standards at the initiative of the management company or resource supplying organization is carried out on the basis of a collective application to the authorized body and is considered within 30 days.
Legislative documents: SNiP 41-01-2003, SP 41-108-2004 and others
The table shows a list of regulatory documents governing the requirements for the construction and quality control of heating systems, taking into account the latest changes as of 2022:
| Normative act | Date of introduction | A comment |
| SNiP 2.04.05-91 | 01.01.1992 | General requirements for ventilation, heating and air conditioning systems, canceled as of 01/01/2004. |
| SNiP 41-01-2003 | 01.01.2004 | Regulates the parameters of internal air, requirements for heating systems, heat supply, fittings, pipeline laying, features of the installation of stove heating, updated version of SNiP 2.04.05-91, not valid from 01/01/2013. |
| SP 60.13330.2012 | 01.01.2013 | Updated version of SNiP 41-01-2003. |
| SP 41-108-2004 | 01.01.2005 | Regulates the requirements for the selection and placement of heat generators, features of gas supply and disposal of combustion products, installation of electricity and heating in apartment buildings. |
| SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 | 10.06.2010 | Hygienic requirements for heating systems. |
| GOST R 56501-2015 | 01.03.2016 | Regulates the management of heat supply systems, the specifics of providing consumers with communal heating resources, requirements for quality control and repair maintenance. |
| GOST 30494-2011 | 01.03.2011 | Features of setting the temperature regime, quality control and measurement procedure. |
| SNiP 41-02-2003 | 01.09.2003 | Features of arrangement of heating networks, quality control. |
| SNiP 01/31/2003 | 01.10.2003 | Some requirements for the placement of heating systems in apartment buildings. |
| Government Decree No. 354 | 06.05.2011 | Features of the provision of utility services for heat supply. |
We calculate the consumption of an electric boiler
You can find out complete information on the selection, operation and maintenance of gas boilers from all manufacturers if you go.
One of the decisive questions in choosing this device is how much it will cost to heat a house with an electric boiler. After all, you can save on the cost of the device itself, and then pay huge bills. To prevent this from happening, consider the following table.
Difference in consumption of ion and heating element boilers.
We will give an example for an inverter and induction boiler, the area of the heating room is a house of 240 m2, with a standard ceiling height of 3 m, where there are good plastic windows, doors with good thermal insulation, the house itself is insulated.
And then, we will give a more specific example with numbers on how to calculate the consumption of an electric boiler, provided that your entire system is connected, the batteries are installed, in general, everything is ready for use. And let’s try to figure out whether a heating element electric boiler or an induction one is beneficial.
Initial data:
Duration of operation is 10 hours, during the day it was heated to the set temperature and turned off. To begin with, we will calculate the invert one, and also take into account the fact that over time its efficiency decreases significantly.
The first year of heating will be the most efficient and least expensive. 24 (power)*10 (operating time)*30 (days per month)*7.2 (cost of electricity) = 19,450 rubles per month or 136 thousand rubles for 222 days.
In the 2nd year, energy consumption will increase by an average of 15%, the heating duration will increase by an hour and a half and, based on these data, the monthly amount is 22,400 rubles, and for the heating season you will have to pay 156,500 rubles for electricity.
In the 3rd operational year, the heating element “wears out” even more and losses will be up to 18%, and the operating time will increase by three hours compared to the first year. The energy consumption will be 24 kW, and the energy output will be 16 kW. However, with proper care, timely cleaning and necessary operational measures, these indicators can increase with less intensity.
Next, let's look at an example in numbers with an induction double-circuit boiler. All data is the same as in the first case. 20 (power)*240 (room area)*30 (calendar month)*2.7 (tariff)*10 (operation duration)=16,200 rub. per month, and for the entire season 113,402 rubles.
An undoubted advantage is the fact that the amount will remain unchanged in subsequent years, provided that the established tariff does not change and electricity consumption remains constant, unlike the first example. The efficiency does not decrease after the service life expires, since there is no scale formation.
If you were in doubt before, then from the calculations it becomes obvious that this boiler is more profitable.
Well, for comparison, let’s give an example of how much electricity a gas boiler consumes. To operate the pump, it needs 60 W, during ignition it consumes about 120 W, and if there is a closed combustion chamber for the fan to operate, another plus 30 W. In total, by adding up all the needs of a particular unit, you will get the total amount of energy consumption for gas equipment.
Convert Gcal to kW/hour
Thermal energy can be measured in various units, but in official documentation from housing and communal services it is calculated in Gcal. Therefore, it is worth knowing how to convert other units to gigacalories.
The easiest way to do this is when the relationships between these quantities are known. For example, it is worth considering watts (W), in which the energy output of most boilers or heaters is measured.
Before considering the conversion to this Gcal value, it is worth remembering that, like a calorie, a watt is small. Therefore, kW (1 kilowatt equals 1000 watts) or mW (1 megawatt equals 1000,000 watts) are more often used.
In addition, it is important to remember that power is measured in W (kW, mW), but kW/h (kilowatt-hours) is used to calculate the amount of electricity consumed/produced. In this regard, it is not the conversion of gigacalories to kilowatts that is considered, but the conversion of Gcal to kWh.
How to do this? In order not to suffer with formulas, it is worth remembering the “magic” number 1163. This is exactly how many kilowatts of energy must be spent in an hour to get one gigacalorie. In practice, when converting from one unit of measurement to another, you simply need to multiply the number of Gcal by 1163.
For example, let's convert into kW/hour 0.05 Gcal required to heat one cubic meter of water by 50 °C. It turns out: 0.05 x 1163 = 58.15 kW/hour. These calculations will especially help those who are thinking about changing gas heating to more environmentally friendly and economical electric heating.
If we are talking about huge volumes, we can convert it not into kilowatts, but into megawatts. In this case, you need to multiply not by 1163, but by 1.163, since 1 mW = 1000 kW. Or simply divide the result obtained in kilowatts by a thousand.
Why do we pay for heat supply in EPD in summer?
The Unified Payment Document (UPD) contains accounts for various sectors of the housing sector, including utility costs for the use of heat in the summer. Tenants justifiably have a question: why do I pay for heat supply in the summer, while the heating season is within autumn-spring.
The legislation of the Russian Federation allows for the collection of payments for heat supply in two ways:
- in equal monthly installments;
- only in winter.
Most often, management companies use the first method, since it allows the monthly payment amount to be “spread out” evenly. When accrued using the second method, the costs of the home budget during the heating season will increase significantly, and the rest of the time will not be charged.
You cannot blindly trust the amounts written on the receipt. If there are any doubts about the integrity of housing and communal services representatives, it is best to make independent simple calculations using a calculator using the above calculation methods. If a discrepancy is identified, contact the utility company with a request to issue an invoice again.
Changes in norms planned in Russia
According to TASS, from 2022 the calculation of the heat consumption standard will depend on the number of floors. The new system was planned to be implemented in 2016, however, at the request of members of the State Duma committee, the project was postponed to 2022. According to the new regulations, the Gcal norm is established depending on the following conditions:
- house material: brick, stone, concrete, wood;
- year of construction: before 1999, after 1999;
- number of floors
According to clarifications from the press service of the Russian Ministry of Construction, the application of new payment conditions will be the right of regional authorities, but not an obligation. As of 2022, the new procedure is not regulated by law, but is already applied in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, for example, in Krasnoyarsk (Resolution of the Government of the Krasnoyarsk Territory No. 137-p).
In Russia, heating is traditionally turned on and off based on weather conditions. But there are often cases when there is no heat supply despite the environment. Read our materials about the reasons for the lack of heating in an apartment and what to do in this situation, the temperature chart and standards for heating water in radiators, and also find out what to do if the battery leaks and who should repair and replace radiators and risers in apartments.
What is a Gigacalorie and how many calories are in it?
The concept of Gigacalories is most often found in documents in the field of thermal power engineering. This value can be found in receipts, notices, payments for heating and hot water.
It means the same thing as a calorie, but in a larger volume, as evidenced by the prefix “Giga”. Gcal determines that the original value has been multiplied by 109. In simple terms: 1 Gigacalorie contains 1 billion calories.
Like the calorie, the Gigacalorie does not belong to the metric system of physical quantities.
The table below shows an example comparison of values:
| Console | Number of calories |
| kcal (kilocalorie) | 1 000 |
| Mcal (megacalorie) | 1 000 000 |
| Gcal (gigacalorie) | 1 000 000 000 |
The need to use Gcal is due to the fact that when heating the volume of water needed for heating and household needs of the population, even 1 residential building releases a colossal amount of energy. Writing numbers denoting it in documents in calorie format is too long and inconvenient.
A value such as a gigacalorie can be found in payment documents for heating
You can imagine how much energy is spent during the heating season on an industrial scale: when heating 1 block, district, city, country.
Requirements for heat supply systems
The legislation of the Russian Federation imposes sanitary, epidemiological and fire safety requirements for heating systems. For safety reasons, heating devices comply with SanPin and SNiP regulations.
We talked more about the rules for organizing heat supply in a separate article.
Hygienic
When installing heating systems, optimal indoor microclimate conditions and air quality are taken into account.
Hygienic requirements are regulated by Section IV SanPin 2.1.2.2645-10 and governs the following conditions:
- no odor;
- uniform air distribution;
- no toxic emissions during operation;
- accessibility for repairs, cleaning and maintenance;
- absence of noise (what are the causes of noise in radiators?).
The temperature does not exceed 90 degrees. Systems heating above 75 degrees are equipped with protective guards. The concentration of chemicals in the air during operation of heat supply systems does not exceed the established safe exposure level.
Fire protection
Fire safety requirements for the construction and operation of heating systems in apartment buildings are regulated by SP 60.13330.2012. For safety reasons, hot water or steam is used as a coolant. In climatic regions with low temperatures, non-explosive substances are used to prevent the liquid from freezing.
In apartment buildings with a height of more than 9 floors, the installation of heat generators operating on gaseous fuel is allowed. Gas supply systems are equipped with automatic systems that shut off the supply of fuel in emergency situations. According to the standards, heat generators are installed in apartments that produce no more than 35 kW of heat. The total heating output does not exceed 100 kW.
This is the ratio of Kal and Gcal to each other.
1 Cal 1 hectoCal= 100 Cal 1 kiloCal (kcal)= 1000 Cal 1 megaCal (Mcal)= 1000 kcal = 1000000 Cal 1 gigaCal (Gcal)= 1000 Mcal = 1000000 kcal = 1000000000 Cal
When they say or write on receipts, Gcal - we are talking about how much heat was supplied to you or will be supplied for the entire period - this could be a day, a month, a year, a heating season, etc. When they say or write Gcal/hour, this means how much heat they will release to you and me in one hour. If the calculation is for a month, then we multiply these ill-fated Gcal by the number of hours per day (24 if there were no interruptions in heat supply) and days per month (for example, 30), but also when we actually received heat.