High-quality communications are one of the most important components of the functioning of any structure. Disruption of hot and cold water supply systems not only creates discomfort, but can cause significant property damage. It is necessary not only to restore the routes, but also to eliminate the consequences of accidents: to compensate for the damage caused by leaks, to restore the finishing of the premises. And in apartment buildings - additionally solve problems with neighbors. A natural question arises: which plastic pipes are best used for heating?
Types of plastic pipes
Types of plastic pipes and marking table:
| Material of manufacture | Russian/international marking |
| Polyethylene | PE/PE |
| Cross-linked polyethylene | PES/PEX |
| Polypropylene | PP (PPR) / PP (PPR) |
| Polybutylene | PB / PB |
| Polyvinyl chloride | PVC/PVC |
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is somewhat different from the others in that it is a polymer of vinyl chloride - a thermally not very resistant material that can withstand temperatures up to +66°C.
This marking can be found on all types of plastic pipes.
Is it possible to use plastic pipes for heating?
Most types of polymer products:
- They have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, which reduces heat loss during transportation of coolant to the batteries.
- Designed for maximum pressure up to 20 atmospheres.
- Able to withstand temperatures of at least +90 ºС.
In modern heating systems, the upper limit for heating the coolant is 70...80 °C, so plastic can easily withstand high temperatures of the circulating fluid and increased pressure levels.
Difference between plumbing and heating systems
Before the advent of plastic pipe products, plumbing and heating system wiring were installed from the same types of metal pipes, only their diameter differed. With the advent of polymer materials, pipes began to be selected depending on their heat resistance.
Any type of plastic pipe product is suitable for cold water supply. And since the operating temperature of heating systems is not less than 50...75 °C, it is recommended to install only such materials in them, the melting of which begins at higher values:
- Cross-linked polyethylene.
- Polypropylene.
- Metal-plastic.
PVC pipes are not the best choice for heating systems as they can melt.
The difference lies in the level of pressure of the working environment. In water supply networks, the pressure level is usually within 4–5 atmospheres. In heat supply systems of multi-storey buildings it already ranges from 2 to 12 atm. (depending on the number of floors), and for private houses - 1.8–2.5 atm.
How much heat should the pipeline supply?
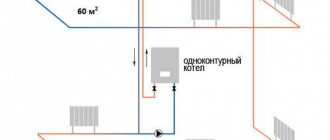
Let's take a closer look at the example of how much heat is usually supplied through pipes, and select the optimal pipeline diameters.
There is a house with an area of 250 sq. m., which is well insulated (as required by the SNiP standard), so it loses heat in the winter by 1 kW per 10 sq. m. To heat the entire house, 25 kW of energy is required (maximum power). For the first floor - 15 kW. For the second floor - 10 kW.
Our heating scheme is two-pipe. One pipe supplies hot coolant, and the other pipe cools it to the boiler. Radiators are connected in parallel between the pipes.
On each floor, the pipes branch into two wings with the same thermal power, for the first floor - 7.5 kW, for the second floor - 5 kW.
So, 25 kW comes from the boiler to the interfloor branch. Therefore, we will need main pipes with an internal diameter of at least 26.6 mm so that the speed does not exceed 0.6 m/s. A 40mm polypropylene pipe is suitable.
From the interfloor branching - along the first floor to the branching on the wings - 15 kW is supplied. Here, according to the table, for a speed of less than 0.6 m/s, a diameter of 21.2 mm is suitable, therefore, we use a pipe with an outer diameter of 32 mm.
7.5 kW goes to the wing of the 1st floor - an internal diameter of 16.6 mm is suitable, - polypropylene with an outer diameter of 25 mm.
For each radiator, the power of which does not exceed 2 kW, you can make an outlet with a pipe with an outer diameter of 16 mm, but since this installation is not technologically advanced, the pipes are not popular; a 20 mm pipe with an inner diameter of 13.2 mm is more often installed.
Accordingly, we use a 32mm pipe on the second floor before branching, a 25mm pipe on the wing, and we also connect the radiators on the second floor with a 20mm pipe.
As you can see, it all comes down to a simple choice among the standard diameters of commercially available pipes. In small home systems, up to a dozen radiators, in dead-end distribution circuits, 25 mm polypropylene pipes are mainly used - “per wing”, 20 mm - “per device”. and 32 mm “to the main line from the boiler”.
What requirements must be met when choosing heating pipes?
Plastic pipes for assembling heating systems must have the following advantages:
- Withstand long-term exposure to circulating liquid heated to a temperature of 70...75 °C.
- Be resistant to increased pressure in the working environment and possible negative processes associated with it (water hammer).
- Have a smooth inner surface so that scale does not deposit on it.
- Do not change the original shape and dimensions when heated (low expansion coefficient).
- Have a soundproofing effect. The movement of the carrier inside the heating system circuit may be accompanied by noise, and since plastic transmits sound less well, the noise level in the room will not increase.
- Do not corrode or oxidize when exposed to aggressive chemicals.
- Maintain tightness for the same period of time as other elements of the heating system.
- Be visually attractive to fit into the interior of the apartment.
Required data for calculation
The main task of heating pipes is to deliver heat to the heated elements (radiators) with minimal losses. We will build on this when choosing the correct pipe diameter for heating a house. But to calculate everything correctly, you need to know:
- pipe length;
- heat loss in the building;
- element power;
- what kind of pipe layout will be (natural, forced, single-pipe or two-pipe circulation).
The next point, after you have all the above data in your hands, will be necessary to sketch out a general diagram: how, what and where it will be located, what thermal load each heating element will carry.
Then you can begin to calculate the required cross-section of the diameter of the pipe for heating the house. You should also be careful when purchasing:
- metal-plastic and steel pipes are marked by the size of the internal diameter, there are no problems here;
- but polypropylene and copper - by outer diameter. Therefore, we need to either measure the internal diameter ourselves using a caliper, or subtract the wall thickness from the external diameter of the pipe for heating the house.
Don’t forget about this, because we need exactly the “inner diameter of the pipe for heating the house” in order to calculate everything correctly.
What materials are they made from?
For the manufacture of plastic pipes, inorganic material based on high-viscosity polymers of artificial or natural origin is used:
- Polypropylene.
- Polyethylene.
- Polybutylene.
- Polyvinyl chloride.
To increase strength, plastic is reinforced by connecting polymer layers with metal foil with a special glue or by adding fiberglass threads to the melt.
Types and characteristics
To assemble heating systems, you can use the following types of plastic pipes:
- Polypropylene.
- Made from cross-linked polyethylene.
- Metal-plastic products.
Polypropylene
For the installation of heating systems, polypropylene pipes are the most budget option. However, they have a high coefficient of linear expansion, which is why pipelines assembled from PP pipes can bend and sag during operation, which negatively affects the performance and aesthetics of the external appearance of the system. Therefore, this type requires a larger number of fasteners during installation.
There are three types of polypropylene pipe products according to the degree of heat resistance:
- Homopolypropylene (PP-N). PP-N pipes are characterized by high strength, chemical inertness, but are unstable to high temperatures. They are used when laying water pipes, ventilation ducts, drainage pipelines, etc.
- Polypropylene block copolymer (PP-2). Products made from PP-2 are intended for low-temperature heating systems, as they are resistant to temperature loads not exceeding +50 ºС. They are mainly used for installing heated floors and hot water supply pipelines.
- Random copolymer PP-3. The material is obtained by introducing ethylene units into the molecules of the main polymer. PP-3 pipes are characterized by increased flexibility, impact resistance, and high resistance to thermal loads. This is the most suitable option for arranging heating wiring from the boiler to the radiators.
The main technical characteristics for polypropylene pipes PP-3 are given in the table.
| Indicator name | Meaning |
| Limit temperature of the working environment during long-term operation | +70 ºС |
| Critical pressure level at maximum temperatures | no more than 10 atmospheres |
| Peak short-term permissible temperature | +90 ºС |
| Operating pressure at media temperature 25 ºС | up to 25 atmospheres |
| Linear expansion coefficient | 0.17 mm/m*ºС |
| Oxygen diffusion rate per day | 900 mg/m² |
Made from cross-linked polyethylene
PEX brand cross-linked polyethylene is a special type of polymer with a modified molecular bond structure. It is based on ethylene polymerized under high or low pressure. Cross-linking significantly improves polyethylene properties such as heat resistance, flexibility, wear resistance and the ability to self-heal after mechanical stress. Therefore, pipes made from cross-linked polyethylene are excellent for heating.
The technical characteristics of polyethylene pipes are as follows:
- Density - 940 kg/m3.
- Low coefficient of linear expansion.
- The maximum operating temperature is 95 ºС.
- Melting point - 200 ºС.
- Peak temperature load (short-term) - 130 ºС.
- Operating pressure parameters at:
- 20 ºС - 2.3 MPa.
- 95 ºС - 0.8 MPa.
Metal-plastic
The wall of metal-plastic products consists of five layers:
- Internal plastic smooth surface, which during operation is in direct contact with the coolant.
- Adhesive layer.
- A barrier layer made of aluminum foil, which increases the strength and durability of pipelines, and also reduces the degree of thermal expansion of products.
- Another layer of special glue.
- Polymer protective layer.
Due to the multilayer wall structure, high mechanical strength of the pipes is ensured, the sound insulation effect is enhanced, and thermal conductivity is reduced. This type of plastic pipe has the following performance characteristics:
- The maximum operating temperature is 95 ºС.
- The maximum temperature (for short-term exposure) is 130 ºС.
- The maximum pressure level at 95 ºС should be 10 bar; at a media temperature of 0 to 25 °С, it should not exceed 25 bar.
- Service life is at least 15–20 years.
Properties of polypropylene
Although polypropylene is the least dense of all plastics, it is more resistant to abrasion, tolerates heat better, begins to soften only at 140°C, is chemically resistant, and almost does not crack as a result of corrosion. The material is plastic. Under loads not exceeding the maximum, it stretches and then returns to its previous shape without any changes in properties and characteristics. So it's a really good and safe option. Pipelines in food factories are made from polypropylene pipes.
An additional plus is that polypropylene pipes are easy to connect - they are welded. In general, not only water pipes and heating are made from polypropylene. This material can be used as a frame for greenhouses, country furniture and a bunch of other useful things.
As you can see, the diameters of polypropylene pipes are different. And that's not all. There is also up to 1600 mm
Polypropylene has two disadvantages: high thermal expansion and reaction to oxygen and ultraviolet radiation. We learned to deal with both. In order for polypropylene to tolerate UV rays and light, stabilizers are added. To reduce thermal expansion, reinforced pipes are made. But even with reinforcement, the increase remains large and compensators must be installed in pipelines.
Another disadvantage of polypropylene pipes is that they become brittle at low temperatures. Some types begin to crumble at -5°C, others at -15°C. So external pipelines made of polypropylene require UV protection and insulation. That's why they probably prefer to bury them.
Which ones are better for heating?
Plastic pipelines perfectly cope with the assigned tasks in heating systems. Each type of polymer pipe may be more preferable under certain conditions. For example, for a hidden gasket it is better to take reinforced propylene, the parts of which are reliably welded together. Metal-plastic pipelines assembled using threaded compression fittings cannot be walled into the wall or filled with screeds. To inspect union nuts, free access is required.
Diameters and reinforcement
To assemble heating systems for residential buildings and industrial facilities, plastic pipes with a diameter of 16, 20, 25, 32 mm are used. The following diameters are suitable for laying heating mains: 40, 50, 63, 75, 90, 110. Wall thickness is 1.9–110.5 mm.
Reinforcement of plastic pipes is carried out for the purpose of:
- Increasing strength characteristics.
- Protection against oxygen penetration into the coolant.
- Reducing thermal expansion of products.
- Increased heat resistance.
The barrier layer can be made of fiberglass, solid or perforated aluminum tape. Some models are stabilized with basalt fiber, which is fused into the plastic during the production process. This method of reinforcement reduces the coefficient of thermal expansion of a plastic pipe by 3 times.
Connection method
As already mentioned, polypropylene is joined by welding. But despite the high level of plasticity, the minimum bending radius does not allow making turns even at an angle of 90°, not to mention steeper ones. All branches and turns are made using fittings. These are special elements for connecting plastic pipes. This is a whole range of different parts for each diameter.
Fittings for polypropylene pipes: types and varieties
The difference is that the marking indicates the diameter of the pipe for which these elements are intended. So you don't need any sizing. If you are using a pipe, say, with a diameter of 25 mm, then simply take fittings with the same marking. It is better to buy both from the same company. Then there will be no problems. If you had to take products from different companies, try them on to be sure. Take a piece of pipe to the store and check compatibility. It should fit in without any problems, but tightly, without gaps.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of plastic pipes for heating is due to their advantages:
- Ecological cleanliness. When heated, plastic does not release toxic substances.
- Low thermal conductivity.
- High throughput.
- Light weight, so they are easy to transport and install without using anchors.
- Does not need painting.
- They retain a pleasant appearance for a long time.
- They cut easily.
- They are simply connected to the pipeline using fittings using the soldering method.
- Suitable for both open and hidden installations.
- They have anti-corrosion properties.
The disadvantages include:
- The uniqueness of the installation technology of each type of plastic pipe.
- Temperature restrictions.
- Inability to use in fire extinguishing systems.
How to choose
Criteria for choosing plastic pipes for a future heating system:
- Design diameter and wall thickness size.
- Acceptable operating parameters.
- The degree of flexibility of pipe products.
- Features of installation (open and hidden type of installation).
It is advisable to select plastic fittings from the same manufacturer.
The products of the German companies Rehau, Banninger and Wefatherm have proven themselves well. Products from these companies can be used for assembling heat supply routes and heating systems with the following coolant performance characteristics:
- Temperature conditions up to 130 ºС.
- Pressure up to 25 bar.
Materials from Czech companies Ekoplastik, FV-Plast and Wavin are to some extent inferior in quality to German products, but Russian builders willingly purchase them. The lower price segment is occupied by plastic products from Turkey and China. However, their operating temperature limit is +95 ºС.
The cost of domestic plastic products is significantly lower than that of foreign analogues. At the same time, in terms of strength and heat resistance, they are not inferior to them, and even superior.
Where can I get the tables?
Everything is simple here. Usually, all detailed tables with all the necessary data can be viewed (or downloaded) on the websites of pipe manufacturers. But it happens that there are still no tables.
You can get out of this situation as follows. If there are no tables for the outer diameter, then take the one for the inner diameter and calculate according to it. Yes, there will be inaccuracies, but, as experience shows, for forced circulation they are completely insignificant and acceptable.
Having analyzed a huge number of already installed and perfectly working systems, experts noticed a certain pattern in the choice of pipe cross-section. It is mainly suitable for small-sized autonomous systems.
In private houses, the pipes that come out of the boiler are most often one-half and three-quarters in size. This diameter of the pipe for heating a house is used until the first fork, and at each subsequent fork the cross-section is reduced by exactly one step.
But this method is applicable only for apartments and one-story houses; for high-rise buildings, alas, everything will have to be calculated very carefully.
If we have a private house or apartment, autonomous heating for no more than 5-8 radiators and 2-3 forks, we can easily calculate everything ourselves. We need to know how powerful each heating point is, the heat loss in the room and a good table for selecting the pipe diameter.
However, as has already become clear, trust experienced specialists to calculate a complex multi-level system with numerous junctions and forks. Well, if you still decide to do everything yourself, then at least read articles like ours and consult with experts.
Source: eurosantehnik.ru/kak-vybrat-diametr-truby-dlya-otopleniya-doma.html
Installation features
Unlike metal elements of heating systems, plastic parts can significantly increase in length when heated. Because of this, during open installation, horizontal pipelines may sag or risers may deviate from the vertical. Recessed sections of wiring, deformed due to linear thermal expansion, can cause considerable damage to the material of the building’s structural elements.
To reduce or eliminate the negative consequences of this property of plastic materials, the following rules must be observed when installing heating systems:
- On long straight sections, round or U-shaped compensation loops should be provided.
- To fix plastic heating pipelines, you need to use not only blind fastening elements, but also sliding clamps. They will allow the elements to move freely.
- If part of the pipeline network of the heating system is filled with concrete, then a protective sleeve made of corrugated or foamed polyethylene must be used.
- To join metal-plastic blanks in hidden heating systems, it is advisable to use compression fittings. They form a stronger and more reliable connection.
The process of assembling heating from plastic pipes with your own hands:
- Develop a general diagram of the pipeline network, determine the location of radiators, shut-off and control valves. Then, according to the drawing, calculate the amount of material required, buy it and deliver it to the installation site.
- Cut into pieces of the required length.
- Heat the soldering iron.
- Insert the nozzle from the soldering iron into the cavity of the pipe workpiece.
- Install a fitting and a piece of pipe with a nozzle onto the heating element of the soldering iron.
- Remove the parts from the soldering tool and join them together.
- Allow time for the connection elements to cool and the weld to harden.