High-quality heating of a house or apartment is the key to comfort and coziness of living. And this depends, not least of all, on the quality of the created heating system. Today, for these purposes, manufacturers offer many different materials that significantly simplify installation work and increase the durability of the systems being created.
XLPE pipes for heating
It is clear that none of the water heating systems can do without a fairly large number of pipes, and their selection should be approached with maximum responsibility. Gone are the days when VGP steel pipes were practically the only option. The modern choice is rich. For example, cross-linked polyethylene pipes for heating are a relatively new material that has many advantages over others. However, it also has its own characteristics that should be taken into account. In order not to make mistakes when considering what suitable heating pipes are, which ones are better, during installation work and further - already during the operation of the heating system, it is necessary to have an idea about the main characteristics and capabilities of this material.
What is cross-linked polyethylene
Crosslinked is polyethylene whose structure is modified at the molecular level. This improves technical and operational properties. During the crosslinking process, the molecular units are linked together and form a cellular three-dimensional network.
Areas of application
The material is used in the arrangement of:
- drinking water pipes;
- distribution of heating and hot water supply systems;
- pipelines for transporting gaseous media;
- underfloor heating systems;
- sewer communications;
- pipelines for supplying process water and compressed air;
- lines for supplying various chemical compositions.
Technical characteristics and properties
After cross-linking, polyethylene is not inferior in strength to many metal alloys and surpasses them in resistance to various destructive influences.
In addition, cross-linked polyethylene is characterized by:
- High density - 940 kg/m³.
- The operating temperature range is from 0 to +95 °C.
- Higher melting point - from +200 ºС.
- Ability to maintain impact resistance and crack resistance at temperatures down to -50 ºС.
- Thermal conductivity - 0.38 W/μ.
- Combustion starts at a temperature of +400 ºС. When burned, cross-linked polyethylene for heating does not emit toxic substances, but decomposes into carbon dioxide and water.
- Very high level of flexibility.
- Tensile strength - from 350 to 800%.
Life time
The service life of cross-linked polyethylene depends on operating conditions:
- In hot water supply systems at temperatures up to 70 ºС - 50 years.
- In underfloor heating structures and low-temperature heating systems through heating devices - 25 years.
- In high-temperature heating systems from heating devices - 10 years.
terms of Use
Cross-linked PE is intended for use in systems with operating pressure up to 20 atmospheres at a maximum temperature of 95 ºС with a permissible short-term increase of up to 110 ºС.
Pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene must be protected from direct sunlight by protective covers when laid externally or embedded in the structural elements of the building.
Overview of species
Cross-linking of polyethylene has become necessary due to its characteristics, which are directly related to the high level of thermal deformation. The new material has a fundamentally different structure, providing higher strength and reliability to products made from it. Stitched polyethylene has additional molecular bonds and has a memory effect. After minor thermal deformation, it restores its previous characteristics.
The oxygen permeability of cross-linked polyethylene has long been a serious problem. When this gaseous substance enters the coolant, persistent corrosive compounds are formed in the pipes, which is very dangerous when using metal fittings or other ferrous metal elements that connect the system during installation. Modern materials do not have this drawback either, since they contain an internal oxygen-impermeable layer of aluminum foil or EVON.
When producing cross-linked polyethylene, up to 15 different methods can be used, affecting the final result. The main difference between them lies in the method of influencing the material. It affects the degree of crosslinking and some other characteristics. Only 3 technologies are most often used.
Physical or based on the effect on the molecular structure of polyethylene by radiation exposure. The degree of crosslinking reaches 70%, which is above the average level, but the thickness of the polymer walls has a significant influence here. Such products are labeled as PEX-C. Their main difference is the unevenness of the connection. The production technology is not used in EU countries.
Production Features
Polyethylene granules are loaded into an extruder, where they are heated to a molten state and homogenized. The molten mass is then forced through a round hole, forming into a tubular-shaped workpiece. Primary cooling of the workpiece occurs when passing through a vacuum chamber, after which the outer diameter of the product is formed. It is then cooled by air droplets or in a water bath. The cooled workpiece is marked and cut into pieces of standard length or wound into coils.
Evaluation criteria for pipe materials
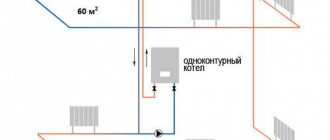
To choose the right pipes for underfloor heating, you need to have a good understanding of the operating conditions of the material. Being inside the screed, the heating line not only transfers heat to the monolith, but in addition experiences mechanical stress from water pressure and its own expansion.
The body of the pipeline experiences pressure from two sides - from the pressure of hot water and the mass of the screed
Accordingly, strict requirements are put forward for the material:
- Warm floors (abbreviated as TP) are a low-temperature heating system where the water is heated to a maximum of 55 degrees, operating mode is approximately 40/30 °C. To quickly transfer energy from the coolant to the concrete slab, the pipe walls must have sufficient thermal conductivity.
- The length of TP loops often reaches 100-120 meters (depending on the selected pipeline diameter). Long length = high hydraulic resistance, aggravated by the roughness of the internal surface. In simple terms: the smoother the pipe walls, the easier it is for the pump to pump water along a long circuit and provide the required coolant flow.
- Heating causes the underfloor heating pipes to elongate. Since there is nowhere to expand inside the concrete screed, one of two conditions must be met: a low coefficient of thermal expansion of the material or high elasticity and strength of the shell, allowing the pipe to fit in a limited space without destruction.
- Emergency situation: due to a breakdown of the control valves at the manifold mixing unit, the heating circuits are filled with boiler water heated to 70...90 °C. The material of embedded pipes must withstand such temperature fluctuations without consequences.
- Other important points are corrosion resistance, protection from oxygen penetration, ease of installation and the absence of joints inside the monolith.
Note. Less stringent requirements are put forward for water circuits laid using the “dry” method in wooden houses. TPs are mounted without a screed; there is plenty of room for thermal expansion. Point 3 of the list loses its relevance.
The method of laying TP inside wooden floors.
Not the least important role is played by the cost of all components of the TP - pipelines, fittings, distribution comb. So let’s compare the materials used according to the above criteria and price.
Pipe stitching method
Cross-linking of polyethylene for making pipes is carried out using several methods:
- Peroxide method. During the heating of polymer granules, hydrogen peroxide is introduced into the composition. The cross-linking level of the material reaches 85%. The resulting products are marked PE-Ha.
- Silane method. The material is treated with a chemical solution containing catalysts and an organic silane. The percentage of cross-linked molecules is 70%. Such pipes are marked with the abbreviation PE-Xb.
- Using electron beam irradiation technology. To form lateral bonds between the molecules of the polyethylene crystal lattice, finished products are exposed to radiation. Pipes of this type are called PE-Xs.
PEX stitching methods
There are about 15 methods of cross-linking polyethylene, but three of them are most widespread.
Today, the following stitching methods are in demand:
- Peroxide (PEX-a);
- Silane (PEX-b);
- By radiation method (PEX-c).
A more expensive, however, and higher quality cross-linking method is peroxide. It is thanks to it that it is possible to bind about 85% of free molecules. This allows the material produced in this way to have increased resistance to mechanical stress and have a higher melting point.
PEX is the best method for producing cross-linked polyethylene; all other options are just an attempt to reduce the cost of the material.
Advantages and disadvantages
Unlike conventional plastic pipes, products made from cross-linked polyethylene do not have thermoplasticity. They are able to withstand high temperatures without losing their shape. This property allows the use of cross-linked polyethylene for the installation of hot water supply systems, heating and heated floors.
In addition, cross-linked polyethylene has many other positive qualities:
- Absolutely resistant to corrosion.
- High strength.
- Light weight.
- Soundproofing properties.
- Resistant to pressure loads and temperature changes.
- High elasticity, due to which cross-linked polyethylene pipes do not crack when frozen. After the water thaws, they restore their shape.
- High technology.
- High wear resistance, especially to abrasion.
- Toxicological safety.
- The presence of the effect of reverse shrinkage, or “shape memory,” when a product, after changing its configuration, can quickly restore its original appearance.
- Resistant to the formation of lime and oxide deposits on the internal surfaces of pipes. During long-term operation, a heating system made of cross-linked polyethylene will completely maintain its throughput.
- Durability.
Despite such a large number of advantages, cross-linked polyethylene also has disadvantages:
- Excessive reaction to ultraviolet radiation.
- Due to their high plasticity, heating pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene may sag over time.
- The likelihood of oxygen diffusion into the coolant, which can cause parts of heating devices to quickly corrode.
Cross-linked pipe design
In most cases, cross-linked pipes have a complex structure. To increase the strength of the pipeline and reduce its ability to expand, they are covered with a reinforced layer, this is:
- Aluminum foil.
- Perforated aluminum;
- Polypropylene.
- Aluminum sheet.
The reinforced layer (for example, polypropylene) levels out pressure drops when using the product for heating. Reinforcement is provided on the top side, at different depths of the product. When stitching pipes, the reinforcement layer is removed by 10 mm. Products used for heated floors have almost no reinforcement. They are called "clean".
In addition to reinforcement, the manufacturer covers all cross-linked polyethylene parts with a layer called a “diffusion barrier.” This is due to the fact that oxygen molecules are able to penetrate into cross-linked polyethylene and slowly destroy it. Therefore, an oxygen protective barrier is required - it is done externally or internally.
What is better for heated floors - cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic?
Cross-linked polyethylene as a material for installing heated floors significantly surpasses its analogues in its characteristics. Compared to metal-plastic and polypropylene, it can withstand higher operating temperatures and a longer service life.
Cross-linked polyethylene has shape memory, which is a definite plus when installing underfloor heating: a large number of bends in the contour can lead to creases in the metal-plastic material. In this case, you will have to cut out the deformed section and connect the pipes using fittings, which is extremely undesirable under screed conditions. A leak can also be caused by delamination of metal-plastic, which occurs when heated due to different coefficients of linear expansion of its layers.
Areas of application
Technical indicators of pipes in various operating conditions
The universal properties of joint venture, including resistance to destructive influences and temperatures, determine the areas where this material is most often used. For example, the Uponor pipe is ideal for heating domestic premises. However, it is often used for the following purposes:
- production of pressure pipes for cold and hot water supply;
- use as elements of industrial heating structures;
- application in systems for supplying consumers with drinking water.
Uponor's high-quality heating pipe, produced by cross-linking, can be used in the installation of heated floor structures, as well as in air conditioning systems for domestic and office premises.
Tips on how to choose
When purchasing cross-linked polyethylene pipes for heating, you should pay attention to:
- Stitching method. PE-Ha products cross-linked using the peroxide method are more suitable for heating systems. They have the highest degree of cross-linking, are more durable and less thermoplastic.
- Availability of anti-diffusion protection.
- Availability of ultraviolet protection.
- Correspondence of diameter and wall thickness to design data.
Popular manufacturers
The products made from cross-linked polyethylene from the following companies are in highest demand:
Rehau
The Rehau concern is a world leader in the production of polypropylene, metal-plastic and PEX pipes. The company uses the peroxide method to crosslink PE, and ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVAL) for the oxygen-protective layer. The range is represented by the following models:
- Rehau Rautitan Flex. Products for universal use. Can be used in heating systems of any type and water supply. They are gray in color and are available with or without factory insulation.
- Rehau rautitan HIS. Designed for the construction of cold and hot water supply lines, white.
- Rehau Rautitan Pink. Sewn by radiation method, dyed pink. Area of application: underfloor heating device.
- Rehau Rautherm S. Equipped with an oxygen barrier, used for heating systems, mainly for heated floors. Color - red.
- Rehau Raubasic Natur. Designed for use in communications with low operating pressure, there is no oxygen-protective layer. White color.
- Rehau Raubasic Eval. Equipped with anti-diffusion protection, they are used for the manufacture of water supply and heating pipelines with low pressure levels.
Uponor
The Finnish company Ononor produces high-tech pipes for water supply, floor and radiator heating, PE cross-linked using hydrogen peroxide (PE-Ha). They make it possible to transport hot water with temperatures up to +95 °C and pressures up to 10 bar.
Valtec (Italy)
The company uses high-density low-density polyethylene (HDPE) as a base. Crosslinking is carried out using the silane method. Valtec products can withstand constant heating up to 80 ºС, but do not have shape memory, so they are preferable for hidden installation.
BIR PEX (Birpex)
Cross-linked polyethylene made in Russia. It is made from English raw materials in accordance with the assortment, has good quality, and is cheaper than analogues of European brands.
approximate price
The cost of cross-linked polyethylene products is determined by the manufacturing company depending on the diameter, characteristics and production features. Its increase may also be affected by brand awareness. I will give approximate prices for several of the most common models from different manufacturers.
Russian pipes Bir Pex
is a Russian manufacturer that has mastered the technology of manufacturing PEX pipes for heating. Our own production lines allow us to respond to market changes in a timely manner. Material – PE-Xb. A special feature of the product is increased wall thickness.
Models:
- Premium Corresponds to class 6 performance characteristics. For open installation, you can use Premium UV Stop.
- Standard. A good option for organizing autonomous heating. Fifth class of performance characteristics. The maximum water temperature in the system is +95°C.
The company offers original Eagle compression and press-on fittings.
Step-by-step installation of heated floors
Underfloor heating technology consists of creating a multi-layer structure, each layer of which is laid in strict sequence. The thickness of this structure depends on the type of insulation and mortar, as well as the presence of reinforcement.
Preparatory work before construction
Before installing a heating system made of cross-linked polyethylene, the following preparatory work must be completed:
- prepare tools;
- remove old flooring and screed;
- clean the floor surface from dust and dirt;
- determine the diameter of pipes and connecting parts;
- buy related materials and equipment.
In addition to the cross-linked polyethylene pipes themselves, the design of underfloor heating consists of several more mandatory elements:
- water heater for heating the coolant;
- expansion tank;
- a special pump or pump that provides forced circulation of the coolant;
- distribution manifold unit;
- a set of control, shut-off and connecting fittings, for example ball valves, fittings, etc.;
- insulation material;
- reinforcing mesh;
- fasteners for fixing insulation boards and heating pipelines made of cross-linked polyethylene;
- damper tape;
- cement-sand mortar or concrete mixture.
Selecting and creating a pipe laying scheme
Heated floor contours can be laid according to several schemes:
- A spiral offset to the center. This is the most common method of laying cross-linked polyethylene, ensuring uniform distribution of thermal energy: in a spiral pattern, supply sections alternate with return sections. Laying cross-linked polyethylene pipes begins around the perimeter of the room and ends in the center of the floor. Heating of the floor near the outer walls is more intense, which makes it possible to install a boiler of lower power without reducing the degree of coolant output.
- Snake. Snake laying is done from one wall to the opposite in several turns. Enhanced heating of the floor is provided at the beginning of its path; as it moves away, the water cools and heats the surface with less intensity.
- Double spiral. With this option, the heating circuit is divided into two spirals. The first is adjacent to the outer wall. The coolant passes through it and enters the second, the main spiral.
When choosing an installation diagram for underfloor heating, you need to take into account the size of the rooms. For small rooms, for example, a bathroom or a corridor, you can use snake laying. A cross-linked polyethylene circuit in the form of a double spiral is convenient for heating large areas or when it is necessary to heat certain areas of the room with different intensities, for example in front of the front door.
Calculation of the number of pipes
There are a number of rules that will help you calculate the future underfloor heating circuit:
- A pipeline made of cross-linked polyethylene with a cross-section of 16 mm should be no more than 100 m long. The length of a circuit made of pipes with a cross-section of 20 mm should not exceed 120 m. If these indicators increase, the pressure in the system will be too low.
- If a system made of cross-linked polyethylene has several contours, then they should be equal in length or differ minimally.
- With sufficient insulation, sections of the heating pipeline should be located in increments of 15 cm. In northern regions, where in winter the thermometer can drop below -20 ºС, the increment should be reduced to 10 cm.
On average, the consumption of cross-linked polyethylene pipes per 1 m² with a step of 15 cm should be 6.7 meters, with a step of 10 cm - about 10 meters. To more accurately determine the length of the contour, you need to divide the area of the room by the size of the laying step. The resulting value should be increased by the size of the bends and the length of the distance to the collector assembly.
Correctly calculating the length
Before you study prices for water floor pipes, you need to calculate the length of your floor. It is necessary to take into account the fact that the maximum size of the contour should not exceed 100 meters. Each loop is a solid segment. On average, a 100-meter set will be enough for 20 m2.
To save money and reduce material costs, do not install floor heating where large furniture will be placed. The desk at which you work, of course, will not be classified as furniture in this case.
When calculating a warm floor, it is also worth taking into account the pitch between the pipes. The wider it is, the less pipeline will be needed. But the distance should not exceed 35 cm (human foot), otherwise a temperature difference will be felt on the floor and heating will be uneven.
Preparing the base for pipes
The floor surface, cleared of the old coating, must be leveled with a sand mixture followed by compaction or a self-leveling compound so that the size of the differences is no more than 5°. To check the evenness, you can use a building level.
The next stage is laying a waterproofing layer of polyethylene or foil film. The sheets of waterproofing material are laid overlapping, the edges and joints are secured with reinforcing tape. A layer of thermal insulation is installed on top. It will redirect the heat flow upward and eliminate its loss through the ceiling. The following can be used as insulation:
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- Styrofoam;
- cork substrates;
- basalt mineral wool.
Extruded polystyrene foam boards are absolutely vapor-tight, have high strength, and can withstand significant mechanical loads. When installing underfloor heating, you can simply connect them together with tongue-and-groove ends and fill the gaps with pieces of insulation and special glue.
Mineral wool and foam plastic are less resistant to deformation under mechanical loads, so they should be laid between wooden or metal slats.
Hygroscopic cork materials and mineral wool require an additional layer that will provide them with vapor and waterproofing. In this case, vapor barrier membrane sheets are overlapped on the insulation, sealing the edges and joints with tape, and the reinforcing mesh is secured with stop brackets at intervals of 50 cm from each other over the entire floor area. It will increase the rigidity of the structure.
Next, a damper tape is laid around the perimeter of the room, compensating for the thermal expansion of the concrete screed when the heating is running. The height of the tape should cover the thickness of the insulation layer, cross-linked polyethylene hoses and reinforced screed.
Comparison of PEX with pipes made from other materials
Why do most people buy heating pipes based on cross-linked polyethylene? Here's how other materials are inferior to them:
- Copper pipes are a very good option, if not for their cost. It exceeds several times all other materials.
- Steel needs good anti-corrosion protection, it is difficult to bend, and sediment and blockages form faster inside it.
- Metal-plastic is the same polyethylene that has not undergone a cross-linking procedure. But it has an aluminum layer. Also an inexpensive pipe. But the ability to withstand increased temperature and pressure is worse. Therefore, the likelihood that it will break through is greater. And opening up a concrete floor for repairs is another “pleasure.”
- Heat-resistant polyethylene PERT has the ability to withstand elevated temperatures, but for a fairly limited time. Constant circulation of hot liquid will reduce its service life to a minimum.
- Polypropylene is cheaper than Pex, but it is also inferior in flexibility and heat transfer. And when they heat up, their strength decreases, so increased reinforcement is required during installation.
In addition, PEX pipes can even withstand freezing of the contents. There will be only slight deformation of the material, but when the temperature returns to a comfortable temperature, the original shape is used.
Installation of polyethylene pipes
After preparing the base you need:
- install the heating boiler and manifold;
- connect the equipment to the water supply.
After this, you can lay cross-linked polyethylene according to the chosen pattern. For convenience, marking the outline of the structure can be applied directly to the insulation.
Next, one end of the cross-linked polyethylene hose is connected to the outlet pipe of the manifold, the contour lines are laid out and secured to the mesh with tightening clamps every 30–50 cm in straight sections, in increments of 10–20 cm in places of bend. After laying the circuit, the other end of the product is connected to the manifold using a fitting.
When working with cross-linked polyethylene, you need to:
- Avoid sharp bends of the material in places where the pipeline turns.
- Carry out installation at temperatures not lower than +18 ºС. Polyethylene products should be brought into the room from the cold, wait until they warm up to room temperature, and only then install them.
- Ensure that the installation is even, and do not allow the hose to twist or put excess tension on it.
- When installing, try not to step on pipe materials made of cross-linked polyethylene, and do not place tools or heavy things on them.
- Reinforce polyethylene connections with thermal insulation for connection to the collector unit, since they are not located in the screed.
The assembled heating system must be tested before it is closed with a screed by pouring coolant into it for 6–10 hours. If during this time it is completely filled with coolant and remains sealed, then you can fill the screed.
Features of using different types of pipes for heating
It is necessary to select pipes for installation of pipelines taking into account the type of heating system. Experts recommend adhering to the following rules:
- Silane pipes are suitable for high-temperature heating pipelines. They are highly resistant to hot fluid and can withstand high pressure for a long time. However, such pipes do not tolerate low temperatures well, so they are not recommended for installation in houses that are not heated throughout the cold season (for example, in a country house). In addition, PEXb pipes have high rigidity, so they can be laid in an open way with fastening on brackets.
- Pipes cross-linked using the radiation method are suitable for low-temperature heating and installation in dachas and other facilities that are not used year-round. These products have low resistance to high temperatures, but can withstand severe temperature drops. Not suitable for heating systems with high coolant pressure.
- Pipes cross-linked with peroxides are ideal for constructing heated floors, although they are the most expensive. They tolerate high and low temperatures well and are very durable. In addition, they can bend under a small radius and have shape memory, that is, they retain the position given to them.
Screed rules
The screed can be made from ready-made cement-sand mortar grade 400 with plasticizers or a self-prepared mixture of cement and sand. Its thickness should be at least 3 cm higher than the laid cross-linked polyethylene. Additional strength is given to the screed using a metal or plastic mesh with a cell size of 10x10 cm. It should not just lie on top of the cross-linked polyethylene pipework, but be located inside the solution layer.
If the room area is more than 33 m² or has a complex configuration, then the screed should be made with expansion joints that break the floor into smaller rectangles. They will avoid cracking of the screed during heating.
Basic rules to follow when installing a screed:
- Work can only be performed at positive temperatures, even if special additives are added to the composition to increase frost resistance.
- While pouring the solution and until it dries completely (after 20–25 days), the pressure in the pipes should be about 1.5–2 atmospheres, and the coolant temperature should not exceed 25 ºС.
- The screed is poured after plastering the walls.
- To set the level of the future floor, you need to use special metal beacons.
The finishing finish on top of the underfloor heating screed can be made from any material.
Manufacturing methods and material differences
The raw material used for cross-linked polyethylene pipes differs in manufacturing method into:
- High pressure polyethylene. Chemically neutral, can withstand high pressure. PE products are used as casing for a well when laying a pipeline, to create a technological opening in monolithic structures, and when laying an electric highway.
- Low-pressure polyethylene. It resists mechanical influence better. Often used in water and gas pipelines. Also for supplying drinking and cold water up to 40 degrees. It can also be used for transporting liquid and gaseous substances that are inert to polyethylene. And for the electrical network, these pipes are used as a box.
Commissioning of the system
You can start operating the heating system at full capacity only after the screed has completely hardened.
Underfloor heating made of cross-linked polyethylene is put into operation in the following sequence:
- Connection to the flow and return line manifold.
- Opening all circuits simultaneously using taps on the manifold unit.
- Opening of air vent valves.
- Starting the circulation pump.
- Setting the desired temperature.
- Raising the pressure in the system to the operating value.
- Shutting down all circuits except the longest.
- Recording data on the flow meter and balancing devices.
- Connecting the next heating circuit along the length and adjusting the pressure level according to the operation data of the first circuit.
- Connecting and balancing the following circuits.
How competently you assembled the heating system will become clear after 2–3 months of constant use.
Tips for use
When products based on joint ventures are put into operation, their throughput increases noticeably. This is explained by the peculiarity of the material used, which tends to gradually expand. Upon reaching the maximum service life, the diameter of such pipes increases by approximately 3%.
Another factor influencing the increase in fluid pumping volumes is a change in the structure of the pipe material, after which the surface acquires additional plasticity. This helps to reduce the resistance to movement of the water carrier and accelerate its movement. Taking these factors into account when operating pipes will allow you to avoid troubles in the form of leaks at joints.
Characteristics of polymer pipes
To transport coolant in water heating systems of apartments and private houses, the following types of plastic pipelines are used:
- PP-R and PP-RCT are polypropylene random copolymer reinforced with a layer of aluminum, basalt or fiberglass. The PP-RCT plastic modification is characterized by increased thermal resistance.
- PE-X - cross-linked polyethylene grades A, B and C. Products must have an oxygen-protective barrier - a thin layer of impermeable polymer. For example, Rehau pipes use a complex compound called ethylene vinyl glycol (EVOH).
- PE-RT - polyethylene thermostabilized products with an oxygen barrier.
- PE-X / Al / PEX and PE-X / Al / PE – five-layer metal-plastic pipelines.
Reference. According to GOST 32415-2013, products made from polybutylene PB, polyvinyl chloride PVC-C, polypropylene block copolymer and homopolymer (PP-B, PP-N) are also suitable for installation of heating networks. These materials are not widely used in private housing construction due to poor technical parameters.
Products made from polyvinyl chloride PVC-C (photo on the left) and polybutylene PB (on the right)
Briefly about the methods of joining pipe polymers during the assembly of home heating:
- PP-R wiring is joined with polypropylene fittings using soldering (thermal polyfusion welding);
- cross-linked and heat-stabilized polyethylene (PE-RT) is mounted using the axial method in 3 stages - flaring the end, tensioning the fitting, installing the sliding sleeve;
- Metal-plastic is connected in 2 ways - compression or pressing.
Now we will give a brief description of each type of pipeline, go through the list of requirements and check how suitable the products are for water heating of floors in living rooms.
Polypropylene - material for radiator heating
Despite the price attractiveness and commitment of many craftsmen to using PP-R, we immediately note that it is impossible to make a warm floor from polypropylene pipes. There is no need to check the statement in practice - just carefully study the technical characteristics of the material and read reviews of homeowners who wanted to save money in this way.
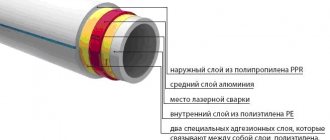
How polypropylene pipelines are arranged (see diagram):
- the inner layer of PP-R, which forms the flow section of the highway;
- aluminum reinforcing foil, which inhibits thermal expansion and prevents the penetration of oxygen;
- 2 adhesive layers holding aluminum to polymer;
- the outer protective layer of PP-R is white or gray (green for some manufacturers).
Important addition. Now polypropylene manufacturers, instead of perforated foil, place a layer of basalt or glass fiber inside the pipe.
Let's figure out how PP-R pipes comply with the requirements for underfloor heating branches:
- Thermal conductivity 0.24 W/(m•°С) is the worst among polymer products. If we take into account the wall thickness of 3.4 mm with Ø20 mm (PP-R reinforced pipelines are not produced with a diameter of 16 mm), we obtain a heat transfer resistance of R = 0.0034 / 0.24 = 0.014 m²•°C/W. The resistance value is too high for active heat transfer.
- There are no questions about the smoothness of the internal walls of polypropylene - a roughness of 0.01 mm does not create increased hydraulic resistance.
- When heated to 50 degrees, a 100-meter PP-R pipe with an aluminum layer will increase in length by 150 mm, with fiberglass - 31 cm. The elasticity of polypropylene is very low, which is why the product inside the monolith will be under high load. The material can crack, first of all, at the joints.
Diagram of elongation of metal and polymer pipes as a result of heating by 50 degrees - Resistance to pressure and temperature is beyond doubt. When the coolant is heated to 70 °C, the PP-R line can easily withstand a working pressure of up to 13 Bar. If you raise the temperature to 95 ° C, the pressure threshold will drop to 9 Bar.
- The polymer is resistant to any chemical influences and practically does not allow oxygen to enter the coolant. The main problem is the large number of joints that fall under the screed, because bending the polypropylene section is unrealistic.
Note. The technical parameters of PP-R products are adopted according to the documentation of the Valtec brand, published on the company’s official website. We also took the prices and characteristics of other pipe polymers from this manufacturer for a fair comparison.
Let's clarify some points. The value of the thermal resistance of the walls R = 0.014 m²•°С/W will not tell the average user anything without comparison with the indicators of other plastics. These calculations are given below in the descriptions of polyethylene and metal-plastic pipes.
The problem with polypropylene heating systems is the inability to visually check the quality of welded joints. Sometimes joints leak a year after high pressure testing (pressure testing). Imagine the consequences of a leak inside a concrete monolith - searching for a defect, destroying the screed and repairing it.
If you solder a heating circuit made of PP-R, a good dozen joints will fall under the solution layer
A separate issue is the lengthy fuss with installation; there will be a lot of joints in the concrete. Examples of heating circuits assembled by home craftsmen from PP-R are shown in the photo above. Even the low price of a pipe Ø20 is 51...83 rubles. (0.8...1.25 USD) per linear meter - is not a basis for using such pipes in heated floors.
Parameters of cross-linked and heat-resistant polyethylene
Pipelines made of PE-X plastic are produced in two varieties - 3 and 5-layer. The difference lies in the location of the anti-diffusion barrier - in the first case, the impermeable EVOH polymer serves as the outer shell of the pipe, in the second, it is embedded inside the wall and glued to polyethylene on both sides. External color – brown, silver, red.
Users often have a question about which polyethylene pipes are better to use for floor heating - PE-X or PE-RT, and how they differ. We answer:
- the molecular lattice of PE-X plastic is cross-linked in 3 ways, hence the three types of polyethylene - A, B and C;
- from the point of view of installation and operation of heating, pipes made of PE-X / A do not differ from PE-X types B and C;
- material of increased heat resistance PE-RT is made from ordinary polyethylene using cheaper technology - a complex polymer molecule is modified with the help of branches;
- PE-RT loses to PE-X in terms of durability, strength and thermal stability;
- PEX is significantly more expensive than PE-RT, by about 20-40%;
- PERT pipe walls do not have an anti-diffusion barrier, so the coolant is saturated with oxygen at a rate of at least 0.1 g/m³•day. (on open air);
- PE-RT material is thermoplastic, the pipeline can be repeatedly melted and welded without loss of properties.
Reference. The cost of a Valtec 16 x 2 mm cross-linked polyethylene pipe is 51 rubles. per meter (about 0.8 USD). A product of the same diameter made of heat-stable plastic PE-RT costs 33 rubles/1 m. p. (0.5 c.u.).
The PE-RT plastic system does not contain an oxygen barrier.
Let's move on to our list of requirements:
- The pipe for warm water floors “PEKS” and “PERT” has the same thermal conductivity - 0.38 W/(m•°C). Let's calculate the thermal resistance of walls 2 mm thick: R = 0.002 / 0.38 ≈ 0.005 m²•°C/W - almost 3 times lower than that of PPR. That is, polyethylene contours transfer heat to the screed much better.
- The equivalent surface roughness of 0.007 mm is an excellent indicator of the smoothness of the pipes.
- Having heated up to 50 °C, a 100-meter free section of the PEX pipeline will lengthen by as much as 100 cm. But thanks to elasticity and some installation techniques, the expansion inside the concrete slab is easily compensated by the material.
- The maximum operating temperature of the PE-X material is 90 °C, PE-RT - 80 degrees, short-term permissible - 95 and 90 °C, respectively. The operating pressure of the coolant is 6…10 Bar, depending on the degree of heating. The parameters meet the requirements for water heating circuits.
The weak point of polyethylene systems is oxygen permeability. Equipped with a barrier, “PEKS” allows less than 0.1 g/m³ per day to pass through, “PERT” - much more. But since the pipes are sealed with cement-sand mortar, the access of air is significantly limited, and the penetration of oxygen is reduced to a minimum.
Polyethylenes have a dual property - molecular memory, which causes the pipeline to bend to its original coil shape. This feature makes it difficult to attach the heating loops to the floor insulation - if the pipe is not rotated around its own axis, the ends will begin to ride up. How to deal with the described phenomenon, watch the video of our expert.
The positive effect of molecular memory is the ability to recover after a break. It is enough to straighten the damaged area and heat it with a hairdryer - the plastic will take its previous shape without losing elasticity and strength.
Analyzing the properties of metal-plastic
In fact, this five-layer pipe is an analogue of the PEX material, where a rigid aluminum frame with a thickness of 0.25...0.4 mm (depending on the diameter of the product) acts as an anti-oxygen EVOH polymer. Inside there is a self-supporting tube made of cross-linked polyethylene, and outside there is a shell made of the same plastic. The layers of the structure are held together with special glue.
Reference. The marking of metal-polymer pipes corresponds to the structure - PEX-AL-PEX. An interesting point: the Rehau brand offers a universal line of RAUTITAN Stabi pipelines with an outer shell made of ordinary (not cross-linked) polyethylene.
Let's analyze metal-plastic according to the initially specified criteria:
- The thermal conductivity of the five-layer structure is 0.45 W/(m•°C), the wall thickness of pipes with a diameter of 16 and 20 mm is 2 mm. This means that the resistance to heat transfer R is equal to 0.002 / 0.45 = 0.004 m²•°C/W.
- The elongation from heating a 100-meter section to 50 °C is only 13 cm.
- Operating temperature at a pressure of 10 bar is up to 95 degrees, short-term emergency temperature is 130 °C. The oxygen permeability of the walls is close to zero.
- The price of Valtec pipe Ø16 x 2 is 60 rubles. (0.9 c.u.), Ø20 x 2 – 97 rub. (1.45 USD) per linear meter.
Please note: the thermal conductivity, operating temperature and relative elongation of metal-plastic structures are the best among all polymer pipes. The smoothness of the material is not mentioned, since the roughness value is identical to polyethylene - 0.007 mm.
An important difference between metal-plastic is the lack of molecular memory. When bent, the rigid aluminum frame takes the required shape, overcoming the elastic force of the polyethylene layers. This property is a great help during installation; the main thing is to maintain a minimum bending radius of 6 and 8 cm for pipes Ø16 and 20 mm, respectively.
Choosing the best option for TP
If you carefully study the analysis of each type of pipeline, you can draw a preliminary conclusion: copper wins in all performance indicators, but significantly loses to polymers in price. Stainless steel corrugation will also not be an alternative to polyethylene - it is twice as expensive and has worse hydraulics.
Which pipe to use for underfloor heating first:
- Number 1 in our rating is PEX-AL-PEX metal-plastic, proven by many years of practice. The material is relatively inexpensive, easy to install with your own hands, durable, transfers heat well and elongates little when heated.
- Cross-linked polyethylene PE-X - pipes for professionals who know how to make high-quality TP contours. “PEX” is easily restored after a break, but it conducts heat worse and expands greatly when the temperature rises.
- Heat-resistant polyethylene PE-RT is a budget option for professional installation. The main disadvantages are oxygen permeability and a significant reduction in service life in case of overheating.
- The fourth place of copper pipe is due to its high price, which is inaccessible to most ordinary homeowners. If you do not take this factor into account, copper will be an ideal option for underfloor heating.
- Stainless steel corrugation is good for short sections, for example, connecting lines and hoses. Laying wavy pipes under the screed is not a very good solution.
- We do not use polypropylene at all.
Comment. When comparing different piping systems, the cost of fittings was not taken into account, since in-floor circuits are installed without connections.
Recommendation for the correct installation and concreting of PE-X and PE-RT pipelines. To reduce the elongation of the heating filaments, do not exceed the number of pipes in one circuit - 100 m, ideally - 80 m. Before pouring the solution, fill the system with water and pump up the test pressure (1.5 times higher than the working one). The TP installation technology is described in detail in a separate article.
Let's add a few arguments in favor of choosing polyethylene or metal-plastic for heating floors. Firstly, polymers have been successfully used in European countries for a long time. Secondly, the chemical composition of the main substance is continuously improved, and the properties are improved. Thirdly, polymer pipes are very durable, the standard service life is 50 years.
How to connect pipes
To connect sections of the cross-linked polyethylene pipeline, a fitting connection is used. Fittings are made of brass, bronze or plastic that can withstand high temperatures. Select bushings and ferrules of a certain diameter. For the water heating main, pipes for heated floors PEX 16*2 mm, 20, 35 mm are chosen. Wall thickness 2 mm. They are produced in bays. The length of the product in a coil is 40-50 m.
For the water main, the sections are connected using a pressed method. For installation, it is necessary to use an expander with nozzles of a certain diameter and pressing pliers. How are the pipes connected?
- It is necessary to align the edge of the pipe. To do this, place it horizontally and cut off the end at an angle of 900.
- Put on the crimp ring.
- A nozzle is installed on the expander that will correspond to the diameter of the product.
- Place the nozzle inside the pipe, turn it 1200. Wait a minute.
- Remove the tool and insert the fitting. After a minute, the material will restore its shape. The polyethylene fits tightly to the fitting.
- Next they work with pressing tongs. Using a tool, slide the ferrule onto the fitting.
The connection between the PEX underfloor heating pipes is strong. There are practically no seams formed. Polyethylene connects to fittings at the molecular level. Sealants are not used. It is impossible to remove the fitting. If such a need arises, the connection section is cut out.