Figure 1. Appearance of the air curtain.
In the article we will consider the definition of an air curtain, we will indicate by what criteria air curtains are divided. Methods for heating the air flow and installing air curtains will be given.
First of all, let us give the definition of an air curtain. An air curtain is a device for creating an air flow in the area of an opening for any purpose, which prevents air from flowing through the opening. From this definition it follows that the air curtain works due to a dynamic barrier to the movement of air through the opening and always creates an air flow in the immediate vicinity of the opening. At the same time, the air curtain has limited efficiency; unlike an impenetrable partition or door, it does not completely separate the air environments located on opposite sides of the opening.
The types and classification of air curtains are determined by their design, purpose and areas of application. Air curtains are divided into air curtains without heating and air curtains with heating, which are called thermal curtains or air-thermal curtains. They, in turn, are divided according to the method of heating the air flow into electric, water and gas, and according to the method of installation into vertical and horizontal. Based on their ability to cover an opening, depending on its size, in accordance with GOST 32512-2013, air curtains are further divided into 5 classes. The belonging of an air curtain to a certain class is determined by its characteristics in terms of specific volumetric air flow (m3/(h m)) and specific impulse flow (N/m), that is, by dynamic capabilities. The higher the class of the curtain, the larger the opening it can be installed on. By purpose, air-thermal curtains are divided into commercial and industrial; according to the degree of protection of the shell, they are marked in accordance with the requirements of the international IP system. Based on their design, air curtains are divided into standard and explosion-proof.
Features of the thermal curtain
Vertical and horizontal thermal curtains can often be seen at the entrance to:
- Administrative building;
- Medical and educational institutions;
- Supermarket;
- Hotel;
- Subway station;
- Railway station;
- Warehouses or hangars;
- Production workshops.
Popular models of thermal curtains
Let's look at the most popular models:
- One of the simplest, but at the same time powerful horizontal thermal protection is the Tropic M-9 model. Its purpose is industrial premises, since it operates on a 380 V network, and its design is not brilliant. Two power levels – 9 kW and 4.5 kW. High productivity - more than 1100 m3/hour. Installation height – no more than 2.3 m. Price 12 – 13 thousand rubles.
Powerful curtain Tropic M-9
- For domestic use in houses and even apartments, Ballu BHC-L06-S03 may be a suitable model. It does not have much power, but is quiet and inexpensive. It operates from a 220 V network and also has two switchable power levels - 3 kW and 1.5 kW with heating from STICCH elements. It is possible to work with the heating switched off. Productivity – 350 m3/hour. Noise level – 46 dB. Its price is 5 – 6 thousand rubles. The disadvantages include the lack of remote control.
Household thermal curtain Ballu BHC-L06-S03
- Domestic manufacturer Teplomash produces a whole line of thermal protective devices. One of the household models KEV-3P1153E. With decent productivity - 500 m3/hour, but low noise - 45 dB. Two-stage power adjustment - 3 and 1.5 kW. Maximum installation height – 2.2 m. Price 6 – 7 thousand rubles.
Thermal curtain Teplomash KEV-3P1153E
Operating principle of a thermal curtain
The design and operating principle of the device is not that complicated. The body of the thermal curtain contains a heat source and a fan of sufficient power. The latter creates a flow of heated air in a certain direction.
In the area of operation of this device, an atmosphere with increased pressure is created, which does not allow during the cold season:
- Bring air from outside into the room;
- Release warm air outside.
Often similar devices are used in the warm season, but in this case the curtain acts as an air conditioner, preventing warm air, exhaust gases, insects and dust from entering from the outside. With the help of thermal curtains you can get rid of drafts.
Other types of air curtains
In addition to the classifications of air curtains, types and installation methods of air curtains indicated in the previous paragraphs, there are other types. They are usually determined by noise level restrictions, interior requirements and other preferences. The moving air in parts of the air curtain and in the opening area always exerts some sound pressure, so a silent air curtain cannot exist. However, some air curtains that allow variable airflow rates allow for compromises in the degree of protection of the opening and the sound pressure levels in the immediate vicinity. Often a compact air-thermal curtain can fit perfectly into the interior and be an organic addition to it.
Figure 5. Air curtain without perforation on the front side.
Sometimes, for practical reasons, it is necessary to use built-in curtains. In this case, the only decorative elements of the interior are the output and input grilles of the air distributors of the curtains, and the built-in thermal curtains themselves are hidden under a false ceiling or inside the wall structures of the room. Floor installation of air curtains is also possible.
The article provides a brief classification of air curtains by purpose, types of air flow heating, and installation methods. The choice of air curtain in each specific case is determined by many factors and represents a creative optimization task in many respects.
Alexey Pukhov, technical director of air curtain manufacturer Tropik-Line
Article provided by the magazine “CLIMATE WORLD” : https://mir-klimata.info/
Varieties by location
It is more rational to place thermal curtains as close as possible to the front door.
Methods for installing thermal curtains can be different:
- Horizontal - installed above the doors, the air flow is directed downwards.
- Vertical - fixed from the side. The device can be installed unilaterally or bilaterally, which depends on the dimensions of the doorway and the power of the fan.
- Column - devices in the form of racks, installed in pairs or individually. The air flow is directed horizontally, separating the exit from the room with a warm curtain.
- Ceiling (hidden installation) - designed for installation in suspended ceilings. Of the structural elements, only the air supply grilles are visible.
Types of installation of air curtains.
Air curtains can be installed on openings vertically, horizontally or in combination. Air curtains are installed horizontally above the opening; vertically they can be installed either on each side of the opening or on both sides at once. Typically, the more air curtains installed on an opening, the better protection they provide. Thus, maximum protection of an opening is usually achieved with the combined installation of air curtains on all sides of this opening. Such installation methods can be used on large openings, for example, on truck gates of warehouses and depots. Typically, all air curtains can be installed horizontally, and some types of air curtains are also designed for vertical installation.
Figure 4. Vertical installation of air curtains
By type of heat source
Sources supplying heat to the curtain can be in two main versions:
Electrical
Such devices are equipped with a heating element that is connected to an electrical network with a voltage of 220V or 380V. Devices of this type are quite compact, easy to operate, install and maintain.
The latest models have adjustments for the degree of heating, air flow power, air temperature, and a timer.
Mermen
The devices are equipped with a tubular heat exchanger that passes the coolant from the heating system of the building. These devices are large and quite difficult to connect. The advantages include increased cost-effectiveness.
There are also devices heated by gas, but such models are extremely rare.
Voltage: 220V and 380V
Small commercial series of air curtains with electrical heating with a power of up to 6 kilowatts can be connected to a single-phase network with a frequency of 50 Hz and a voltage of 220V or 230V in accordance with the interstate standard GOST 29322-92. Electric air curtains with a power of over 6 kW are designed for connection to a 3-phase electrical network with a voltage of 380V (or 0.4 kV) and a frequency of 50 Hz. Air curtains without heating or water air curtains of even powerful industrial series can be connected to a single-phase network with a voltage of 220-230V if their engines, the only consumers of electricity in these types of air curtains, allow this possibility.
Heating element type
The electric heater of the thermal curtain can be in the form of a spiral or a heating element.
Spiral
An effective but not durable heating element option. Efficiency is achieved due to the strong heating of the wire, and the service life depends on its quality and endurance.
heating element
This heater is more modern than the previous version and has a tubular body filled with quartz sand. There is a spiral running inside it. This device has high heat transfer and a long service life.
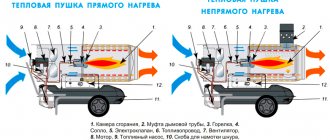
Design and principle of operation
A thermal curtain is a type of air curtain to which a heating element is added. This design has the following device:
- Fan
- can be axial or tangential. The first option is used for heating large rooms with openings up to 10 meters high, the second - in curtains of small openings. - Motor
- the more powerful this component, the more air the curtain can pump. They differ in power consumption class and shaft power. - Housing
- made of plastic or metal. - Thermal curtain control system
- this can be a wired or wireless remote control, as well as various buttons, levers and rotors on the device body. - Heating element
- electric and water heat exchangers separate. The first option is the most common and is essentially a classic tubular heating element or heating element.
The purpose of a thermal curtain is to prevent the penetration of external air flow. It creates a flat flow of warm masses and prevents them from leaving the room. Thus, the devices effectively maintain a comfortable temperature in areas where doors are frequently opened.
Selecting a thermal curtain
There are some tips for choosing a thermal curtain, one of which recommends taking into account the following points when purchasing:
- Dimensions of the open opening;
- The height of the ceiling in the room;
- Installation level;
- Curtain dimensions;
- Type by location;
- Productivity;
- With room heating or not;
- The need to adjust the heating;
- Heater type;
- Pair or single installation is needed;
- Specifications;
- Features of the installation site;
- Compliance with desired requirements.
Key parameters to consider when choosing.
Specifications
To understand how to choose a suitable thermal curtain, you need to understand the basic technical parameters of these devices. Choose the device that will protect your door:
- Dimensions. The length of the device must ensure that the heat flow completely covers the width of the doorway. Even a small gap will significantly reduce the effectiveness of protection from external influences. To select protection over wide doors in large rooms - supermarkets, auto repair shops - you can install several devices located along the entire width of the opening. The height of the device also matters. If it is larger than the free space above the protected opening, then you will probably have to abandon the horizontal type of curtain and consider only options with a vertical type, located on the side of the doors.
Creating a long thermal curtain from four elements
- Airflow performance. The task of a thermal curtain is not to heat the room - this role is performed by other devices. Therefore, the fan power and, accordingly, the volume of air flow per unit time and its speed are the main parameters of the thermal curtain. To reliably set up a protective flow, its speed at the farthest point is required to be about 2 m/s. To ensure such a flow rate near the floor, it is necessary that the device located at a height of 2.5 m “produce” a speed of about 8 m/s. To ensure such speeds, devices with a capacity of more than 600 m3/hour are required.
- Noise level. If for industrial premises and large supermarkets this is not the most determining parameter, then for household devices it is critical. At home, a noise level of less than 70 dB is required for comfort.
- Availability of automatic control. Manual mode is only good for the simplest and cheapest options. Automatic control of the operation of the curtain and the temperature of its heating elements ensures its efficiency and economy.
- Protective devices. For safety, it is necessary to be able to automatically shut down the system when it overheats.
Thermal power
If the room is equipped with sufficient heating, then you can choose a curtain model with no heating function.
Often, devices with a power of 6 to 12 kW are installed for standard door openings, but in practice it turns out that a less powerful device is sufficient for these places.
It is important that the consumption of the device matches the capabilities of the premises network. Particular attention should be paid to the technical characteristics of the network and equipment in the case when the curtain is used as additional heating.
Areas of use
There is an urgent need for the use of such devices in rooms where a large flow of people constantly open and close doors, creating drafts.
Such premises include:
- restaurants;
- the shops;
- metro;
- warehouses and industrial workshops;
- checkpoints;
- office halls class=”aligncenter” width=”800″ height=”600″[/img]
Additional selection criteria
For the thermal curtain to operate efficiently, so that it can fully cope with all its functions, you need to pay attention to some design features of the device and follow certain rules for its operation:
- Possibility of emergency shutdown;
- If the device is equipped with an air conditioning function, it is able to maintain the desired temperature, while reducing energy costs. In addition, these models cut off hot air and dust coming from the street in the summer, which creates a comfortable and beneficial atmosphere for the human body;
- It is advisable if the device is installed single, with sufficient power. This way the flow will be distributed evenly, eliminating breaks, which provides excellent protection against penetrating cold air.
- The most economical thermal curtains are those with ceramic heaters. They consume 20-30% less electricity than heating elements, but their cost is quite high and they are less efficient.
When choosing a thermal curtain, reliability and ease of use play a huge role.
You should not forget about the purpose, which may be its intended purpose, as backup or auxiliary heating of the room. It is also worth considering that in Russia these devices are untenable as an independent source of heating.
Control methods
Monitoring and control of the operation of thermal protective devices can be carried out manually and automatically. Basic management methods:
- Turn the device on or off. Automation, synchronized with door opening, saves money and the air curtain's lifespan. The protective flow is activated only when the doors are open.
- Air flow temperature control. In simple devices it is carried out using a manual temperature switch. In expensive devices, the degree of heating is adjusted depending on the outside temperature. In hot weather, the heating elements can be turned off, and the curtain ensures that the room remains cool.
- Remote control of operating modes is carried out using a portable remote control.
Photos of the best thermal curtain options
Who can do a better job of calculating the curtain?
The power of the air curtain is calculated, very roughly, as follows: at least 0.1 kW per 1 m² of unheated room with minimal thermal insulation.
When selecting a thermal air curtain✎, calculations are made based on a questionnaire. It is better to entrust this to professionals. Especially when it comes to shut-off curtains (shutter type) - too many parameters should be taken into account in this case.
Calculations for the performance of mixing-type heat curtains (m³/h):
| Opening height, m | Curtain performance |
| <1,5 | at least 300–400 m³/h |
| <2 | at least 500–650 m³/h |
| >3 | not less than 1200 m³/h |
Today there are many reliable brands of thermal curtains on the market. For example, Teplomash, Tropic, Ballu, Daire, Frico, Kupol, General, Hintek, Systemair, Aeronik, Vectra, Antares and that’s not all. Here is a more complete list of air curtain brands.
CALCULATION OF THE THERMAL CURTAIN FOR GATES >>
How to choose the best air curtain for gates? Calculation example.
Advantages and disadvantages
A description of the positive characteristics of thermal curtains can be made in the following paragraphs:
- They protect buildings from the penetration of cold air masses, insects, and dust from outside.
- Maintains a favorable indoor microclimate.
- Quiet operation.
Automatic adjustment is an absolute advantage and distinctive feature of a thermal curtain, regardless of the design features and breadth of its capabilities.
Setting up the heat curtain can be done quite simply. You can adjust the time it takes for the fan motor to start running and stop, set the heating intensity, etc.
As you can see, a silent thermal curtain has many advantages, but it is worth mentioning its disadvantages:
- the device is relatively difficult to install;
- for the water type, connection to the central heating network is required;
- significant energy consumption.
Limited effectiveness
Room temperature without air curtain
Room temperature with air curtain
A functioning air curtain prevents this alignment, although it is unable to completely resist the transfer of matter through the opening.
Moreover, if the device has excessive characteristics in terms of air flow speed, then its action will not contribute to the separation of temperatures or other characteristics of the media, but to their faster alignment on different sides of the opening - the curtain in this case will become useless.
Any real air curtains cannot completely separate the media and in the best cases have an efficiency of no more than 70-75%. This is not due to a flaw in their design, but to physical principles: even for small openings with a height of 1-2 meters and air flow speeds of several meters per second, the jets of the devices are turbulent. And any turbulent jet implies the movement of matter not only along, but also across its main flow.
Assuming that when the opening height is less than 1 cm and the air speed is less than 1 cm/s, the flow of the air curtain will become laminar. This implies the theoretical possibility of 100% efficiency, that is, complete separation of the media on opposite sides of this opening).
Air flow generation efficiency
There are two obstacles to the conversion of electrical power, which is taken from the power supply network, into the power of the air curtain flow. An electric motor cannot completely convert electricity into shaft rotation energy - some of it is always lost due to the useless heating of parts of the device. The energy that is supplied to the fan shaft from the motor is also partially lost due to slight heating of the moving air.
These losses determine the efficiency. electric motor and fan, and the overall efficiency determined by their product. For example, efficiency motor 0.6, and fan 0.4. Then the efficiency conversion of electrical power into air flow movement power will be equal to 0.24. This means that for 1 kW of power taken from the network, 240 W of mechanical power is produced for the ordered movement of air in the air curtain flow.
Efficiency values motors and fans are mainly determined by their types, of which there are several for both motors and fans. For electrically heated curtains, the efficiency of motors and fans is not decisive for the choice of device - the main attention should be paid to optimal coverage of the opening.
Air curtains Tropic Line Large selection of air-thermal curtains for commercial, industrial and domestic use.
Go to catalog
What are underflows and why do they occur?
Underflow is a deviation of air temperature from the standard downward. The temperature does not reach 18 degrees, so residents have to wrap themselves in warm clothes and turn on electric heaters and gas burners.
One of the reasons for insufficient heating is the negligence of utility services. In the centralized heating system, the thermal and hydraulic conditions need to be adjusted. This is necessary to maintain a difference between supply and return pressure, and then the coolant will circulate evenly in the system. If the system is not adjusted, some apartments will be too hot, while others will be too cold. Also, sometimes service companies save fuel or do not take into account weather changes.
Only regulating equipment will help you forget about the failures once and for all.
But violation of network maintenance rules is not the only reason for insufficient heating; sometimes residents are to blame. They install additional batteries and install larger diameter pipes during repairs. This leads to the fact that the pressure in the pipes decreases and hot water circulates unevenly. It is better to regulate the heating system in summer; in winter it is problematic. Setting up the heating and hot water supply system is one of the reasons why hot water is turned off in the summer.
How to get compensation for underproduction
The residents are cold, but they will receive bills as if the apartments were heated according to regulations. You need to act in the same way as in case of overheating: invite a housing and communal services worker to record the deviation from the temperature regime and draw up a report, and then demand a recalculation. But the problem of underheating can be completely solved only by modernizing the control equipment: the automatic control unit will maintain optimal temperature conditions.
The installation of regulatory equipment (heat energy metering and regulation systems, automatic control units, individual heating points, etc.) should be discussed at a meeting of residents. Such work is financed both from collected own funds and from capital repairs, if the appropriate funds have been accumulated. Another issue that needs to be discussed at the meeting is also directly related to insufficient heating - the heat loss of the house itself. It is possible that the building needs to be insulated both from the inside and outside, from the facades. No need to endure the cold and overpay for heating! Start by upgrading your heating and hot water supply systems - this is the most expensive part in the cost of consuming heating services, and heating bills will begin to decrease.