During operation, coolant leaks may occur from the heating system circuit.
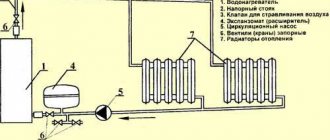
After the elevator, the return line will also be counted. Logbook for recording instrumentation, issuing work permits, operational records, recording defects identified during inspection of installations and networks, testing knowledge, as well as briefings. Diagram of a heating unit Adjustment of the coolant supply is carried out by the elevator heating units of the house. How do heating points work in apartment buildings? The hot water supply is made up from the cold water supply system. Water in the circulation circuit moves in a circle through circulation pumping equipment for hot water supply from the heating point to consumers and back. Overall it's worth it!
The heating system is also a closed loop through which the coolant moves with the help of circulation pumps from the heating point to consumers and back. The project budget is million. In it, it is heated by network water coming from the supply pipeline of the external network. Constant flow of hot network water is ensured by an automatic flow regulator PP. For such a unit to operate, it is necessary to have a sufficiently high power source of electricity.
ITP check
Independent (closed) heating system
Currently, when installing new boiler houses, an independent connection scheme for the heating system has become more often used.
It contains a main and an additional circulation circuit, hydraulically separated by a heat exchanger. That is, the coolant from the boiler room or thermal power plant goes to the central heating point, where it enters the heat exchanger, this is the main circuit. The additional circuit is the heating system of the house; the coolant in it circulates through the same heat exchanger, receiving heat from the network water from the boiler room. The operating diagram of the independent system is shown in the figure: For reference. Previously, bulky shell-and-tube heat exchangers were installed in such systems, which took up a lot of space. This was the main difficulty, but with the advent of high-speed plate heat exchangers, this problem ceased to exist.
But what about the centralized supply of hot water, because now you can’t take it from the mains, the temperature there is too high (from 105 to 150 ºС)? It's simple: an independent connection diagram allows the installation of any number of plate heat exchangers connected to the main pipelines. One will provide heat to the heating system of the house, and the second can prepare water for household needs. How this is implemented is shown in the diagram:
To ensure that hot water always flows at the same temperature, the DHW circuit is made closed with automatic replenishment in the return pipeline. In apartment buildings, the DHW circulation return line can be seen in the bathroom; heated towel rails are connected to it.
It is obvious that operating an independent heating system has many advantages:
- the home heating circuit does not depend on the quality of the external coolant, the condition of the main networks and pressure drops. The entire load falls on the plate heat exchanger;
- it is possible to regulate the temperature in the rooms using thermostatic valves;
- the coolant in a small circuit can be filtered and cleaned of salts, the main thing is that the pipes are in good condition;
- The hot water supply system will contain drinking quality water entering the house through the water main.
However, due to dirty, low-quality coolant in the central network, periodic flushing of the independent heating system, or more precisely, the plate heat exchanger, will be required. Fortunately, this is not so difficult to do. Another disadvantage is the higher costs of purchasing equipment, namely: heat exchangers, circulation pumps and shut-off and control valves. But a closed system is more reliable and safer than an open one, it better meets modern requirements and is better adapted to new equipment.
Approval for operation
To prepare an individual heating point in a house for permission to operate, you must submit the following list of documents to Energonadzor:
- Current technical conditions for connection and a certificate of their implementation from the energy supply organization.
- Project documentation with all necessary approvals.
- An act of responsibility of the parties for operation and division of balance sheet, drawn up by the consumer and representatives of the energy supply organization.
- Certificate of readiness for permanent or temporary operation of the subscriber branch of the heating point.
- ITP passport with a brief description of heat supply systems.
- Certificate of readiness for operation of the thermal energy meter.
- A certificate confirming the conclusion of an agreement with an energy supply organization for heat supply.
- Certificate of acceptance of completed work (indicating the license number and date of issue) between the consumer and the installation organization.
- Order on the appointment of a person responsible for the safe operation and good condition of heating installations and heating networks.
- List of operational and operational-repair persons responsible for servicing heating networks and heating installations.
- A copy of the welder's certificate.
- Certificates for the electrodes and pipelines used.
- Acts for hidden work, as-built diagram of the heating point indicating the numbering of the fittings, as well as diagrams of pipelines and shut-off valves.
- Certificate for flushing and pressure testing of systems (heating networks, heating system and hot water supply system).
- Job descriptions, fire safety and safety instructions.
- Operating Instructions.
- Certificate of admission to operation of networks and installations.
- Logbook for recording instrumentation, issuing work permits, operational records, recording defects identified during inspection of installations and networks, testing knowledge, as well as briefings.
- Order from heating networks for connection.
Open heating systems
Open heat supply systems are characterized by the fact that hot water is collected for consumer needs directly from the heating network, and it can be either full or partial. The remaining hot water in the system continues to be used for heating or ventilation.
With this method, the water consumption in the heating network is compensated by an additional amount of water that is supplied to the heating network. The advantage of an open heating system lies in its economic benefits. During the Soviet period, almost 50% of all heating systems were open type.
At the same time, one cannot discount the fact that such a heat supply system also has a number of significant disadvantages. First of all, this is the low sanitary and hygienic quality of water. Heating appliances and pipeline networks give the water a specific smell and color, various foreign impurities appear, as well as bacteria. Various methods are usually used to purify water in an open system, but their use reduces the economic effect.
An open heat supply system can be dependent by the method of connection to heating networks, i.e. connect through elevators and pumps, or connect according to an independent scheme - through heat exchangers. Let's look at this in more detail.
Dependent heat supply systems
Dependent heat supply systems are systems in which the coolant through a pipeline enters directly into the consumer’s heating system. There are no intermediate heat exchangers, heating points or hydraulic insulation. There is no doubt that such a connection scheme is understandable and structurally simple. It is easy to maintain and does not require any additional equipment, for example, circulation pumps, automatic regulation and control devices, heat exchangers, etc. Most often, this system attracts with its, at first glance, cost-effectiveness.
However, it has a significant drawback, namely, the inability to regulate heat supply at the beginning and end of the heating season, when excess heat appears. This not only affects the comfort of the consumer, but also leads to heat loss, which reduces its initially apparent efficiency.
When energy saving issues become relevant, methods for transitioning a dependent heat supply system to an independent one are developed and actively implemented, this allows heat savings of about 10-40% per year.
Independent heating systems
Independent heat supply systems are systems in which the heating equipment of consumers is hydraulically isolated from the heat producer, and additional heat exchangers of central heating points are used to supply heat to consumers.
An independent heat supply system has a number of undeniable advantages. This:
- the ability to regulate the amount of heat delivered to the consumer by regulating the secondary coolant;
- its higher reliability;
- energy-saving effect, with such a system heat savings are 10-40%;
- it becomes possible to improve the operational and technical qualities of the coolant, which significantly increases the protection of boiler installations from contamination.
Thanks to these advantages, independent heat supply systems have become actively used in large cities, where heating networks are quite extensive and there is a large variation in heat loads.
Currently, technologies for reconstructing dependent systems into independent ones have been developed and are being successfully implemented. Despite significant investment, this ultimately has its effect. Naturally, an independent open system is more expensive, but it significantly improves the quality of water compared to a dependent one.
Checking the operating status of the elevator unit
Malfunctions can be identified quite easily; you need to analyze the readings of pressure gauges installed at different control points.
Frequently, excessive clogging with small abrasive particles leads to excesses in work; this is expressed in a drop in pressure compared to previous values. Jumps are caused by the formation of corrosive deposits or incorrect operation of the nozzle.
Periodic cleaning of the mud traps will protect the elevator unit from many problems and troubles; to determine some malfunctions, you will need to check all components of the unit.
It is also necessary to inspect the grids when opening the drain valves, and if corrosion appears, it is better to immediately replace the elevator nozzle with a new one to avoid vertical misalignment of the system circuit.
Video on the topic
Features of work
The transition to a closed system requires financial investments, but these investments pay off in the future. The decision to make the transition is made by the overwhelming majority of companies providing heat supply services to the population. The organization of heat supply work is constructed in various ways; there may or may not be dependence on electrical energy.
A steel or cast iron boiler running on solid fuel can be used as a heat generator. The constant loading of flammable material becomes a significant disadvantage, however, compared to the temperature loss during a power outage, this does not seem to be a serious problem.
To ensure independent heating in a private home, the following technical solutions will help:
- bunker and transport belt (supply of firewood or sawdust, minus - the belt requires electricity to operate);
- pyrolysis boiler (solid fuel is burned at the first stage, and the resulting gas is burned at the second stage);
- top combustion boiler (capable of operating for about 5 days on one burner, a fan is required for operation).
It is impossible to automate the heating system using these methods without the use of electrical energy. An alternative is gas boilers equipped with a mechanical thermostat. If the temperature is lost, the gas supply and heating of the coolant are resumed.
The advantage of an independent heating scheme over an open one is clear, but there are nuances in organizing such a system. Options for creating heat supply using a closed model are characterized by diversity. There is no universal solution; for each specific case, special approaches are practiced; consultations with professionals will help you choose the appropriate option.
What does the cost depend on?
For efficient operation of IHP, it is important to calculate heat losses at the design stage, taking into account the individual characteristics of each room. Often the efficiency of a heating point depends on a certain sequence of equipment in the circuit.
The cost of ITP consists of taking into account various factors:
- Number and load of energy consuming systems.
- Difficulty of operation and functioning in given conditions.
- Total thermal load.
- Price for selected equipment.
You may also be interested in seals and plates for heat exchangers.
Types of circulation in heating circuits
To deliver heat to the batteries, you need to move the coolant heated by the boiler. Natural circulation is used in the heating system and forced movement of water using a circulation pump. Natural circulation is used in simple heating systems; it requires a minimum of equipment with minimal installation and operating costs.
To implement this method of moving the coolant, a change in the physical properties of water when heated is used. The speed of movement depends on the temperature difference and on the magnitude of hydraulic resistance, which is reduced by increasing the diameter of the pipes.
Open heating circuit
An open gravity heating system with natural circulation has undoubted advantages.
Advantages of open natural coolant circulation:
- simplicity and low installation costs;
- efficiency;
- easily converted into a system with forced circulation; the circulation pump is usually installed in the “return”.
Therefore, the heating system for a one-story house with natural circulation is very popular and is successfully used. The main disadvantages of such heating are high inertia. In addition, the presence of an open expansion tank determines the answer to the question - is it possible to pour antifreeze into the heating system of a house. You can fill it, but it will constantly evaporate, which will make the operation of the system unprofitable.
Closed heating circuit
The coolant in a closed heating system has no contact with atmospheric air. To compensate for thermal expansion, sealed membrane expansion tanks are installed. A closed heating system can have any design; it is equipped with a circulation pump to move the coolant. The absence of contact of the coolant with air significantly increases the service life of pipes and heating circuit equipment.
If during installation the slope of the pipes is provided, then in the absence of mains voltage and the bypass is switched, natural circulation will occur in the closed heating system of the house. Of course, the efficiency of the system will drop, but the heating will be operational and will continue to heat the home.
The main advantages of a closed heating system:
- the use of a sealed expansion tank eliminates the evaporation of liquid; in closed systems, antifreeze can be used as a coolant;
- the absence of contact between water and air protects circuit elements from internal corrosion;
- a closed heating circuit has low inertia and high efficiency;
- the use of a circulation pump allows you to reduce the diameter of the pipes and reduce the cost of purchasing them;
- for heated floors and complex branched circuits, an additional pump is installed in the heating system, which will ensure their efficient operation.
ITP for a single building
Designed to serve one residential building, administrative building, industrial premises. When designing ITP, ready-made block heating units can be used.
TsTP - central TP
They are designed to provide heating and hot water supply for microdistricts, several buildings, and large industrial enterprises. When creating central heating stations, block heating points can be used. Houses and buildings with ITP installed in them can be connected to the central heating point.
BTP - block heating point
BTP, or block heat substation, is a product completely ready for commissioning, which is used to create an ITP or central heating substation. The BTP is supplied assembled and is quickly connected to the heating network using flanges. To significantly reduce the costs of designing and installing an IHP or central heating point and simplify the design of the heating point itself, it is enough to buy a block heating point from a company specializing in the sale and maintenance of heat exchangers and BTP.
Dependent heat supply scheme
If you imagine the elevator unit of a residential building (you can see what it looks like in the photo), then it is arranged as follows:
- the elevator is separated from the heating main by inlet valves;
- behind them, at the supply and return points, valves or gate valves are located. Hot water supply is connected through them from the supply or return pipelines. Often in modern elevators there are two taps on the supply and return lines, which are separated by a retaining washer. Their purpose is to ensure constant circulation of hot water;
- after inserting the elements to provide DHW, there is a nozzle with a chamber where mixing is carried out. The flow of hotter liquid coming from the direct pipeline under high pressure heats up part of the water in the return and is sent for recirculation;
- house valves shut off the heating system of the building - they are open in winter and closed in the warm season.
Dependent and independent heating systems differ in that in the first version, water enters the hot water supply and heating systems directly from the heating main.
Advantages of the elevator
Some users argue that the elevator design is irrational, and it would be much easier to supply coolant at a lower temperature to consumers. In reality, this approach involves increasing the diameter of the main pipelines to supply colder water, which leads to additional costs.
It turns out that a high-quality design of a thermal heating unit makes it possible to mix with the supply volume of water a portion of the return water that has already cooled down. Despite the fact that some sources of elevator units of heating systems belong to old hydraulic units, in fact they are efficient in operation. There are also newer units that have replaced the elevator unit circuits. This heat supply scheme for an apartment building is more efficient and economical.
These include the following types of equipment:
- plate type heat exchanger;
- mixer equipped with a three-way valve.
Comparison of solutions
The dependent heating connection scheme has, in essence, only one advantage, but a very important one - low cost of implementation. You can assemble an elevator unit for a small cottage with your own hands from consumer-grade shut-off valves
The only thing noticeable against the background of wiring batteries around the house will be the cost of manufacturing the nozzle - the only exclusive one made, the diameter of which determines the thermal power of the elevator.
What are the assets of an independent scheme?
Incomparably more flexible adjustment of the coolant temperature for the heating system. It is enough just to reduce the flow of coolant through the heat exchanger - and the house will become colder.
- The practical consequence of flexible adjustment of heating to the needs of the home is efficiency. Relative to the dependent system, it is estimated at 10-40 percent.
- Finally, the main thing: in a dependent system we are forced to use water with a lot of pollution. It carries sand, scale and a lot of mineral salts.
There is no talk of using water as drinking water; moreover, in some regions it is undesirable to even wash with hot tap water. An independent circuit makes it possible to use purified water or even non-freezing coolants as a coolant.
It is not a problem to heat drinking water for DHW needs.
Advantages and disadvantages of connections
Dependent circuit
Dirty coolant in the main leads to damage to expensive radiators.
Water is supplied and supplied to heating and water supply from the heating main, which leads to a number of advantages:
- simplicity of design and inexpensive cost of subscriber devices;
- the ability of the system to withstand temperature fluctuations;
- smaller reinforcement diameter;
- economical coolant consumption;
- low operating costs.
Negative factors of using a dependent heating system include:
- Formation of dirt, rust and scale in lines. They enter aluminum and bimetallic devices and cause pipe ruptures.
- Frequent pressure fluctuations, water hammer due to reduced water intake. The phenomena can lead to ruptures of polymer reinforcement.
- Low quality coolant, despite cleaning and desalting in the boiler room.
- Difficulty in adjusting temperature even with full bore valves.
To remove blockages, additionally install a dirt trap on the mixer.
Independent circuit
With independent heating, it is possible to install a filter on the coolant and keep the radiators clean.
If there is a closed circuit, water from the plate heat exchanger can be supplied to any wiring. The dependent heat supply scheme has several advantages:
- the temperature of the coolant in the pipes is regulated by the user;
- good energy saving indicators;
- compatibility with any heat carrier;
- absence of impurities in the DHW main;
- the ability to purify and filter water in circuits;
- no risk of pressure surges and water hammer.
The disadvantages of an independent connection include:
- difficult maintenance;
- impossibility of self-repair;
- large financial costs for the organization.
An independent type main saves water consumption by 10-40%.
Independent heating system and its types
An independent heating system is divided, in turn, into two subtypes according to the implementation of the method of circulating energy in pipelines:
- Gravitational, otherwise called non-volatile. The liquid moves through the pipes due to the different densities of the cold and heated substances. Therefore, the heated carrier coming from the heat exchanger tends upward due to its lower specific gravity, while the cold carrier, on the contrary, settles at the lowest points of the heating main. This feature imposes several strict requirements for full functionality:
- The heat exchange device or hot water boiler, if the heating is autonomous, must be placed at the lowest point of the building. If radiators are also installed on this floor, you will have to install a pit below floor level.
- All horizontally laid pipelines should be mounted at a slope of two to three degrees in the direction of movement of the coolant in the pipe. That is, the feed will have a positive angle relative to the general vector, and the return will have a negative angle.
- To minimize the negative impact of hydraulic resistance, the bore diameter of the pipes must be large. For a two-story cottage with five to seven heated rooms, a diameter of 35 millimeters will be sufficient. The principle of more is better is in full effect here.
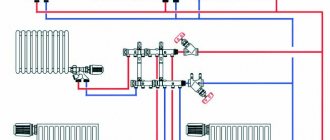
- Circulating or energy dependent. The coolants of the centralized supply system and the heat distribution hydraulics have no physical contact with each other. Heat transfer from one to another occurs in the so-called heat exchanger, which is a tank in which there are tubes with liquid circulating through them. That is, an independent connection of the heating system makes it possible to flexibly adjust the temperature regime of heated structures, simplify the modification and expansion of the network and save on heating costs. There are also features:
- The cost of construction significantly exceeds the cost of the first method.
- Increased demands are placed on the quality of secondary circuit coolants.
- There is almost always a need for a continuous power supply to ensure the circulation process.
Heating network pipes
Currently, domestic ones are in disrepair. Due to the high wear and tear of communications, it is cheaper to replace the pipes for the heating main with new ones than to engage in constant repairs.
It is impossible to immediately update all old communications in the country. During the construction or major renovation of houses, new pipes are installed to reduce heat loss several times. Pipes for the heating main are made using a special technology, filling the gap between the steel pipe located inside and the shell with foam.
The temperature of the transported liquid can reach 140°C.
Using polyurethane foam as thermal insulation allows you to retain heat much better than traditional protective materials.
Electricity addiction
Now let's return to energy dependence. When does a heating system need electricity to function, and when can it be done without?
Solid fuel boilers
The canonical solution is a conventional steel or cast iron boiler with a water jacket in the firebox and mechanical adjustment of the blower using a thermostat. This unit is completely energy independent.
The photo shows a classic solid fuel boiler.
However, this design has an important drawback: the boiler requires frequent loading of fuel. Three technical solutions allow you to make heating as independent from humans as possible:
- A hopper and a conveyor belt supply new portions of sawdust or pellets as the fuel burns out. Electricity is required at a minimum for the transporter to operate.
- A solid fuel pyrolysis boiler divides combustion into two stages: pyrolysis of wood with a limited supply of oxygen and combustion of the resulting gas. In this case, the gas combustion chamber is located below the pyrolysis chamber. The movement of combustion products against the vector of natural draft requires the operation of an electric fan.
- An upper combustion boiler can operate on one load of coal for up to five days. Only the top layer of fuel smolders; air is supplied to it from top to bottom, and the ash is carried away by a stream of hot combustion products. Air circulation is provided by... that's right, an electric fan.
Gas
Non-volatile gas heating boilers use manual ignition using a piezoelectric element and flame regulation by a mechanical thermostat. When the main burner is extinguished at a high coolant temperature, the pilot burner continues to operate.
Floor-standing gas boiler with piezo ignition.
Boilers with electronic ignition stop the gas supply completely when idle. As soon as the coolant cools below the critical temperature, the discharge ignites the main burner and heating resumes. In addition, electricity often drives a blower fan that supplies air to the burner.
Which scheme is better? If you have frequent power outages, a non-volatile gas heating boiler would be more appropriate. Precisely because he is able to do without electricity in principle. On the other hand, these devices are less economical: up to 20% of the total gas consumed is spent maintaining the pilot flame.
Another useful feature that gas-independent heating boilers lack is the ability to control the weather and control it using an external thermostat, which takes the temperature, for example, in a remote room. Of course, we are also not talking about programming the temperature for a day or a week.
Solara
Everything is simple here: solar boilers are COMPLETELY identical to gas boilers with electronic ignition. Only the burners differ. In fact, a lot of dual-fuel units are being produced.
It is clear that without a forced-air fan and electronic ignition, the devices simply will not be able to work.
There are no rules without exceptions. The independent household heater OB1 0010 is equipped with its own generator and does without external power, generating electricity for the fan independently.
Solid fuel boilers
Truly independent, of course, is a solid fuel boiler.
It does not require either electricity or a centralized fuel supply system (compare with gas).
A house equipped with such a unit will be warm, even if completely isolated from the outside world, if only the owner has a sufficient supply of coal or firewood.
However, it must be borne in mind that all of the above applies only to a solid fuel boiler in its simplest design, into which fuel must be added manually every 4 hours. Any modifications designed to reduce user participation require power supply:
- Pellet boiler: uses fuel in the form of granules - pellets, which are pressed chips, cake, etc. The granules are small and uniform in size, so they can be fed into the firebox with a screw feeder. That is, the user only needs to load a supply of fuel into the bunker, for example, for several days, and all this time the boiler will operate automatically. Electricity in this case is required to power the screw feeder motor.
- Pyrolysis boilers: the firebox of such a boiler consists of two chambers, in one of which the firewood is kept at high temperature and limited air supply (it is called primary). Under such conditions, the wood releases a mixture of flammable gases (this process is called pyrolysis), which enters the second chamber of the firebox and is burned there. To burn the gas, a large amount of air, called secondary air, is pumped into the chamber. To maintain optimal operating conditions, air in certain volumes must be supplied to both the first and second chambers, which is only possible with the use of fans. Of course, they require electricity to operate.
- Top combustion boilers. Here, perhaps, you can find an exception: some models of top-combustion boilers are non-volatile. The duration of work on one stowage is achieved by the fact that the fuel is stacked in the form of a kind of tower or column and ignited from above.
- Boilers with forced air supply: the firebox of this boiler is a regular single-chamber one, only slightly enlarged. The difference from a conventional boiler is that a fan and a gravity damper are installed in the ashboard, which, when the fan is not working, lowers under its own weight and blocks the access of air to the firebox.
Pellet boiler
A device with forced air supply operates according to the following scheme:
- While heating of the coolant is required, the fan operates, holding the damper open and pumping air into the firebox.
- When the temperature sensor signals the controller that the coolant has reached a certain temperature, it turns off the fan. The damper falls and the air supply to the firebox stops, as a result of which the fire in it goes out.
- When the coolant cools down, the controller, based on a signal from the temperature sensor, will turn on the fan again and it will fan the fire in the firebox.
Obviously, such a boiler cannot operate without electricity - both the fan and the automation system (controller + temperature sensor) need it.
Safety and efficiency of independent heating systems
To be able to save money on heating, several conditions must be met:
- Develop and approve the project with the permitting authorities. Without an approved GIP and a project agreed upon with all authorities, all modifications will be illegal. Therefore, you will not be able to use the results.
- Install or reconstruct existing equipment according to the design solution.
- Install a heat energy meter. This will allow you to pay for the received thermal energy exactly in the volume in which it was consumed.
- Provide the necessary level of automation or manual regulation. CHP plants do not respond particularly quickly to temperature changes in weather conditions and can continue to fire their boilers to the fullest. And through the heat exchange tank, unclaimed energy will be transferred to the networks of consumers who open windows and vents from excess heat.
Dependence of systems on electricity
Energy dependence of systems is defined as the ability to operate in the presence or absence of electricity. Non-volatile communications are installed in conditions of long-term lights out. Several methods are used for normal heating operation:
- Installation of an electric generator or inverter batteries. The devices start powering after the network is de-energized.
- Providing energy-independent heat generation. You will need an automatic boiler - pellet, liquid fuel or gas. The equipment operates without electricity, but uses basic fuel uneconomically.
- Creation of gravitational pressure. The liquid moves through the difference in density when heating and cooling. Heated water masses go up, cooled ones go down. Gravity pressure is created by installing the boiler at the lowest point and sloping the horizontal pipeline along the movement of water.
When implementing circulation or energy-dependent heat supply, you will need a circulation pump. The system is connected to pipes of any diameter; special convectors and heated floors also work for heating. The water temperature is maintained at a given level. In case of a lack of electricity, generators are installed.
Calculation and selection of elevator
Guided by special formulas, first of all, you need to calculate the diameter of the mixing chamber, then select the required number of the heating elevator, after which the size of the nozzle is determined. Unknown kilocalories should be immediately converted into common units; they are often converted to Bar.
The narrow part of the elevator nozzle is calculated in millimeters; there is also a formula for this process. The calculations were not difficult for me, although when looking at the notebook, all the operations seemed huge. Having calculated the pressure at the outlet from the central line, it is worth applying an alternative formula to determine the diameter. But I want to point out that the result will be expressed in centimeters.
Dependent system
The coolant flowing along the highways enters directly into the home. The system is also called open, since the selection of coolant for the purpose of heating the building (also to provide warm water) occurs from the outlet pipeline (another name is the supply pipeline). This scheme is popular for buildings designed for several families and buildings of government agencies, shops, banks, and many other buildings.
If the temperature of the coolant inside the supply pipeline has not reached 95 degrees Celsius, it is sent to the heating apparatus. When the temperature reaches this limit, but still remains less than 105 degrees Celsius, intervention of the mixing elevator unit is required. It is installed at the entrance to the cottage so that liquid, gas or antifreeze from radiators is added to the hot coolant so that the latter becomes warm and not hot.
The dependent system operates based on the laws of molecular physics and thermodynamics. Antifreeze or other coolant gets to the top, which causes high pressure to form at the outlet of the heating boiler, and at the same time, a slight vacuum is created at the inlet of the heat generator. After this, the liquid tends to enter an area where the pressure is lower. This system operates according to the natural circulation of coolant.
This scheme was very often used in the USSR. The dependent heating system functions properly and without interruption. Repair, installation, materials require small investments. There is no need to install additional pipes used to supply warm water to the room.
Minuses:
- waste and debris from pipelines end up inside the battery;
- when equipment is repaired or replaced, pressure drops and water hammer often occur;
- the coolant cannot be called high-quality, since it runs along old highways, which are most often already rusty;
- the quality of the water or antifreeze mixture affects the thermostatic valves, they break;
- it is almost impossible to regulate the temperature at home on your own;
Types of dependent systems
The single-pipe system is ideal for private homes. This circuit is closed. A pipeline is laid from the heating apparatus, and the radiators are connected one by one and then taken back to the boiler.
Typical single-pipe heating circuit
There are horizontal and vertical patterns. The first is more suitable for one-story houses; it is carried out from below and above the floor, the batteries are installed at the same level. In the vertical direction from the boiler, the wiring moves upward and is already distributed among the batteries there. After cooling it descends.
The system does not require many components for installation, is easy to install, does not cause problems during operation and is inexpensive. It is ideal for small country houses; it can be installed without the help of professionals. The disadvantages include the fact that radiators that are closer to the heating device (boiler) heat up more and faster than those located further away.
Leningradka is one of the most popular systems, a system invented back in Soviet times. In it, all heating devices are combined into a single circuit through which the coolant moves freely. A special boiler heats the water or antifreeze mixture; radiators are usually connected along the walls, mainly near the windows. Leningradka has a very low cost, easy installation and a good level of performance, but it requires balancing during operation.
Spider - the system was considered obsolete not so long ago, but still remains popular due to its low cost. There is no need to install vertical wiring around the perimeter of the entire house, but the rooms are still heated evenly. The main advantage of the Spider is that the system is not dependent on the electric generator. It is very easy to adjust during operation. Installation of this type of system is difficult. It only needs to be installed in the attic, which increases the cost of additional insulation. Antifreeze cannot be used in such a system due to its evaporation inside the expansion tank. Such a system spoils the interior; only people with certain skills are allowed to install it due to the complex design stage.
HZ system for outdoor installation
HZ system for outdoor installation
The advantages of outdoor installation when modernizing heating systems are obvious: no need to hollow out channels in masonry walls, no construction waste in living quarters, no need for additional repair work, short installation, cost savings.
Modern pipes used for wiring the heating system differ from the heat pipes of the last century in the quality of workmanship and ease of daily maintenance. But at the same time, they remain elements of equipment, in the factory design they are laconic and do not carry any aesthetic load. Therefore, the desire of residents to move away or somehow artistically design the internal heating pipeline is quite understandable. As a rule, there are more horizontal sections of the heating pipeline in an apartment than vertical ones, and they are located along the perimeter of the room in its lower part - the area where baseboards are traditionally located. Therefore, the most natural design for such heat pipes is a finish using a baseboard box for heating .
Buy plinth for heating pipes
Which heating system is more profitable and why?
With the onset of the cool season, from autumn to early spring, every owner of his home thinks about heating it. One option for achieving this goal is a dependent heating system. It is a consistent, direct method of transferring the thermal properties of the coolant from the heating source & CHP & to the end user & your heating device. The pressure throughout the entire heating network is constant and equal to the pressure in the heating system.
Connection diagram for batteries in a heating system with natural coolant circulation: 1 - Boiler; 2 - Overflow pipe; 3 - Expansion tank; 4 - Supply pipeline; 5 - Heating and water heating control valves for each heating device; 6a - Diagonal battery connection; 6b - Lateral battery connection; 7 - Return water supply; 8 - Sewer drain; 9 - Valve for draining water from the heating system; 10 - Heating and water heating control valves for the entire system; 11 — Valve for replenishing the system with water; 12 — Fine mechanical filter; 13 - Mayevsky crane.
Circulation in the heating system is achieved by a pressure difference in the supply and return pipelines.
To maintain the nominal operating mode of the entire heating system, a CHP employee needs to monitor the pressure in the supply pipeline; on your part, all that is required is to paint the pipeline and pay for the use of heat.
Dependent heating schemes
- direct connection diagram;
- scheme using an elevator;
- diagram with installation of a pump on a jumper;
- diagram with installation of a pump on the supply line;
- diagram with installation of a pump and an elevator at the same time.
Dependent heating helps reduce coolant costs.
Each of them has its own differences, advantages and disadvantages, but the main thing is that the heating is efficient. Thus, the direct connection scheme is easy to install and operate, but the main drawback is the lack of heating in the cold season, according to the CHP schedule, and overheating in the warm season, which does not subsequently have a very good effect on human health and the appearance of indoor plants. The same drawback can be attributed to all other heater connection schemes. But, looking at the economic indicators obtained per year when using this particular method of heat transfer, the management of the thermal power plant is very interested in maximally adapting the temperature to the optimal one for a comfortable stay in the room. Every year, such enterprises make changes to the heat supply scheme to the consumer, purchasing more expensive equipment, so its cost to the consumer increases in direct proportion to their costs.
A dependent heater connection scheme, in contrast to an independent one, allows you to obtain a larger temperature difference in the heating system, as well as reduce coolant consumption.
In addition, the connection pipelines are used with a smaller diameter, and the costs of operating the necessary equipment are also significantly reduced. An independent heating connection scheme is more economical and controllable by the end consumer of heat, since it involves automation, which is its main difference from the above type of heating. Date: September 25, 2022
Flaws
The design of the thermal unit and the device itself, despite all its positive aspects, has disadvantages, which include the following:
- The dimensions of the device components are quite difficult to calculate, but if this is not done, then maximum productivity will not be ensured.
- When ensuring a pressure difference between two lines, it is necessary to adhere to an indicator not exceeding 2 Bar.
- For regulation it is necessary to equip the unit with an electric drive.
To control the temperature, you will need to change the diameter of the nozzle, but not all models of the device are equipped with such devices; I consider this the main problem in the operation of the elevator unit of the heating system.