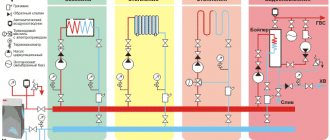
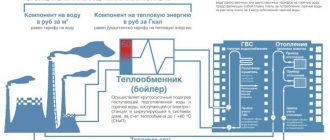
One of the most expensive items in utility bills is heating. You can regulate electricity yourself by purchasing devices with low energy consumption. But it is unlikely that it will be possible to reduce heating costs. In new buildings, individual heating is installed, but in old apartment buildings, a central system is predominant. In the first case, the calculation is made using meters for actual heat consumption. With central heating, payments must be made according to the established standard.
Who sets the standard for thermal energy consumption for heating?
The standard for thermal energy consumption for apartment buildings is established by a special institution that monitors organizations. Most often, this is a regional energy commission, which is an executive body of government and regulates tariffs for the services of organizations that operate in the city. All changes are made on the official website of the commission, which can be viewed by anyone. Management companies must promptly monitor new tariffs and set payment standards.
Any utility service has a consumption standard, which is presented for payment in the absence of metering devices. If the apartment has an individual water meter, then payment is made based on actual consumption.
Standards are established not only for separate services for residential premises, but also for general household needs.
ORDER A SERVICE FROM ACCREDITED COMPANIES
Comparison of induction and heating element boilers
1: Induction boiler - manufacturers claim more than 30 years without special maintenance (100,000 hours).
The question arises - where does the data come from if this is a new product that has only recently appeared on the market?
2: A heating element boiler loses 40% of its power over 4 years of operation, while an induction boiler does not lose at all.
What happens - from a 9-kilowatt boiler after 4 years only 3.6 kW remains?
For example, I installed one electric boiler; I have not observed any loss of power for more than 7 years; I have not changed the heating elements and completely forgot about them; it heats perfectly.
3: The heating temperature of the heating element coil is 750°C, which characterizes its fire hazard.
How can a heating element located inside an iron pipe threaten a fire?
Yes, I agree, it gets very hot. But I can’t imagine how this affects the fire hazard...
Unless you pull out the heating element, put it on a wooden floor and apply voltage - nothing else will work.
4: A large number of sealing connections (heating elements, flanges), the need for constant monitoring. What connections and flanges?
It’s been a long time since people learned how to make electric boilers themselves in a normal way - simply and reliably.
In the design that I use, there is only one large nut into which a single/three-phase heating element is screwed in - ALL.
There are no more flanges or sealing joints. There are only suitable heating pipes, just as in the case of an induction boiler.
5: A large number of electrical contacts (terminals of heating elements) located in the high temperature zone require constant maintenance of good electrical contact (tightening, etc.), which complicates the design.
Very interesting... Why does a three-phase induction boiler have fewer wires? No, the same amount.
Three phases - three coils in an induction boiler, each coil has two outputs, for a total of six contact connections. And it also requires “maintaining good electrical contact...”
From my experience, by the way, there are no problems with this. Use the main copper wire of the required cross-section and, when connecting, stretch the contact well.
6: “due to the high watt load, intensive scale deposition occurs on the surface of the heating element and clogging of the boiler and system with sludge falling from the heating elements.”
For those who don’t understand what a high watt load is, look at how the water is heated in an electric kettle, that’s what it is.
You just need to choose the right electric boiler.
Elementary switching on of two heating elements in series at 380 and there is no watt load.
In addition, now almost always an electric boiler is made with a circulation pump and the water has enough time to remove heat from the heating elements.
In addition, this problem is relevant only for very powerful and short heating elements. If you choose the heating element correctly, there will be no problem with the watt load.
Regarding boiler clogging and scale deposits, it’s not all that bad. This is not a instantaneous water heater and heating is a closed system. Of course, during the period of operation, a small deposit forms on the heating element, but it is a small deposit, and not a scale crust.
And this has almost no effect on the efficiency of the heating element.
How many Gcal is needed to heat 1 sq.m. according to the standard
Gcal is a measuring unit for calculating thermal energy. You can calculate heating in Gcal yourself, but you need to study information about energy.
Payment for heating in an apartment building depends on which meter is installed in the house and apartment. If there is no common household appliance, then tariffs are calculated in accordance with the standard. Local authorities set consumption standards and payment schedules. For example, pay throughout the year or only during the heating season.
The heat consumption standard is related to the temperature standards in the room. On average per 1 sq.m. residential premises require 0.0342 Gcal per month. The indicator may vary depending on the region and climatic conditions.
Owners of residential premises can apply for a recalculation of heating payments. The utility organization cannot refuse and is obliged to provide data. Thus, you can adjust the payment already made.
If the apartment owner has the opportunity to install a meter, then the standards will be increased in accordance with the increase factor. Heating calculations are carried out according to standards. The established standard is multiplied by the total area, as well as the tariff that is adopted in a certain region. Then you should add the payment for the general building consumption of thermal energy according to the standard and divide it among all apartments. The total amount must be paid monthly during the heating season or the entire year, depending on the chosen payment option.
Costs with a heat pump
Now let's look at the costs of heating a house with a heat pump. This is a new, complex topic. This is a very promising direction, but only if the equipment costs less and there are more specialists. Let’s skip the technical part and find out the cost of 1 kW.
In this case, we take into account the cost of 1 kW/h of electricity in the Moscow region for 2022 - 4.04 rubles. We take exactly this maximum tariff value.
Heat pump efficiency (conversion coefficient or thermal coefficient COP) is 3.61. This coefficient means that for every 1 kW of electricity consumed we will receive 3.61 kW of heat. Based on this, the cost of 1 kW/h of heat from a heat pump is 1.12 rubles.
Let's calculate the cost of 1 kW of heat from a gas boiler. Calorific value of 1 cubic meter m of natural gas – 10.11 kW/h.
- The cost of 1 kW/h of electricity in the Moscow region is 4.04 rubles.
- The efficiency of a gas boiler is 0.92.
- The cost of 1 kW/h of heat from a natural gas boiler is 0.43 rubles.
Calculation of heating in an apartment according to the standard per square meter
In order to calculate the heating in the apartment, you need to find out the heating standard for 1 sq.m. from your service provider. and tariff. Then you can calculate the price of heating m2 of living space.
When calculating heating in an apartment, it is necessary to take into account which meters are installed in the house:
- A common house appliance has been installed, and individual rooms have individual ones.
- A common building system has been installed, but individual meters are not installed in the apartments.
- There is no metering device in the apartment building.
Do not forget about the consumption of thermal energy for heating water for household needs when making calculations.
Option 1
In an apartment building there is a common device, and in some non-residential premises or apartments there are individual devices, then payment is made according to formulas 1 and 2.
The first calculation is performed:
2*1300=2600 rub., where:
- 1300 – payment for 1 Gcal of heat;
- 2 – volume of heat in Gcal, which is shown by the meter.
Formula 2 is used to calculate:
0.0342*80*1300=3556 rub., where:
- 0.0342 Gcal – consumption rate per 1 sq.m.;
- 80 – apartment area.
Calculation of heating in an apartment depends on whether there is a personal meter in the apartment. The second part of the receipt is calculated using formulas 10 and 13. The first part is used to calculate payment for heat, and the second part is calculated for the volume of service.
(250-10-6000*0.25-9-28)*806000, where:
- 6000 – area of all apartments;
- 10 – the volume of thermal energy that is spent on heating non-residential premises;
- 9 – volume of heat spent in apartments;
- 28 – the amount of thermal energy that is spent on hot water supply.
In order to calculate the cost, it is necessary to multiply the resulting volume by the established tariff.
Option 2
For the calculation, a third formula is used, which uses standard heating indicators or meter parameters. All values are taken into account in Gcal:
- the resource consumed was 250 Gcal;
- the total area of all premises is 6 thousand sq.m.;
- apartment area – 80 sq.m.;
- the tariff is 1300 rubles.
Calculation: 250*80/6000*1300=3900 rubles.
In accordance with the example, you can calculate the first part of the receipt, while the second is calculated using formulas 10 and 14. To determine the volume, the area of residential and non-residential premises should be taken into account.
If the area is 6000 sq.m., then the calculation is as follows: 250* (1-6000/6000)*80/6000.
Consequently, payment for thermal energy will be the amount obtained according to the first and second formulas.
Calculation of the number of radiator sections
Once we know the power required to heat the room, we can calculate the heating radiators.
In order to calculate the number of radiator sections, you need to divide the calculated total power by the power of one section of the device. To carry out calculations, you can use average statistical indicators for different types of radiators with a standard axial distance of 50 cm:
- for cast iron batteries, the approximate power of one section is 160 W;
- for bimetallic – 180 W;
- for aluminum – 200 W.
Help: the axial distance of the radiator is the height between the centers of the holes through which coolant is supplied and discharged.
For example, let's determine the required number of sections of a bimetallic radiator for a room with an area of 15 square meters. m. Let's assume that you calculated the power in the simplest way based on the area of the room. We divide the 1500 W of power required to heat it by 180 W. We round the resulting number 8.3 - the required number of sections of the bimetallic radiator is 8.
Important! If you decide to choose batteries of a non-standard size, find out the power of one section from the device data sheet.