Modern production offers a wide selection of heating elements. Steel, aluminum, cast iron, bimetallic in material, they can be panel, tubular and sectional in shape. Not every type of appliance can withstand a centralized heating system. Application experience shows that bimetallic or cast iron radiators do not rust in 2-3 seasons and do not burst from pressure changes.
Cast iron and bimetallic elements are considered the most resistant for a long heating season
Features of cast iron radiators
Since cast iron heats up slowly, it needs a large volume of water to effectively extract heat. Therefore, the channels in cast iron batteries have a large diameter. Unlike other types of radiators, each section of cast iron consists of two parallel channels for better heat transfer.
In some classic models, feathers are installed between the channels - they allow you to slightly increase the heating efficiency due to convection. The effectiveness of this option is 5-10% better than the basic one.
The volume of water in a cast iron radiator is greater than in a bimetallic one. This affects the cost of coolant for refilling the system if it is closed. This is not a very fundamental question, but if we are talking about heating a large house...
Internal structure of a bimetallic radiator.
Let's talk about the difference in the price of radiators
Cast iron is undoubtedly cheaper, especially when produced domestically. So, the cheapest section of the MC model, for example, costs only about 300 rubles. However, only classic models will have such a “tasty” price. But retro-style radiators made by artistic casting are several times more expensive. Similar models from the Konner brand cost from 2,000 rubles (for one section).
Sectional models of bimetallic radiators will be slightly more expensive than similar cast iron ones. For example, one radiator section from Rifar (Russia) will cost at least 500 rubles. The price of a section of the same Italian radiator starts from 600-700 rubles.
Price: Cast iron + | Bimetallic -
Heat transfer of cast iron and bimetal
The heating power of radiators indicated by manufacturers rarely corresponds to reality. It depends on the temperature of the coolant and the air in the room. On average, the heat transfer of one section 50 cm high is:
- Cast iron - 140-195 W (depending on depth);
- Bimetal without air cutoffs – 140-155 W;
- Bimetal with air cutoffs - 170-190 W.
It is worth noting that cast iron heats up very slowly, but also takes a long time to cool down. Bimetallic batteries do this much faster. Cast iron radiators allow you to maintain temperature in the event of a heating shutdown.
Heating of a room with cast iron radiators is carried out mainly by radiation rather than by convection. For bimetallic ones - due to convection. Therefore, they quickly heat the air in the room.
Structural differences and appearance
Cast iron
Let's start with cast iron radiators, which today have changed their design, but, as before, have wide water channels and are made up of several cast sections. Heat-resistant gaskets made of rubber or paronite, which are placed between the sections, provide the necessary tightness. The length of the finished radiator is determined by the number of sections, the height varies from 0.35 to 1.5 meters, and the depth can be 0.5 meters or several centimeters. Depending on the volume of the room, you can select the desired radiator size, and it is possible to modify it (for example, remove an extra section or add several new ones).
Types of cast iron heating radiators.
It is worth mentioning the models of radiators artistically cast from cast iron. They not only perfectly warm the room, but are also able to give it charm and charm. Such radiators with skillfully molded patterns on their surface are produced mainly by foreign manufacturers. Like any piece of art, such devices cost a lot of money.
Several types of artistic cast iron heating radiators.
Bimetal
The body of bimetallic radiators is aluminum, its shape is ribbed. This is how it is designed for better heat transfer. A durable steel core is hidden under the body - this refers to “real” bimetallic radiators. However, there are also semi-bimetallic (or pseudo-bimetallic) radiators - their difference is that only the vertical channels of the radiator are reinforced with steel.
The rest of it is made of aluminum. Such a device costs 20 percent less than a completely bimetallic one, and produces more heat. But it is less reliable and durable, and using it in a centralized network is highly undesirable.
Construction of a bimetallic heating radiator.
Like cast iron radiators, their bimetallic counterparts are usually sectional, which allows them to be modified. Models with an even number of sections are usually sold. A small segment of the market is occupied by monolithic models that cannot be disassembled, assembled or improved. The design of all bimetal radiators is very attractive.
Appearance: Cast iron + — | Bimetal +
Working pressure and its differences
Cast iron radiators can withstand up to 12 atmospheres, which is enough for normal functioning in multi-storey buildings. Bimetal is resistant to coolant pressure of at least 20 atmospheres, and some models - up to 50.
In the event of a water hammer, cast iron can simply burst and crack, since it is a brittle alloy. In bimetallic radiators, the internal steel or copper part allows them to withstand extreme loads.
The weak point of bimetallic radiators is the junction of the sections. If they use sealant rather than gaskets or copper O-rings, then the likelihood of breakage is high. But this applies mainly to cheap manufacturers.
A short review of MS-140 radiators
This is a Soviet cast iron battery, which was installed in both residential and industrial facilities. A distinctive feature of the MS-140 is that the sections are wide and capacious, thanks to this it was possible to achieve minimal hydraulic resistance. But we had to sacrifice efficiency, which dropped to 40-60%. The material used for manufacturing is cast iron; the sections are connected to each other using nipples made of cold-rolled steel or ductile cast iron. Old samples were primed and painted.
But today, MS cast iron heating radiators have been somewhat modernized. Of course, their main characteristics, such as heat dissipation, weight and dimensions, have changed little, but their appearance has become completely different. Moreover, models have appeared designed to work in aggressive environments, places with frequent temperature changes and high humidity. In this case, the characteristics of cast iron heating radiators are somewhat different from conventional products. The sections are additionally sanded from the top as well as the front side, and painting is carried out using a two-stage method. The paint used is durable epoxy enamels, which are processed by polymerization at a temperature of 200 degrees Celsius. As a result, you get a battery that will withstand any load and will work for many years.
Actual service life
Bimetallic radiators appeared on our market not so long ago. Manufacturers give them a guarantee of 10-15 years. But this does not mean that they will last that long. The actual service life is usually 25-30 years.
The warranty for cast iron products varies from 10 to 25 years. But practice has shown that the minimum service life is 40 years or more. Suffice it to remember that in houses built in the 50s, cast iron batteries still function normally.
Aluminum heating devices
Devices of this type have a sectional design, but outwardly they are a neat one-piece product. Manufactured by casting from a special aluminum alloy.
We advise you to study - How to understand the variety of types of door hinges
Advantages
Aluminum products are characterized by excellent thermal conductivity and high heat transfer. These criteria are considered the main advantages. Their thermal conductivity is much better than that of devices made of bimetal or cast iron. Good quality batteries will last up to 10 years.
However, heat transfer makes aluminum elements uneconomical in the absence of good insulation. After all, their operating pressure is designed for approximately 16 atmospheres, while in urban heating networks it is only 8-10 atmospheres.
Flaws
The disadvantages of this type of device include the demands on water quality (the pH value of the coolant must be at least 7.5) and the formation of corrosion in places where the paintwork is damaged, which can gradually lead to leaks.
In addition, the interaction of aluminum oxide with an acidic environment is always accompanied by the release of hydrogen, which can lead to the formation of air pockets in the absence of a release device. Unfortunately, the high requirements for water quality in domestic heating systems are not yet feasible.
Practice has shown that the service life of aluminum radiators in city apartments rarely exceeds the threshold of 7 years. As a result, aluminum heat exchangers in Russian conditions are fully justified mainly in autonomous heating networks (private houses, individual buildings).
It is not difficult to make water better, for example, by installing filter systems or using special additives that reduce the acidity of the coolant. No matter how much effort is put in, the radiators will last for so long.
Price
Despite the disadvantages, aluminum batteries are very popular among the population. Consumers are impressed by the attractive design and affordability of the devices. The cost of aluminum radiators depends on the manufacturer and product warranties, but in general it is one third lower than that of bimetallic devices.
If one section from Chinese manufacturers costs 260 rubles, then the Russian Global Vox can cost from 800 rubles.
Operating temperature
The water in a central heating system usually has a temperature of 55 to 90 degrees. In the event of an accident or malfunction in the boiler room, it can warm up to +130 ° C, after which it will begin to boil away. The boiling point is higher than the standard 100 degrees due to the fact that the water is under pressure (remember physics).
In addition, water expands when heated, which creates additional pressure on the walls of heating devices.
Cast iron is fragile, so at a coolant temperature of more than 100 ° C it can crack. The steel or copper core in a bimetallic radiator is more resistant to pressure. Therefore, manufacturers claim that the maximum operating temperature for cast iron batteries is +110, and for bimetal +130 degrees.
Which radiators are easier to install?
There is nothing to argue about here - naturally, with cast iron there will be more problems during installation and transportation. And one person cannot lift such a battery, and special brackets are needed for it - especially strong, and a plasterboard wall will not support it.
And one more thing: when purchasing cheap domestic radiators, you need to be prepared for the fact that they will additionally need painting and broaching.
But working with bimetallic radiators is, one might say, a pleasure. They are so light and neat that hanging them (and on any surface) is not difficult. And if ease of installation is your first priority, then the answer to the question of which is better - bimetallic radiators or cast iron ones is clear. Of course, bimetal.
Ease of installation: Cast iron - | Bimetal +
Coolant quality requirements
The water in the central heating system does not differ in quality. It may have high acidity or alkalinity. It also contains a suspension of small particles of dirt, sand, etc.
Cast iron is chemically resistant and the quality of water does not affect it. But due to the large diameter of the channels, the volume of water in the radiator is large. The flow rate in it slows down and small particles of pollution settle in the lower part of the radiator. Over time, this leads to silting, a decrease in throughput and a decrease in heating efficiency.
Silting of heating pipes. The same dirt can settle on the walls of a cast iron radiator.
In a bimetallic radiator, the steel core is subject to slight corrosion during the warm season, when there is no water in the heating system. If the inside is made of copper, it becomes covered with a patina and the process of destruction stops.
Construction of steel radiators
Steel radiators used in heating systems are either panel or tubular.
Panel radiators
These are rectangular panels of different sizes. They have convector properties and have a fairly simple design, while:
- two profiled plates are welded together along the perimeter, and inside this structure, thanks to stamped profiles, vertical channels are formed for coolant circulation;
- U-shaped ribs made of thin cold-rolled steel welded on the back side enhance heat transfer;
- the structure can contain up to three panels protected by a common casing.
Tubular radiators
Products of this type are several separate pipes connected by manifolds. Pipes can be vertical or horizontal.
Easy to install
Cast iron batteries are heavy. Because of this, they are inconvenient to carry and install. They require special strong brackets, which can only be mounted in a concrete or brick wall.
Bimetallic radiators are quite light, because their bulk is aluminum. They can even be installed on a plasterboard partition if installed correctly.
As for adding or removing sections, there are no differences between different types of radiators.
Aluminum: what are they and how are they different?
Aluminum radiators are popular due to their low cost and excellent heat transfer. The technical characteristics depend on the manufacturing method.
Injection molding
For the production of cast radiators, they do not use pure aluminum, but a more durable alloy - silumin (aluminum + silicon). Such batteries can withstand up to 16 atmospheres. They have wide water channels that prevent pipes from clogging and therefore do not require additional flushing.
What to pay attention to: the quality of the alloy. As a rule, European manufacturers use a durable alloy, thereby reducing the risk of corrosion and improving heat transfer
Extrusion or extrusion
It is planned to manufacture the radiator sections separately, after which they are welded to the cast manifolds.
Photo 1. Comparison of the design of different types of aluminum radiators: two cast and extruded.
What to pay attention to: the individual parts of the battery must be connected to each other by welding or pressing. In cheap models, sections are connected with composite glue, which slightly increases the risk of leakage
Anodic oxidation
Behind this name is a chemical process that protects aluminum from corrosion and pressure changes. They cost more and are rarely used in everyday life.
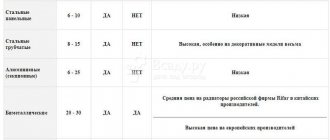
Comparison of cast iron and bimetallic radiators - table
| Evaluation criterion | Cast iron | Bimetallic |
| Heat dissipation | — | + |
| Pressure resistance | + | — |
| Life time | + | — |
| Temperature resistance | — | + |
| Coolant requirements | — | + |
| Appearance and Design | + | — |
| Easy to install | — | + |
How to make the right choice
Cast iron products are suitable for private and residential buildings up to five floors. In high-rise buildings, very high pressure can occur, which can lead to rupture, so bimetallic models are chosen.
Aesthetically, classic cast-iron models look ugly, but when designing a room, decorative grilles are often used to hide the appearance of radiators.
When purchasing, experts recommend paying attention to the following characteristics:
- heat transfer quality;
- frequency of performing necessary preventive maintenance to extend the service life of heating devices;
- lifetime;
- pressure retention;
- aesthetics.
Is it worth replacing cast iron batteries with bimetallic ones?
If old cast iron radiators do not satisfy you with the quality of heating, it makes sense to clean them - they may be silted. Over time, dirt is deposited on the walls, which is a kind of heat insulator and does not allow the coolant to effectively transfer heat.
If you live in your own home and have your own individual heating system, there will be no sudden changes in pressure and temperature. In this case, it makes sense to install cast iron batteries. They will be able to effectively retain heat if you forget to add fuel to the boiler and will provide soft, even heat.
It is better to install bimetallic radiators if you live in an apartment with a central heating system. They will withstand extreme temperatures and pressure in the event of an accident, will not silt up and will last quite a long time.
What is the difference
One of the main features of cast iron is its ability to heat up slowly. This phenomenon is called thermal inertia. If you need to warm up a cold room, it may take some time. According to this criterion, cast iron is much inferior to its bimetallic counterparts, which heat up very quickly. But it should be noted that they also cool down very quickly; the cast iron version of the radiator cools down much more slowly and continues to heat the room even after the heating is turned off, maintaining a comfortable atmosphere in the room.
The coolant has a high temperature and is heated in boilers, then it is supplied through a centralized heating system directly to the apartments. The steel core of the bimetallic battery interacts with the hot liquid and is necessary to transfer heat to the aluminum body, which performs the main function of the radiator - heating the room.
Reaction to bad coolant
Cast iron performs better in terms of endurance and resistance to the effects of low-quality coolant. It is a neutral metal and does not react with the liquid flowing through the pipes.
Debris and dirt in the radiator
The presence of small pebbles, rust, chemical elements and scale in the coolant causes slight damage to the internal walls of the batteries. Under their influence, the radiators slowly wear out in the middle. But this happens so slowly and insignificantly that it is not a problem for thick radiator walls.
Bimetallic batteries also react calmly to the composition of water. A more detrimental effect is exerted by the air that enters the products after the heating season ends and the liquid is drained from the system. Steel cores are susceptible to corrosion.
Corrosion inside bimetallic radiators
Difficulty of installation
Trying to understand which is better, cast iron or bimetal for central heating, depending on the complexity of installation, we can come to the following conclusion: in this parameter, bimetallic radiators win an unconditional victory - with the same dimensions as cast iron, they weigh several times less. They are much easier to transport, carry and install, so if ease of installation is critical, then bimetallic products would be the obvious choice.
Cast iron radiators, in turn, cause a lot of problems during installation:
- Firstly, they weigh a lot, so lifting and hanging them is very difficult;
- Secondly, due to the weight, even delivering radiators to the apartment will be problematic;
- Thirdly, the same heavy weight does not allow such radiators to be hung on plasterboard walls, and special brackets will be required to attach them to brick walls.
In addition, when purchasing cheap domestically produced radiators, there is a high probability that they will additionally have to be painted and stretched.
Best answers
Dragas Zlatibor:
No supernatural qualities can be attributed to bimetallic radiators, except, perhaps, that in terms of ergonomics and design they are in no way inferior to aluminum ones. In addition, they are perfectly suited to the standard pressure system of the Russian Federation due to the complementary alloy of steel and aluminum. This means that for old houses, according to technical parameters, this type of radiator is suitable.
The first and very significant advantage of cast iron as a material for radiators is that it is very reluctant to corrode. The cast iron battery is practically “eternal” - it lasts more than 50 years. You can dry mittens on it and heat kefir. The disadvantage of a cast iron radiator is lower heat transfer compared to aluminum, huge weight (difficult to install) and large internal volume. And if the weight of a battery hanging on the wall doesn’t bother us very much, then a large volume of water inside the radiator (according to my calculations, about three liters per edge of the MS-140) is bad, because the system with such radiators takes a long time to heat up. Such a radiator will not allow you to quickly regulate the temperature in the room, however, for many rooms this is simply not necessary.
scorched by years:
so that heat transfer is high
Guy from the Future...:
What you don’t mind spending money on (or what you have enough for)
Svyatoslav Taushkanov:
if cast iron, then with iron piping and high-quality bimetal is expensive, it doesn’t hold pressure well and you need a very smart technician
Scarifier:
Bimetal definitely has better heat transfer, and it doesn’t clog like in apartments
Oleg Zhestov:
I am for cast iron, I have aluminum ones, they warmed up for 5 minutes, cooled down for 5 minutes, cast iron has a higher heat capacity, it has one drawback - its appearance.
Ruslan Fazlyev:
but I live in Europe and here only rich people install cast iron... I am for cast iron!!!
Farit Gafuanov:
It’s just a purely personal question: heat transfer is better with bimetal, while cast iron is worse
husky:
Lately, for some reason, people have been looking for their own worries and problems. And with radiators too. They tried to replace cast iron abroad for a long time. And only when the production of aluminum radiators became cheaper did they begin to offer them for sale. But in terms of heat capacity, cast iron will hold its mark for a long time. All the rest are just pretty. Is the cast iron design outdated? And look at the cast iron radiators made in Cheboksary. There are not ribs, but planes along the outer surface of the sections. In my house they are like this
Price
There is no need to talk for long about the cost of radiators - the relationship between price and quality is direct, so in most cases it is possible to determine which battery is better - cast iron or aluminum - based on this parameter. The cheapest are simple cast iron radiators, especially domestic ones. The quality of such products is appropriate. The next most expensive are bimetallic radiators, the price of which exceeds the cost of similar cast iron products by 1.5-2 times. Cast iron radiators made by artistic casting are the most expensive - one section of such a product can cost 10 times more than a regular one.
Best answers
Irina Dedushenko:
Cast iron radiators are more durable than bimetallic ones (especially if the water quality is poor). Bimetallic ones are lighter, more beautiful (although now cast iron ones have appeared - nice with a smooth surface), Bimetallic ones are easier to install. Heat transfer depends on the size; with equal sizes, the heat transfer of bimetallic ones is slightly greater (the thermal conductivity of the metal is greater). Cast iron has greater inertia (heats up and cools down more slowly)
This is important if you have a house with its own automatic temperature control system - bimetallic ones will respond better to automation.
Marina Efimova:
I have bimetallic ones. Oh, very good heat dissipation, the wrapped ones last all winter, otherwise the house becomes stuffy. It’s more aesthetically pleasing and can be adjusted.
vyachko:
Take bimetal, but it will be more expensive than cast iron. As I understand it, the heating is centralized, if so, then don’t try to save money and take aluminum (it is weak for centralized heating).
Romik:
Install bimetal! only BIMETAL! not aluminum! since in bimetal there is a metal tube inside! Not bad and not expensive BREM brands
Askar Khasenov:
Cast iron radiators do not rust and have good heat transfer. bimetallic ones have a flat shape, which reduces the heat transfer area; brittle metal breaks easily.
VOVA VETROV:
Cast iron ones are more reliable, and bimetallic ones are more beautiful and lighter!
Alexander Tsybin:
Cast iron also heats if the heating risers are at the proper temperature, bimetal is the same horseradish, only a side view, just expensive aesthetics. If there is no temperature in the risers, they are no better than cast iron, only the service life is half as long.
All the same boys:
install cast iron, now there are very nice cast-iron batteries, bimetal heat transfer is worse, aluminum ones with central heating will be thrown away in three years
Oleg Khrebtov:
And I think cast iron will come back everywhere...
Grandfather Au:
Nowadays there are a lot of imported cast iron batteries with excellent design, but the bimetal does not like our water and fistulas are possible
avaks:
bi better not listen to anyone that they are not driving for our water for 13 years
Elena N:
Choose bimetallic ones. We've had them for 3 years now and have no complaints. The heat dissipation is excellent. In no way inferior to cast iron. And the look is more aesthetic.
genset:
after a long study we chose bimetal. But we found one thing - if the number of sections is more than 12, it is better to connect diagonally (entrance from above, exit from below on the opposite side)
Ivan Spiridonov:
German cast iron radiators are twice as expensive as bimetal; if the economical option is aluminum, they are no worse, choose only the design. For example, our Thermal can withstand 24 kg of working pressure. Contact Service501
Avgulij:
Definitely cast iron I do autonomous heating myself. No radiators have heat transfer like cast iron.
Luke' :
Tubular steel in polymer
Functionality
If we compare which radiators are better (cast iron or bimetallic) in terms of functionality, then the absolute advantage here belongs to the second option.
Bimetallic batteries are lightweight, making them much easier to install. They do not place such high demands as cast iron radiators on the strength of the wall on which they are installed.
Special conditions when ordering more than 1000 radiator sections →
An important difference between bimetallic radiators and cast iron ones is their small internal volume. Thanks to this, they can be equipped with modern metering devices and temperature controllers (manual and automatic).
Taking into account all the characteristics, bimetallic radiators can be called the more preferable option.
Where can I buy
You can purchase heating radiators in the following stores:
- TuT plumbing – more than 7,500 models;
- MirCli – all types of coolants;
- AllTools – fast delivery and low prices;
- Ulmart - products from 8 major manufacturers;
- Ozon – classic sectional samples are presented;
- Baucenter – when purchasing Buderus products, additional points are added to the bonus card;
- RAIBT – for the convenience of the buyer there is an information, service and delivery service;
- Leroy Merlin – various products: aluminum, steel, bimetallic.
Power and dimensions
We have decided on the material, now it’s time to calculate the number of sections and dimensions of the device that is most suitable for us. In a good way, many room parameters are taken into account here:
- square;
- ceiling height;
- wall thickness;
- the number of windows and how they are glazed;
- presence of a balcony;
- location: corner or in the middle of the building, first, last or middle floor.
In addition, it is important to take into account the climatic features of your region and personal preferences: do you like it when your home is cool or, conversely, hot.
There is even a special calculator that, using a complex formula, will select the required power, taking into account the entered parameters.
Simplified, this formula looks like this:
N = S x 100 / Pc,
where N is the number of sections,
S – room area in square meters. m.,
Pc – power of one segment of the model you have chosen (indicated in the product passport)
There is an option where the ceiling height (h) is also taken into account:
N = S xhx 41 (34) / Pc.
Separately, it should be explained what the numbers 41 and 34 are, and which one should be used in your calculations. This is the power of the heating system per 1 sq. m. room, which is:
- 41 W in panel houses;
- 34 W in brick.
As for the height of the battery, it all depends on the place where you install it: if under a window, then you need to measure the distance from the top edge of the battery to the window sill, and from the bottom to the floor. There should be at least 10 cm of free space on each side. This is necessary to ensure proper convection. There are two standard values: 35 and 50 cm, so choose the one that best matches the dimensions of your apartment.
The depth also varies from 7 to 10 cm, so if you are limited in space, you can always take equipment of greater depth and thus increase its efficiency.
It is also important to know that placing it in a deep niche or installing a screen in front of the radiator leads to a decrease in heat transfer efficiency. In this case, it is advisable to increase the power of the installed device.
Approximately the number of parts can be calculated as follows: for every 1.5 - 2 sq. m. there is one section or 100 W.
There are devices that can be expanded by adding additional elements after installation. If you suddenly freeze in winter, you can buy a couple more parts and build them up.
For those cases where it is not possible to expand sections, you will have to buy an electric room heater to create a comfortable environment.
Varieties and their characteristics
Before deciding which radiators are better for heating: cast iron or bimetallic, or perhaps an aluminum type or a steel one, you need to understand what is unique about each of the materials.
Bimetallic
If you have a question about how to choose the right bimetallic radiators for heating your apartment, you need to find out what the features of this product are. Firstly, bimetallic models have a modern appearance, as well as high-quality content from the inside. Secondly, equipment made from this material should not be installed in production, since the resulting pressure surges can damage it or cause internal corrosion of the metal.
Bimetallic radiators are distinguished by their long-term operation, as well as their stability and ability to withstand pressure up to 50 atmospheres.
They tend to warm up quickly and at the same time have a beautiful design.
But bimetallic models also have minor disadvantages, which include slag deposits and a decrease in heat transfer due to the use of different material options.
Cast iron
This material is different in that it is familiar to many, since previously cast iron radiators were installed in almost every apartment. Now modern models have practically nothing in common with their predecessors, except for the material, and differ from them both in appearance, power, and efficiency.
It is cast iron that differs from others in having the best thermal conductivity.
Despite the fact that it tends to heat up for a long time, it does not cool down for a long time. Even after turning off the heating, the batteries continue to retain heat for some time. The remaining retained heat can reach 30%, which is twice as high as that of steel and aluminum options.
The cast iron radiator is distinguished by its strength and durability, thanks to which the pressure indicator reaches 30 atmospheres. The batteries will not be afraid of water hammer or accidents in the central heating system.
The advantage of cast iron models is that they have a universal connection. They are unpretentious during operation, corrosion does not form inside, and the smooth outer surface does not require special care. Various types of cast iron heating radiators allow you to choose the appropriate option for any requirement.
The advantages of cast iron radiators:
- low cost;
- strength and reliability;
- highly compatible with any pipe materials;
- simplicity and ease of use;
- no corrosion occurs;
- long term use.
In addition, there are several disadvantages of such products: they are difficult to install, since they are quite heavy, and have poor inertia.
If you install this radiator yourself, then you should adhere to all the points specified in the instructions.
Aluminum
Cast iron or aluminum radiators, which is better for heating. In answering this question, the following should be noted. Despite its rather attractive appearance, it is better not to purchase this option for a centralized heating network.
They are more suitable for rooms with autonomous heating.
Several advantages that can be identified from an aluminum radiator:
- it is light in weight;
- ease of installation;
- has a stylish design;
- the price category is low;
- increased heat transfer.
But at the same time, it is worth considering several disadvantages that may appear when installing the product in a central heating network:
- cannot withstand water hammer;
- has a short service life;
- pressure in the system is allowed up to 12 atmospheres.
It is best to select an aluminum model based on the type of heating system of the building.
Steel
Steel batteries from a modern manufacturer can be distinguished both by design and construction. That is why the types of steel radiators are divided into two types: panel and tubular.
The advantages of this option include light weight, simple installation, a wide variety of different models, as well as absolutely not excessive requirements for the heating system.
Popular types of radiators
Bulky cast iron batteries are slowly becoming a thing of the past, being replaced by elegant radiators. Such designs give off excellent heat and look attractive.
The cost of the products is relatively high, but taking into account the long-term service, the investment pays off in the long term. By updating the heating system, the consumer will find out which heating radiators are best for a private home
There are bimetallic and aluminum sections available in stores, and each type has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Pros and cons of aluminum heating radiators
Neat and attractive aluminum batteries include several sections connected by nipples and sealed with special gaskets. The inner side has a ribbed surface, increasing the heat transfer area to 0.5 m2. According to the manufacturing method, they are divided into solid cast and extruded. The first ones are more expensive and more durable, the second ones are light and budget-friendly.
Let's look at the main advantages and disadvantages of such radiators:
The disadvantage of such models is considered to be poor tolerance to pressure surges and fragility during water hammer. The working pressure of an aluminum radiator is 6-16 atmospheres, less often 20. Needless to say, the installation of aluminum radiators in multi-storey buildings is not recommended, because it is difficult to control the centralized heating supply. In private construction, such a problem does not arise, because a separate heating system (HS) is not subject to uncontrolled changes in operating pressure and water hammer. In terms of heat transfer, an aluminum product leaves other types of heating structures far behind. One sectional unit emits up to 200 W of thermal energy: part transmits convection heat, while the second transmits infrared radiation. There is also minimal thermal inertia, which is extremely useful in a private home. Almost immediately after starting the system, the room becomes more comfortable. The most common coolant is plain water. The product is available, but at the same time, the salts and other components contained in the water react aggressively with the aluminum surface
Due to the chemical activity, it is extremely important to monitor the pH status. An indicator that exceeds 8 units is detrimental to the radiator - it will be “eaten up” by corrosion
Hydrogen is also released which can cause a fire or battery explosion. Air should be removed from the sections in a timely manner. The maximum coolant temperature should not exceed 110 degrees, which is also a disadvantage of aluminum radiators.
Bimetallic radiators - a combination of the best qualities of metals
First, let's figure out how bimetallic heating radiators differ from aluminum ones? The main difference is the bimetal’s resistance to pressure changes. This allows radiators to be used universally both in apartment buildings and in private homes. Bimetallic radiators are reliable in conditions of water hammer. This is ensured by an internal steel or copper core through which the coolant moves. This structure allows you to withstand operating pressure within 20-40 atmospheres. Here is a list of other benefits:
- Low requirements for coolant. Steel and copper are not as susceptible to chemical composition, therefore, oxidation and corrosion processes do not develop as quickly as in an aluminum battery.
- The highest temperature of the coolant is 130 degrees.
- Durability - service life is on average 1.5-2 times higher than that of aluminum.
Bimetallic radiators still have some disadvantages compared to single-component metal products. Heat transfer rates are lower: depending on the manufacturer, the difference can reach a 5-fold value in favor of aluminum. The price for one section made of bimetal is higher, which is also not considered an advantage.
Key points when choosing batteries
An autonomous heating system is one of the advantages of a private home, as it is calculated and installed individually for a specific building and is fully controlled by the owner. Choosing radiators for a home is easier than for an apartment that is connected to the heating network of an entire neighborhood. The closed system of a private house has positive aspects compared to the general network:
- Stable operation at low pressure is possible;
- it is possible to create the most favorable operating environment;
- due to the absence of water hammer, the range of choice of heaters is significantly expanded;
- subject to the technical conditions of the acid balance of water, the list of battery selection increases.
The main emphasis in choosing batteries should be on maximum heat transfer and a suitable price-quality ratio. For long-term stable operation in a home heating system, you can use any heaters: steel, aluminum, bimetallic and even cast iron.
Features of the functioning of the central heating system
The requirements for heating devices are determined by the operating heating system. As a rule, most apartments in Russia are serviced by central systems. Therefore, it is necessary to select devices whose technical characteristics coincide with their operating parameters.
Here are the main ones:
The central system is a set of equipment operating in a closed circle. The central heating unit produces heat, which is then transported through distribution lines. To ensure transportation, forced circulation is used. Pumps create pressure that helps deliver coolant to each apartment. Its indicators vary everywhere, but experts note that, on average, heating devices must withstand a pressure of 16 atmospheres. When choosing radiators, you need to take into account that the coolant pressure is not constant. It can significantly decrease or increase, forming dangerous water hammers. Therefore, the material from which batteries are made must be durable and reliable. Any radiator must function under conditions of frequent filling and draining of the system. There are also frequent violations in the conservation of the central heating system, which are carried out in the summer.
They should not become reasons for failure of radiators. And one more important circumstance. Considering the percentage of wear and tear of existing equipment, the poor quality of the coolant cannot be discounted
The hot water supplied by the central system for heating apartments contains special technical impurities, debris and rust. The former reduce heat losses during coolant transportation. And the latter quickly clogs the risers and the internal body of the radiators. Heating devices must cope with this difficult task. It is also useful to take into account the features of the piping of apartments and the materials from which it is made. As a rule, most engineering accidents occur due to poor compatibility of metals and materials with which the selected batteries are connected.
Resistance to temperature changes
Just as in the case of pressure and quality of the coolant, the temperature in centralized heating is not stable - the pipes can be either barely warm or very hot. There are no problems with low temperatures (except for insufficient heating, of course), but the maximum temperature is an important indicator that allows you to determine which battery is better - cast iron or bimetallic.
Cast iron products can safely withstand temperatures up to 110 degrees. The upper temperature threshold for bimetallic radiators is slightly higher and amounts to 130 degrees. In general, we can say that both types of radiators, in terms of temperature conditions, can be used in centralized heating without problems. Perhaps the only nuance is that bimetallic radiators may crack slightly when temperature changes, which is due to different levels of linear expansion of aluminum and steel during heating and cooling.