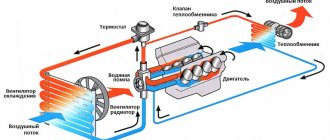
When a car's heating system fails, a common cause of problems is a faulty heater core. Therefore, there is an urgent need to replace this element on your car. The procedure for changing the stove element itself may differ depending on the design features of the car. But the key issue here is the right choice. The main dispute is over aluminum and copper products. It is not always possible to give a definite answer to which radiator is better - aluminum or copper. To do this, you need to study their features, strengths and weaknesses. This will allow you to give an objective assessment of the devices and understand whether there is an obvious leader among them.
Recommendations for choosing a radiator.
Construction of aluminum radiators
The design of devices of this type can be monolithic or sectional.
A sectional radiator usually consists of 3-4 sections. Aluminum alloy contains components such as zinc, titanium and silicon. They impart strength and resistance to corrosion to the base material.
The sections are connected to each other using special fasteners, most often a threaded connection. Tightness at the junctions of the channels is achieved using silicone gaskets. The internal coating of the channels is performed using polymers.
Solid batteries are made from profiles obtained by extrusion. The profiles are connected to each other by welding. This type of connection is the most reliable and durable. The inner surface of the channels is also covered with a polymer layer to prevent corrosion.
Since aluminum heats up quickly and cools down quickly (low inertia), the thermal performance of radiators made from this material can be easily adjusted. Therefore, both sectional and one-piece structures can be equipped with thermostats.
Ability to hold pressure
In a traditional central heating system, typical of multi-storey buildings, the pressure is by no means stable. Sometimes even water hammer occurs. After all, according to the rules, the taps of circulation pumps should turn on smoothly, but often workers do not follow these rules. And when the hot water is suddenly turned off, its pressure in the entire system jumps so much that many batteries burst. Therefore, apartment residents should definitely choose radiators with a good pressure reserve.
Cast iron radiators can withstand 9-12 atmospheres of pressure. This may be sufficient until a strong water hammer occurs. If it does happen, then the brittle cast iron, unfortunately, may burst. Therefore, if you look from this point of view, whether cast iron or bimetallic radiators are better, then it is better, of course, to play it safe and take a bimetallic one.
Installation of copper radiators
The simplest copper batteries consist of pipelines through which the working substance circulates, and a heat exchange part - plates or tubes necessary to increase the area of contact with the environment.
The main channel through which the coolant moves is made from a single pipe without welding, since copper pipes are easy to bend.
Shut-off valves are installed at the inlet and outlet of the radiator, which allows you to regulate the volume flow of the coolant in order to increase or decrease the amount of thermal energy released.
Modern models are equipped with aesthetically attractive grilles that improve convective heat transfer, and automatic temperature controllers for economical use of coolant and maintaining a comfortable room temperature.
What does thermal conductivity depend on?
Studying the ability of heat transfer by metal products, it was revealed that thermal conductivity depends on:
- type of metal;
- chemical composition;
- porosity;
- sizes.
Metals have different crystal lattice structures, and this can change the thermal conductivity of the material. For example, in steel and aluminum, the structural features of microparticles affect differently the rate of transfer of thermal energy through them.
The thermal conductivity coefficient can have different values for the same metal when the exposure temperature changes. This is due to the fact that different metals have different melting degrees, which means that under other environmental parameters, the properties of the materials will also differ, and this will affect thermal conductivity.
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum radiators
Aluminum appliances have the following advantages:
- Small overall dimensions and weight of both individual sections and the finished device in comparison with other types of radiators.
- High heat transfer coefficient, fast heating and cooling, making it possible to adjust the heating output.
- Cost-effective and long service life if all requirements are met.
- Easy installation and aesthetically attractive appearance.
- Relatively low cost.
Flaws:
- Susceptibility to corrosion when the polymer coating layer is damaged.
- Leaks may occur at the places where the sections are attached.
- The need to install an air vent.
- Relatively low pressure of the working medium.
Advantages and disadvantages of copper radiators
Copper radiators are one of the best heating devices due to the following advantages:
- High heat transfer coefficient and efficiency. According to the latter indicator, these devices are almost 5 times superior to their cast iron counterparts.
- The good mechanical properties of the material determine the strength of copper radiators.
- High temperature resistance. Possibility of use in systems with high operating temperatures (up to 150 degrees Celsius).
- Resistance to microorganisms due to the antiseptic properties of copper.
- Lack of chemical interaction with almost any type of coolant (for example, the use of antifreeze is acceptable).
- Long service life.
Disadvantages of copper appliances:
- High cost relative to prices for other types of radiators.
- Combination with pipes made of other metals is unacceptable.
- Reduced service life in the presence of abrasive impurities in the working substance.
Aluminum or copper - which base is better?
(click on the picture to enlarge) The radiator on the condenser was cleaned 1mm. But that's not all, among the first three capacitors - the second one is slightly higher, by about 0.01mm. Recommended 2-3mm! Still, be sure to clean it so that the socket and capacitors do not interfere. Experimental technique and hardware
To compare coolers with aluminum and copper cores, a stand with the following configuration was used:
* Motherboard: ASUS A7N8X-E Deluxe 1009 (nVidia nForce2 Ultra 400), Socket 462; * Processor: AMD AthlonXP 2500+/1833MHz, 512Kb, 333MHz; * Memory: 2*256MB DDR Hynix HY5DU56822BT-D43 PC3200 400MHz (3-3-3- ; * Hard drive: 160Gb SATA-II Samsung HD160JJ, 7200RPM, 8MB; * Video card: 64MB Sapphire RadeOn 9500, 277/270 MHz, EtronTech 3.3ns; * Drive: MATSHITA CD-RW CW-7586, 8x/4x/32x; * Case: Chieftec DG-01W 310W(ATX-310-202) + two Maxxtron 80mm case coolers (~2650RPM, 12v).
The operating system Windows 2000 Pro SP4 was used for testing. To determine the processor temperature, a sensor built into the motherboard was used, and to display its results in a readable form, the PC Probe v2.21.08 utility supplied with the motherboard was used. The resulting temperatures are presented in the figure below.
Testing was carried out in the following order:
1) Immediately after loading the system, the PC Probe v2.21.08 utility took data on the processor temperature - this is the processor temperature at idle.
2) The CPU Burn-in v1.01 utility was launched in the Enable error checking mode and after one hour of running this test, the processor temperature was again measured using the PC Probe v2.21.08 utility - this is the temperature of the warmed-up processor. Note: D9TB testing - room temperature was 22C.
After modification S754-07B832A it was 18.5C. Resetting the temperature by 5 degrees during idle time after warming up was accomplished by the S754-07B832A in 4 minutes, by the D9TB in almost 6.2 minutes.
Conclusion
I think the answer to the question in the title of the post has been received. There are no miracles in the computer industry: whatever cools better costs less. I in no way want to “bury” aluminum coolers, they have served us all faithfully and will continue to do so, but for high-frequency Athlon64/Sempron processors the best choice would be “copper”. For extreme situations, when all possible gigahertz are squeezed out of the processor, you cannot do without the S754-07B832A (or RF).
Rating: Pros:
* Affordable price; * High overclocking margin; * No noise, just rustling.
Minuses:
* The socket and capacitors on the A7N8X-E Deluxe interfere; * There is no clamp for Socket 462.
Discuss in the conference: All in one...
How are aluminum models connected?
To connect aluminum heating radiators, the following components are required:
- Mayevsky tap with the required connecting size;
- Gaskets for sealing section connections;
- Radiator mounting brackets;
- Right and left passage nuts with a diameter corresponding to the diameter of the device pipes;
- A plug with a diameter that matches the diameter of the internal passage nut.
Before installation, the sections of the device are assembled, if it is sectional, a location for installation is selected, and markings are applied. Most often, indoors they are mounted under a window or on a wall. The number of fastening elements is selected depending on the number of sections and the mass of the radiator.
Connection diagrams
Most often, one of three options for connecting radiators is used: bottom, diagonal or side.
The lower type of connection involves the supply and removal of coolant from the bottom of the radiator. Thermal energy losses are 15%. Due to the possibility of hiding the system pipes, this connection method is beneficial from a design point of view.
The diagonal type is the most common because heat loss is only 2%. The method is applicable for two-pipe systems and devices with a large number of sections. The coolant supply pipe is connected to the underwater radiator pipe located at the top, and the coolant is discharged from the opposite side from the bottom.
The side type differs from the diagonal type by placing the outlet and inlet pipes on one side of the radiator. Not suitable for devices containing a large number of sections.
Importance in everyday life and production
Why is it important to consider thermal conductivity? A similar value is indicated in various tables for each metal and is taken into account in the following cases:
- In the manufacture of various heat exchangers. Heat is one of the important carriers of energy. It is used to provide comfortable living conditions in residential and other premises. When creating heating radiators and boilers, it is important to ensure rapid and complete heat transfer from the coolant to the end consumer.
- In the manufacture of outlet elements. You can often encounter a situation where you need to remove heat rather than supply it. An example is the case of heat removal from the cutting edge of a tool or gear teeth. To ensure that the metal does not lose its basic performance qualities, rapid removal of thermal energy is ensured.
- When creating insulating layers. In some cases, the material should not conduct thermal energy transfer. For such operating conditions, a metal is selected that has a low heat conductivity coefficient.
How copper models are installed
Installation of copper devices is permissible using one of the connection diagrams listed above. Connection to galvanized steel pipes is not permitted. Ideally, the pipes along the flow of the coolant should also be copper. If this is not possible, brass fittings are used as pipeline connecting elements.
To create a thermal curtain, it is recommended to install the battery under the window opening. The gap between the device and the window sill should be 15 cm, the distance to the wall should be at least 3-5 cm. For installation, support posts or anchors are used.
Rubber or polymer gaskets are installed at points of contact with fasteners to avoid damage to the structure, since copper is a soft material.
Maintainability
Welding is considered a common procedure when repairing radiators. Aluminum is lighter than copper, and this provides better maintainability to aluminum radiators without subjecting them to unnecessary wear. This also helps aluminum radiators withstand the stress of repairs more easily and increases the lifespan of the aluminum radiator. In addition, an aluminum radiator lasts longer than its copper “colleague” even after several repairs. However, copper is softer in nature, and this property is very useful when the need for repairs arises.
Final comparison - which type of radiator is better?
One of the main criteria for choosing a device is the system to which it will be connected. It is characterized by the following parameters:
- Working substance pressure;
- Chemical composition of the coolant;
- Temperature of the working environment.
If in an autonomous heating system, which is installed in private houses, the above parameters can be controlled, then in apartments of multi-storey buildings, the heating devices of which are connected to a centralized system, this cannot be done.
Also, in the latter, there is a high probability of water hammer occurring (a sharp increase in pressure in the working medium), which may result in the integrity of the structure being compromised.
What to choose for an apartment
Copper models are much more expensive than aluminum ones, but are able to withstand high pressure, are less susceptible to water hammer, corrosion, and are insensitive to the composition of the coolant.
This makes them ideal for use in an apartment connected to a centralized heating system. Their only, but rather significant, drawback is their high cost. But it pays off with use.
What to choose for a private home
Aluminum devices are not much inferior in thermal performance to copper ones, but have a number of disadvantages, due to which their connection to the centralized heating system is not recommended.
For an autonomous system installed in a private house, you can use ordinary water, which does not have an adverse effect on the aluminum device. It also allows you to regulate the pressure, avoiding a sudden increase (water hammer). Therefore, to install a radiator in a private house, it is advisable to choose an aluminum model.
5 / 5 ( 23 voices)
Where to choose
The question of choice still remains open. But you need to try to answer it as objectively as possible. Despite the shortcomings mentioned, when choosing a radiator several years ago, everyone would definitely have opted for a copper product. Such designs were objectively better and could ensure excellent performance of the entire heating system of the car. But now the situation is different. There are many manufacturers, but there are no truly high-quality copper elements as they used to be. This is due to the desire to reduce the cost of production.
As a result, all sorts of impurities began to be added to copper, which negatively affect strength, quality, thermal conductivity and other aspects that have always been considered the main advantages. Therefore, it is more logical to choose aluminum. This material does not need to be reduced in price due to impurities, therefore it actually completely retains its advantages. And car owners say the disadvantages are not so significant, since the radiator is still a consumable item that can be changed every few years.
Under current conditions, aluminum is objectively better than copper. But if you manage to find the highest quality product without any admixtures of other metals, then you can safely opt for a copper stove radiator. But what you should categorically refuse is painted heating radiators. The presence of a layer of paint significantly reduces heat transfer. In addition, when the paint coating heats up, it begins to emit an unpleasant odor that enters the interior of the car. Try to carefully monitor the heating system to prevent clogging of the channels. If they turn out to be clogged, the fact of what material these elements of the car heating system are made of will no longer play any role.
Manufacturers
If you have been able to determine for yourself which radiator is better, then all that remains is to resolve the issue with the manufacturer. Copper and aluminum are actively used in the production of their products by various companies that create components for automotive heating systems. There are a lot of good manufacturers, but everyone has their own experience in working with certain factories. It is impossible to objectively determine the best company. Some people speak well of them, others were not particularly pleased. The question is quite subjective.