The productivity of a boiler, heating or sauna stove can be increased by installing a simple and at the same time effective device on the pipe - a heat exchanger. However, for its productive operation, you need to know the design features and manufacturing rules of the device. Do you agree?
We will tell you how to make a heat exchanger for a chimney with your own hands. We will list which modifications are suitable for self-installation and explain how the air model differs from the water model. Taking into account our recommendations, you can significantly increase the heat transfer of heating units.
Types of installations
This unit uses thermal energy from the chimney pipe, which it transfers to the coolant. The configuration of the device depends on the type and design of the chimney and the material from which it is made. The coolant can be:
- plain water;
- air;
- any liquids that do not freeze;
- oil.
All heat exchangers are divided into air and liquid. Air installations have a fairly simple design. You can make them yourself using available materials. The disadvantage of this unit is its low productivity.
A heat exchanger that uses liquid as a coolant has a more complex design. For this installation to work effectively, you need to follow some installation recommendations. But if everything is done correctly, a chimney with a heat exchanger can serve as a full-fledged heating system for a small country house or bathhouse.
Bacteria/Mold
Recommendations to reduce the risk of bacteria and mold formation:
- Condensate drainage to reduce humidity in the pipe: laying pipes on a slope and designated condensate collection points {3}.
- Filtration of incoming air: reducing the amount of fine particles to reduce the amount of food for bacteria [2].
- The use of antibacterial coated pipes with silver ions [2].
- Maintaining constant speed in pipes: continuous use.
Air heat exchanger design
The air heat exchanger for the chimney is a hollow body that is connected to the heating system using special pipes. A special braking device is installed inside the housing for gases that are formed during fuel combustion. Most often this is a specific damper system with small cutouts for air flow. In some models of heat exchangers, it is possible to regulate the draft force in the smoke exhaust channel, which affects the productivity of the unit.
This device works thanks to the principle of convention. There is a hole at the bottom of the heat exchanger through which cold air enters the body. It quickly heats up from the high temperature of the chimney, after which it returns back into the room. Thus, in a few minutes the room where this unit is installed becomes noticeably warmer.
Sauna stove with heat exchanger - advantages and operating features
Let us highlight the main advantages of bathhouse stoves with a heat exchanger.
- A sauna system of this design solves two problems at once - it heats the waiting room and steam room, and also heats the water.
- The tank can be located in the room closest to the steam room.
- Despite the relatively low cost of stoves with a heat exchanger per pipe in the bath, they are characterized by a long service life due to the use of high-quality materials in their manufacture.
- Because the firebox of a modern stove is equipped with fireproof glass, you can enjoy the flames and control the combustion process.
- The system is unpretentious in care;
- Attractive appearance.
- The small dimensions of the stove with a heat exchanger on the pipe in the bathhouse help save space in the steam room.
- The power of such a system is quite enough to quickly warm up the steam room to the desired temperature.
The design of a sauna stove with a heat exchanger is not complicated, and the tank can be located in a room adjacent to the steam room
Safety issues come first for every person. This factor requires that the system be operated correctly. The pipes connecting the tank to other parts of the structure cannot be fixed to the wall, since their linear parameters change when heated.
The volume of the water container should be selected taking into account the fact that it should be heated within two hours from the moment of ignition of the fuel in the firebox. Otherwise, the water will simply turn into steam.
The power of the created heat exchanger to the chimney pipe into the bathhouse should not affect the functioning of the stove itself. In this case, the level of permissible power reduction should not exceed 10%. When the system is heated to a high temperature, it should not be filled with water.
Liquid heat exchanger design
This unit is a regular coil with water, which is in contact with the outer surface of the chimney. Thin tubes are inserted into a metal casing and insulated with basalt wool. Copper is used as a material for the manufacture of coolant tubes. It has a high thermal conductivity coefficient, which makes it possible to minimize the diameter of the pipeline.
The coil is directly connected to the heating system and installed on the chimney. At the top point of the unit there should be a special tank, which is designed to collect liquid that has expanded from heating.
Operating principle of liquid heat exchanger:
- due to the high temperature that forms inside the chimney, the liquid in the pipeline heats up;
- hot water expands, causing it to move along the coil and flow by gravity into the heating radiator;
- in a heating device, hot liquid displaces cold liquid;
- the process is repeated from the beginning. Cold water flows back into the heat exchanger, where it is heated again.
Despite the high productivity of this unit, it has many disadvantages. First of all, a liquid heat exchanger is quite difficult to install; you need to constantly monitor the operation of the heating system and monitor pressure indicators. This installation cannot be used in winter, when the liquid in the coil may freeze. You can also get the opposite effect when, due to the reduced temperature in the chimney, the draft decreases, which entails an increase in the volume of firewood to obtain a certain amount of heat.
Air convector for home heating
The main difference between a convector and other heating devices is that it is possible to choose a convector for absolutely any room, since modern models of these devices have an excellent design and are able to decorate the interior, giving it an elegant appearance.
Speaking about heating devices, experts note a characteristic feature - the development of convectors is moving along the path of reducing their mass and internal volume. A heavier device retains heat longer, that is, it has greater thermal inertia. Once heated, it cannot be quickly cooled by the thermostat and continues to radiate the accumulated heat, making the room temperature unnecessarily high.
Thermal convectors are devices that allow you to distribute heat throughout the room more evenly than radiators or other heating systems. As a result, the formation of moisture and fungus is prevented. In addition, we know that the main heat transfer from a radiator occurs due to radiation. A convector transmits more than 90% of the heat by convection, which is an undeniable advantage for creating an efficient, comfortable and healthy indoor climate. Temperature regulators allow you to quickly set and maintain the temperature with an accuracy of 0.4 to 1 °C.
The efficiency of convectors, combined with automatic temperature control, allows you to get exactly as much heat as needed. And it is no coincidence that convectors have been used effectively and successfully in Western Europe for 20 years. It has long been calculated that heating rooms with a convector is 30-40% more economical compared to traditional heating methods. There are various models of convectors on the Russian market, which differ from each other both in the heating element and in design. But the greatest success has been with gas convectors, the production of which has been mastered by many domestic and foreign manufacturers supplying heating appliances to the Russian market.
What materials can be used?
A high-quality heat exchanger for the chimney is made of food-grade austenitic stainless steel. It works great under constant exposure to high temperatures. Nickel, which is contained in the alloy, forms a special film on the surface of the pipeline that is resistant to aggressive environments.
Galvanized steel can be used as a material for the heat exchanger pipe. With strong heating above 200°C, the zinc contained in the metal begins to evaporate. At a temperature of 500°C, its concentration in the air becomes dangerous to human health. But if your heating system operates in a smaller temperature range, this material is completely safe.
How to make this device yourself?
Making a heat exchanger for a chimney with your own hands is quite simple. To do this, use the following materials:
- metal sheet measuring 0.35 m x 0.35 m - 2 pcs.;
- pipe with a diameter of 0.032 m and a length of 2.4 m - 1 pc.;
- pipe with a diameter of 0.058 m and a length of 0.3 m - 1 pc.;
- cylindrical metal container with a volume of 20 l – 1 pc.
Step-by-step instructions for making a heat exchanger:
- Cut two circles with a radius of 0.15 m from sheets of metal. They will act as plugs.
- On a sheet of metal, mark the locations for placing the pipes. The largest circle with a diameter of 58 mm should be in the center, and along the contour there should be eight small circles with a diameter of 32 mm.
- A pipe with a diameter of 5.8 cm must be cut into eight equal parts using a grinder.
- Weld a plug to one end of the largest size pipe.
- Weld each pipe with a diameter of 3.2 cm to a metal circle one by one.
- Place another plug on the opposite side of the pipes, then weld it.
- Using a grinder, cut off the bottom of the metal container.
- On the side surface of the metal casing, cut two holes on opposite sides. Their diameter must correspond to the parameters of the chimney.
- Weld pipes to the prepared holes, with which the unit will be connected to the chimney.
- Insert the prepared core into the casing with pipes. Carefully secure the structure using welding.
- Connect the heat exchanger to the chimney.
- Treat the finished unit with heat-resistant paint.
Bibliography […]
- De Paepe M, Janssens A (2003) Thermo-hydraulic design of earth-air heat exchangers. Energy Build 35:389–397
- REHAU ECOAIRTM GROUND-AIR HEAT EXCHANGE SYSTEM
- Yupeng Wu, Guohui Gan, Anne Verhoef, Pier Luigi Vidale, Raquel Garcia Gonzalez. Experimental measurement and numerical simulation of horizontal-coupled Slinky Ground Source Heat Exchangers. Applied Thermal Engineering, Elsevier, 2010
- Saqib Javed, Thermal Modeling and Evaluation of Borehole Heat Transfer, Thesis for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, Building Services Engineering Department of Energy and Environment, CHALMERS UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, Göteborg, Sweden 2012
- Trilok Singh Bisoniya, Anil Kumar, Prashant Baredar, “Study on Calculation Models of Earth-Air Heat Exchanger Systems,” Journal of Energy, vol. 2014, Article ID 859286, 15pages, 2014.
- Bisoniya, TS Design of earth–air heat exchanger system. Geotherm Energy 3, 18 (2015).
- Larwa, Barbara, et al. “Heat conduction in the ground under natural conditions and with heat exchanger installed.” Czasopismo Techniczne (2015).
- Łukasz Amanowicz, Janusz Wojtkowiak, Thermal performance of multi-pipe earth-to-air heat exchangers considering the non-uniform distribution of air between parallel pipes, Geothermics, Volume 88, 2020
DIY copper tube heat exchanger
This unit is a coil of copper pipe that wraps around the chimney. It heats up quickly, and the air that moves inside becomes warm. To ensure high efficiency of this system without the use of a pump, the length of the coil should not be more than 3 m.
This design can be made using argon welding. The option of fastening using tin is allowed. In this case, all surfaces must be degreased with phosphoric acid.
The ends of the copper pipe must have an external thread for connecting an external water tank. It must be located above the coil, which will ensure maximum productivity of the system.
Options for connecting structures
The heat exchanger on the chimney can operate in two main modes. And each of them has its own process of heat transfer from smoke to the inner pipe of the heat exchanger.
So, in the first mode, we connect a remote tank with cold water to the heat exchanger. Then water condenses on the inner pipe, causing the heat exchanger itself to heat up solely due to the heat of condensation of water vapor from the flue gases. In this case, the temperature on the pipe wall will not exceed 100°C. And the water in the tank will take a long time to heat up.
In the second mode, condensation of water vapor on the inner wall of the heat exchanger does not occur. Here the heat flow through the pipe is more significant, and the water heats up quickly. To more fully understand this process, conduct this experiment: place a pan of cold water on a gas burner. It will be clearly visible how condensation will appear on the walls of the pan and it will begin to drip onto the stove. And despite the flame being 100°C, this state will continue for a long time until the water in the pan itself warms up. Therefore, if you use a heat exchanger on a pipe as a register for heating water, then give preference to small designs with thick walls of the inner pipe - this way there will be much less condensation.
Pipe on tin - simple and durable!
This option is simple, practical and convenient. In fact, here the chimney is simply wrapped around a metal or copper pipe, it is constantly heated, and the air distilled through it quickly becomes warm.
You can weld the spiral to your chimney using an argon torch or semi-automatic welding. You can also solder with tin - if only you degrease it with phosphoric acid in advance. The heat exchanger will hold on to it especially tightly - after all, samovars are soldered with tin and last a really long time.
Corrugation - cheap and cheerful
This is the simplest and lowest-budget option. We take three aluminum corrugations and wrap them around the chimney in the attic or second floor. The air will be heated in the pipes from the chimney walls, and it can be redirected to any other room. Even a fairly large room will be heated to hot temperatures while you heat the steam room stove. To make heat removal more efficient, wrap the corrugated spirals with regular food foil.
Heat exchanger-hood - for warming up the attic
Also, in the chimney section in the attic room, you can install a heat exchanger that would work on the principle of a bell-type stove - this is when hot air rises up, and cools down slowly. This design has its own huge advantage - an ordinary metal chimney on the second floor usually becomes so hot that it cannot be touched, and such a heat exchanger will significantly reduce the risk of fire or accidental burns.
Some craftsmen also cover such heat exchangers with a mesh with stones to accumulate heat and decorate the heat exchanger stand. In this case, the attic becomes even more comfortable and can be used as a living space. After all, based on practice, the temperature of the sauna stove pipe does not exceed 160-170 °C if there is a heat exchanger on it. And the highest temperature will already be located only in the gate area. Warm and safe!
What is an air heat exchanger and what is it used for?
Most often, hot air from dryers, chimneys, combustion chambers of various equipment is used. Warm exhaust air can be used for domestic purposes. The purpose of using the device is to heat the fresh supply air to a certain temperature that the exhaust medium can achieve.
Depending on the heating efficiency, warm air can be used for different purposes:
The supply of unprepared air to residential or industrial premises will create conditions for intensive heat removal, which will affect heating costs. If the air outside has a temperature of -20°C, and the air exchange rate in the room is 1, then the entire volume will change completely every hour, necessitating the need to quickly heat it to ensure a comfortable environment. This situation is very uneconomical and forces us to look for ways to prepare the supply jet. The main one is recovery.
General characteristics of air heating
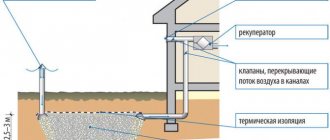
The complete HE system consists of a heat generator, heat exchanger, fan, air filter and air duct system (Figure 5). The heat generator is closely connected to the heat exchanger. Heat exchangers can be divided into two types: direct heating heat exchangers (Figure 3) and indirect heating heat exchangers (Figure 4). In the latter, an intermediate coolant, for example water or antifreeze, circulates between the heat generator and the heat exchanger. In direct heating heat exchangers, fuel is burned in the heat exchanger itself, or heating elements or spiral electric heaters are used as a heat exchanger.
Figure 5. General diagram of the heating system of the house: 1 - diesel heating boiler; 2 - pipes for the water part of the heating (for the water heat exchanger of the air heater); 3 - chimney of a diesel boiler; 4 — ventilation (for the bathroom and kitchen); 5 - recuperator; 6 — fresh air supply duct (connected to the SVO return air duct system); 7 — release of “dirty” air (from the bathroom and kitchen) after the recuperator; 8 - main supply air duct; 9 — supply terminal air ducts; 10 — feeding grids; 11 - return air ducts.
Industrially produced heat exchangers for direct heating of HE systems operate on gas (natural or liquefied), diesel fuel or electricity. These air heaters are initially equipped with fans of appropriate power.
As noted earlier, on solid fuel stoves such as “Buleryan” and “Professor Butakov”, which are direct heating heat exchangers, you can create an VO system by adding supply air ducts to the system, which, as a rule, are not intended for pumping air through air ducts. They are not able to create the pressure necessary for the VO system. And even if they are capable, they have unacceptably high noise characteristics. You can use them in the garage, but not in the bedroom.
Indirect heating air heaters with water heat exchangers are usually called fan coils (Figure 4).
Fan coils have a number of advantages compared to industrially produced direct-heated air heaters:
- fan coil units can work with any water heating boiler, operating on any type of fuel, and which can be located outside the heated building;
- one boiler can be used for heating and for heating water in the hot water supply system (DHW);
- for several houses (main, guest, bathhouse) you can have one heating boiler (or two connected in parallel for reliability).
- the presence of an intermediate coolant makes it possible to create a combined heating system: those rooms that have specific air properties (garage, bathhouse, stable, etc.) are heated by a convection heating system (water heating radiators), and the living area is heated by an air heating system;
What is recovery
It is unreasonable to waste the thermal energy of the removed exhaust air; it can and should be used to prepare the newly incoming supply air. This problem became relevant not so long ago, the main reason for its occurrence is the widespread use of plastic or aluminum windows and doors, the design of which eliminates the presence of leaks, does not let air inside and makes ventilation of rooms a very pressing issue.
Insufficient air exchange in rooms means people feel unwell, wall materials get wet, condensation occurs and other troubles, which can be eliminated with a properly organized supply and exhaust ventilation system. At this stage, the task arises of preparing the incoming fresh air, increasing its temperature, otherwise, along with freshness, frost will appear in the room. Heating systems will have to be overloaded to keep indoor temperatures at an acceptable level, which means increased load on equipment and excessive heating costs.
Advantages and disadvantages
VO systems are relatively rare in the residential sector of our country, and they are still looked at as exotic. As a rule, the VO system requires commissioning work “over the air” and “through the automation system,” which can only be done by trained specialists who have the appropriate instruments and instruments.
Errors in the design of the system and its installation can lead to an increased noise level in the premises, an imbalance in the air supply throughout the premises and, as a result, an imbalance in temperature.
Air ducts, in addition, occupy a certain volume and therefore it is very important that this is taken into account at the design stage of the house. With the right approach, almost all air ducts can be hidden so that the useful volume of the house is almost not reduced.
When designing an air duct system, it is important to have a design project for the arrangement of furniture and household equipment. It is highly undesirable for supply ventilation grilles to be located in areas where people will stay for a long time.
The VO system is electrically dependent, so it is advisable to have a backup power supply system and a backup heating system in the house (for example, an industrial fireplace).
All of the above can be attributed to the disadvantages of the VO system. But it also has undeniable advantages over convection systems.
The main advantage of this system is the ability to combine heating and ventilation in one system. It must be said that the need for ventilation in our houses, built using energy-saving technologies and equipped with modern sealed windows and doors, is increasingly recognized by developers. The lack of normal supply and exhaust ventilation can lead to the accumulation of moisture in the walls and the appearance of mold. And an air system that simultaneously performs the functions of heating and ventilation will cost less than two specialized systems.
Filters must be installed in the VO system. They come in several types: regular mechanical, which removes dust particles up to 0.3 microns; electronic filter - removes dust particles up to 0.01 microns in size; carbon filter - removes unpleasant odors. For example, pollen and tobacco smoke do not pass through the electronic filter, and its maintenance is reduced to periodic washing under running water.
Figure 6. Layout diagram of the air heating system: 1 - heat exchanger; 2 - supply air ducts; 3 — return air ducts; 4 — fresh air intake; 5 - recuperator; 6 - chimney.
In the simplest case, the return air duct system provides a hose that takes air from the street and mixes it with the indoor air (Figure 6). This air mixture, passing through the filter and heat exchanger, is heated and evenly distributed throughout all rooms. This eliminates the problem of open windows and drafts. The windows simply do not open, and a slight excess pressure is created in the house, which prevents the penetration of “outside” air into the premises and creates conditions for better ventilation of “dirty” rooms.
When the VO operates on the lower floor of the house, the main part of the air is taken from below, and on the upper floor - from the ceiling. This ensures equalization of air temperature throughout the entire volume of heated premises.
In addition, a duct humidifier can be installed in the air duct system, which provides controlled humidity in the house, and an air conditioner, which will maintain a comfortable temperature during the hot months. You can also install an ultraviolet air sterilizer, which is turned on to prevent infectious diseases or in case someone in the household gets sick.
List of sources used:
- Magazine "Home" No. 8, 2008.
- Engineering equipment of the house and site. Author: V.S. Samoilov; LLC "Adelant", 2004.- 320 p.
Features of the ventilation system with heat recovery
Ventilation systems using recuperative techniques require an effective heat exchanger and devices for forced movement of air flows - fans. The presence of this equipment automatically means the need for electricity. At the same time, the recuperators (heat exchangers) themselves do not consume any energy and operate in a passive mode, i.e. the process of energy transfer occurs independently, by contact methods.
Condensate
However, their work has several features, of which the most serious and requiring attention is the formation of condensation . The process begins after warm air is supplied to cold areas of the equipment and continues until the metal is heated to a certain temperature. Considering that internal air, saturated with water vapor from cooking food and people’s breathing, is subjected to treatment, the volumes of condensate are quite large and create certain problems during the operation of recuperators. Manufacturers take certain steps by installing various valves or icing sensors, which to some extent solve the issue, but the problem as a whole remains and requires constant attention from the owner.
Constant power supply
Among other, less important, but existing features of recuperation systems is the need for an uninterrupted supply of electricity . Despite the fact that the recuperators themselves do not require any external energy and operate in a passive mode, fans that circulate the flow require connection and a constant supply of energy, without which the system will simply stop.
Saving
In addition, an important indicator is the ratio of the cost of equipment and the amount of savings on space heating. Since one of the goals of recovery is to reduce heating costs, the cost of the equipment must be justified by these savings for the foreseeable time, otherwise the purchase of equipment will not bring any economic effect.
Determining the effectiveness of a system must be done before purchasing or manufacturing a system, since it is always useful to protect yourself from unnecessary expenses and waste of time. The efficiency of the device and its cost should be taken into account in order to compare the amount of savings and costs. Thus, plate heat exchangers for private houses are ineffective and are significantly inferior to other designs.
Air heating options
So, our task is to heat the air masses and supply them to the premises of a country cottage or apartment. How to organize air heating:
- From the fireplace, wood stove.
- Use VRF systems using freon. Simply put, inverter air conditioners, air source heat pumps.
- Install a combined boiler + chiller + fan coil air conditioning system.
- Organize centralized air heating (abbreviated as VO), combined with ventilation of a private house. Use an electric heater or a gas air-heating furnace as a heat source.
A veranda with a large glass area can be conveniently heated with hot air supplied from the floor
Reference. The latter option is often implemented in American and Canadian cottages built using frame technology. The heater is a gas oven.
For heating/cooling large production workshops, a slightly different scheme is implemented. There are 2 networks of air ducts built in the premises - supply and exhaust. Both converge to a ventilation unit - a central air conditioner, consisting of the following blocks:
- 2-3-stage filters purify air masses before being supplied inside the building and emitted outside;
- heat exchanger-heater No. 1 heats the flow using hot water from the boiler room;
- heat exchanger No. 2 serves to cool the air and works in conjunction with a chiller;
- a plate cross (or rotary) recuperator removes heat from the exhaust flow and transfers it to the supply flow, saving 50...80% of energy;
- humidification unit;
- Centrifugal fans force flows through sections of the central air conditioner and further along the air ducts.
Why did we describe the design of an industrial climate control system? So that you immediately understand: installing full-fledged air heating + ventilation + cooling is not an easy and expensive task. But, as the owner of a country house, you can consider all heating methods, choose the simplest and cheapest, or return to the water scheme - heated floors, radiators.
Industrial series heating system running on natural gas
How to organize stove heating
An important advantage of any stove: it simultaneously heats the air and surrounding surfaces with intense infrared radiation. No batteries or coolant pipes are needed.
Clarification. Stoves or fireplace inserts with a water circuit can be used to heat 2-3 small rooms. The coil is connected to a gravity or closed system with a pump.
How to use a stove for pure air heating:
- For 1 room it is enough to install a cast iron or steel potbelly stove.
- To heat 2–3 rooms with a total area of up to 40 m², place a brick stove of a suitable design in the wall between the rooms.
- It is not easy to build a stove in a lived-in house. If there are no high aesthetic requirements, we install a potbelly stove, attach convection casings to the firebox and connect air ducts.
Cast iron stove with air pipes and a ceramic heat accumulator on the chimney
Option No. 3 involves laying air ducts into adjacent rooms and installing duct fans that can withstand the temperature of the moving medium 100–150 °C. Air can move through the pipes on its own, but too slowly, and the ventilation duct must slope upward. How such an air heating system works, see the video below.
The first two options are well known, but not always applicable:
- It is generally unrealistic to install a stove in an apartment;
- even a large Russian stove is not able to cover an area of more than 50 square meters (on one floor), so it is suitable for heating a dacha or a small house;
- the foundation plus a brick stove-fireplace is erected during the construction or major renovation of the building;
- a metal potbelly stove takes up space and is dangerous for small children (in terms of burns).
You can install an iron stove with your own hands - this is a tangible plus. But you will also have to heat it, which results in a lot of inconveniences: frequent loading, the smell of firewood and smoke in living rooms, dust. The author of the video acted wisely by placing the potbelly stove in a separate furnace room.
We do not recommend repeating one thing after the home craftsman - installing air ducts made of aluminum corrugations. Such pipes create high aerodynamic resistance and greatly slow down the flow. It is better to use galvanized boxes.
Preliminary conclusion. Solid fuel stoves are a budget option for air heating with their own advantages and disadvantages. Suitable for small buildings - country houses, garages, greenhouses.
Application of air conditioners and heat pumps
As you know, modern split systems are able to operate in heating mode, consuming three times less electricity than a conventional electric boiler of the same power. Hence, a completely workable solution is to buy and install an inverter air conditioner in each room.
Reference. Why an inverter? The compressor in such “splits” does not stop, and therefore does not freeze in the cold. The air conditioner successfully heats the air down to -5 °C outside, after which the efficiency noticeably decreases.
The advantages of this scheme are obvious:
- lack of batteries, pipes, boilers and other heating equipment;
- relative ease of installation;
- aesthetic appearance of the indoor unit;
- cooling mode in summer;
- Possibility of installation in apartments.
The air-conditioned heating method is viable in the southern regions, where the temperature rarely drops below -15 °C. To the north, “splits” are used only during the transition period – in spring and autumn.
Other disadvantages of heating with a split system:
- Air conditioners will have to be installed in all rooms, which is unacceptable for cottages of 2–3 floors. A multi-split VRF system will cost more than the same number of single coolers/heaters.
- The device “can” clean, dry and change the temperature of the air flow. Rare models are designed to mix in outside air. This means that you will have to do separate ventilation.
- When the external unit of the air conditioner is operating, the distinct noise of the fan and the hum of the compressor can be heard from behind the wall.
The problem of efficiency at low temperatures is solved by an “air vent” heat pump, whose performance remains intact down to -30 degrees below zero. The design and operating principle are identical to the split system, the differences being the larger size and price. If the external unit is installed on the ground and carried 2-3 m from the building, the noise of the unit will become inaudible.
Brief conclusion. VRF systems are good for apartments and small houses located in the southern regions. Heat pumps can also be installed in northern latitudes, but the cost of the equipment plays a role here. If desired, you can install the air conditioner yourself.
Combined multi-zone systems
In this case, the coolant is still used, which is why the system is called combined. How this equipment works:
- Each room has an air heating/cooling unit - a four-pipe fan coil unit that looks like an indoor air conditioner unit.
- One pair of pipes supplies the units with coolant from the boiler. Hot water passes through a heat exchanger blown by a fan, causing the room air to heat up.
- When it is necessary to switch to cooling, the automation switches the fan coil to the second pair of pipes supplying cold water from the chiller.
- Users in rooms can set different air temperatures, but they cannot turn on cooling and heating at the same time. Hence the second name of the air conditioning system – multi-zone.
Note. Chiller is a type of refrigeration machine designed to cool liquid. Usually located on the street under a canopy or in an open place (depending on the design).
Various fan coil units are used inside the building - wall-mounted, duct-mounted, floor-mounted, ceiling-mounted. It all depends on the wishes of the homeowner and aesthetic requirements. Duct-type units can be built inside ventilation ducts to heat/cool the supply air.
Connection diagram of a cassette, duct and floor fan coil to a chiller and boiler
Advantages of multi-zone air systems:
- applicable in large buildings with 20 or more rooms - administrative and residential buildings, warehouses, and so on;
- can work in conjunction with forced ventilation of the cottage;
- any heat generator is used for air heating - a boiler using solid fuel, gas, electricity, diesel fuel;
- pipes with coolant (coolant) take up little space, air units are easily built into the ceiling, hung on the wall or hidden behind the cladding;
- closed terraces with stained-glass windows covering the entire wall are heated by in-floor convectors or wall-mounted fan coil units;
- possibility of adjusting the temperature in individual rooms, remote control.
We believe that the boiler + fan coil + chiller scheme is the most universal and successful from the point of view of aesthetics and operation. Of course, you can’t do this type of air heating yourself; this is a minus. It is necessary to make calculations, select equipment, install, adjust... without knowing the basics, it is extremely difficult to carry out these works.
Let's list other negative points:
- high price of air conditioning units;
- the boiler and chiller are quite large devices, occupying 2–3 m² of area;
- the operation of the system depends entirely on electricity; when the lights are turned off, the heat supply will stop.
Conclusion. A multi-zone combined scheme is the best way to air-heat a home. But implementation will require significant investments.
Heating combined with ventilation
This is a classic method of heating buildings with air, used in enterprises since the last century. Subsequently, manufacturers began to produce small-sized analogues of industrial ventilation units installed in private homes. Thanks to less stringent requirements for air purity, the treatment scheme has also been simplified.
Let us explain the principle of operation of the “ventilation + heating” system step by step:
- The heat source is a stove, usually a gas one. A burner, an air heat exchanger, a fan and an electronic control unit are installed inside.
- The first network of ducts radiates from the furnace, distributing heated air throughout the rooms. With the help of diffusers, grilles and other supply devices, jets are supplied to the premises (usually to the upper zone).
- The second network of channels collects polluted/cooled air from the lower zone of the rooms into a common collector connected to the stove from below.
- Having passed through the collector, the exhaust air masses are cleaned in a mesh or cell filter, then sent to a heat exchanger, where they are heated by a burner.
- Electronics monitor the safe operation of the gas air heater, maintain the outlet temperature, and signal when the filters are dirty.
Typical air heating circuit with recirculation. The heater is a furnace and an air conditioner with a ducted indoor unit
Addition. Since the heater dries the air, an automatic humidifier with an electronic hygrometer is usually installed on the supply duct. The latter is located on the return air duct to measure the humidity of the flow.
The air heating stove is a rather noisy unit, so it is installed in a separate room. Combustion products are removed through a conventional or coaxial chimney (depending on the design of the heater). Air ducts made of galvanized steel are laid in several ways:
- in the basement or ground floor;
- hide in floors and wooden ceilings;
- in the attic;
- vertical channels run along the walls and are covered with facing materials.
Large ventilation ducts are laid under plasterboard finishing.
The supply air temperature reaches 40...45 °C, the speed of movement through the ventilation ducts is 4-5 m/s. You can't go any faster; there will be additional noise. In this situation, the diameter of the main collector reaches 300 mm, we took a typical flow rate of 1000 m³/h, although it can be more.
A logical question: why heat air masses to 40 °C if 22 degrees is sufficient in the house? We answer: the heating system must compensate for 2 types of heat loss - through building structures and energy consumption for heating the inflow, since ventilation is needed in any case. Accordingly, we bring the air to a temperature of 20–24 °C (compensating for losses at home), then overheat it to 40…45 °C.
Conclusion. The “ventilation + heating” scheme is the most cumbersome and expensive. The building must be prepared in advance - even at the design stage, otherwise the air ducts will go directly through the rooms. Operating efficiency is highly dependent on the way the building is ventilated, which we will discuss next.
Air heat exchanger for ventilation
Plate air heat exchanger
The most common type is a plate air heat exchanger, which is a set of metal plates with high thermal conductivity, assembled in a stack with small gaps through which fresh and outgoing air streams are passed in independent streams. Inside the device, the flows are separated alternately, which allows for effective equalization of the temperatures of the supply and exhaust air.
The high thermal conductivity of metal plates makes it possible to intensively remove heat from the exhaust stream and actively heat the supply stream. Since the distances between the plates are very small, air filters are installed on both channels to clean the air from suspended matter, dust, and various particles that can fill the gaps and disrupt the operation of the heat exchanger. The resulting condensate flows into the pan and is then removed through a special channel. Air purification, no matter how thorough it may be, is not sufficient; it requires periodic washing of the heat exchanger plates and cleaning them of fatty deposits that accumulate in between over a certain period of time.
Rotary recuperator
The second, no less common type of heat exchanger is a rotary recuperator. It is a drive rotor made of corrugated metal (most often aluminum) plates assembled in the form of very closely spaced concentric cylinders. The rotor rotates using an electric motor with a chain drive. The supply and exhaust flows are supplied simultaneously to different sections of the rotor so that they pass through the gaps between the corrugated plates.
The principle of operation is to heat the plates when passing through the exhaust air zone and cooling with energy transfer when passing through the supply flow sector. In this case, partial mixing of the exhaust and supply streams occurs.
Both types of heat exchangers cope well with their functions and are widely used in ventilation systems of residential or industrial buildings. However, there are other types of devices that deserve special mention.
Installing a coil on a chimney
For small steam room ovens, heat exchangers can be installed directly on the chimney. The design of a water heating coil is practically no different from built-in heat exchangers; the only inconvenience is the need to install an additional storage tank for hot water.
Many owners of steam rooms install both types of heat exchangers on the heater stove, the internal one made of alloy steel and the external one made of copper or a copper alloy. The first water circuit is used to produce hot water and boiling water, the second is constantly filled with liquid and looped into the heating system.
Other types of air heat exchangers
There are other, very interesting designs.
Ground heat exchanger
For example, a ground heat exchanger. It is designed so simply that you don’t even want to call it a technical device. Its essence is to immerse the ventilation pipe, which takes in air, into the ground to a depth of about 2 m. The length of the pipe must be long enough so that the air passing through it has time to change its temperature.
Moreover, summer supply air, taken at a temperature of 25-30°, passing underground, will give up some of the heat and enter the ventilation system cooled, which eliminates the issue of air conditioning indoor air.
Heating the air inside the chimney
Another, no less interesting option is heating the air inside the chimney. The removed smoke has a fairly high temperature, which makes it possible to place a tube with supply air inside it. Passing through it, the flow will heat up and be ready for use for ventilation or air heating. Sometimes the tube is installed outside the chimney, it is tightly wound around it to increase the efficiency of heat transfer. It is best to cover such a structure with bricks on the outside for protection and heat preservation.
rsvgroup.ru
Additional Simulation Results
Images of air movement by option
Performance and efficiency of heat exchangers of different shapes
Aerodynamic characteristics for different forms of ground heat exchanger
Friction losses are higher for ring and serpentine heat exchangers. This can be compensated for by adding booster fans.
Outlet temperature for different forms of ground heat exchanger
For ring and serpentine heat exchangers, the outlet temperature is closer to the ground temperature. This means higher efficiency and more heat received from the ground.
Do it yourself
Before starting to manufacture a heat exchanger, it is necessary to decide what principle of heat transfer will be implemented in such a device.
Manufacturing of plate heat exchanger
To make such a device, you need to prepare the following materials and tools:
- welding machine;
- Bulgarian;
- 2 sheets of stainless corrugated steel 4 mm thick;
- flat sheet of stainless steel 4 mm thick;
- electrodes;
Build process:
- from stainless, corrugated steel , in the amount of 31 pieces.
- Then , a tape with a width of 10 mm and a total length of 18 meters is cut from a flat stainless steel. This tape is cut into pieces 300 mm long.
- The corrugated squares are welded to each other , with a 10 mm strip on two opposite sides, so that each subsequent section is perpendicular to the previous one.
- As a result , you get 15 sections facing one way and 15 facing the other in one cubic body. The corrugated surface of such sections allows you to effectively transfer heat from one coolant to another, while there is no mutual movement of different or homogeneous media.
- In the case when not an air mass, but a liquid is used to transfer heat, a stainless steel manifold is welded to those sections in which water will circulate. The collector is made of flat stainless steel. For this purpose, rectangles are cut out with a grinder: 300 * 300 mm – 2 pcs; 300 *30 mm – 8 pcs. Thus, you get a kit from which 2 collectors are welded, which resemble in shape a square box lid.
- A hole is made in each of the collectors , to which a pipe is welded for subsequent connection to the pipes of the heating system or to provide hot water supply.
- Holes on the collectors are made at one of the corners a, and when installing them on a heat exchanger, the inlet pipe should be located in the lower part of such a structure, and the outlet pipe in the upper part.
The heat exchanger discussed above is installed with the open side into the hot gas circulation system.
Thus, the hot gaseous coolant will transfer heat to the corrugated walls of the stainless steel plates, which, in turn, will heat the liquid.
Drawing:
Manufacturing a water heat exchanger for a furnace
A conventional wood stove can not only heat a room in the traditional way, but can also be used to heat water for heating rooms in which this heating device is not installed.
To make such a device you will need the following materials and tools:
- steel pipe with a diameter of 325 mm, a length of 1 meter;
- steel pipe with a diameter of 57 mm, a length of 6 meters;
- steel sheet 4 mm thick;
- welding machine;
- electrodes;
- cutting torch;
- white marker;
Manufacturing process:
- A cylinder made of a pipe with a diameter of 325 mm is installed vertically on a steel sheet and outlined with a marker or chalk.
- The outlined circle is cut out with a gas cutter. Then, using the resulting metal pancake, another circle of the same diameter is made.
- In each of these pancakes, 5 holes with a diameter of 57 mm are cut. Such holes should be equidistant from each other, as well as from the middle of the pancake and its edge. The pancakes are welded to the cylinder so that their holes are located opposite each other.
- A 57 mm pipe is cut with a grinder into sections 101 cm long. It is necessary to prepare 5 such sections.
- Each piece of pipe is installed in the holes so that the edges of this pipe protrude 1 mm from the holes of the upper and lower “pancakes”. Pipe sections are welded using electric welding. The result is a metal cylinder, inside of which there are pipes of smaller diameter. Hot air and flue gases will pass through these pipes, as a result of which the pipe will heat up and transfer heat through its walls to the liquid that will be located inside the cylinder.
- To circulate liquid inside the metal cylinder, pipes are welded in its lower and upper parts. Cold water will be supplied from the bottom of this design, and the liquid heated in this way will be taken from the top.
Air heat exchanger
An air heat exchanger is a plate device that is manufactured according to the same principle as the plate heat exchanger described above in this article, the only difference being that the collector is not installed on such a device.
Both in the vertical and horizontal planes, gas is used as a coolant through the device. Only for heating are hot gases formed as a result of fuel combustion used, and the heated gas is air, which, for greater efficiency, can be forced through the heat exchanger using a fan.
Pipe in pipe
Heat exchangers of this design are very simple to manufacture and operate.
In order to make such a device yourself, you will need the following materials and tools:
- electric welding;
- electrodes;
- Bulgarian;
- pipe with a diameter of 102 mm, a length of 2 meters;
- pipe with a diameter of 57 mm. 2 meters long;
- steel sheet 4 mm thick;
Manufacturing process:
- out of sheet steel , in the middle of which holes with a diameter of 57 mm are made.
- These plugs are welded to a 102 mm pipe, so that the holes of the plugs are in the middle of the pipe diameter. A 57 mm pipe is inserted into these holes and welded efficiently around the circumference.
- In the main 102 mm pipe, 2 holes are made for installing inlet and outlet pipes. These holes should be located as far apart as possible.
The operating principle of such a heat exchanger is very simple: hot coolant, passing through a pipe of smaller diameter, through the metal walls of the pipe transfers heat to the liquid, which is located in the cavity of a pipe of larger diameter. In this way, thermal energy is transferred without mixing liquids that may not be homogeneous, such as water and mineral oil.
O.
Drawing of an assembled water-to-water heat exchanger pipe in pipe:
Water
The device has two sectors that heat each other. Water circulation at high power occurs in a closed circuit in the heating system tank, where it heats up to 180 degrees. After flowing around the installed tubes, the water is directed to the main system, where the heating temperature increases.
To make a water heat exchanger, prepare:
- Container in the form of a steel tank. Install it to the beginning of the system. For water circulation, 2 pipe branches are needed, the lower one for cold water inlet, the upper one for hot water inlet.
- Check the tank for leaks.
- Place copper tubular spirals inside the tank; 4 meters of pipe per 100 liters of tank is enough.
- Connect the power regulator to the copper tube.
- To prevent pressure and temperature changes from destroying the container, install the anode closer to the heating element.
- Seal the tank hermetically.
- Fill with water.
- Check the system in operation.
Flushing the heat exchanger
Timely washing and cleaning of such devices allows such devices to serve for many years without failure. Heat exchangers that use heated gases from burning solid fuels as a coolant are especially in need of timely cleaning.
As a rule, in such systems, the plate channels become clogged with soot, which sharply reduces the efficiency of such a device, and if the working holes are excessively clogged with combustion products, the device can completely fail.
For high-quality cleaning of such heat exchangers, the device is completely dismantled and the channels are thoroughly cleaned of soot, followed by washing the plates.
The circuit in which high-hardness water circulates must be washed with a special descaling agent or citric acid solution. If there is a significant layer of lime deposits, the plates are cleaned mechanically. For this purpose, the collector is cut along the seam with a grinder. The plates are cleaned of scale, then the collector is welded in its original place.
The “pipe-in-pipe” heat exchange system is cleaned in a similar way. If it is not possible to effectively remove scale by chemical means, the pipe is cut and the scale is removed mechanically. Then the device is assembled.
Kinds
There are 2 types of heat exchangers:
Surface
The most common type of heat exchanger, which has become widespread not only in building heating systems, but also in many production processes. Not only water, but also water vapor, various mineral oils and chemicals are used as a coolant that can be used to transfer heat in such devices.
Surface models are divided into recuperative and regenerative:
- Recuperative - transfer heat through the wall of the coolant.
- Regenerative - such heat exchangers operate in periodic mode. First, the hot coolant heats the surface of the heat exchanger, then the cold coolant is supplied to the walls that accumulated the heat.
Mixing
When using this type of device, hot coolant penetrates into cold coolant. As a result of this mixing, direct heat transfer occurs. This type of heat transfer is rarely used in a heating system.
Typically, the mixing method is used for solar heating of water, when the coolant from the heat generator enters a storage tank in which hot and cold liquids are mixed.
Gas convectors and heaters
Gas convectors are independent heating equipment that represents a real alternative to traditional heating devices. They provide not only the ability to maintain a set temperature in the range from 8 to 33°C in a heated room, but also allow you to set different temperatures in different rooms.
Convectors operate on the principle of burning natural gas in a metal heat exchanger, which ensures highly efficient heat transfer to the room. At the same time, combustion products are removed outside and combustion air is taken in. This ensures the environmental cleanliness of the room and its effective ventilation. Compared to a traditional heating system, which requires boilers, radiators, room piping, fittings, pumps and other components, when using convectors, all this equipment is not required, since there is no water circuit. It is this feature of gas convectors that allows them to be used for efficient heating of country houses, cottages, garages, greenhouses, etc. The gas-air mixture in these devices is ignited either by a spark from the electronic unit or by the wick of the pilot burner, which, in turn, ignites when the button of the built-in “piezo lighter” is pressed. In the latter case, no electrical energy supply is required.
Blitz tips
- To avoid scale formation in the heating system , you must use only distilled water. A large amount of distilled water for this purpose can be produced at home by passing water vapor through a “pipe-in-pipe” heat exchanger.
- Using a homemade device for heat exchange between gases formed as a result of fuel combustion and liquid, it is necessary to carry out all installation work with the utmost care so that, as a result of insufficient sealing of the chimney, carbon monoxide does not enter the room.
- When using boilers or stoves that use natural air draft in the chimney, the cross-sectional area of the chimney inside the heat exchanger should not be less than the area of the boiler or stove pipe.
housetronic.ru
Video
Sources
- https://vsegdanarybalke.ru/raznoye/palatka/teploobmennik-dlya-zimney-ryibalki/
- https://househill.ru/kommunikacii/otoplenie/element/ustrojstva/teploobmenniki.html
- https://CatFishing.ru/poleznoe/teploobmennik-dlya-palatki/
- https://housetronic.ru/otoplenie/element/device/teploobmenniki-svoimi-rukami.html
- https://ogon.guru/otoplenie/komponenti-sistemi/teploobmennik-svoimi-rukami.html
- https://wlooks.ru/palatki/teploobmennik-svoimi-rukami/
- https://remont-system.ru/pechi-i-kaminy/chto-predstavlyaet-soboy-teploobmennik-dlya-palatki-i-kak-ego-sobrat